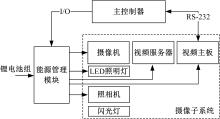
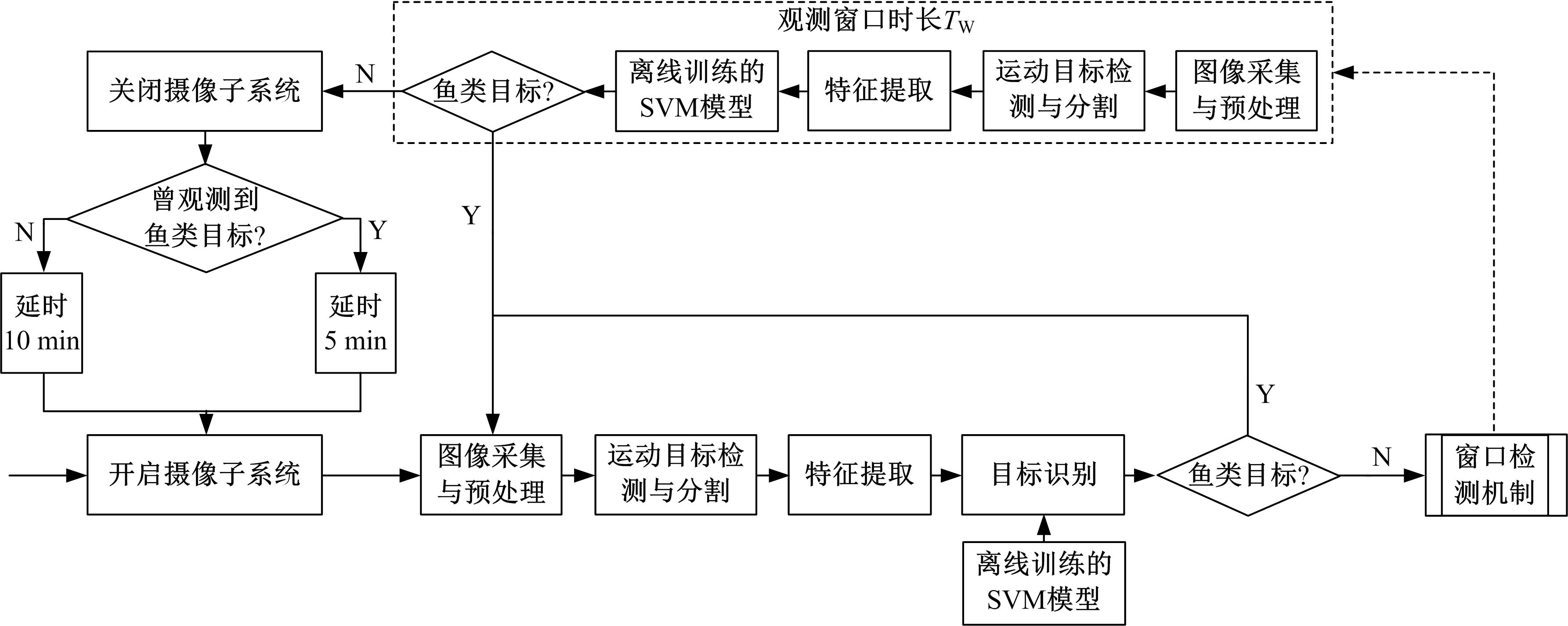
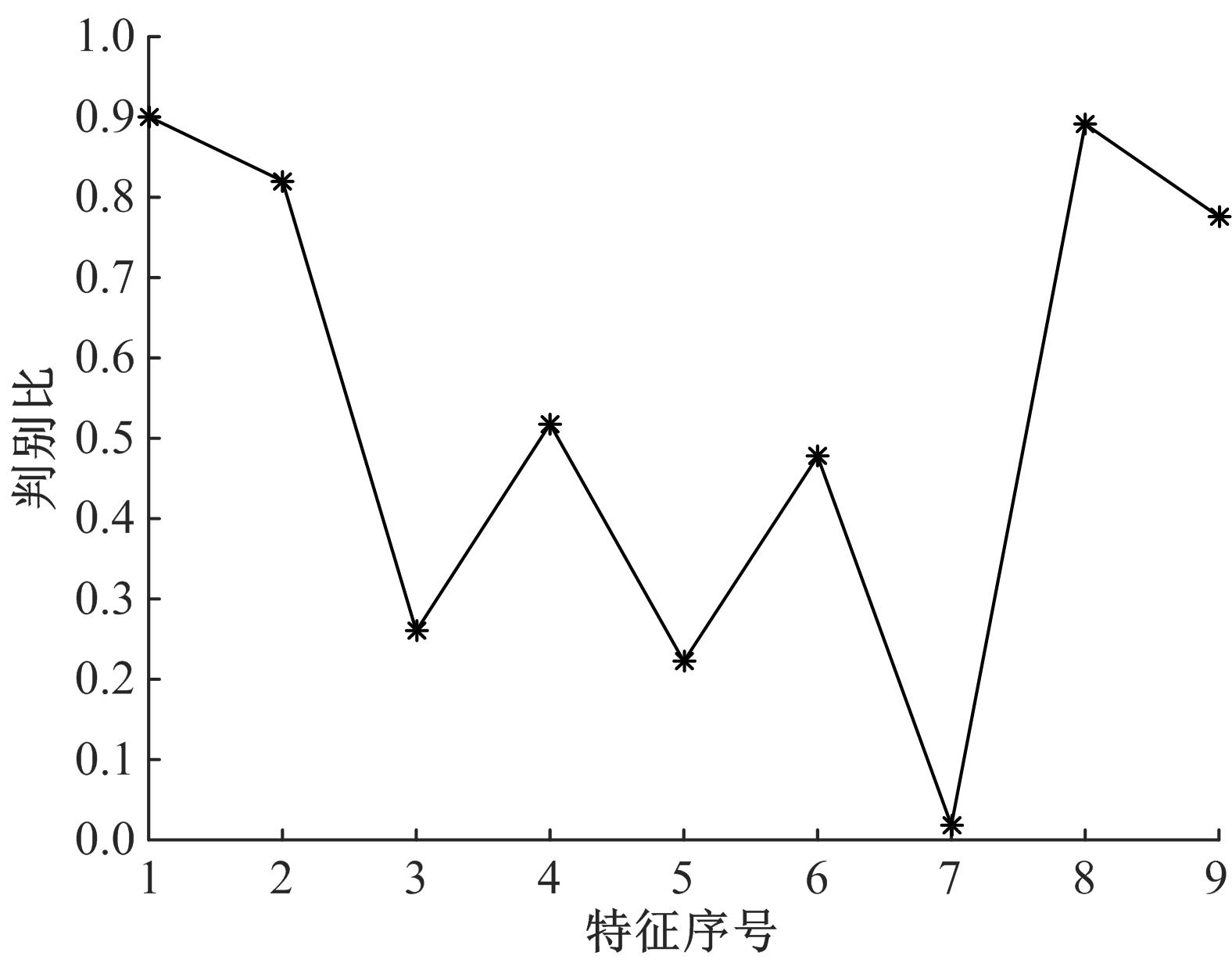
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 953-962.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180160
基于深渊鱼类识别的原位自主观测方法
- 1. 中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所 机器人学国家重点实验室,沈阳 110016
2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3. 中国科学院深海科学与工程研究所,海南 三亚 572000
In⁃situ autonomous observation method based onhadal fish recognition
Jun CHEN1,2( ),Qi⁃feng ZHANG1(
),Qi⁃feng ZHANG1( ),Ai⁃qun ZHANG1,3,Du⁃si CAI3
),Ai⁃qun ZHANG1,3,Du⁃si CAI3
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Robotics, Shenyang Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenyang 110016, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100049, China
3. Institute of Deep?sea Science and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572000, China
摘要:
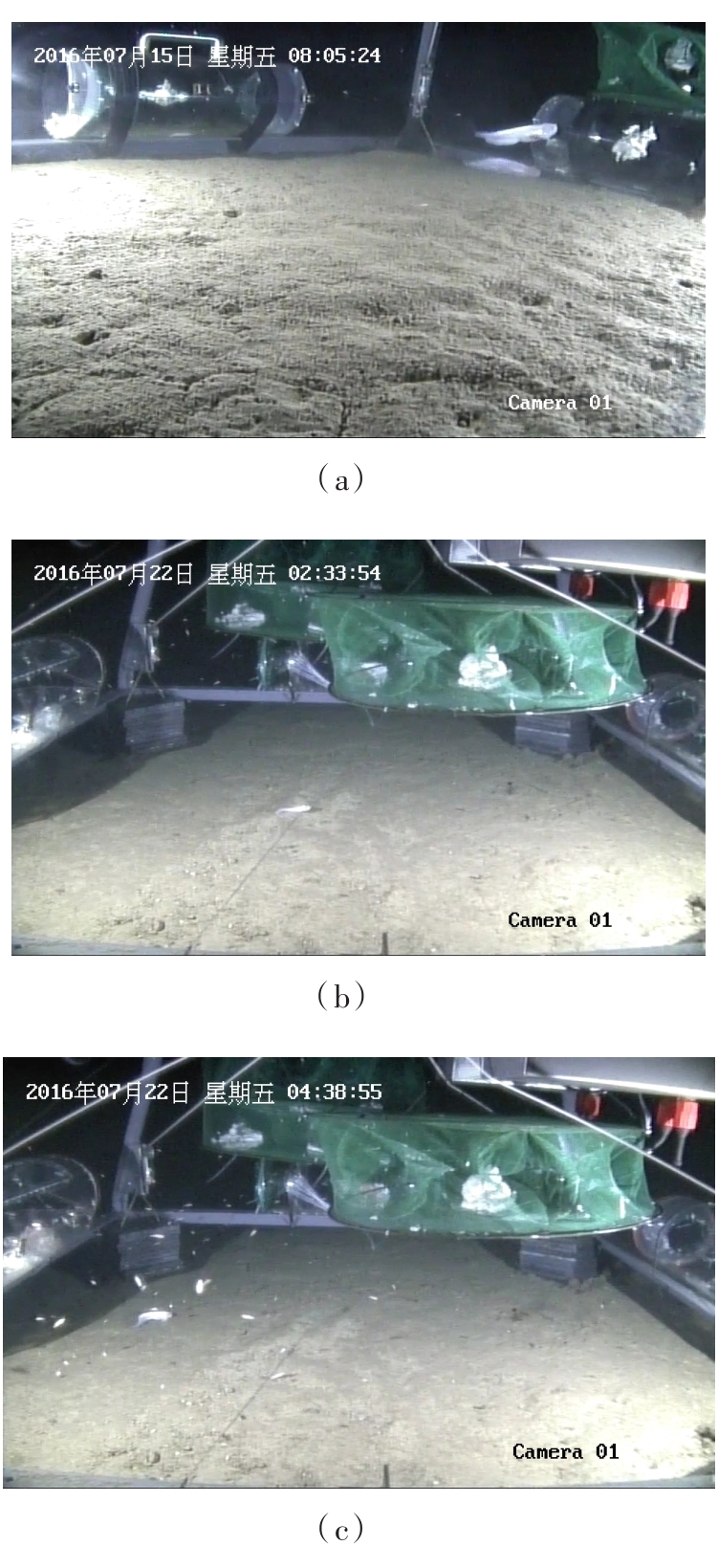
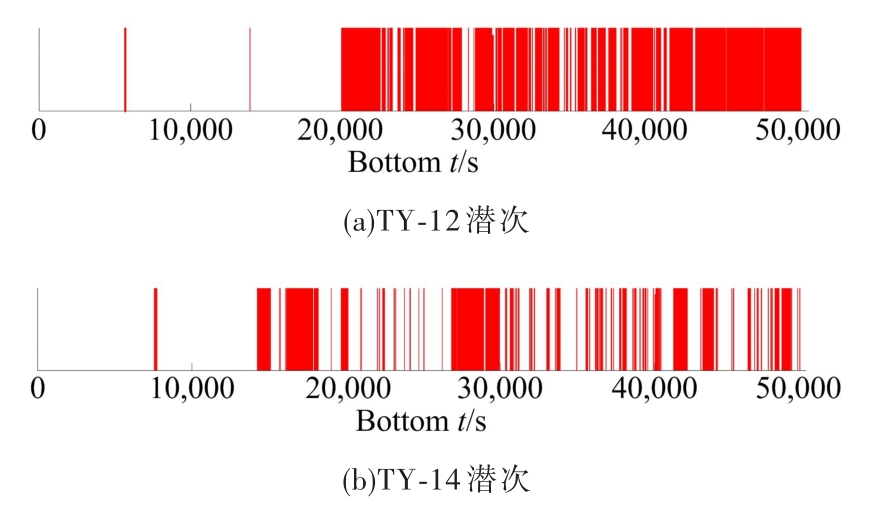
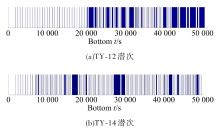
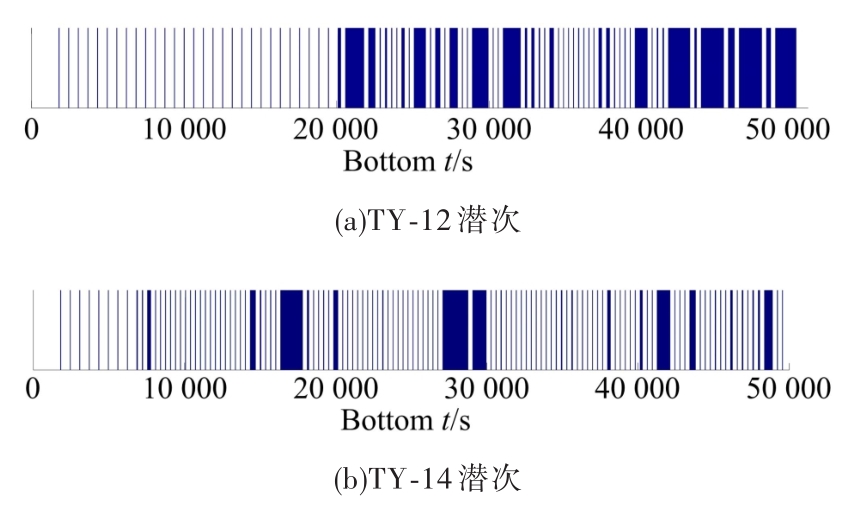
为提高深渊鱼类观测效率,针对传统预编程式观测方法无法感知目标的不足,提出了一种基于鱼类识别的自主观测方法。首先,通过改进的背景差分法快速分割运动目标;其次,结合深渊生物特点提出了基于Fisher判别函数的形状特征提取方法,然后使用粒子群优化(PSO)算法的支持向量机(SVM)分类法实现了鱼类的识别。最后,设计了深渊鱼类的自主观测算法,并提出了一种观测效率的评价方法。使用深渊原位观测视频进行模拟观测实验的结果表明,本文算法可有效提高观测效率。
中图分类号:
- TP274
| 1 | JamiesonA J, FujiiT, MayorD J, et al. Hadal trenches: the ecology of the deepest places on earth[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2010,25(3):190⁃197. |
