吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2532-2541.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210322
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
应用数据驱动算法提高涡粘模型分离流动模拟精度
- 哈尔滨工业大学 能源科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150001
Applying data driven algorithm to promote prediction accuracy of separation boundary simulation with eddy viscosity model
Zhong-hua GU( ),Pei-gang YAN,Pan-hong LIU,Xiang-feng WANG(
),Pei-gang YAN,Pan-hong LIU,Xiang-feng WANG( )
)
- School of Energy Science and Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150001,China
摘要:
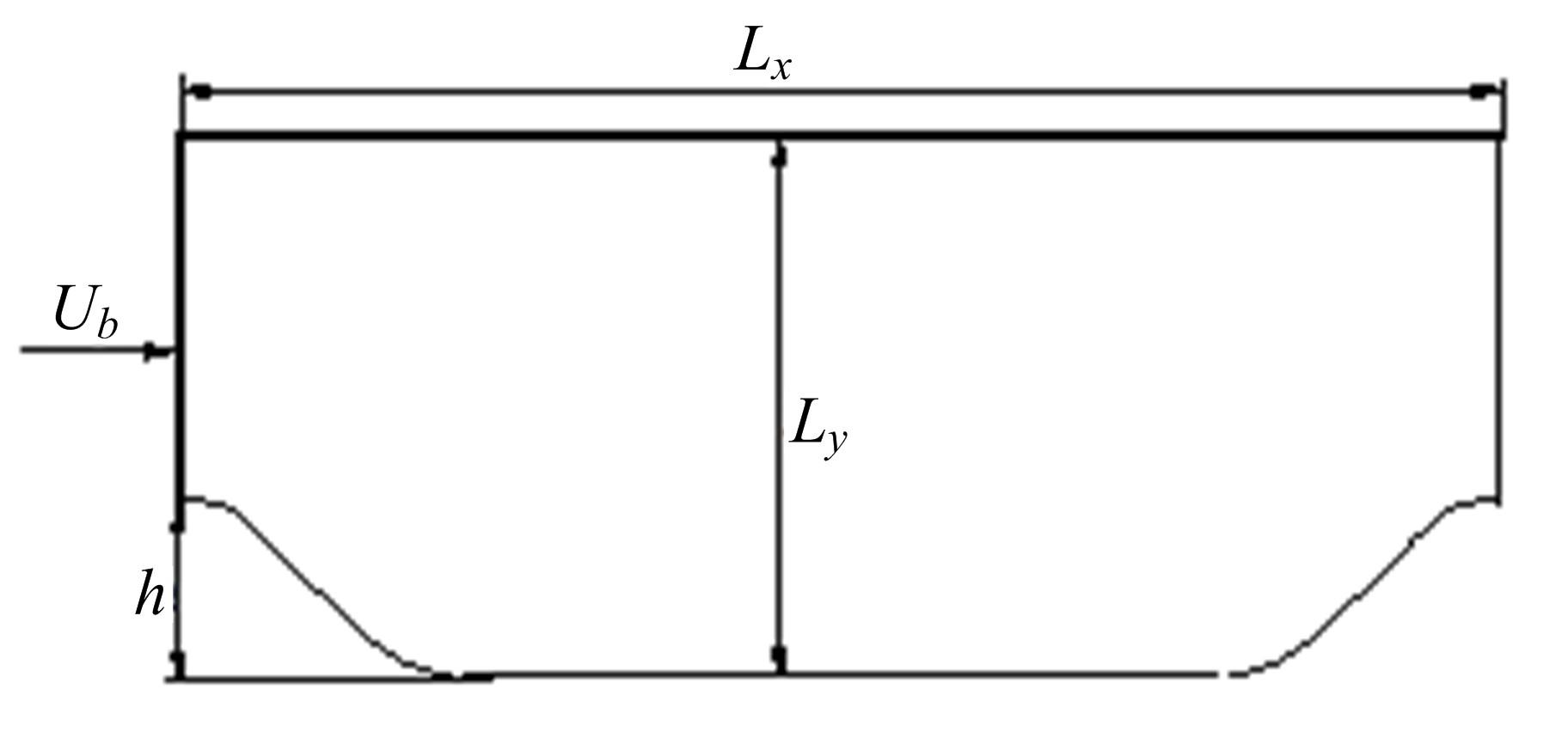
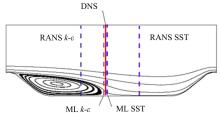
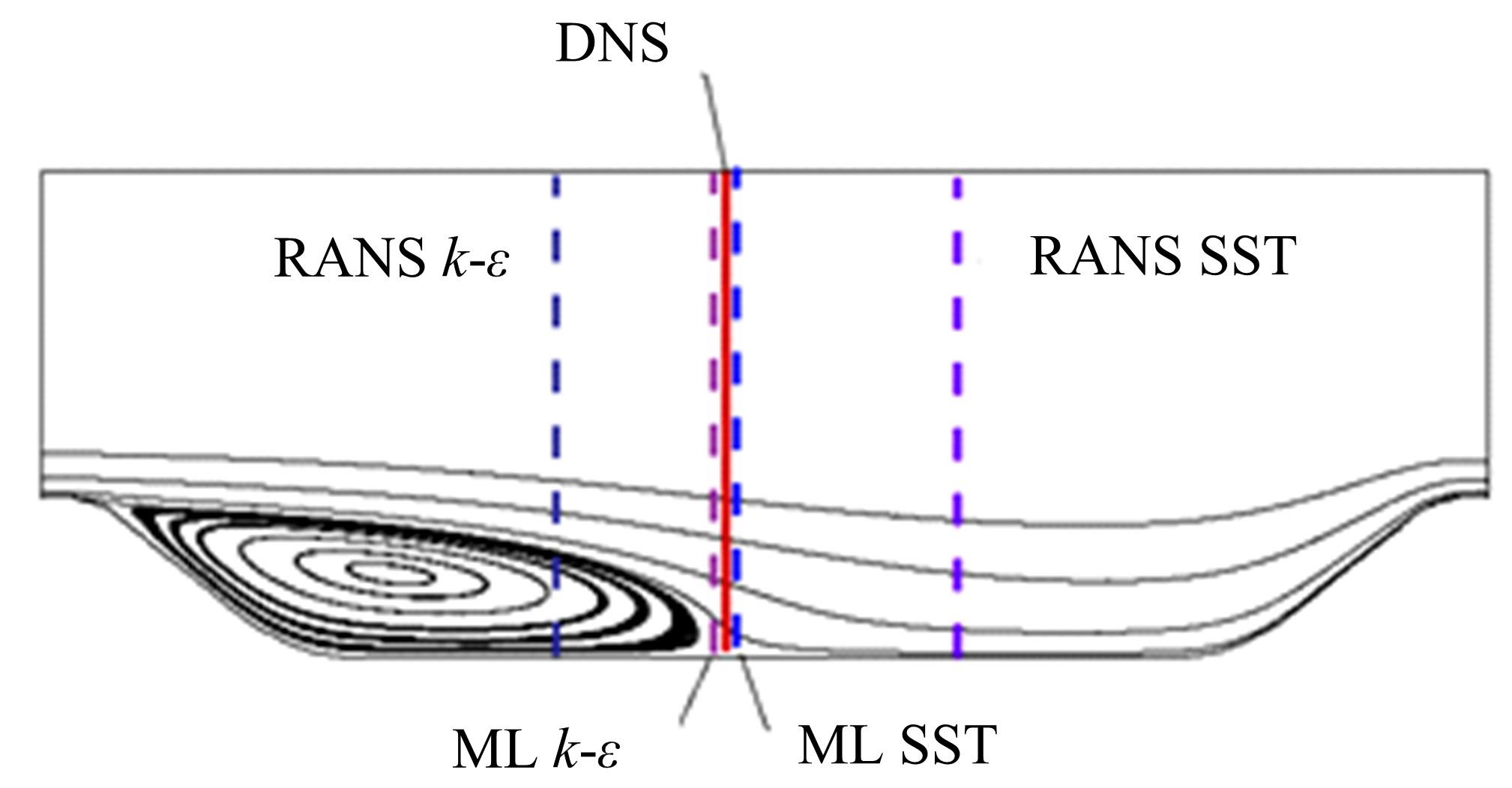
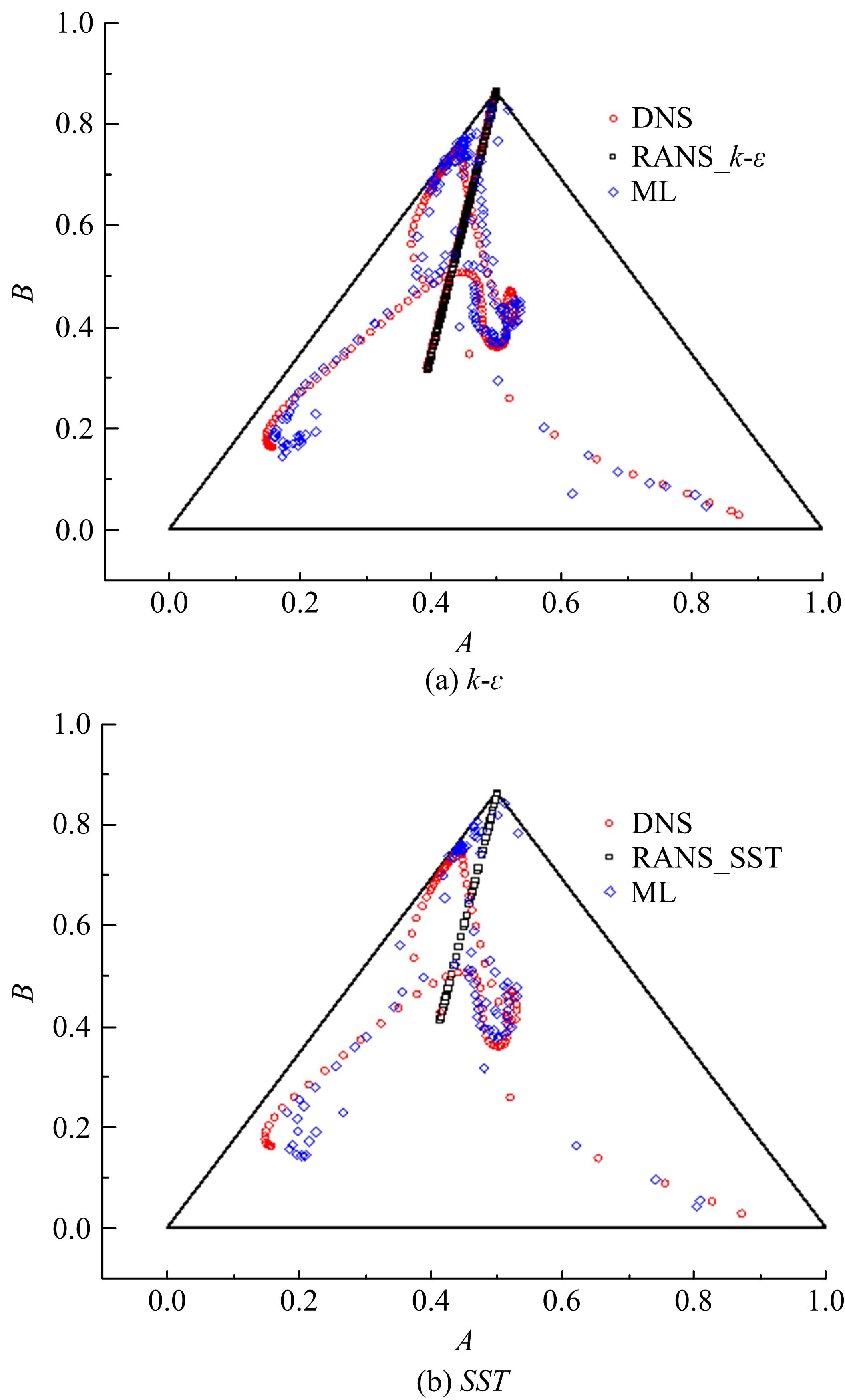
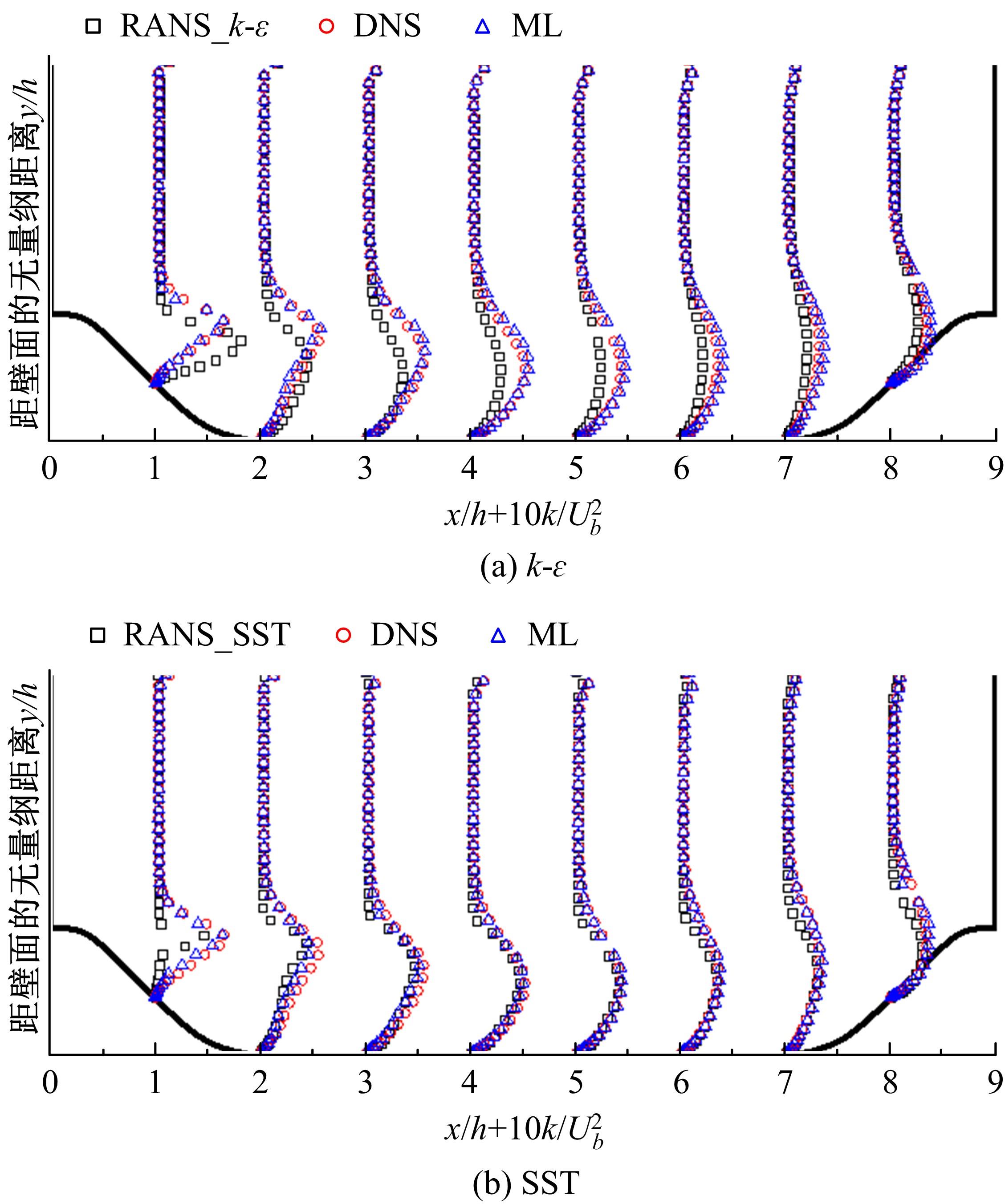
