吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1673-1683.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200409
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑个体风险偏好差异的高速公路出行选择模型
- 1.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广州 510640
2.广州市城市规划勘测设计研究院 交通规划设计所,广州 510060
Model of highway travel selection considering individual risk preference difference
Ying-ying MA1,2( ),Si-yuan LU2(
),Si-yuan LU2( ),Xiao-ming ZHANG2,Wen-shu WEI2
),Xiao-ming ZHANG2,Wen-shu WEI2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
2.Transportation Planning and Design Studio,Guangzhou Urban Planning & Design Survey Research Institute,Guangzhou 510060,China
摘要:
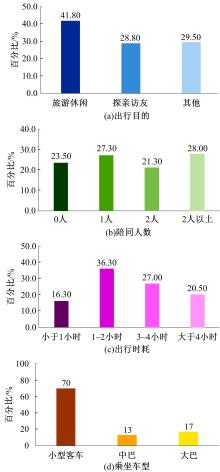
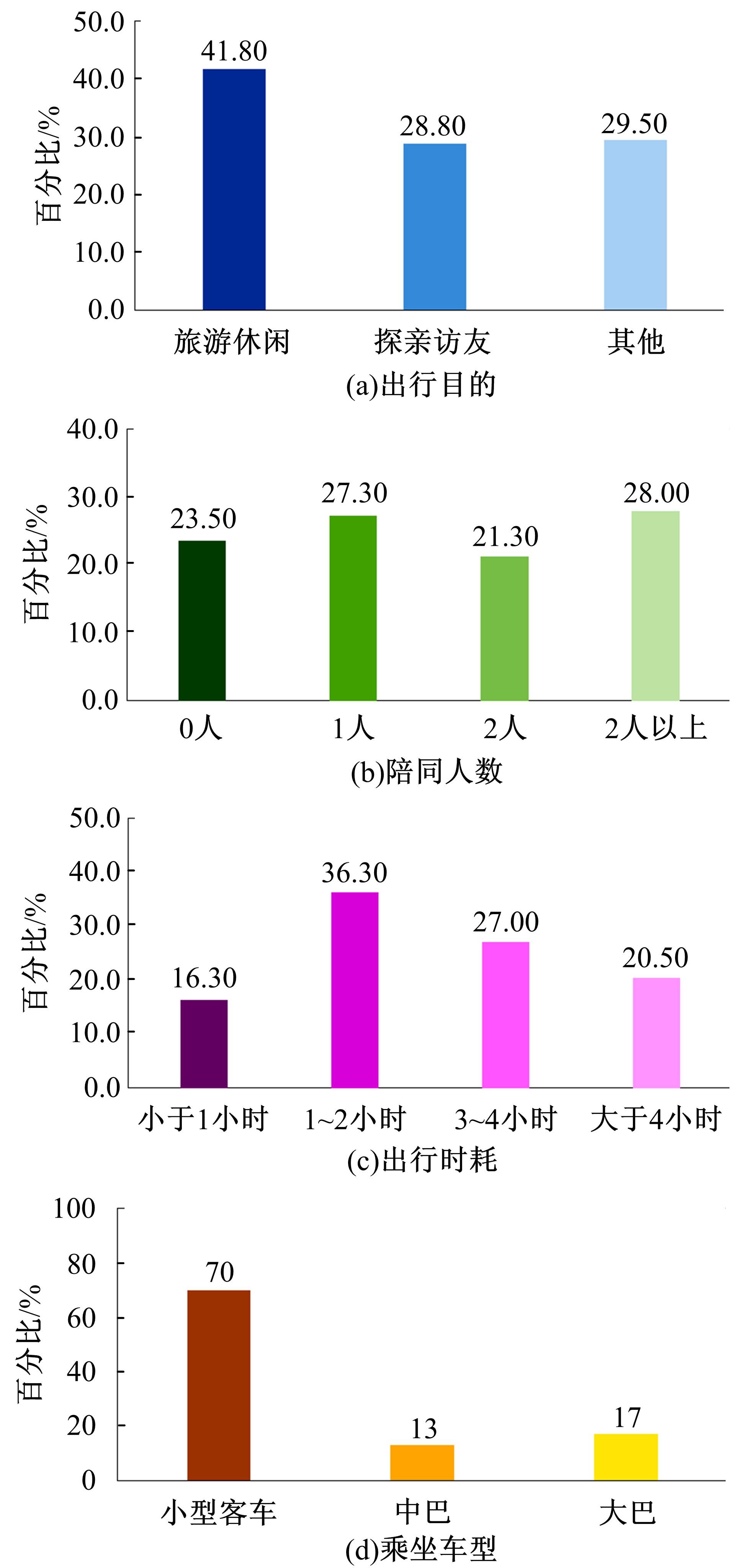
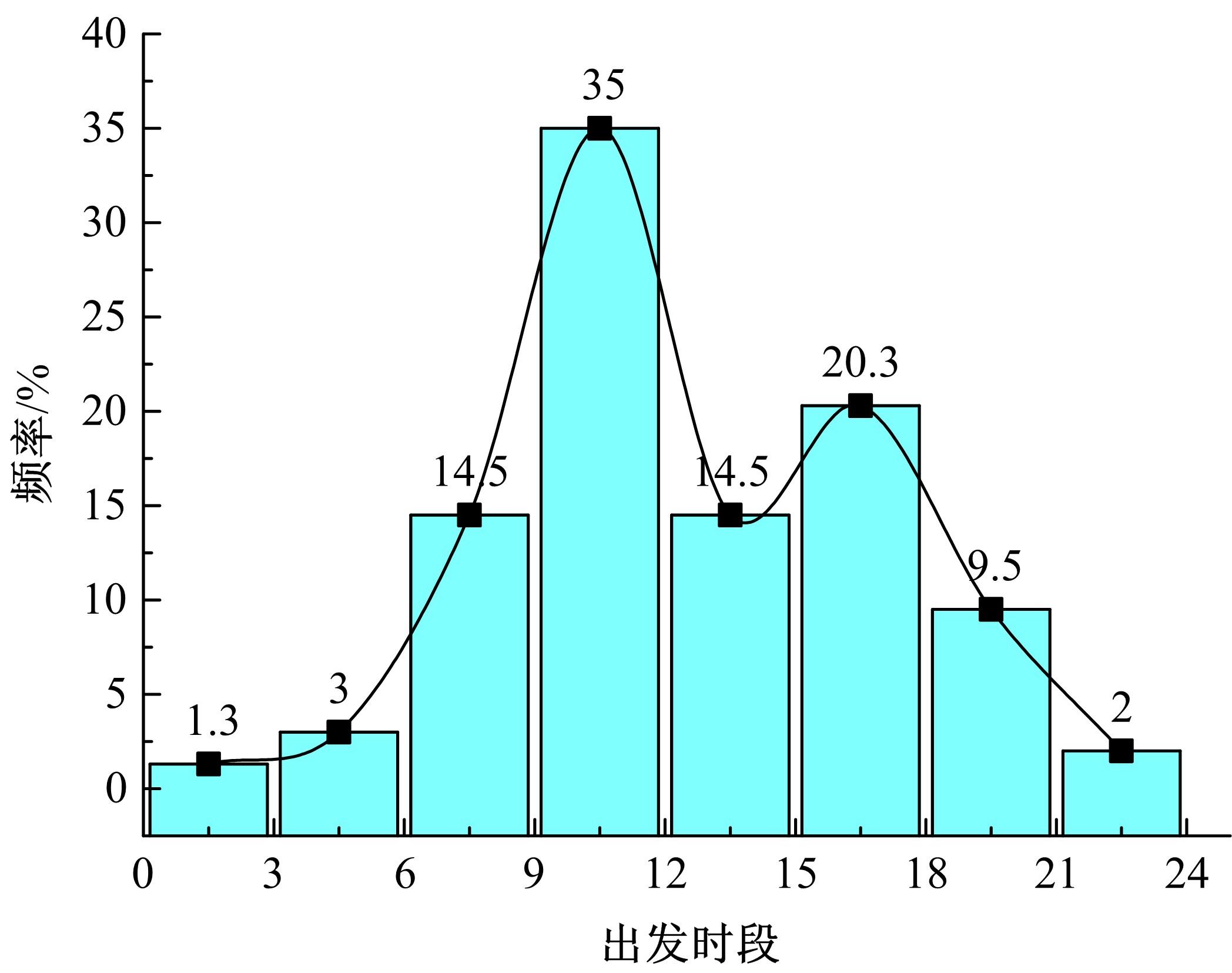
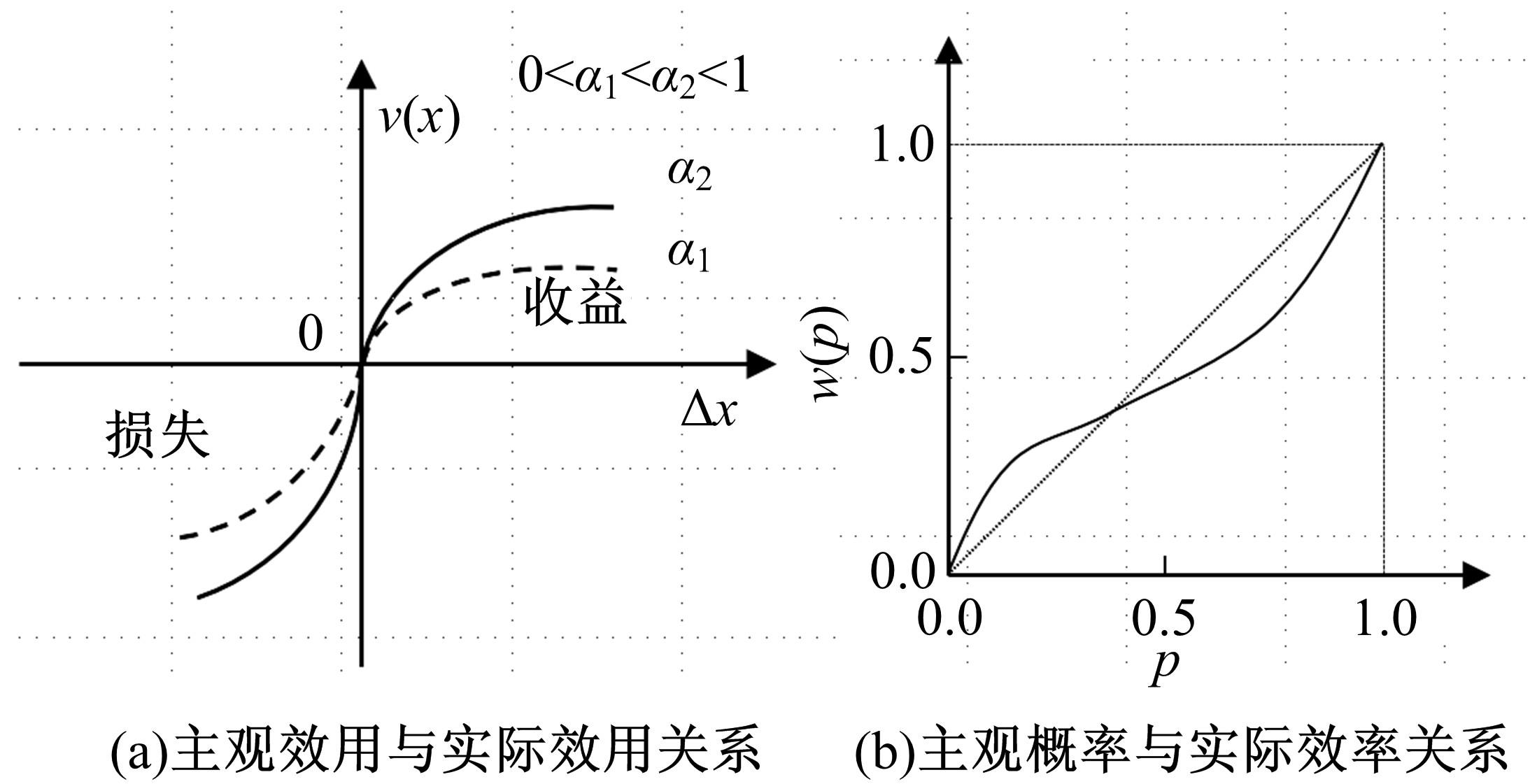
本文旨在进行节假日高速公路出行特征分析及出行行为决策建模。首先,进行节假日高速公路出行行为特性调查和分析,总共回收有效问卷数量500份;其次,考虑个体风险偏好差异性,提出基于巢式Logit-累积前景理论模型的高速公路出行时段选择模型,进一步了解节假日高速公路出行行为决策;最后,以广东省节假日高速公路为对象进行案例研究,并进行模型精度检验。研究表明:本文模型总体预测误差为14.14%,仅基于巢式Logit模型预测误差约为22.22%。与其他模型相比,本文模型有利于提高预测结果的精度。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 贾洪飞, 龚勃文, 宗芳. 交通方式选择的非集计模型及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2007, 37(6): 1288-1293. |
| Jia Hong-fei, Gong Bo-wen, Zong Fang. Disaggregation model of traffic mode selection and its application[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2007, 37(6): 1288-1293. | |
