吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 572-580.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181017
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
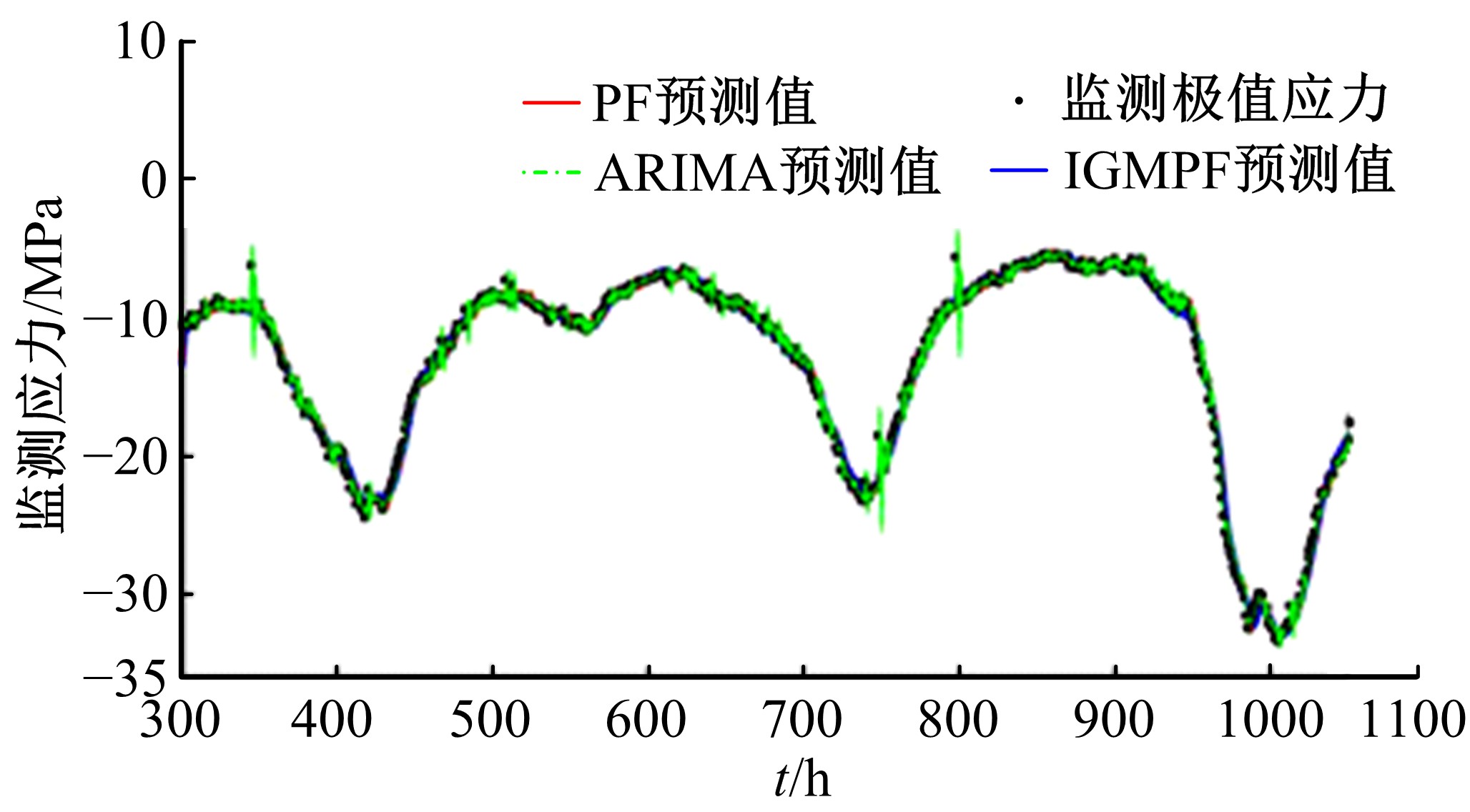
应用新数据同化算法的桥梁极值应力预测
- 1.兰州大学 西部灾害与环境力学教育部重点实验室,兰州 730030
2.兰州大学 土木工程与力学学院,兰州 730030
Bridge extreme stress prediction based on new data assimilation algorithm
Xue-ping FAN1,2( ),Guang QU1,2,Yue-fei LIU1,2
),Guang QU1,2,Yue-fei LIU1,2
- 1.Key Laboratory of Mechanics on Disaster and Environment in Western China of the Ministry of Education, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Mechanics, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, China
摘要:
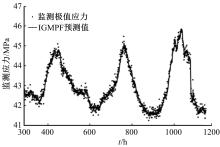
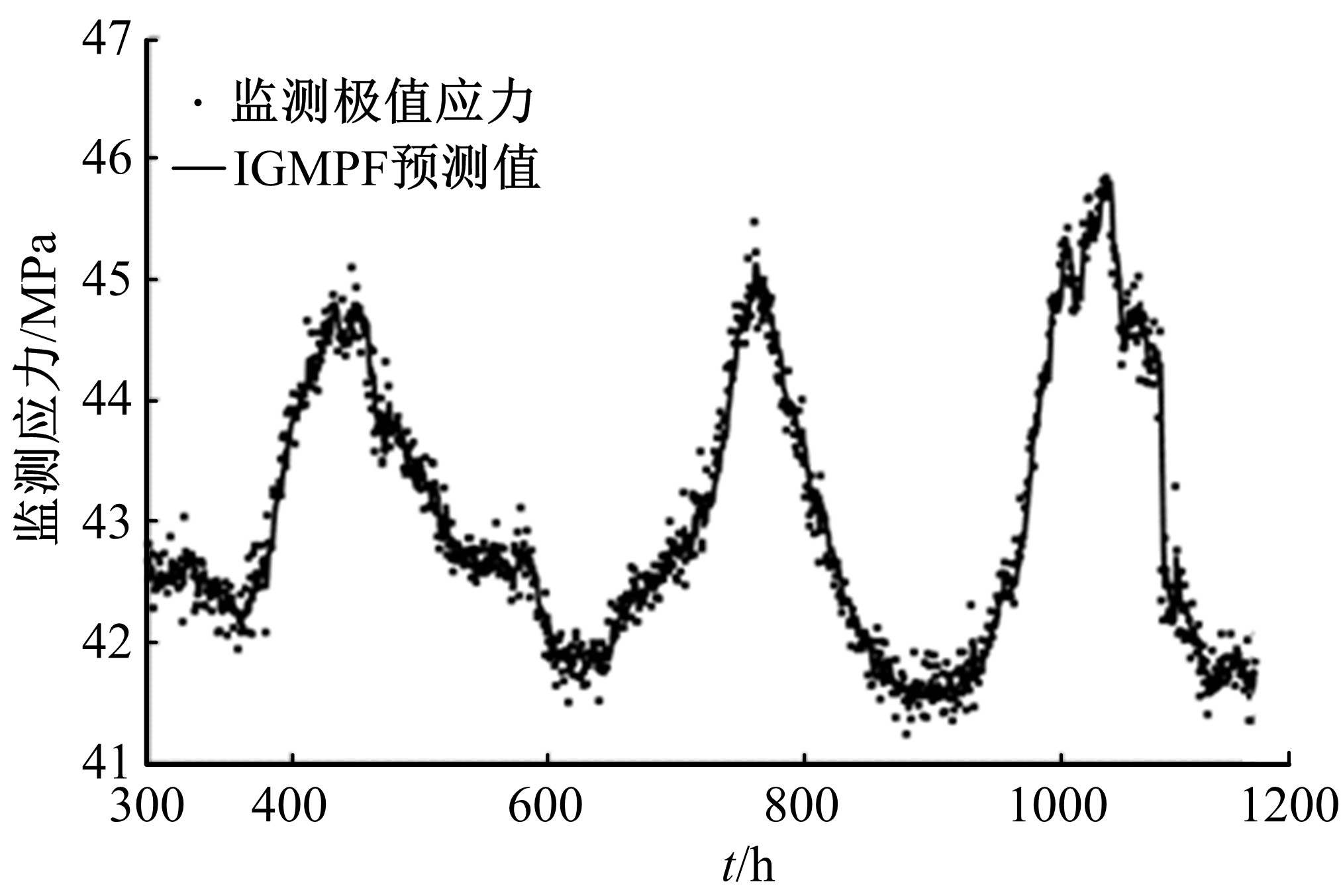
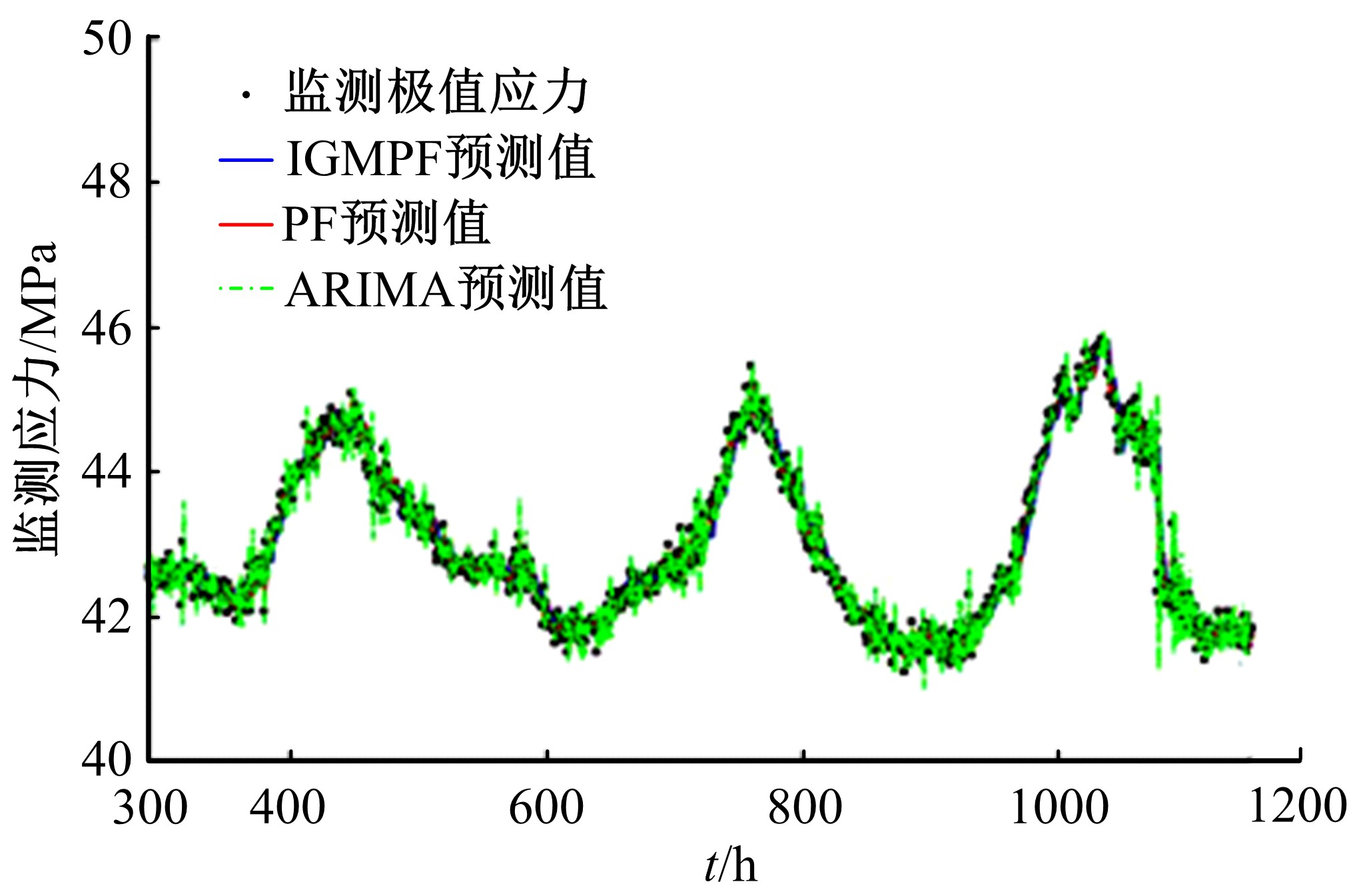
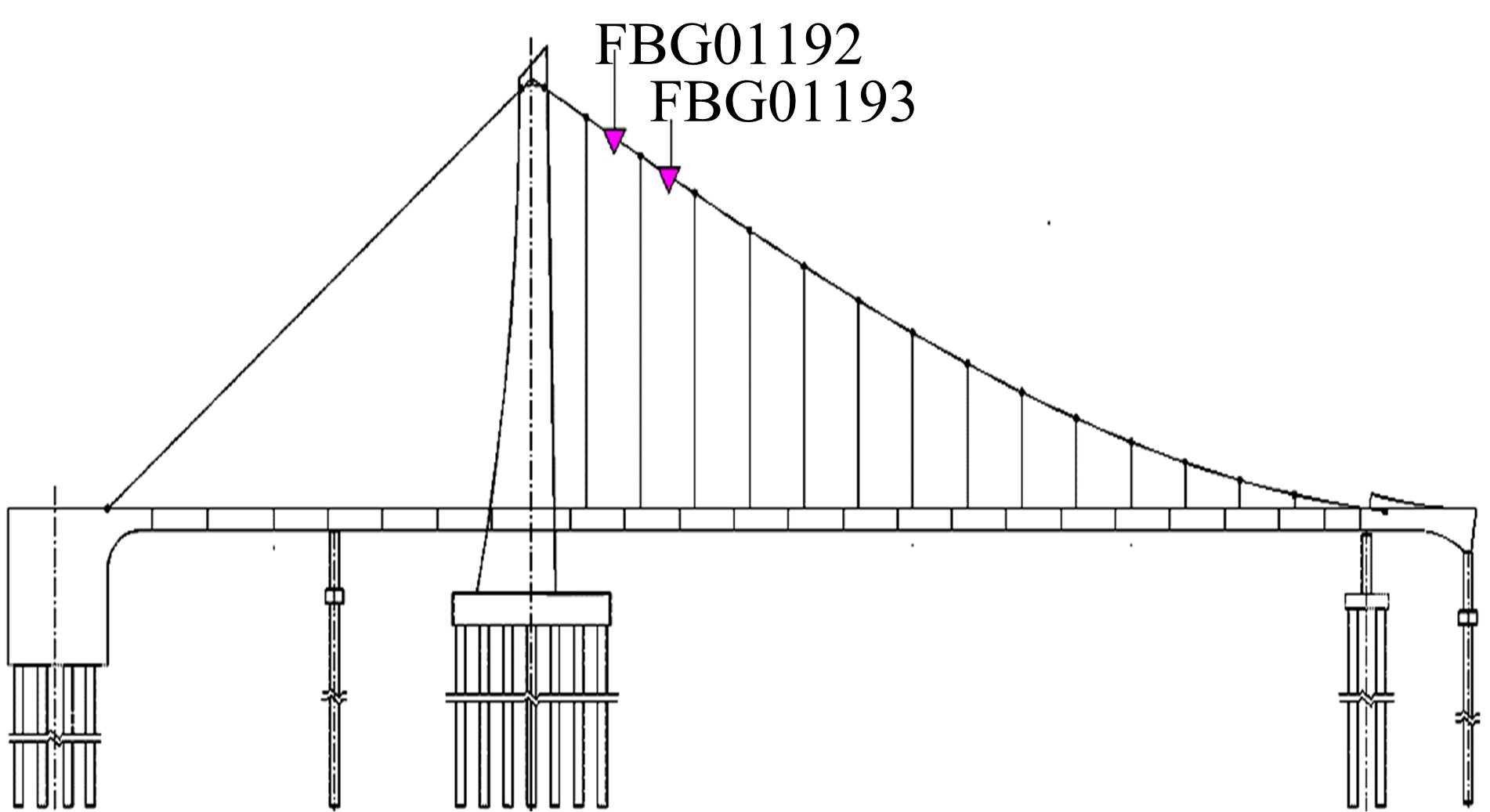
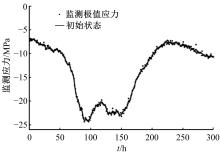
