吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1466-1476.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210021
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
无线传感器网络中基于动态簇的节点调度算法
- 哈尔滨工程大学 信息与通信工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
Nodes scheduling algorithm based on dynamic cluster in wireless sensor network
Qiang GUO( ),Yu-qiang CUI,Yong WANG
),Yu-qiang CUI,Yong WANG
- College of Information and Communication Engineering,Harbin Engineering University,Harbin 150001,China
摘要:
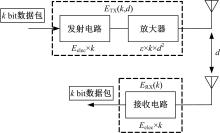
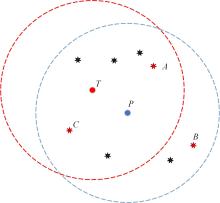
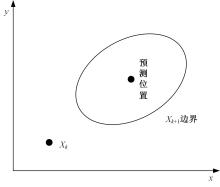
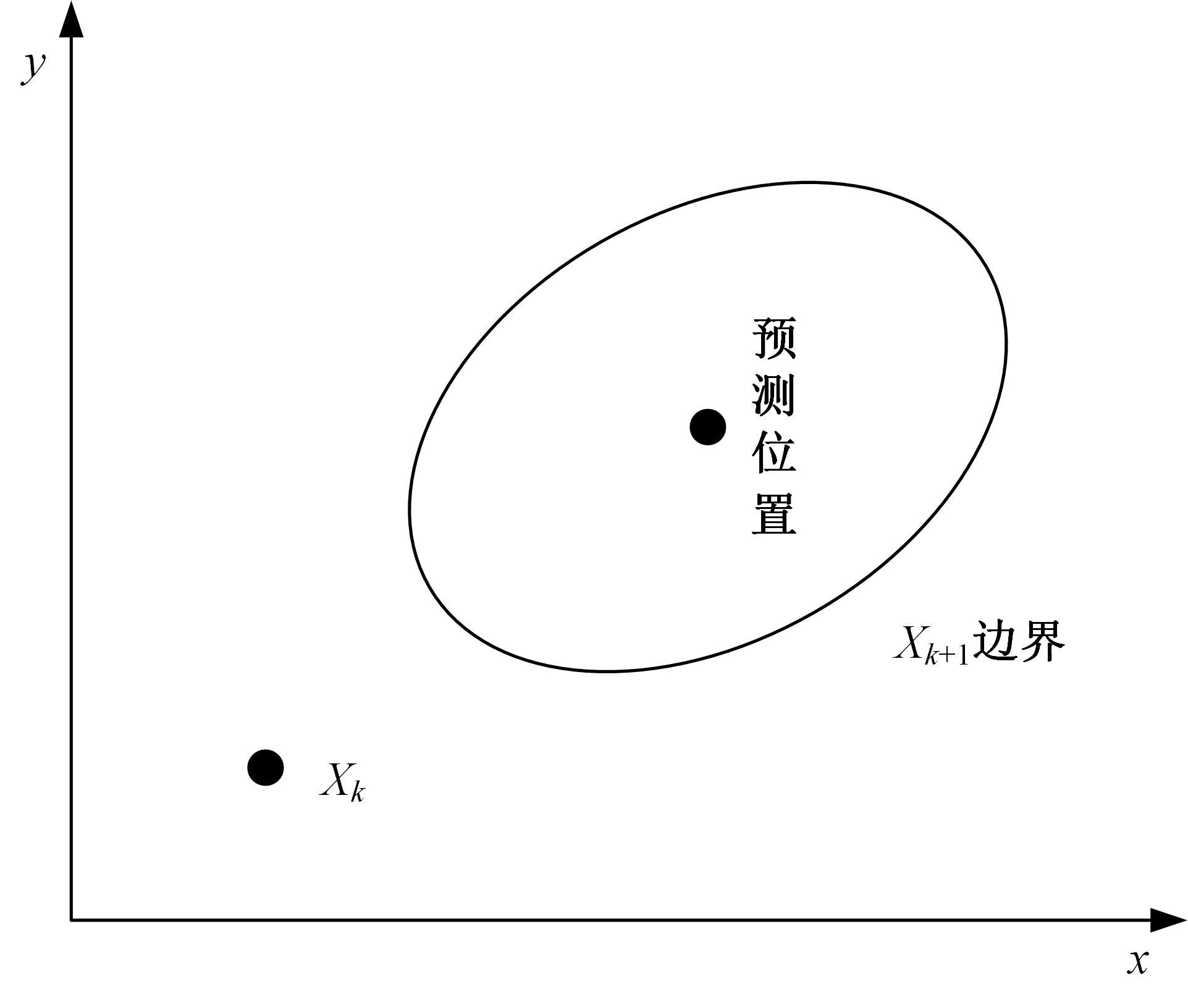
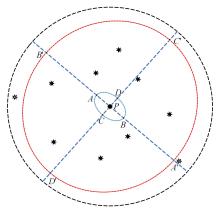
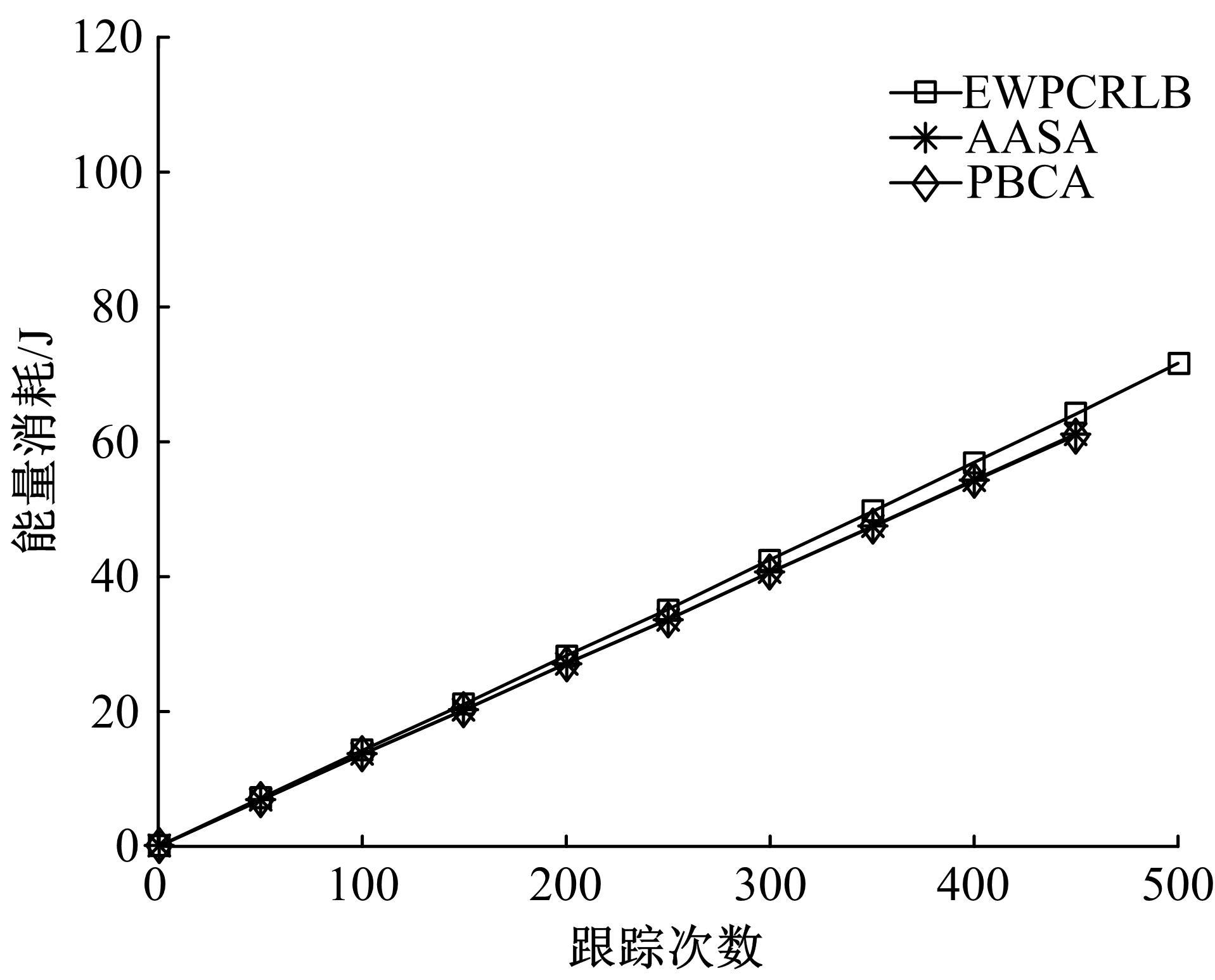
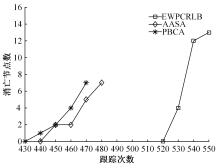
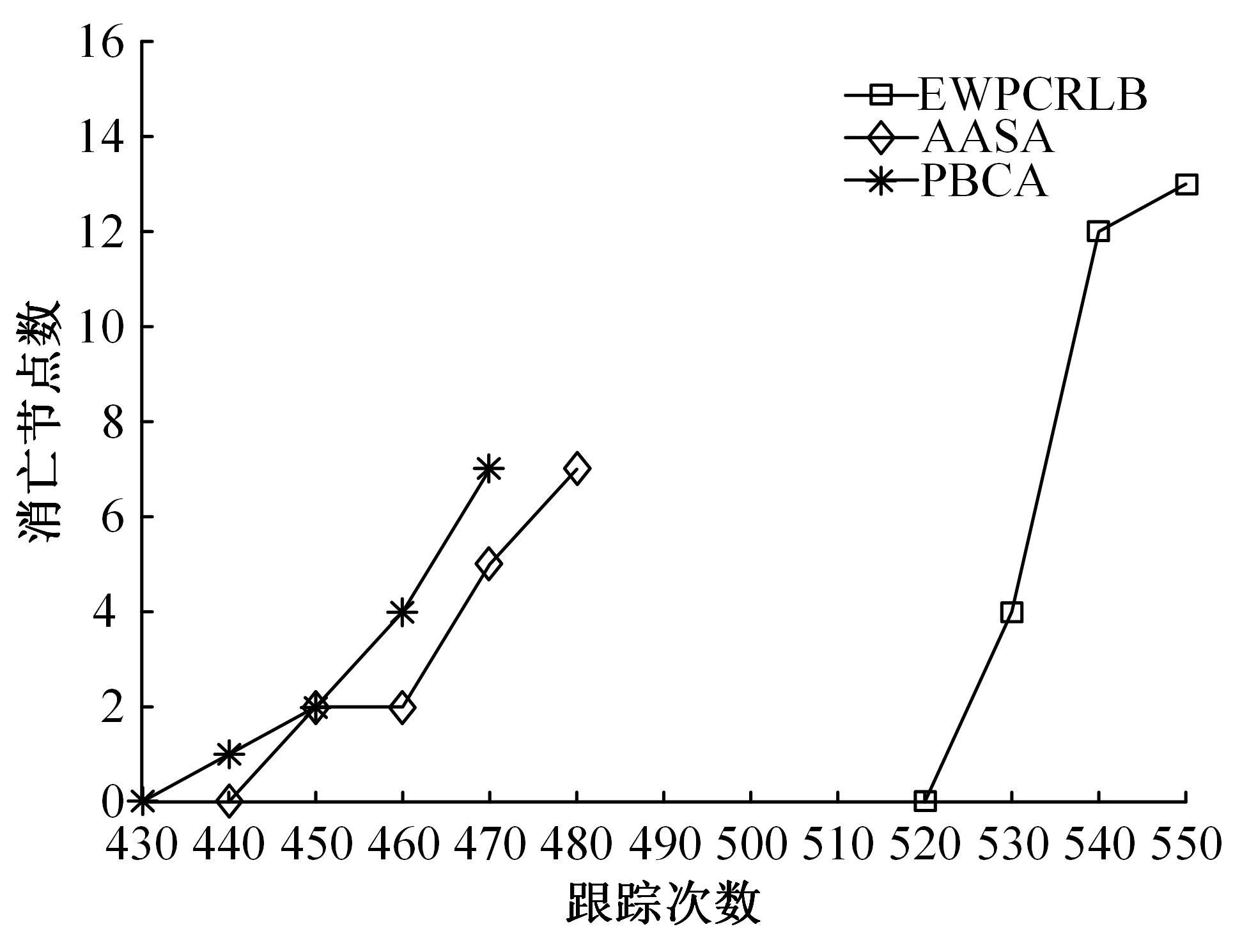
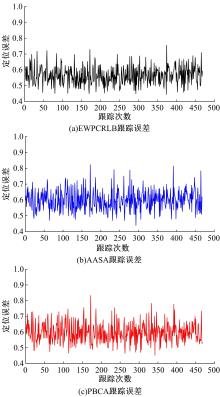
在基于无线传感器网络(WSN)的目标跟踪系统中,为了合理地制定节点之间的协作方式,在保证目标跟踪精度的同时减少节点的激活时间、平衡节点的能量消耗、延长网络的生存期,提出了一种根据节点剩余能量和PCRLB信息组建动态簇的节点调度算法。首先,利用粒子滤波的方法预测目标在下一时刻的位置,根据预测位置和预测协方差矩阵确定目标在下一时刻的椭圆区域,从而确定下一时刻的候选节点区域。然后,在候选节点区域,根据节点的剩余能量和PCRLB信息选择部分传感器节点组成动态簇对目标进行跟踪。仿真结果表明,本文算法不仅能够降低跟踪误差,而且可以平衡节点的能量消耗,延长网络的生存期。
中图分类号:
- TN915
| 1 | Hussain M A, Khan P, Kwak K S. WSN research activities for military application[C]∥Proceedings of the 11th international conference on Advanced Communication Technology,South Korea,2009: 271-274. |
| 2 | Rahman G, Wahid K A. LDAP: lightweight dynamic auto-reconfigurable protocol in an IoT-Enabled WSN for wide-area remote monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(19): No. 3131. |