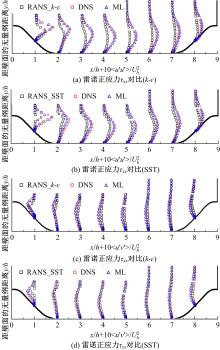
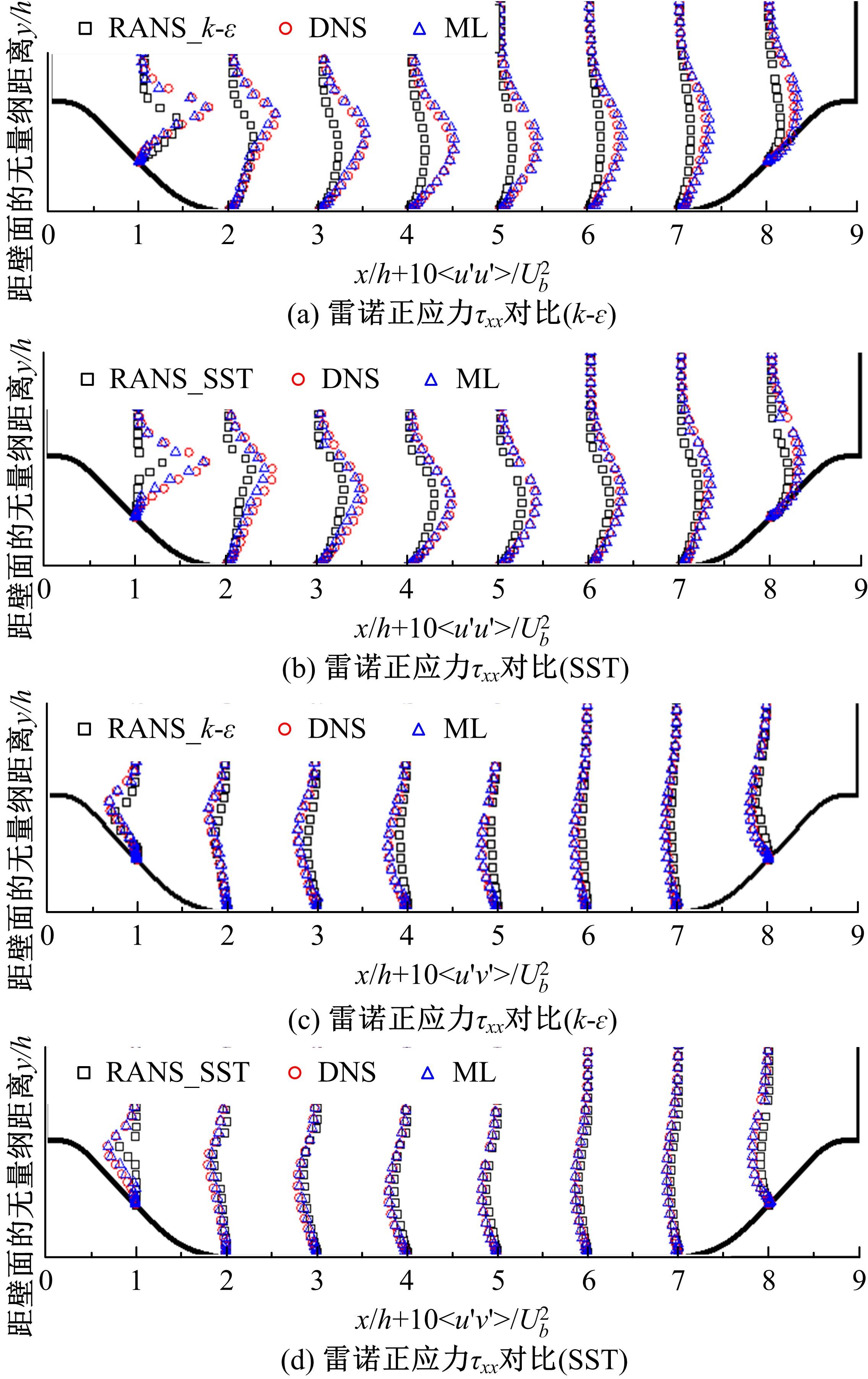
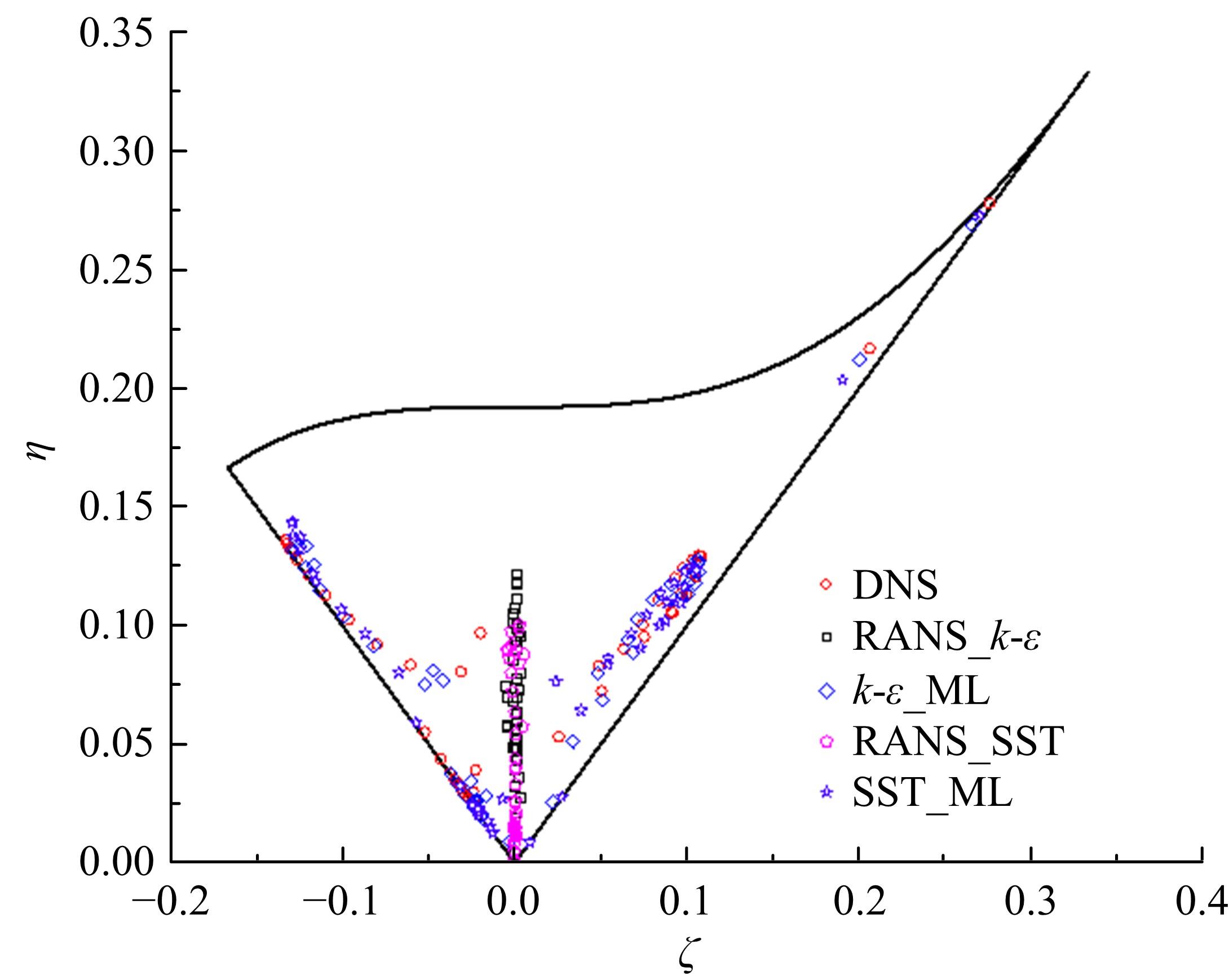
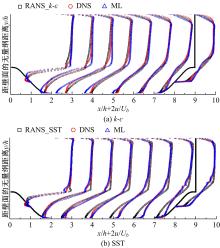
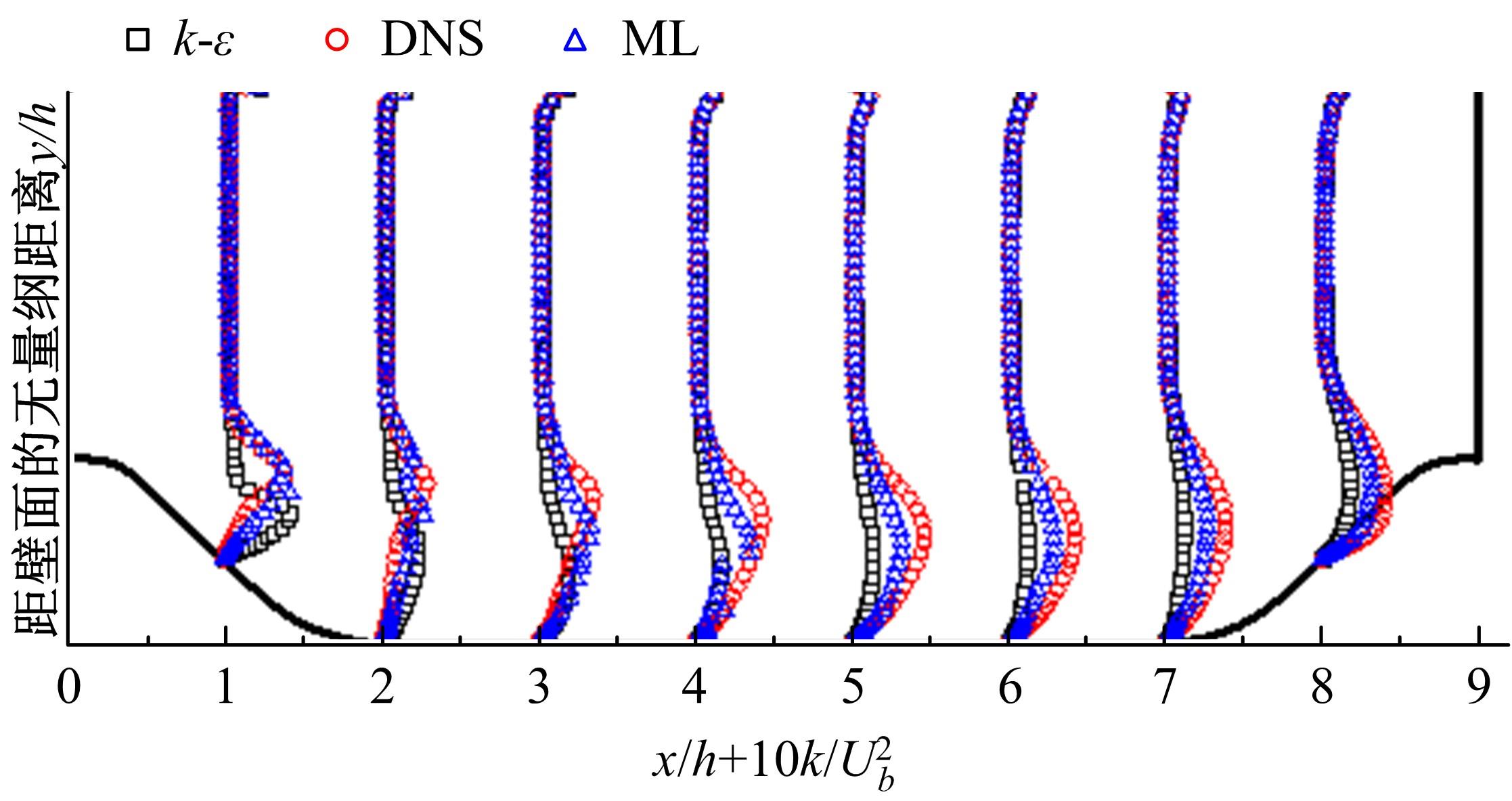
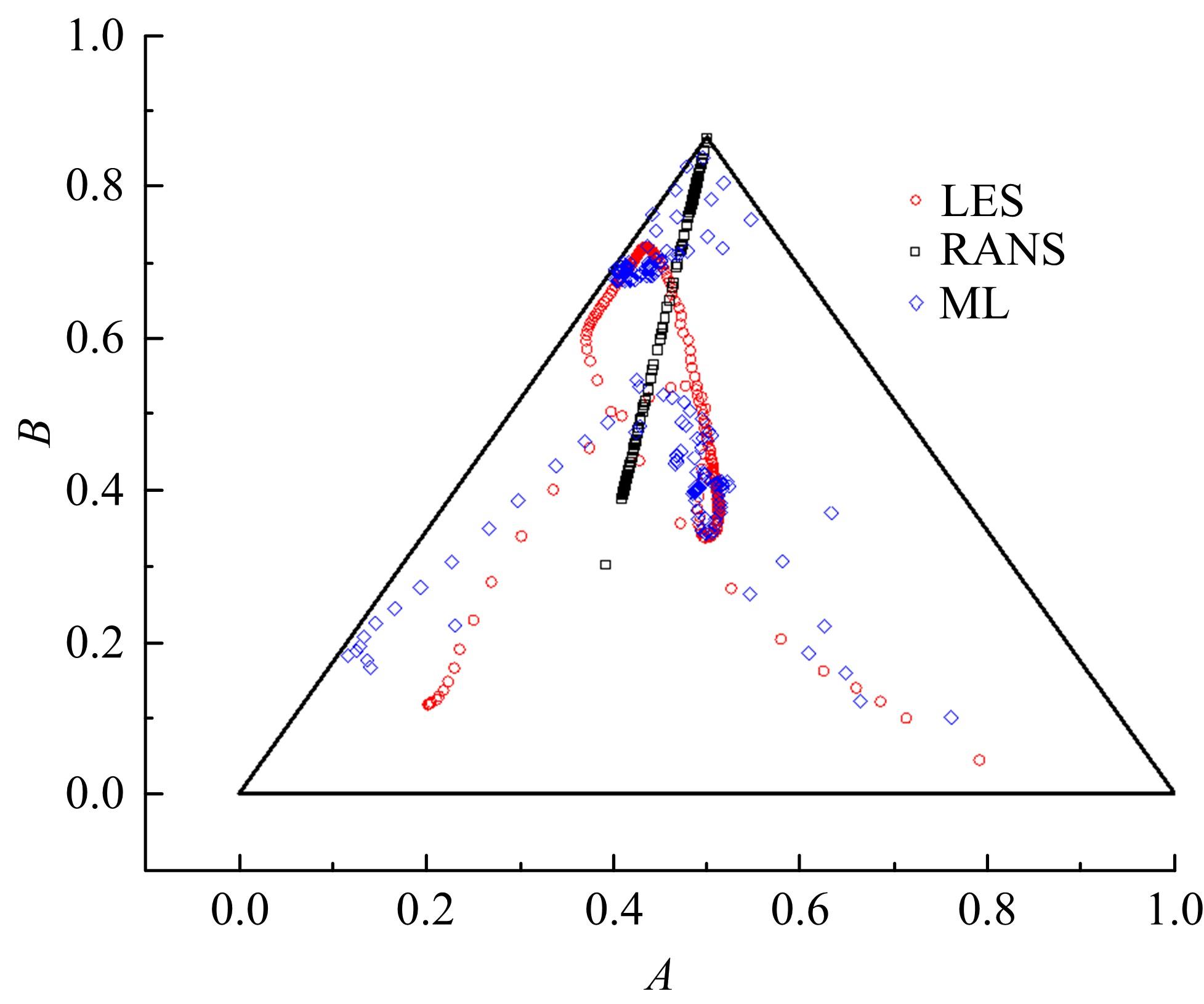
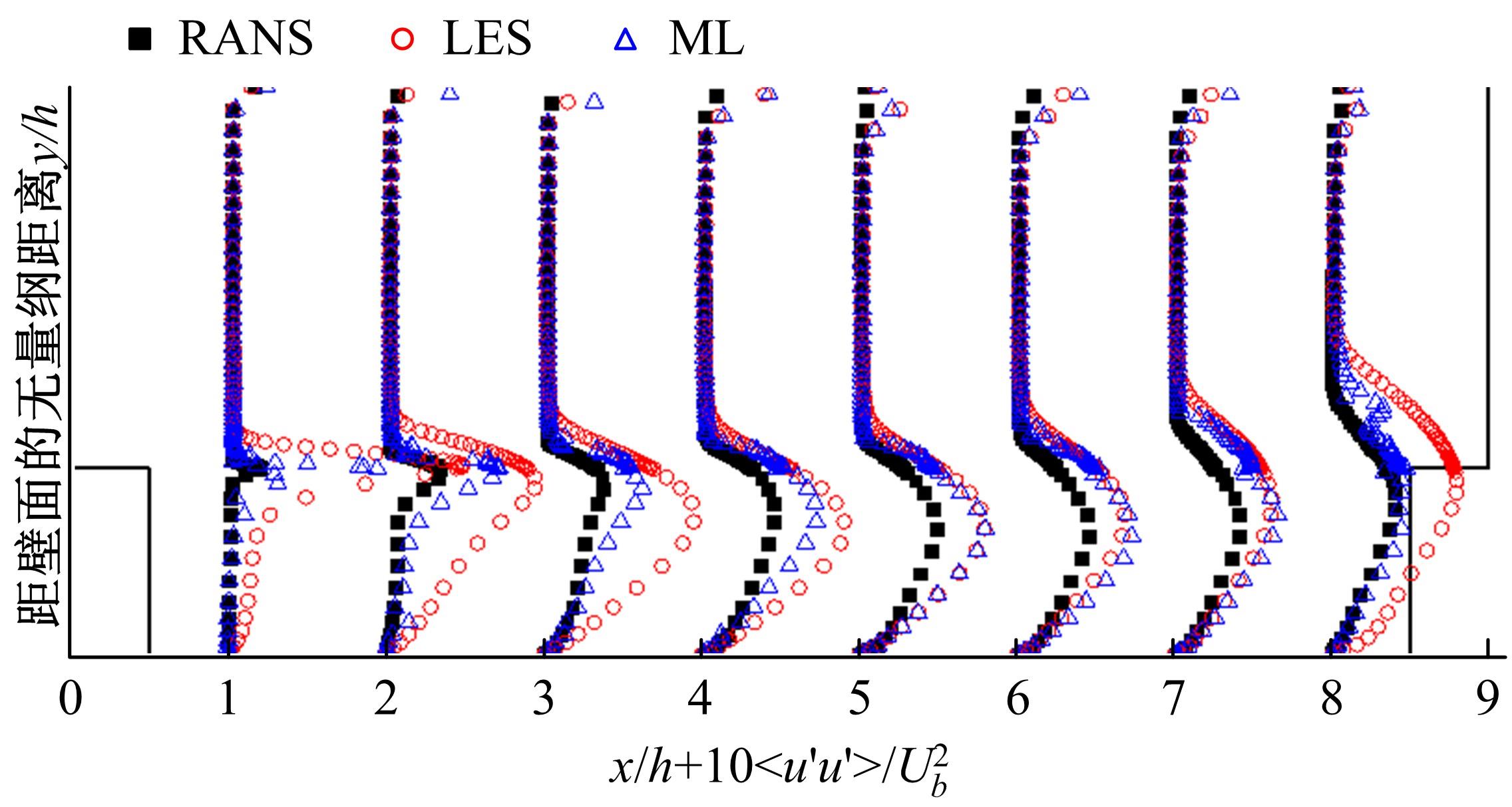
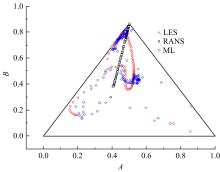
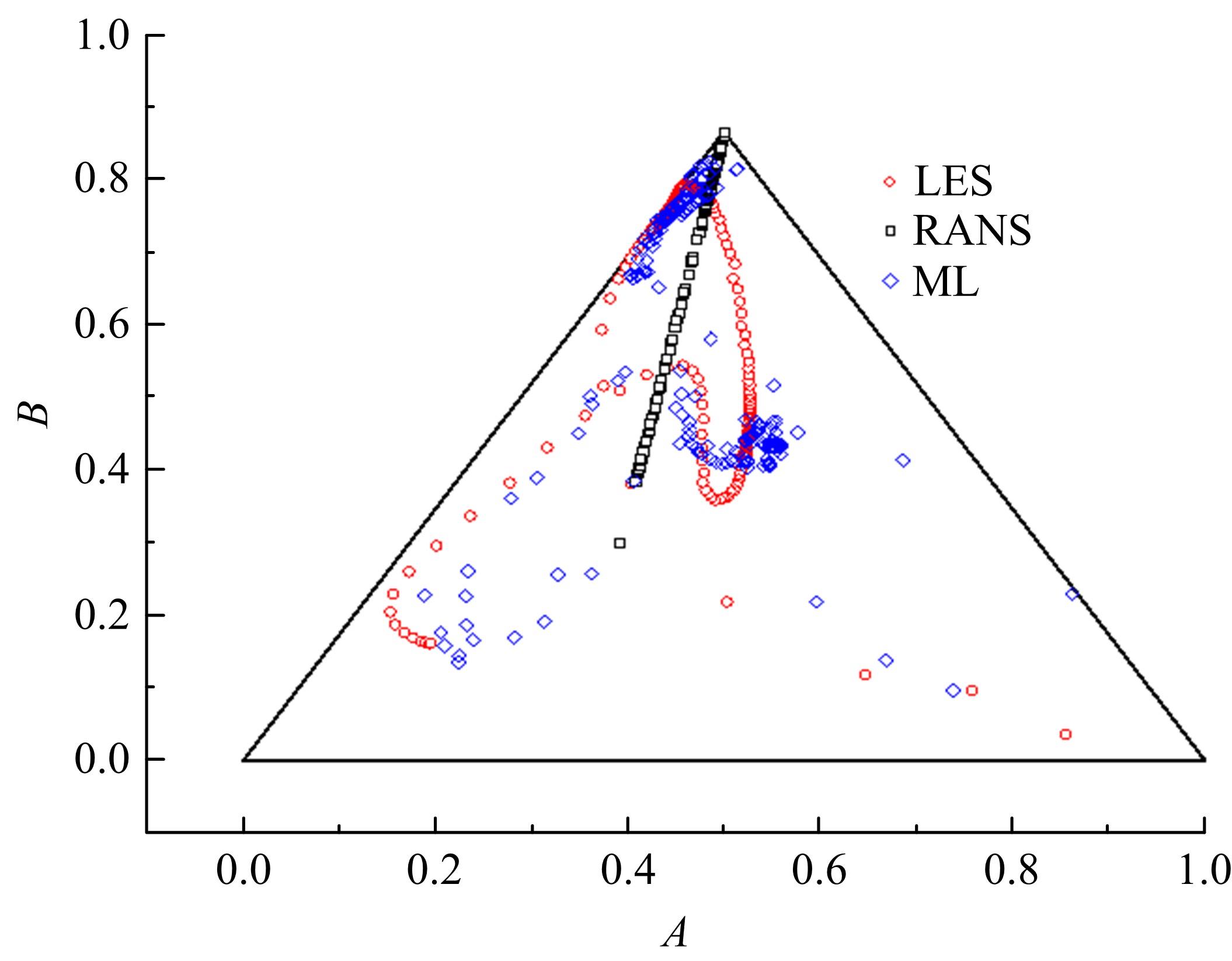
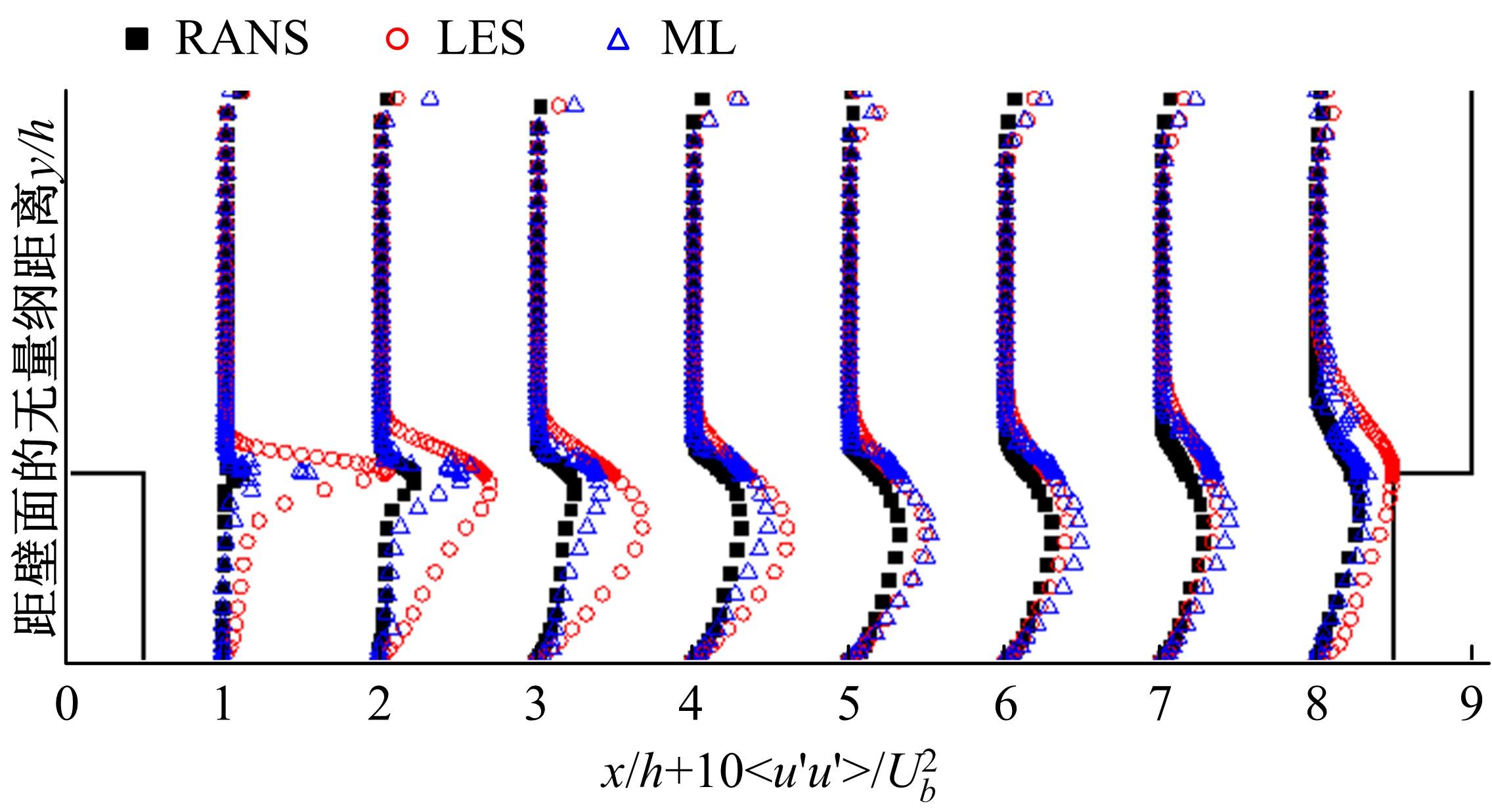
针对雷诺平均N-S方程中涡粘模型对分离流动预测精度这一关键问题,开发了基于人工智能数据驱动机器学习算法,克服了传统涡粘模型对分离边界层流动预测过于依赖经验参数等问题,并提高了数值模拟精度。根据影响湍流演化的物理机理,通过将涡粘模型计算分离流动的计算结果作为基准,选取多个由平均流状态表征的变量作为输入变量,以高阶雷诺应力模型计算结果构建高保真度数据库,并将雷诺应力进行分解的6个变量作为输出变量,建立基于随机森林回归的由基准流场到高保真度数据的映射关系和预测模型。结果表明:预测模型对分离流动的预测精度都有明显提高。
中图分类号:
- V231.3
| 1 | Marusic I, Candler G, Interrante V, et al. Real time feature extraction for the analysis of turbulent flows[J]. Data Mining for Scientific and Engineering Applications, 2001(2): 223-238. |