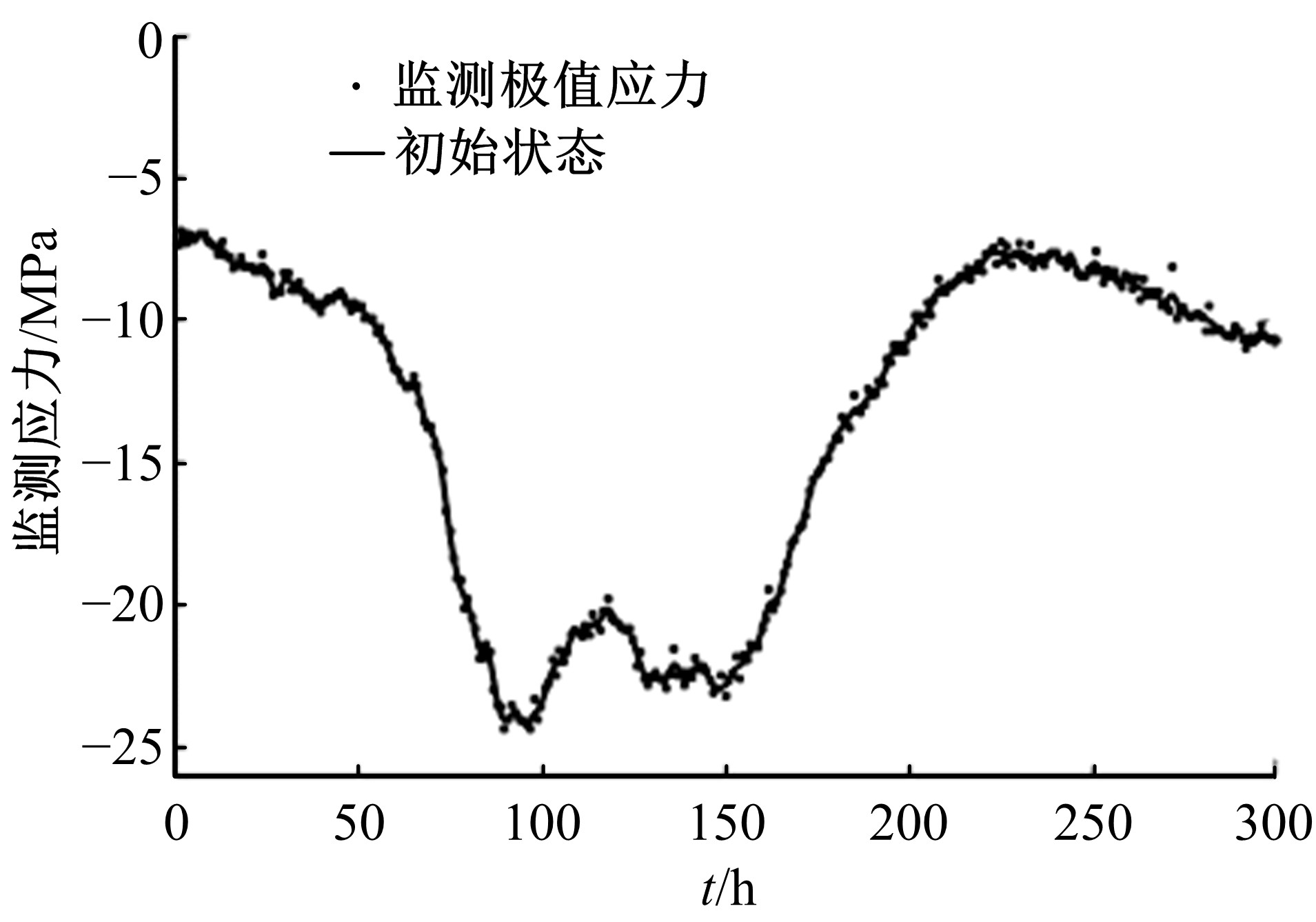
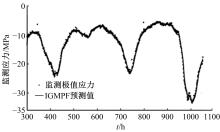
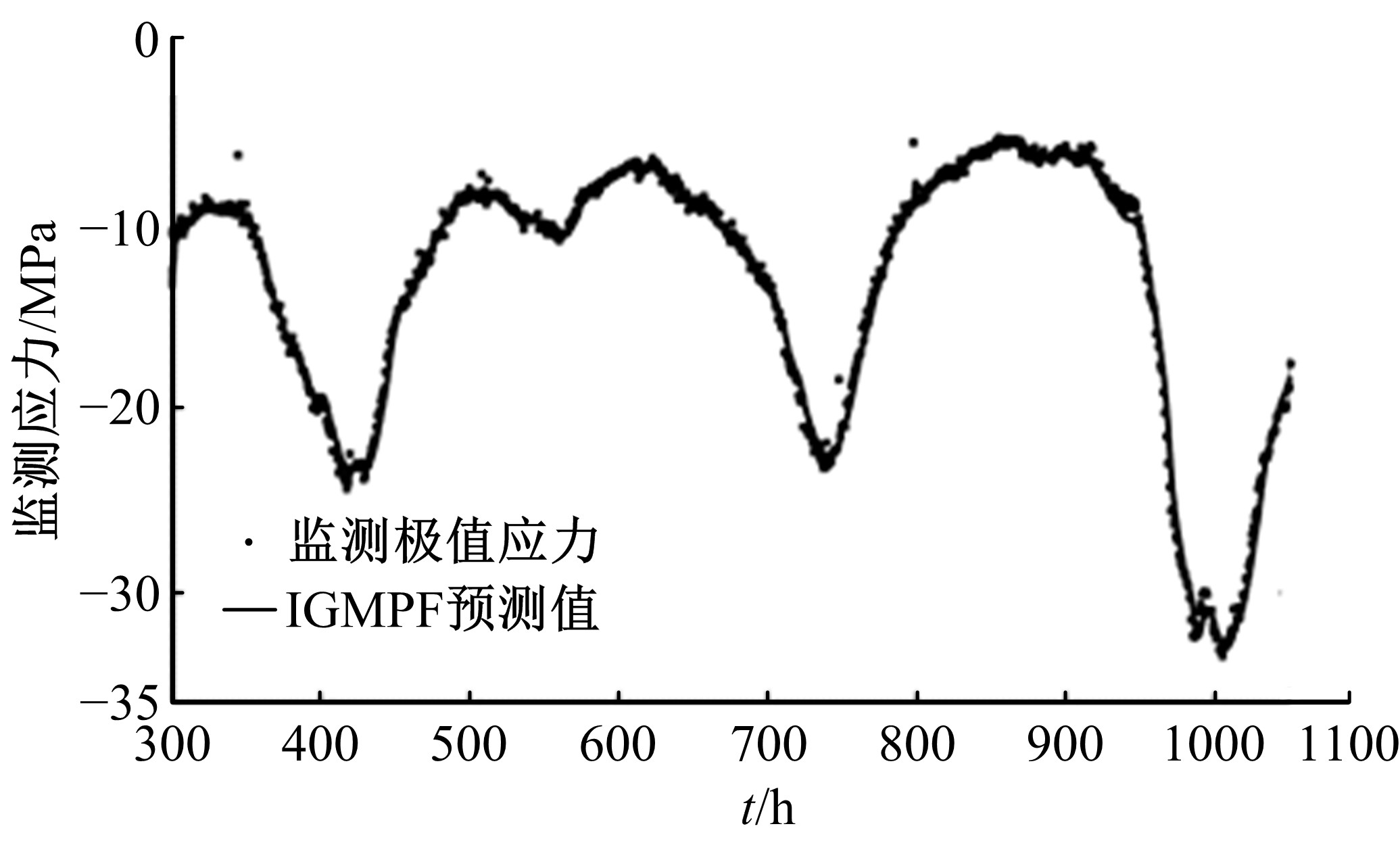
为合理动态预测桥梁极值应力,将极值应力监测数据视为时间序列,提出桥梁极值应力预测的数据同化新方法。利用极值应力监测数据建立动态非线性模型,引入 K均值聚类算法与最大期望算法,并将两者融合嵌入到高斯混合粒子滤波器,得到改进高斯混合粒子滤波算法,结合监测数据实现桥梁极值应力的动态预测,通过在役桥梁监测数据对所提算法的合理性进行验证,并与其他预测算法进行比较,结果发现改进算法更具可行性且预测精度较高。
中图分类号:
- TU391
| 1 | Ou J P, Li H. Structural health monitoring in Mainland China: review and future trends[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2010, 9( 3): 219- 231. |
| 2 | Tropp J A, Gilbert A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53( 12): 4655- 4666. |
| 3 | 李惠, 周文松, 欧进萍, 等. 大型桥梁结构智能健康监测系统集成技术研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2006, 39( 2): 46- 52. |
| Li Hui, Zhou Wen-song, Jin-ping Ou, et al. A study on system integration technique of intelligent monitoring systems for soundness of long-span bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2006, 39( 2): 46- 52. | |
