吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 1146-1152.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200108
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析
王康1( ),姚猛1,李立犇2,李建桥2,邓湘金1,邹猛2,薛龙3(
),姚猛1,李立犇2,李建桥2,邓湘金1,邹猛2,薛龙3( )
)
- 1.中国空间技术研究院 北京空间飞行器总体设计部,北京 100094
2.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
3.江西农业大学 江西省现代农业装备重点实验室,南昌 330045
Mechanical performance identification for lunar soil in lunar surface sampling
Kang WANG1( ),Meng YAO1,Li-ben LI2,Jian-qiao LI2,Xiang-jin DENG1,Meng ZOU2,Long XUE3(
),Meng YAO1,Li-ben LI2,Jian-qiao LI2,Xiang-jin DENG1,Meng ZOU2,Long XUE3( )
)
- 1.Beijing Institute of Spacecraft System Engineering,China Academy of Space Technology,Beijing 100094,China
2.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Changchun 130022,China
3.Key Laboratory of Modern Agricultural Equipment of Jiangxi Province,Jiangxi Agricultural University,Nanchang 330045,China
摘要:
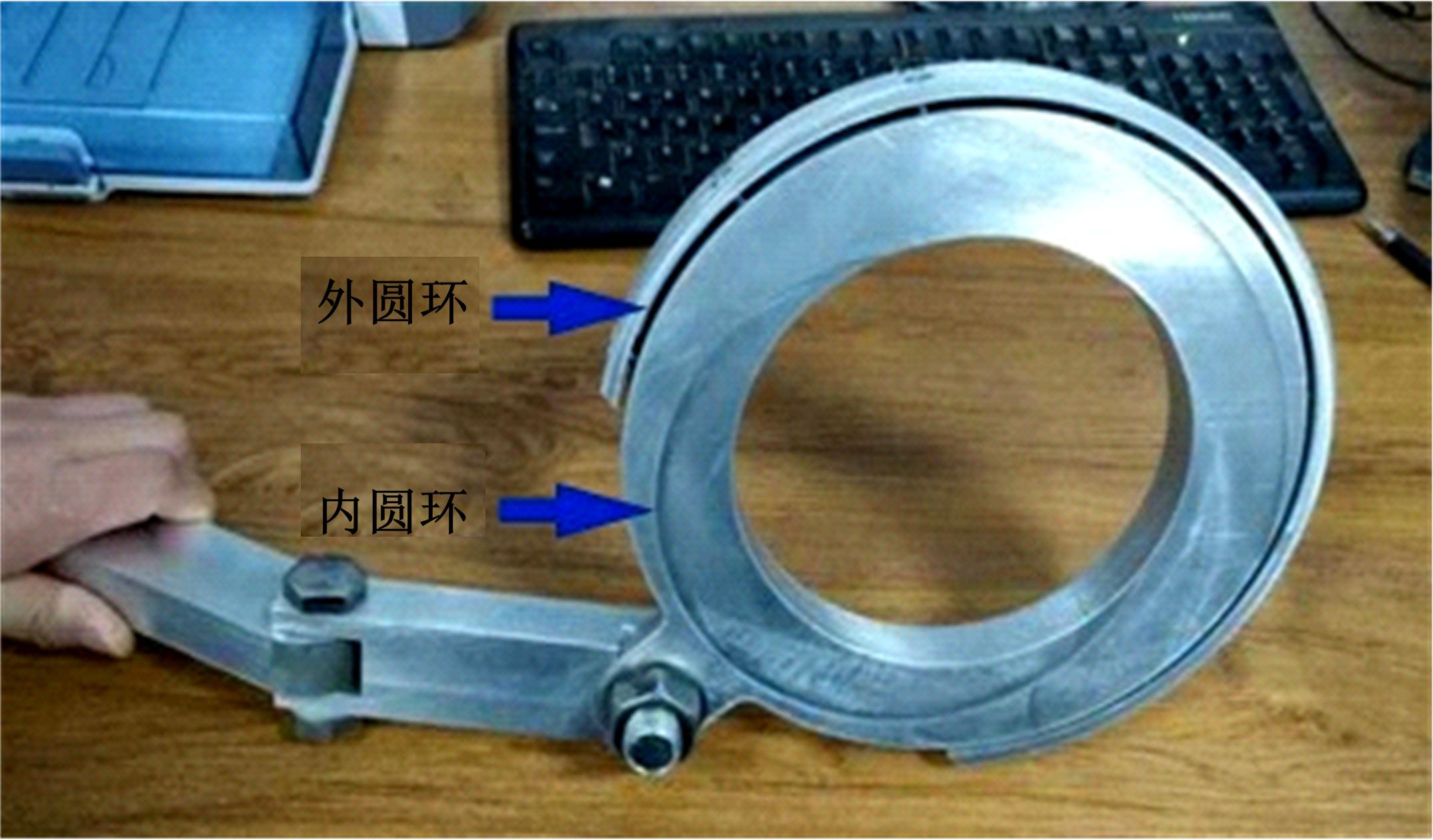
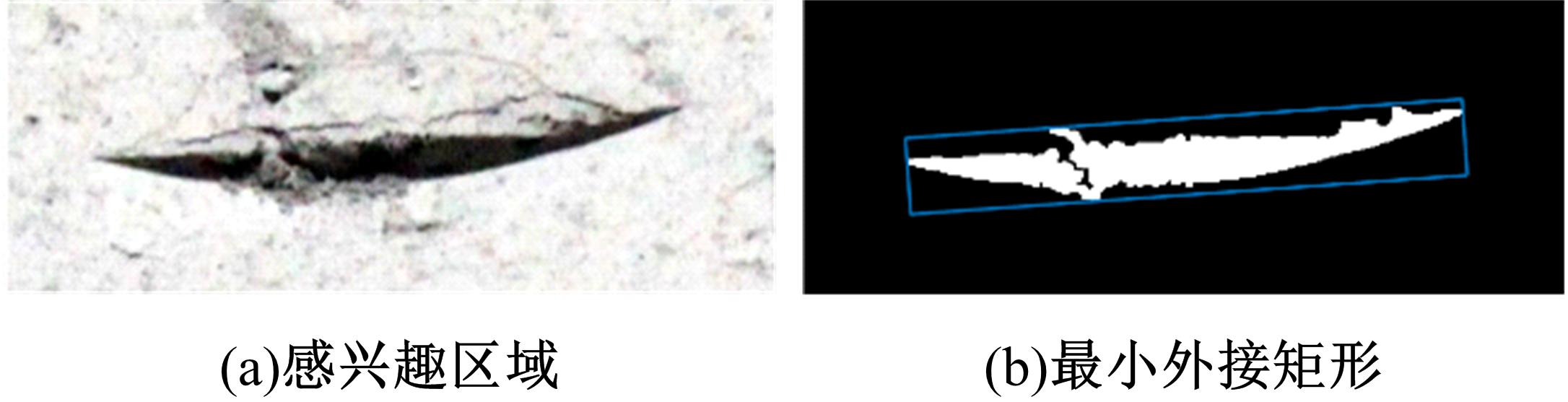
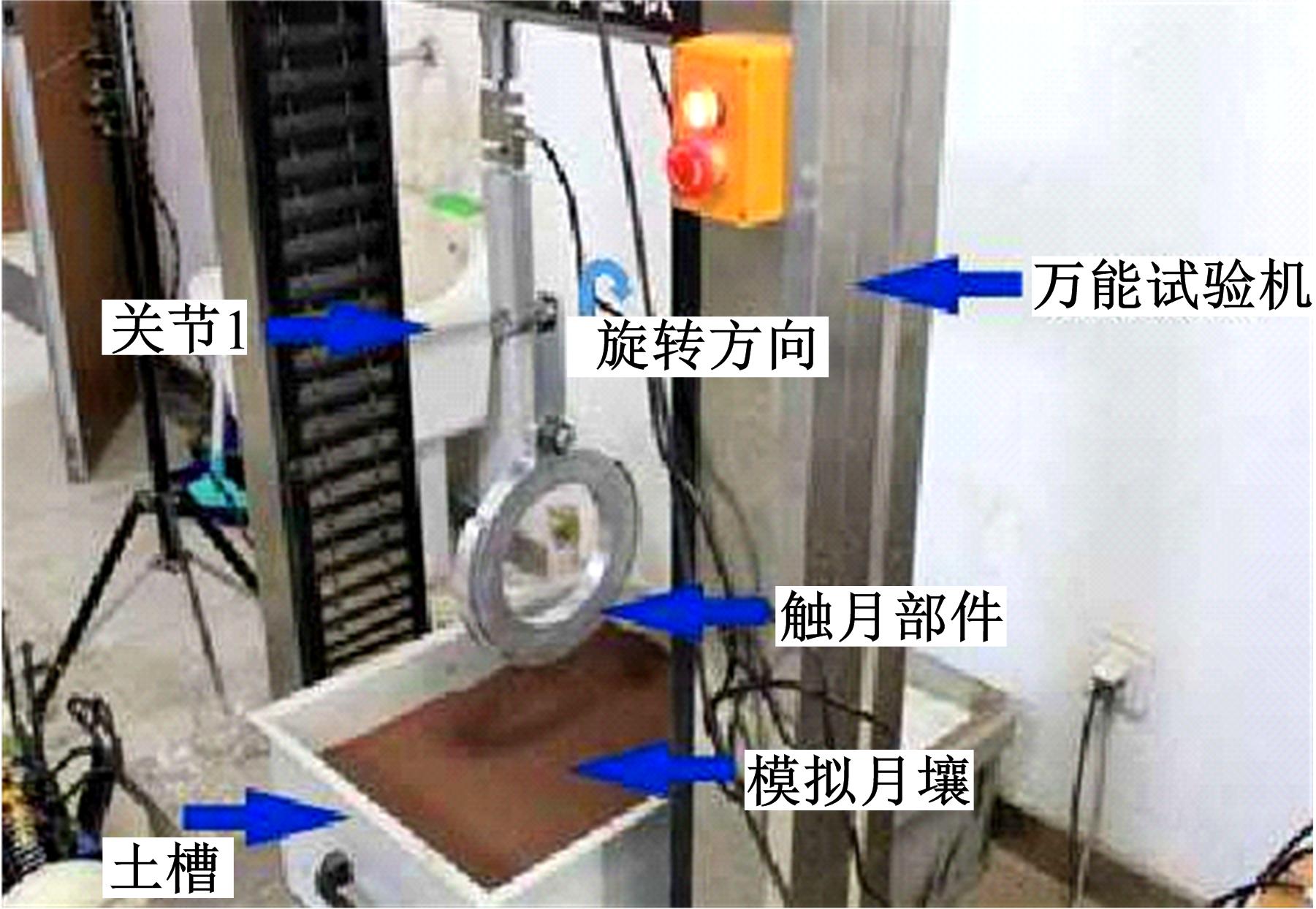
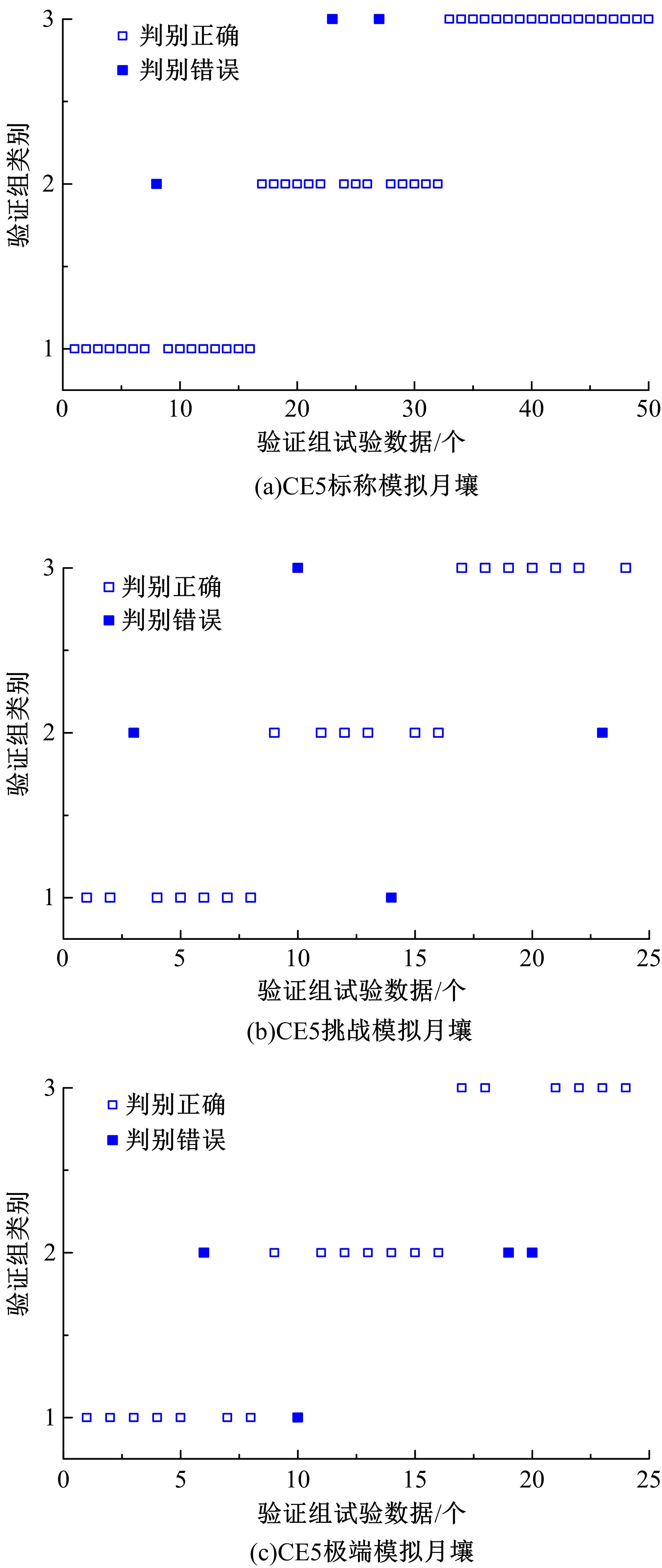
以表取采样机械臂的触月传感组件与月表接触留下的压痕为研究对象,通过监视相机提取压痕的几何特征参数,结合偏最小支持向量机(LSSVM)建立评估月壤力学状态模型。采集压痕试验数据264组,按力学状态把数据随机划分为建模组和验证组,以压痕的深度、长边长、压痕周长和面积为输入变量,建立LSSVM模型,验证组预测精度分别为93.75%、83.33%和87.50%。结果表明,该模型可作为一种有效的判别手段,为表取采样深度的确定提供参考。
中图分类号:
- TB17
| 1 | 陈百超,邹猛,党兆龙,等. CE-3月球车筛网轮月面沉陷行为试验[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(6):1836-1843. |
| Chen Bai-chao, Zou Meng, Dang Zhao-long, et al. Experiment on pressure⁃sinkage for mesh wheels of CE⁃3lunar rover on lunar regolith[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6):1836-1843. | |
