吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1617-1626.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190493
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型
- 1.重庆大学 机械工程学院, 重庆 400044
2.重庆大学 机械传动国家重点实验室, 重庆 400044
3.重庆文理学院 智能制造工程学院, 重庆 402160
A transfer learning model for bearing fault diagnosis
Gen-bao ZHANG1,2,3( ),Hao LI1,Yan RAN1,2(
),Hao LI1,Yan RAN1,2( ),Qiu-jin LI1
),Qiu-jin LI1
- 1.College of Mechanical Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmissions, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
3.School of Intelligent Manufacturing Engineering, Chongqing University of Arts and Sciences, Chongqing 402160, China
摘要:
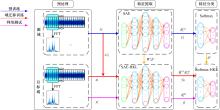
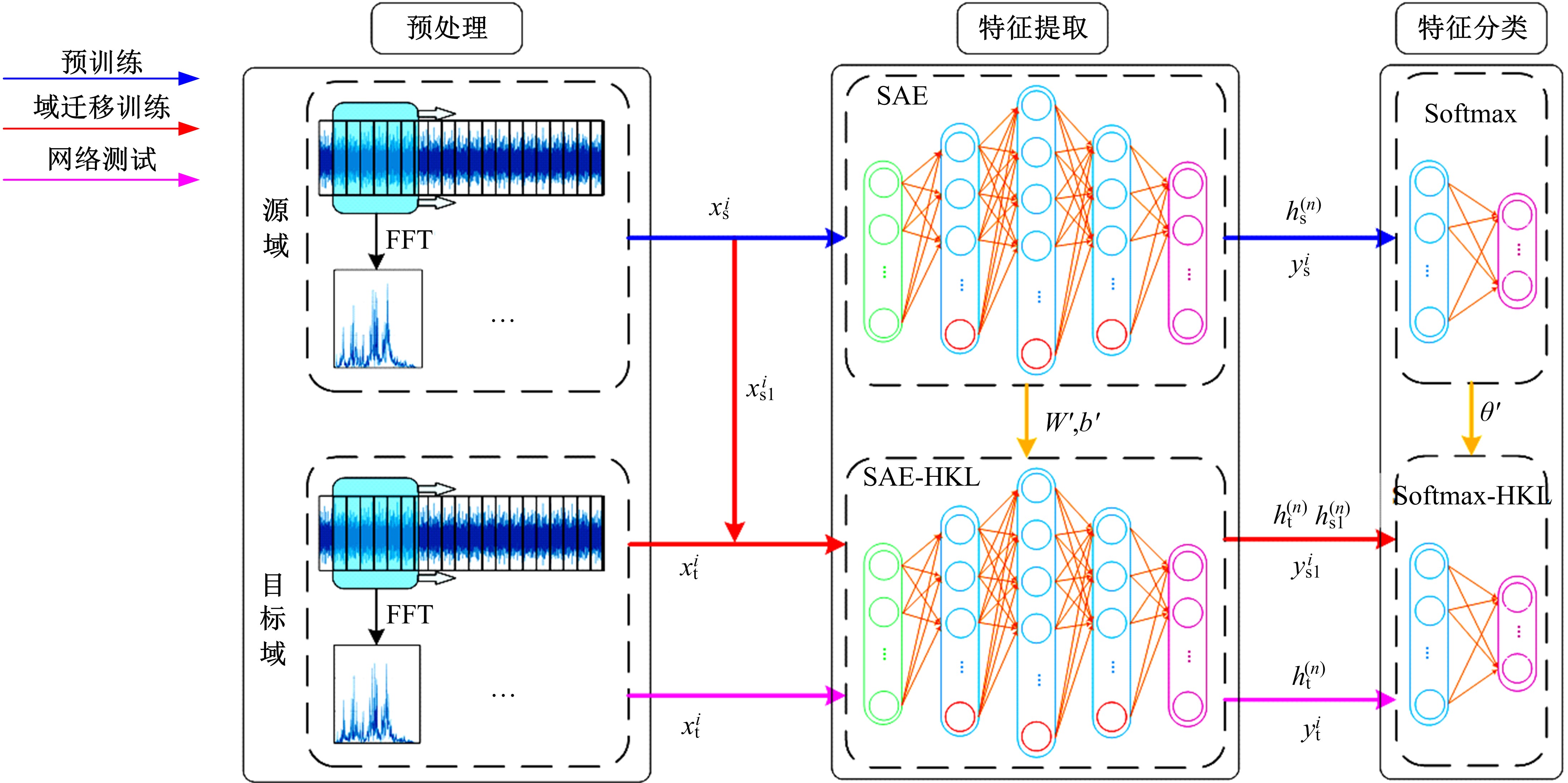
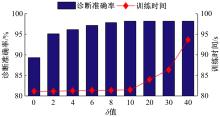
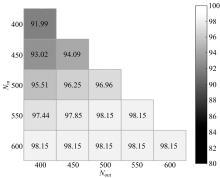
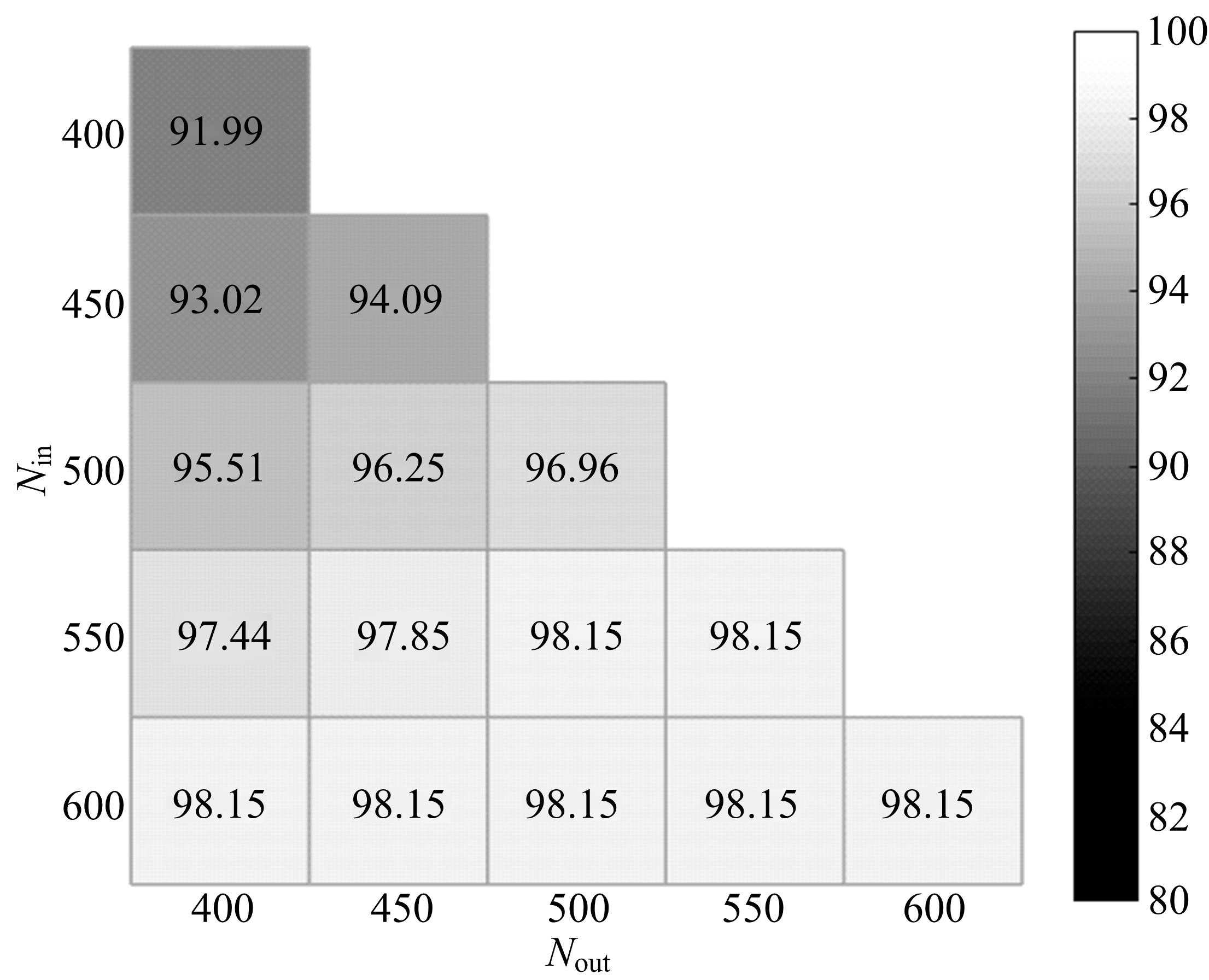
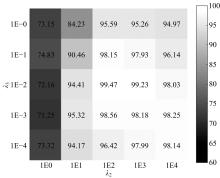
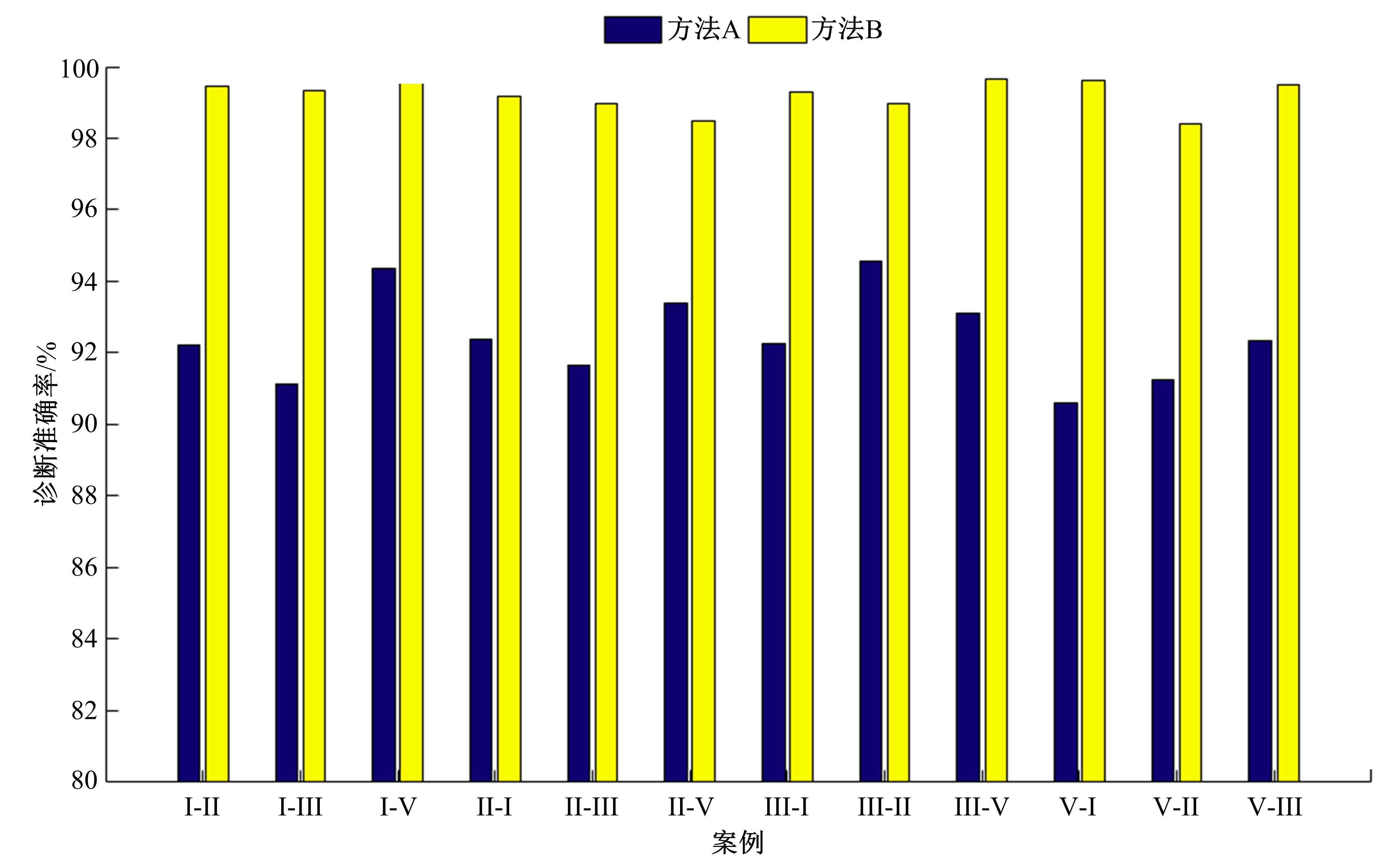
基于人工神经网络的智能故障诊断方法能有效识别设备的健康状况,但传统人工神经网络需要大量有标签样本进行训练,这极大限制了人工神经网络在设备故障诊断中的应用,并且对于不同工况的适应性较差。为解决该问题,提出了一种基于迁移学习理论的轴承故障诊断模型,该模型由栈式稀疏自动编码器(SAE)和柔性最大值函数(Softmax)回归组成,引入高阶KL散度(HKL)训练域自适应能力,可从具有大量已知数据的工况迁移到仅有少量数据的相似工况中。当工况改变时,仅需少量数据进行训练即可适应新工况。采用凯斯西储大学公开的轴承实验数据集验证了该模型的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TH17
| 1 | Yin J L, Wang W Y, Man Z H, et al. Statistical modeling of gear vibration signals and its application to detecting and diagnosing gear faults[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 259: 295-303. |
| 2 | Li W, Zhu Z C, Jiang F, et al. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery with a novel statistical feature extraction and evaluation method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 50/51: 414-426. |