| 4 | 李爱群, 缪长青, 李兆霞, 等. 润扬长江大桥结构健康监测系统研究[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 33( 5): 544- 548. |
| Li Ai-qun, Miao Chang-qing, Li Zhao-xia, et al. Health monitoring system for the Runyang Yangtse River Bridge[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2003, 33( 5): 544- 548. | |
| 5 | 宗周红, 褚福鹏, 牛杰. 基于响应面模型修正的桥梁结构损伤识别方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2013, 46( 2): 115- 122. |
| Zong Zhou-hong, Chu Fu-peng, Niu Jie. Damage identification methods of bridge structures using response surface based on finite element model updating[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2013, 46( 2): 115- 122. | |
| 6 | 宗周红, 周儒勉, 郑沛娟. 基于健康监测的桥梁结构损伤预后和安全预后研究进展及挑战[J]. 中国公路学报, 2014, 27( 12): 46- 57. |
| Zong Zhou-hong, Zhou Ru-mian, Zheng Pei-juan. Damage and safety prognosis of bridge structures based on structural health monitoring: progress and challenges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27( 12): 46- 57. | |
| 7 | 魏锦辉, 任伟新. 基于响应面方法的桥梁静动力有限元模型修正[J]. 公路交通科技, 2015, 32( 2): 68- 73. |
| Wei Jin-hui, Ren Wei-xin. Static and dynamic bridge finite element model updating based on response surface method[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, 32( 2): 68- 73. | |
| 8 | Abudayyeh O Y, Barbera J, Abdelqader I, et al. Towards sensor-based health monitoring systems for bridge decks: a full-depth precast deck panels case study[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2010: 10. 1155/ 2010/ 579631. |
| 9 | 赵卓. 基于ARMA模型的伊通河桥监测数据建模与可靠度分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2012. |
| Zhao Zhuo. Health monitoring data modeling and reliability analysis for Yitong river bridge based on ARMA model[D]. Harbin: School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2012. | |