| 2 | Kumagai S J, Uchiyama H, Takashima S. Formation of bus network based on traffic mode selection model with disaggregate data[J]. Physics Letters A, 2011, 375(17): 1831-1838. |
| 3 | Ozbay K, Yanmaz-Tuzel O. Valuation of travel time and departure time choice in the presence of time-of-day pricing[J]. Transportation Research Part A Policy & Practice, 2008, 42(4): 577-590. |
| 4 | 张旭, 栾维新, 赵冰茹. 基于非集计模型的武广线高铁与民航竞争研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12(6): 17-21. |
| Zhang Xu, Luan Wei-xin, Zhao Bing-ru. Research on competition between Wuhan Guangzhou high speed railway and civil aviation based on disaggregation model[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2012, 12(6): 17-21. | |
| 5 | McFadden D, Train K. Mixed MNL models for discrete response[J]. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 2000, 15(5): 447-470. |
| 6 | 李华民, 黄海军. 基于一种新效用函数形式的分层Logit模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(): 63-65. |
| Li Hua-min, Huang Hai-jun. Layered logit model based on a new utility function form[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(Sup.2): 63-65. | |
| 7 | 唐洁, 隽志才, 高林杰. 城市居民出行空间和方式联合选择模型研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(5): 83-87. |
| Tang Jie, Zhi-cai Juan, Gao Lin-jie. Research on joint choice model of urban residents' travel space and mode[J]. Highway Transportation Technology, 2010, 27(5): 83-87. | |