| 2 | LinleyT D, GerringerM E, YanceyP H, et al. Fishes of the hadal zone including new species, in situ, observations and depth records of Liparidae[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 114:99⁃110. |
| 3 | LinleyT D, StewartA L , McmillanP J, et al. Bait attending fishes of the abyssal zone and hadal boundary: Community structure, functional groups and species distribution in the Kermadec, New Hebrides and Mariana trenches[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 121:38⁃53. |
| 4 | JamiesonA. The hadal zone: life in the deepest oceans[M]. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press, 2015. |
| 5 | BaileyD M, KingN J, PriedeI G. Cameras and carcasses: historical and current methods for using artificial food falls to study deep⁃water animals[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 350: 179⁃191. |
| 6 | WhitmarshS K, FairweatherP G, HuveneersC. What is big BRUVver up to? Methods and uses of baited underwater video[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology & Fisheries, 2016: 1⁃21. |
| 7 | JamiesonA J, FujiiT, SolanM, et al. HADEEP: free⁃falling landers to the deepest places on earth[J]. Marine Technology Society Journal, 2009, 43(5):151⁃160. |
| 8 | WHOI. HADal Ecosystem Studies[EB/OL]. 2018-01-10.https:⫽web.whoi.edu/hades/. |
| 9 | JamiesonA J, KilgallenN M, RowdenA A, et al. Bait⁃attending fauna of the Kermadec Trench, SW Pacific Ocean: evidence for an ecotone across the abyssal–hadal transition zone[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2011, 58(1):49⁃62. |