| 10 | 樊学平. 基于验证荷载和监测数据的桥梁可靠性修正与贝叶斯预测[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2014. |
| Fan Xue-ping. Bridge reliability updating and Bayesian prediction based on proof loads and monitored data[D]. Harbin: School of civil engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014. | |
| 11 | Fan X P. Bridge extreme stress prediction based on Bayesian dynamic linear models and non-uniform sampling[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2017, 16( 3): 253- 261. |
| 12 | Han H, Ding Y S, Hao K R, et al. An evolutionary particle filter with the immune genetic algorithm for intelligent video target tracking[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2011, 62( 7): 2685- 2695. |
| 13 | 樊学平, 刘月飞, 吕大刚. 应用高斯粒子滤波器的桥梁可靠性在线预测[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48( 6): 164- 169. |
| Fan Xue-ping, Liu Yue-fei, Da-gang Lyu. On-line reliability prediction of bridges based on Gaussian particle filter[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016, 48( 6): 164- 169. | |
| 14 | 樊学平, 刘月飞, 吕大刚. 桥梁极值应力的改进高斯混合粒子滤波器动态预测[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 44( 11): 1660- 1666. |
| Fan Xue-ping, Liu Yue-fei, Da-gang Lyu. Improved gaussian mixed particle filter dynamic prediction of bridge monitored extreme stress[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2016, 44( 11): 1660- 1666. | |
| 15 | Fan X P, Liu Y F. Dynamic extreme stress prediction of bridges based on nonlinear mixed Gaussian particle filtering algorithm and structural health monitoring data[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 8( 6): 1- 10. |
| 16 | Elangasinghe M A, Singhal N, Dirks K N, et al. Complex time series analysis of PM 10, and PM 2.5, for a coastal site using artificial neural network modelling and k-means clustering[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 94: 106- 116. |