| 2 | Spencer A, Rivlin R. Isotropic integrity bases for vectors and second-order tensors[J]. Archive for Rational Mechanics & Analysis, 1964, 18(1): 51-82. |
| 3 | Tracey B D, Duraisamy K, Alonso J J. A machine learning strategy to assist turbulence model development[C]∥53rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Kissimmee, USA, 2015: 1287. |
| 4 | Zhang Z J, Duraisamy K. Machine learning methods for data-driven turbulence modeling[C]∥22nd AIAA Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, Dallas, USA, 2015: 2460. |
| 5 | Duraisamy K, Zhang Z J, Singh A P. New approaches in turbulence and transition modeling using data-driven techniques[C]∥53rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Kissimmee, USA, 2015: 1284. |
| 6 | Singh A P, Duraisamy K, Zhang Z J. Augmentation of turbulence models using field inversion and machine learning[C]∥55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Grapevine, USA, 2017: 0993. |
| 7 | Wang J X, Wu J L, Xiao H. Physics informed machine learning approach for reconstructing reynolds stress modeling discrepancies based on DNS data[J]. Phys Rev Fluids, 2017(3): 1-22. |
| 8 | Ling J, Kurzawski A, Templeton J. Reynolds averaged turbulence modelling using deep neural networks with embedded invariance[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 807: 155-166. |
| 9 | Ling J, Templeton J. Evaluation of machine learning algorithms for prediction of regions of high Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes uncertainty[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2015, 27(8): 085103. |