| 2 | 马常友,高海波,丁亮,等. 机器人末端执行器自更换机构设计及对接策略[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(6):2027-2037. |
| Ma Chang-you, Gao Hai-bo, Ding Liang, et al. Mechanism design and docking strategy forend⁃effectors exchange of robot[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6):2027-2037. | |
| 3 | Moore H J, Bickler D B, Crisp J A, et al. Soil-like deposits observed by Sojourner, the Pathfinder rover[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 1999, 104(E4):8729-8746. |
| 4 | Arvidson R E, Anderson R C, Bartlett P, et al. Localization and physical property experiments conducted by opportunity at meridiani planum[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5702):1730-1733. |
| 5 | Arvidson R E, Anderson R C, Bartlett P, et al. Localization and physical properties experiments conducted by Spirit at Gusev crater[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5685):821-824. |
| 6 | Seneviratne L, Althoefer K, Zweiri Y, et al. The modelling and estimation of driving forces for unmanned ground vehicles in outdoor terrain[J]. International Journal of Modelling, Identification and Control, 2009, 6(1):40-50. |
| 7 | Hutangkabodee S, Zweiri Y H, Seneviratne L D, et al. Soil parameter identification for wheel-terrain interaction dynamics and traversability prediction[J]. International Journal of Automation and Computing, 2006, 3(3):244-251. |
| 8 | 崔平远, 刘冰, 居鹤华. 月壤力学参数在线估计算法研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2008, 16(2):245-247. |
| Cui Ping-yuan, Liu Bing, Ju He-hua. Research on mechanical parameters online estimation of lunar soil[J]. Computer Measurem & Control, 2008, 16(2):245-247. | |