| 8 | 诸葛承祥, 邵春福, 李霞, 等. 通勤者出行时间与出行方式选择行为研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2012, 12(2): 130-135. |
| Cheng-xiang Zhu-ge, Shao Chun-fu, Li Xia, et al. Study on commuter travel time and travel mode selection behavior[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2012, 12(2): 130-135. | |
| 9 | 陈林. 基于Logit模型的成渝通道交通选择行为研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2013. |
| Chen Lin. Study on traffic choice behavior of Chengdu Chongqing corridor based on logit model[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 10 | Kahneman D, Tversky A. Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk[J]. Econometrica, 1979, 47(2): 263-292. |
| 11 | Kahneman A T. Advances in prospect theory: cumulative representation of uncertainty[J]. Journal of Risk & Uncertainty, 1992, 5(4): 297-323. |
| 12 | Avineri E J T S. The effect of reference point on stochastic network equilibrium[J]. Transportation Science, 2006, 40(4): 409-420. |
| 13 | 施海燕, 施放. 期望效用理论与前景理论之比较[J]. 统计与决策, 2007(11): 22-24. |
| Shi Hai-yan, Shi Fang. Comparison of expected utility theory and prospect theory[J]. Statistics and Decision Making, 2007(11): 22-24. | |
| 14 | 刘玉印, 刘伟铭, 吴建伟. 基于累积前景理论的出行者路径选择模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 38(7): 84-89. |
| Liu Yu-yin, Liu Wei-ming, Wu Jian-wei. Travel path selection model based on cumulative prospect theory[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(7): 84-89. | |