| 3 | Saleh N, Kassem A, Haidar A M. Energy-efficient architecture for wireless sensor networks in healthcare applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 6478-6486. |
| 4 | Mendoza E, Fuentes P, Benitez I, et al. Network of multi-hop wireless sensors for low cost and extended area home automation systems[J]. Revista Iberoamericana De Automatica E Informatica Industrial, 2020, 17(4): 412-423. |
| 5 | Hu X Y, Yang L Q, Xiong W. A novel wireless sensor network frame for urban transportation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2015, 2(6): 586-595. |
| 6 | Zheng J, Bhuiyan M Z A, Liang S, et al. Auction-based adaptive sensor activation algorithm for target tracking in wireless sensor networks[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2014, 39: 88-99. |
| 7 | Darabkh K A, Albtoush W Y, Jafar I F. Improved clustering algorithms for target tracking in wireless sensor networks[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2016, 73(5): 1-26. |
| 8 | Zhang S, Chen H, Liu M. Adaptive sensor scheduling for target tracking in underwater wireless sensor networks[C]∥2014 International Conference on Mechatronics and Control (ICMC), Jinzhou, China, 2014: 55-60. |
| 9 | Luo J H, Han Y. A node depth adjustment method with computation-efficiency based on performance bound for range-only target tracking in UWSNs[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 158: 79-90. |