| 3 | Shen C Q, Wang D, Kong F R, et al. Fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on the statistical parameters of wavelet packet paving and a generic support vector regressive classifier[J]. Measurement, 2013, 46(4): 1551-1564. |
| 4 | 马辉, 车迪, 牛强, 等. 基于深度神经网络的提升机轴承故障诊断研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019(16): 123-129. |
| Ma Hui, Che Di, Niu Qiang, et al. Fault diagnosis of elevator bearing based on deep neural network[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019(16): 123-129. | |
| 5 | 刘文朋, 廖英英, 杨绍普, 等. 一种基于多点峭度谱和最大相关峭度解卷积的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(2): 146-151, 163. |
| Liu Wen-peng, Liao Ying-ying, Yang Shao-pu, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based onmultipoint kurtosis spectrums and the maximum correlated kurtosis deconvolution method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(2): 146-151, 163. | |
| 6 | 郝研, 王太勇, 万剑, 等. 基于经验模式分解和广义维数的机械故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(2): 392-396. |
| Hao Yan, Wang Tai-yong, Wan Jian, et al. Mechanical fault diagnosis based on empirical mode decomposition and generalized dimension[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(2): 392-396. | |
| 7 | 高立新, 张建宇, 崔玲丽, 等. 基于小波分析的低速重载设备故障诊断[J]. 机械工程学报, 2005, 41(12): 222-227. |
| Gao Li-xin, Zhang Jian-yu, Cui Ling-li, et al. Research on fault diagnosis technology of low speed and heavy duty equipments based on wavelet analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2005, 41(12): 222-227. | |
| 8 | 李文军, 张洪坤, 程秀生. 基于小波和神经网络的传感器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2004, 344(3): 491-495. |
| Li Wen-jun, Zhang Hong-kun, Cheng Xiu-sheng. Sensor fault diagnosis based on wavelet and neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2004, 34(3): 491-495. | |