| 9 | Ding L, Deng Z Q, Gao H B, et al. Planetary rovers' wheel-soil interaction mechanics: new challenges and applications for wheeled mobile robots[J]. Intel Serv Robotics, 2011, 4(1):17-38. |
| 10 | 丁亮, 高海波, 邓宗全,等. 基于月球车轮地作用地面力学积分模型的月壤力学参数辨识方法[J]. 航空学报, 2011, 32(6):1112-1123. |
| Ding Liang, Gao Hai-bo, Deng Zong-quan, et al. An approach of identifying mechanical parameters for lunar soil based on itergrated wheel-soil interaction terramechanics model of rovers[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(6):1112-1123. | |
| 11 | Long Xue, Li Jian-qiao, Zou Meng, et al. In situ identification of shearing parameters for loose lunar soil using least squares support vector machine[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 53:154-161. |
| 12 | Cross M. Estimating terrain parameters with a rigid wheeled rover using neural networks[D]. Canada: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Carleton University, 2012. |
| 13 | Chen Chong-bin, Quan Qi-quan, Shi Xiao-meng, et al. Multi-state autonomous drilling for lunar exploration[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(5):1397-1404. |
| 14 | Shaw A, Arvidson R E, Bonitz R, et al. Phoenix soil physical properties investigation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2009, 114(E1):E00E05. |
| 15 | Wilkinson A, DeGennaro A. Digging and pushing lunar regolith: classical soil mechanics and the forces needed for excavation and traction[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2007, 44(2):133-152. |
| 16 | Zweiri Y H, Seneviratne L D, Althoefer K. Parameter estimation for excavator arm using generalized Newton method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2004, 20(4):762-767. |