| 10 | Alaybeyoglu A, Kantarci A, Erciyes K. A dynamic distributed tree-based tracking algorithm for wireless sensor networks[C]∥International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Networks,Ankara, Turkey,2010:295-303. |
| 11 | Wang X B, Fu M Y, Zhang H S. Target tracking in wireless sensor networks based on the combination of KF and MLE using distance measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2012, 11(4): 567-576. |
| 12 | Wang Y, Jie H, Cheng L. A fusion localization method based on a robust extended kalman filter and track-quality for wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2019, 19(17): No.3638. |
| 13 | Zhang Y, Gao L J. Sensor-networked underwater target tracking based on grubbs criterion and improved particle filter algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 142894-142906. |
| 14 | Ren Q, Gao H, Jiang S, et al. An Energy-efficient Object Tracking Algorithm in Sensor Networks[M]. Berlin:Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2008. |
| 15 | Sha C, Zhong L H, Bian Y, et al. A type of energy-efficient target tracking approach based on grids in sensor networks[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2019, 12(5): 1041-1060. |
| 16 | Ahmad T, Abbas A M. EEAC: An energy efficient adaptive cluster based target tracking in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Interdisciplinary Mathematics, 2020, 23(2): 379-392. |
| 17 | Toumi M, Maizate A, Ouzzif M. Dynamic cluster algorithm for improving percolation of targets in a sensor network[J]. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 2019, 20(3): 179-191. |