| 9 | Jia F, Lei Y G, Lin J, et al. Deep neural networks: a promising tool for fault characteristic mining and intelligent diagnosis of rotating machinery with massive data[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 72/73: 303-315. |
| 10 | 牟亮, 王凯, 李彦, 等. 层叠P阶多项式主成分分析在轴承故障诊断中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(2): 25-32. |
| Mu Liang, Wang Kai, Li Yan, et al. Bearing fault diagnosis based on the stacked P-order polynomial principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(2): 25-32. | |
| 11 | 程利军, 张英堂, 李志宁, 等. 基于时频分析及阶比跟踪的曲轴轴承故障诊断研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(19): 73-78. |
| Cheng Li-jun, Zhang Ying-tang, Li Zhi-ning, et al. Research on fault diagnose of main bearing based on time-frequency analysis and order tracking[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(19): 73-78. | |
| 12 | 陶新民, 徐晶, 刘兴丽, 等. 基于最大小波奇异谱的轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2010, 30(1): 78-82. |
| Tao Xin-min, Xu Jing, Liu Xing-li, et al. Fault diagnosis of bearing using maximum wavelet singular spectrum[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2010, 30(1): 78-82. | |
| 13 | 庄福振, 罗平, 何清, 等. 迁移学习研究进展[J]. 软件学报, 2015, 26(1): 26-39. |
| Zhuang Fu-zhen, Luo Ping, He Qing, et al. Survey on transfer learning research[J]. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(1): 26-39. | |
| 14 | Zhang R, Tao H Y, Wu L F, et al. Transfer learning with neural networks for bearing fault diagnosis in changing working conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2017(5): 14347-14357. |
| 15 | Han D M, Liu Q G, Fan W G. A new image classification method using CNN transfer learning and web data augmentation[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 95: 43-56. |