| 10 | JamiesonA J, PriedeI G, CraigJ. Distinguishing between the abyssal macrourids Coryphaenoides yaquinae and C. armatus from in situ photography[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Paper, 2012, 64:78⁃85. |
| 11 | StaufferC, GrimsonW E L. Adaptive background mixture models for real⁃time tracking[C]⫽IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Piscataway, IEEE, 1999. |
| 12 | PiccardiM. Background subtraction techniques: a review[C]⫽IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Piscataway, IEEE, 2005. |
| 13 | 刘鑫, 刘辉, 强振平, 等. 混合高斯模型和帧间差分相融合的自适应背景模型[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2008, 13(4):729⁃734. |
| LiuXin, LiuHui, QiangZhen⁃ping, et al. Adaptive Background Modeling Based on Mixture Gaussian Model and Frame Subtraction[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2008, 13(4):729⁃734. | |
| 14 | HsiaoY H, ChenC C, LinS I, et al. Real⁃world underwater fish recognition and identification, using sparse representation[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2014, 23:13⁃21. |
| 15 | SpampinatoC, GiordanoD, SalvoR D, et al. Automatic fish classification for underwater species behavior understanding[C]⫽ACM International Workshop on Analysis and Retrieval of Tracked Events and Motion in Imagery Streams. ACM Paper, 2010:45⁃50. |
| 16 | SunX, ShiJ, DongJ, et al. Fish recognition from low⁃resolution underwater images[C]⫽International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Datong, China, 2016:15⁃17. |
| 17 | ChenJ, ZhangQ, ZhangA, et al. 7000M lander design for hadal research[C]⫽OCEANS, St. John's, NL, Canada, 2014:1⁃4. |