| 17 | Blouin S, Hemami A, Lipsett M. Review of resistive force models for earthmoving processes[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2001, 14(3):102-111. |
| 18 | 郑燕红, 姚猛, 金晟毅,等. 月面复杂地形表层采样可采点确定方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2019, 39(2):41-48. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Yao Meng, Jin Sheng-yi, et al. Lunar surface sampling point selection for uneven terrain[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2019, 39(2):41-48. | |
| 19 | 姚猛, 郑燕红, 赵志晖, 等. 一种月表采样器合理铲挖深度的研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2017, 26(3):50-56. |
| Yao Meng, Zheng Yan-hong, Zhao Zhi-hui, et al. Research on reasonable excavation depth for lunar regolith sampler[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(3):50-56. | |
| 20 | 郑燕红, 邓湘金, 庞勇,等. 月球风化层钻取采样过程密实度分类研究[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(4):223391. |
| Zheng Yan-hong, Deng Xiang-jin, Pang Yong, et al. Research on classification of relative density in lunar regolith drilling[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(4):223391. | |
| 21 | 薛龙, 邹猛, 李建桥,等. 基于轮地作用参数和PLSDA方法的月壤力学性能评估[J]. 航空学报,2015, 36(11):3751-3758. |
| Xue Long, Zou Meng, Li Jian-qiao, et al. Mechanical performance estimation of lunar soil using wheel-soil interaction parameter and PLSDA[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(11):3751-3758. | |
| 22 | 李雄飞, 王婧, 张小利, 等. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(1):227-236. |
| Li Xiong-fei, Wang Jing, Zhang Xiao-li, et al. Multi-focus image fusion based on support vector machines and window gradient[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1):227-236. | |