| 16 | Chen D M, Yang S, Zhou F N. Incipient fault diagnosis based on DNN with transfer learning[C]∥International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Hangzhou, China, 2018: 303-308. |
| 17 | Karsten M B, Arthur G, Malte R, et al. Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy[J]. Bioinformatics, 2006, 22(14): 49-57. |
| 18 | Lu W N, Liang B, Cheng Y, et al. Deep model based domain adaptation for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(3): 2296-2305. |
| 19 | Wen L, Gao L, Li X Y. A new deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(1): 136-144. |
| 20 | Ding Z M, Fu Y. Robust transfer metric learning for image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 660-670. |
| 21 | Jiang L, Ge Z Q, Song Z H. Semi-supervised fault classification based on dynamic sparse stacked auto-encoders model[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2017, 168: 72-83. |
| 22 | Zheng Y L, Wang T Z, Xin B, et al. A sparse autoencoder and softmax regression based diagnosis method for the attachment on the blades of marine current turbine[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(4): 826. |
| 23 | Qian W W, Li S M, Wang J R. A new transfer learning method and its application on rotating machine fault diagnosis under variant working conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2018(6): 1-11. |
| 24 | 朱冰, 蒋渊德, 邓伟文, 等. 基于KL散度的驾驶员驾驶习性非监督聚类[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(11): 1317-1323. |
| Zhu Bing, Jiang Yuan-de, Deng Wei-wen, et al. Unsupervised clustering of driving styles based on KL divergence[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(11): 1317-1323. | |
| 25 | Case Western Reserve University. Bearing data center[DB/OL]. [2019-04-28]. file |