| 10 | Xiao H, Wu J, Wang J, et al. Quantifying and reducing model-form uncertainties in reynolds-averaged navier-stokes equations: a data-driven, physics-informed bayesian approach[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 324: 115-136. |
| 11 | Xiao H, Wu J, Wang J, et al. Physics-informed machine learning for predictive turbulence modeling: progress and perspectives[J]. 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Grapevine, USA, 2017: 1712. |
| 12 | Gamaharam M, Hattoriy Y. Searching for turbulence models by artificial neural network[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2017, 2(5): 054604. |
| 13 | Maulik R, San O, Rasheed A, et al. Sub-grid modelling for two-dimensional turbulence using neural networks[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 858: 122-144. |
| 14 | Wang Z, Luo K, Li D, et al. Investigations of data-driven closure for subgrid-scale stress in large-eddy simulation[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2018, 30(12): 125101. |
| 15 | Wu J, Xiao H, Paterson E. Physics-informed machine learning approach for augmenting turbulence models: a comprehensive framework[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2018, 3: 074602. |
| 16 | Thompson Roney L, Sampaio Luiz Eduardo B, de Braganca Alves Felipe A V, et al. A methodology to evaluate statistical errors in DNS data of plane channel flows[J]. Computation of Fluids, 2016, 130: 1-7. |
| 17 | Banerjee S, Krahl R, Durst F, et al. Presentation of anisotropy properties of turbulence, invariants versus eigenvalue approaches[J]. Journal of Turbulence, 2007, 8(32): 1-27. |