| 18 | ChenJ, ZhangQ, ZhangA, et al. Sea trial and free⁃fall hydrodynamic research of a 7000⁃meter lander[C]⫽OCEANS, Piscataway, Washington, DC,USA,2015:1⁃5. |
| 19 | 陈俊, 张奇峰, 李俊,等. 深渊着陆器技术研究及马里亚纳海沟科考应用[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2017, 36(1):63⁃69. |
| ChenJun, ZhangQi⁃feng, LiJun, et al. Research on the application of the hadal lander technology in the mariana trench[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2017, 36(1):63⁃69. | |
| 20 | 曾祥进, 黄心汉, 王敏. 不变矩的改进支持向量机在显微目标识别中的应用研究[J]. 机器人, 2009,31(2): 118⁃123. |
| ZengXiang⁃jin, HuangXin⁃han, WangMin. Application of invariant moment's improved support vector machine to micro⁃target identification[J]. Robot, 2009,31(2): 118⁃123. | |
| 21 | HuM K. Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1962,8(2): 179⁃187. |
| 22 | 李强, 薛开, 徐贺, 等. 基于振动采用支持向量机方法的移动机器人地形分类[J]. 机器人, 2012, 34(6): 660⁃667. |
| LiQiang, XueKai, XuHe, et al. Vibration⁃based terrain classification for mobile robots using support vector machine[J]. Robot, 2012, 34(6): 660⁃667. | |
| 23 | 陈建华, 奚如如, 王兴松, 等. 外骨骼机器人的非结构地面行走步态分类算法[J]. 机器人, 2017, 39(4): 505⁃513. |
| ChenJian⁃hua, XiRu⁃ru, WangXing⁃song, et al. Walking gait classification algorithm for exoskeleton robot on unstructured ground[J]. Robot, 2017, 39(4): 505⁃513. | |
| 24 | Azimi⁃SadjadiM R, YaoD, JamshidiA A, et al. Underwater target classification in changing environments using an adaptive feature mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2002, 13(5):1099⁃1111. |
| [1] | 隗海林, 包翠竹, 李洪雪, 李明达. 基于最小二乘支持向量机的怠速时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1360-1365. |