| 23 | Suykens J A K, Gestel T V, Brabanter J D, et al. Least Squares Support Vector Machines[M]. Singapore: World Scientific,2002. |
| [1] | 李健,刘孔宇,任宪盛,熊琦,窦雪峰. 基于自适应阈值的Canny算法在MRI边缘检测中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 712-719. |
| [2] | 刘富,刘璐,侯涛,刘云. 基于优化MSR的夜间道路图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 323-330. |
| [3] | 李雄飞,王婧,张小利,范铁虎. 基于SVM和窗口梯度的多焦距图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
| [4] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,李明昭,刘静,胡黄水,王丹,臧雪柏. 基于自然性和视觉特征通道的场景分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [6] | 卢洋,王世刚,赵文婷,赵岩. 基于离散Shearlet类别可分性测度的人脸表情识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1715-1725. |
| [7] | 赵金钢,张明,占玉林,谢明志. 基于塑性应变能密度的钢筋混凝土墩柱损伤准则[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1124-1133. |
| [8] | 陈俊,张奇峰,张艾群,蔡笃思. 基于深渊鱼类识别的原位自主观测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 953-962. |
| [9] | 刘哲, 徐涛, 宋余庆, 徐春艳. 基于NSCT变换和相似信息鲁棒主成分分析模型的图像融合技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1614-1620. |
| [10] | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [11] | 隗海林, 包翠竹, 李洪雪, 李明达. 基于最小二乘支持向量机的怠速时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1360-1365. |
| [12] | 耿庆田, 于繁华, 王宇婷, 高琦坤. 基于特征融合的车型检测新算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 929-935. |
| [13] | 蔡振闹, 吕信恩, 陈慧灵. 基于反向细菌优化支持向量机的躯体化障碍预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 936-942. |
| [14] | 梁士利, 柴宗谦, 张玲, 吴颜生, 曹春雷. 基于偏X型细胞自动机的图像加密方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1653-1660. |
| [15] | 黄晗, 李建桥, 陈百超, 吴宝广, 邹猛. 着陆器足垫冲击特性模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1194-1200. |
|
||