| 26 | Yang B, Lei Y G, Jia F, et al. An intelligent fault diagnosis approach based on transfer learning from laboratory bearings to locomotive bearings[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 122: 692-706. |
| [1] | 江涛,林学东,李德刚,杨淼,汤雪林. 基于人工神经网络的放热规律的量化预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1747-1754. |
| [2] | 王德军, 魏薇郦, 鲍亚新. 考虑侧风干扰的电子稳定控制系统执行器故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1548-1555. |
| [3] | 宋大凤, 李广含, 张琳, 潘冰, 曾小华, 彭宇君, 王庆年. 模糊逻辑在混合动力汽车电机故障检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 354-359. |
| [4] | 欧阳丹彤,迟晋进,王晓宇,赵相福,孟祥宇. 一种高阶离散事件系统的诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 562-568. |
| [5] | 陶涛,徐洪泽. 高速列车浸入与不变自适应容错控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 554-561. |
| [6] | 宋宝玉,解志杰,张锋,王瑞泽,郝明晖,苏代忠. 基于角度域同步平均和阶次分析的低速斜齿轮故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 454-459. |
| [7] | 吴坚, 赵阳, 何睿. 基于支持向量机回归算法的电子机械制动传感器系统故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1178-1183. |
| [8] | 郝研, 王太勇, 万剑, 张攀, 刘路. 基于经验模式分解和广义维数的机械故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 392-396. |
| [9] | 陈筠翰1,秦贵和1,2,于赫1,黄玥1. 基于OSEK/VDX直接NM规范的车载网络系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1407-1413. |
| [10] | 孔繁森,吴雅夫,李聪. 基于信息熵的设备电气故障诊断复杂性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 697-701. |
| [11] | 贾志新, 张宏斌, 郗安民. 利用神经网络扩充数控机床可靠性数据[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(02): 403-0407. |
| [12] | 高印寒, 孙强, 丛玉良, 池俊成, 唐荣江. 基于神经网络的非稳态噪声品质的评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(增刊): 110-0114. |
| [13] | 夏红伟, 凌明祥, 李莉, 马闯, 王礼. 不确定网络控制系统鲁棒故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 501-0505. |
| [14] | 殷涌光,丁筠. 基于计算机视觉的食品中大肠杆菌快速定量检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 344-0348. |
| [15] | 刘玉梅,苏建,曹晓宁,熊伟,宋学忠. 基于模糊数学的汽车悬架系统故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 220-0224. |
|
||