| 18 | Kumar V, Frohnapfel B, Jovaanovic J. Anisotropy invariant reynolds stress model of turbulence and its application to attached and separated wall-bounded flows[J]. Flow Turbulence Combust, 2009, 83: 81-103. |
| 19 | 颜培刚, 杜明杰. 燃气涡轮带肋冷却通道流动与换热的大涡模拟[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(1): 75-81. |
| Yan Pei-gang, Du Ming-jie. Numerical research of flow and heat transfer in a ribbed channel based on les approach[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(1): 75-81. |
| [1] | 汤东,韩宇彬,华伦,潘金冲,刘胜. 润滑油灰分对直喷汽油机颗粒捕集器性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2501-2507. |
| [2] | 王乔,孙万臣,郭亮,程鹏,范鲁艳,李国良. 丁醇/柴油混合燃料对压燃式发动机燃烧及微粒排放特征的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1920-1928. |
| [3] | 江涛,林学东,李德刚,杨淼,汤雪林. 基于人工神经网络的放热规律的量化预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1747-1754. |
| [4] | 孙正, 黄钰期, 俞小莉. 径向滑动轴承润滑油膜流动-传热过程仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 744-751. |
| [5] | 刘忠长, 孙士杰, 田径, 徐瑞辰, 汪泊舟. 瞬态工况下喷油参数对柴油机排放及燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1639-1646. |
| [6] | 包堂堂, 胡宗杰, 胡俊超, 阮逸平, 邓俊, 吴志军. 基于超声雾化的柴油/汽油混合燃料液滴群燃烧特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 903-908. |
| [7] | 于秀敏,谭兴闻,马君,李国良,董伟,齐万强,崔峰云. 缸内直喷汽油机起动控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1554-1558. |
| [8] | 刘成材,高青,马纯强,金英爱,李玥. 发动机可变组分进气系统的膜气体分离特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 625-0629. |
| [9] | 刘发发,谷艳华,彭亚平,李华,郭英男 . 乙醇均质压燃燃烧的化学反应动力学模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(01): 21-26. |
|
||