| 18 | Wang G J, Bhuiyan M Z A, Zhang L. Two-level cooperative and energy-efficient tracking algorithm in wireless sensor networks[J]. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2010, 22(4): 518-537. |
| 19 | Aydogmus O, Talu M F. Comparison of extended-kalman and particle-filter-based sensorless speed control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(2): 402-410. |
| 20 | Heinzelman W R, Chandrakasan A, Balakrishnan H. Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 2000: 1567-1576. |
| 21 | Deldar F, Yaghmaee M H. Designing a prediction-based clustering algorithm for target tracking in wireless sensor networks[C]∥2011 International Symposium on Computer Networks and Distributed Systems (CNDS) Tehran, Iran, 2011: 199-203. |
| 22 | 周非, 安康宁, 范馨月, 等. 无线传感网络中基于误差椭圆的自适应节点选择目标跟踪算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2017, 30(10): 1548-1553. |
| Zhou Fei, An Kang-ning, Fan Xin-Yue, et al. Target tracking in wireless sensor network based on error ellipse and adaptive selection of nodes[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2017, 30(10): 1548-1553. | |
| 23 | Keshavarz-Mohammadiyan A, Khaloozadeh H. Interacting multiple model and sensor selection algorithms for manoeuvring target tracking in wireless sensor networks with multiplicative noise[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2017, 48(5): 899-908. |
| [1] | 李建坡,李美霖,杨涛,薛鹏. 大规模MIMO⁃OFDM系统中低复杂度维纳滤波信道估计算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 211-218. |