| 17 | Mclachlan G M, Krishnan T. The EM algorithm and extensions[J]. Journal of Classification, 1998, 15( 1): 154- 156. |
| 18 | Al-Zoubi M B A, Rawi M A. An efficient approach for computing silhouette coefficients[J]. Journal of Computer Science, 2008, 4( 3): 252- 255. |
| 19 | 于金霞, 刘文静, 汤永利. 粒子滤波重采样算法研究[J]. 微计算机信息, 2010, 26( 16): 44- 45. |
| Yu Jin-xia, Liu Wen-jing, Tang Yong-li. Study on the resampling algorithms of particle filter[J]. Microcomputer Information, 2010, 26( 16): 44- 45. | |
| 20 | 秦大同, 詹森, 漆正刚, 等. 基于K-均值聚类算法的行驶工况构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46( 2): 383- 389. |
| Qin Da-tong, Zhan Sen, Qi Zheng-gang, et al. Driving cycle construction using K-means clustering method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46( 2): 383- 389. | |
| 21 | 李霞, 邵春福, 曹鹏. 基于快速K均值聚类的经济水平与货运量模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008, 38( 5): 1040- 1043. |
| Li Xia, Shao Chun-fu, Cao Peng. Economy level and freight model utilizing quick K-means cluster method[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2008, 38( 5): 1040- 1043. |
| [1] | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. |
| [2] | 戴岩, 聂少锋, 周天华. 带环梁的方钢管约束钢骨混凝土柱-钢梁节点滞回性能有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| [3] | 杨昕卉, 薛伟, 郭楠. 钢板增强胶合木梁的抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 468-477. |
| [4] | 王少杰, 徐赵东, 李舒, 王凯洋,Dyke Shirley J. 基于应变监测的连续梁支承差异沉降识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1090-1096. |
| [5] | 宿晓萍,王清. 复合盐浸-冻融-干湿多因素作用下的混凝土腐蚀破坏[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 112-120. |
| [6] | 姜浩, 郭学东. 基于地震激励的混凝土桥梁模态参数识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 185-188. |
|
||