| 15 | Hu L, Dong J, Lin Z. Modeling charging behavior of battery electric vehicle drivers: a cumulative prospect theory based approach[J]. Transportation Research, 2019, 102: 474-489. |
| 16 | Guan Y, Annaswamy A M, Tseng H E. Cumulative prospect theory based dynamic pricing for shared mobility on demand services[C]∥2019 IEEE 58th Conference on Decision and Control(CDC), 2019: 04824. |
| 17 | Jhala K, Natarajan B, Pahwa A. Prospect theory-based active consumer behavior under variable electricity pricing[J]. Smart Grid, IEEE Transactions on, 2019, 10(3): 2809-2819. |
| 18 | 邢睿. 基于前景理论的城市居民交通出行方式选择研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学交通运输工程学院, 2014. |
| Xing Rui. Research on urban residents' travel mode selection based on prospect theory[D]. Changsha: School of Transportation Engineering, Changsha University of Technology, 2014. | |
| 19 | 马书红, 周烨超, 张艳. 基于NL-累计前景理论的出行方式选择预测模型研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2019, 19(4): 135-142. |
| Ma Shu-hong, Zhou Ye-chao, Zhang Yan. Study on travel mode selection prediction model based on NL cumulative prospect theory[J]. Transportation System Engineering and Information, 2019, 19(4): 135-142. | |
| 20 | 杨志勇. 基于前景理论的出发时刻和出行路径选择模型研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2007. |
| Yang Zhi-yong. Research on departure time and travel path selection model based on prospect theory[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007. | |