| [2] | 孙大洋,王雪莹,韩双雪,钟辉,戴江南. 虚拟锚点高维坐标的非视距识别及定位优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2207-2215. |
| [3] | 李建坡,薛鹏,杨涛,李美霖. 基于分组导频复用的大规模多输入多输出系统导频污染抑制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2225-2236. |
| [4] | 徐涛,马克,刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [5] | 马彦,黄健飞,赵海艳. 基于车间通信的车辆编队控制方法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 711-718. |
| [6] | 刘毅,肖玲玲,王改静,张武军. 基于联合优化的D2D资源分配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 306-314. |
| [7] | 李翠然,于永生,谢健骊. 基于次用户优先级的频谱共享动态博弈算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 315-323. |
| [8] | 王金鹏,叶政鹏,曹帆,邹念育. 5G移动通信中基于同频干扰分布的协同分布式天线传输系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 333-341. |
| [9] | 李文军,华强,谭立东,孙悦. DV⁃HOP和接收信号强度指示结合的改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1689-1695. |
| [10] | 于斌斌,胡亮,迟令. 可抵抗内外部攻击的无线传感器网络数字签名方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1676-1681. |
| [11] | 王鹏宇,赵世杰,马天飞,熊晓勇,程馨. 基于联合概率数据关联的车用多传感器目标跟踪融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1420-1427. |
| [12] | 王洪雁,房云飞,朱圣棋,裴炳南. 非均匀噪声条件下考虑互耦效应的DOA估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1706-1714. |
| [13] | 王宏志,姜方达,周明月. 基于遗传粒子群优化算法的认知无线电系统功率分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [14] | 刘勇,邓方顺,刘小林,闵思婕,王鹏. 基于双混沌振子的最小频移键控信号频率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1357-1362. |
| [15] | 周彦果,张海林,陈瑞瑞,周韬. 协作网络中采用双层博弈的资源分配方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1879-1886. |
|
||