| [2] | 耿庆田, 于繁华, 王宇婷, 高琦坤. 基于特征融合的车型检测新算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 929-935. |
| [3] | 蔡振闹, 吕信恩, 陈慧灵. 基于反向细菌优化支持向量机的躯体化障碍预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 936-942. |
| [4] | 袁哲明, 张弘杨, 陈渊. 基于特征选择和支持向量机的HIV-1型蛋白酶剪切位点预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 639-646. |
| [5] | 梁士利, 魏莹, 潘迪, 张玲, 许廷发, 王双维. 基于语谱图行投影的特定人二字汉语词汇识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 294-300. |
| [6] | 赵云鹏, 于天来, 焦峪波, 宫亚峰, 宋刚. 异形桥梁损伤识别方法及参数影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1858-1866. |
| [7] | 商强, 杨兆升, 张伟, 邴其春, 周熙阳. 基于奇异谱分析和CKF-LSSVM的短时交通流量预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1792-1798. |
| [8] | 周炳海, 徐佳惠. 基于支持向量机的多载量小车实时调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2027-2033. |
| [9] | 卢英, 王慧琴, 秦立科. 高大空间建筑火灾精确定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2067-2073. |
| [10] | 马知行, 赵琦, 张浩. 基于傅立叶分析的持家基因预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1639-1643. |
| [11] | 王品, 何璇, 吕洋, 李勇明, 邱明国, 刘书君. 基于多特征支持向量机和弹性区域生长的膝软骨自动分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1688-1696. |
| [12] | 张静, 刘向东. 混沌粒子群算法优化最小二乘支持向量机的混凝土强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| [13] | 申铉京, 翟玉杰, 卢禹彤, 王玉, 陈海鹏. 基于信道补偿的说话人识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 870-875. |
| [14] | 宗芳, 王占中, 贾洪飞, 焦玉玲, 吴杨. 基于支持向量机的通勤日活动-出行持续时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 406-411. |
| [15] | 张浩, 刘海明, 吴春国, 张艳梅, 赵天明, 李寿涛. 基于多特征融合的绿色通道车辆检测判定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 271-276. |
|