| 21 | 秦世环. 基于前景理论的出行方式与路径联合选择行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Qin Shi-huan. Research on joint choice behavior of travel mode and route based on prospect theory[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. |
| [1] | 孙宗元, 方守恩. 高速公路出入口运动车辆轨迹分层聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1696-1702. |
| [2] | 李烨, 王炜, 邢璐, 王昊, 董长印. 自动巡航与可变限速协同控制对高速公路基本路段通行效率的改善[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1420-1425. |
| [3] | 李鹏辉, 张文会, 胡孟夏, 李一兵, 吴彪. 高速公路驾驶人超车过程中的扫视行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 114-119. |
| [4] | 杨庆芳, 马明辉, 杨聚芬, 邴其春, 梁士栋. 高速公路交通流运行稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1596-1603. |
| [5] | 詹伟, 吕庆, 尚岳全. 高速公路隧道群交通事故灰色马尔可夫预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 62-67. |
| [6] | 徐铖铖, 刘攀, 王炜, 李志斌. 恶劣天气下高速公路实时事故风险预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 68-73. |
| [7] | 王琳虹, 李世武, 周茹波, 杨志发, 冀秉魁, 姚雪萍. 高速公路路侧景观色彩对驾驶员心率指标的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 74-80. |
| [8] | 张文会, 许洪国. 高速公路交通事故现场路段限速方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(02): 316-320. |
| [9] | 徐亮,程国柱. 基于车速离散度和经济车速的高速公路最低车速限制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 661-0665. |
| [10] | 程国柱, 裴玉龙, 池利兵. 基于汽车行驶广义费用最小的高速公路最高车速限制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(04): 900-905. |
|
||