吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2852-2863.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210457
自动驾驶汽车双车道换道最优轨迹规划方法
彭浩楠1( ),唐明环1,查奇文1,王伟忠1(
),唐明环1,查奇文1,王伟忠1( ),王伟达2,项昌乐2,刘玉龙3
),王伟达2,项昌乐2,刘玉龙3
- 1.中国工业互联网研究院,北京 100102
2.北京理工大学 机械与车辆学院,北京 100081
3.清华大学 车辆与运载学院,北京 100084
Optimization⁃based lane changing trajectory planning approach for autonomous vehicles on two⁃lane road
Hao-nan PENG1( ),Ming-huan TANG1,Qi-wen ZHA1,Wei-zhong WANG1(
),Ming-huan TANG1,Qi-wen ZHA1,Wei-zhong WANG1( ),Wei-da WANG2,Chang-le XIANG2,Yu-long LIU3
),Wei-da WANG2,Chang-le XIANG2,Yu-long LIU3
- 1.China Academy of Industrial Internet,Beijing 100102,China
2.School of Mechanical Engineering,Beijing Institute of Technology,Beijing 100081,China
3.School of Vehicle and Mobility,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
摘要:
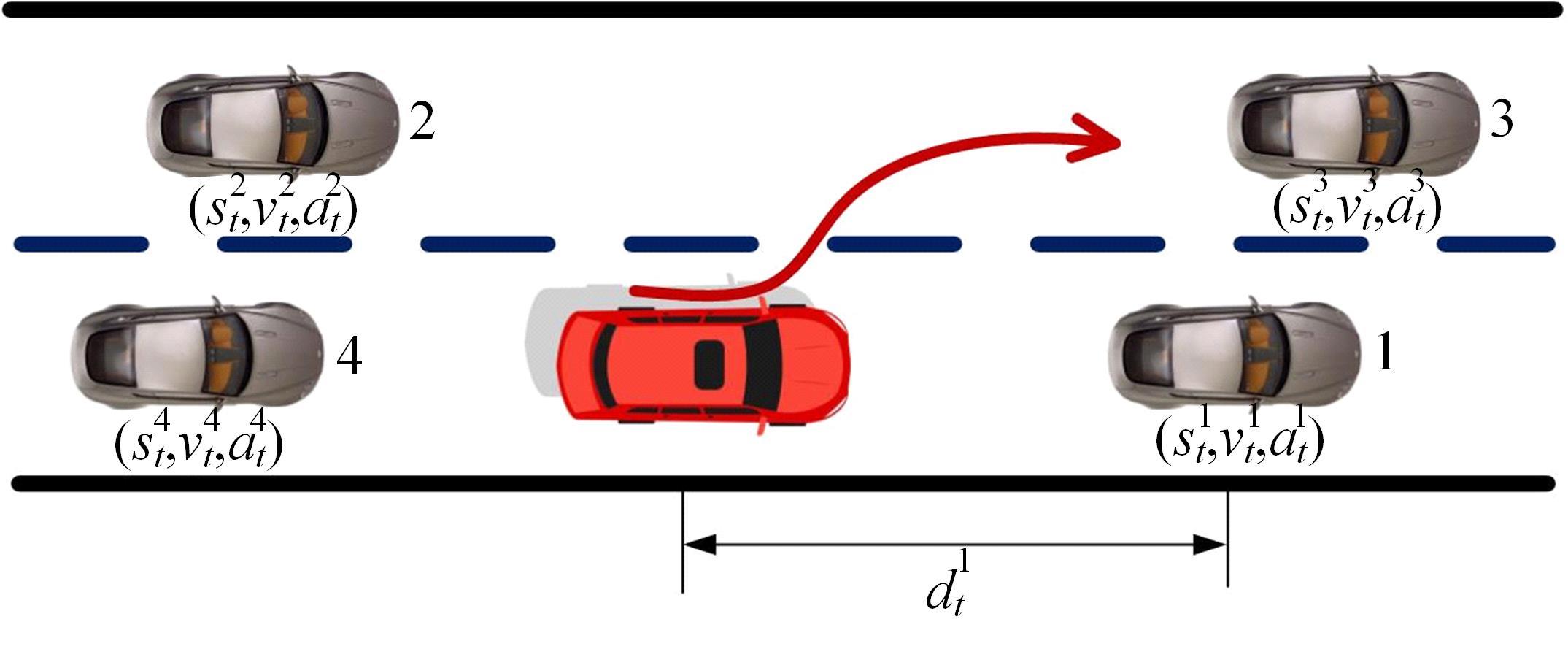
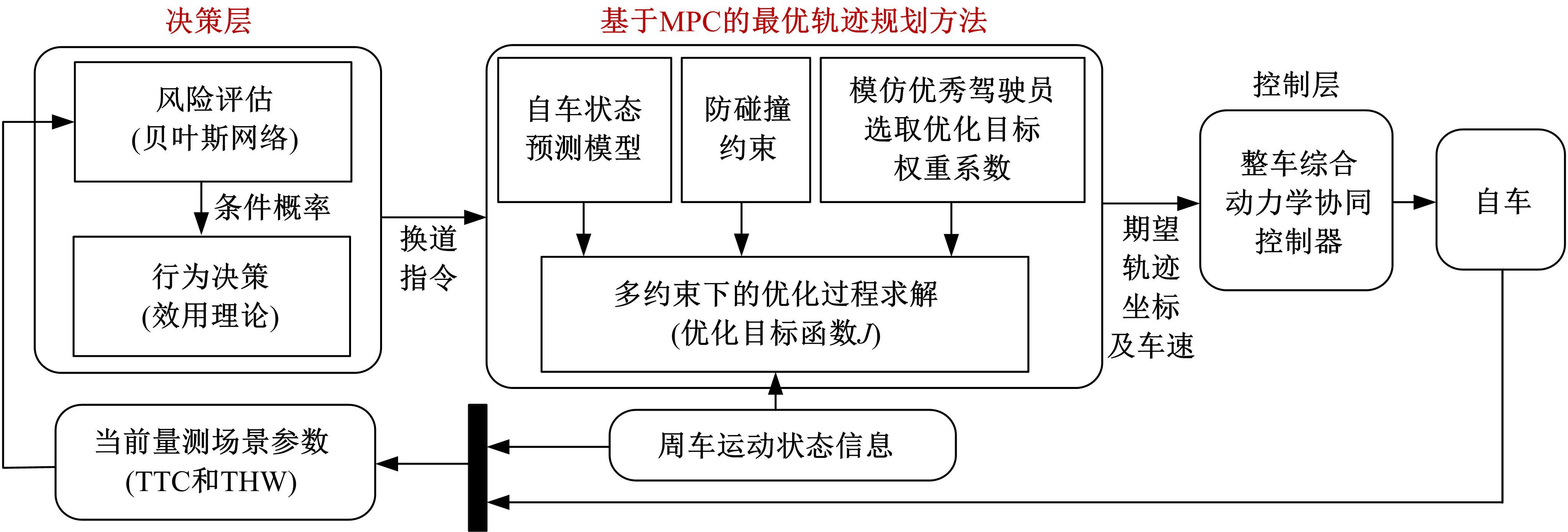
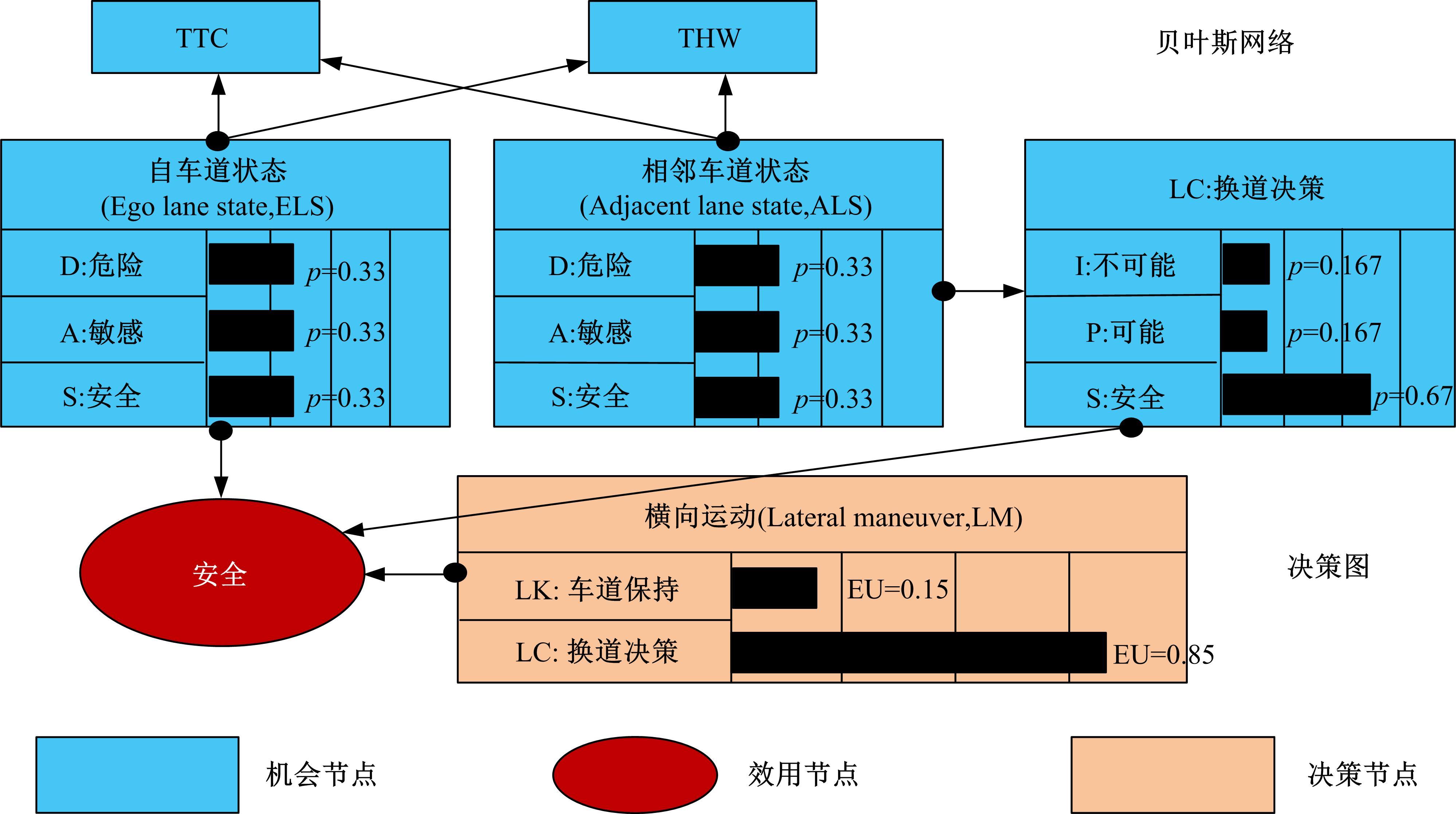
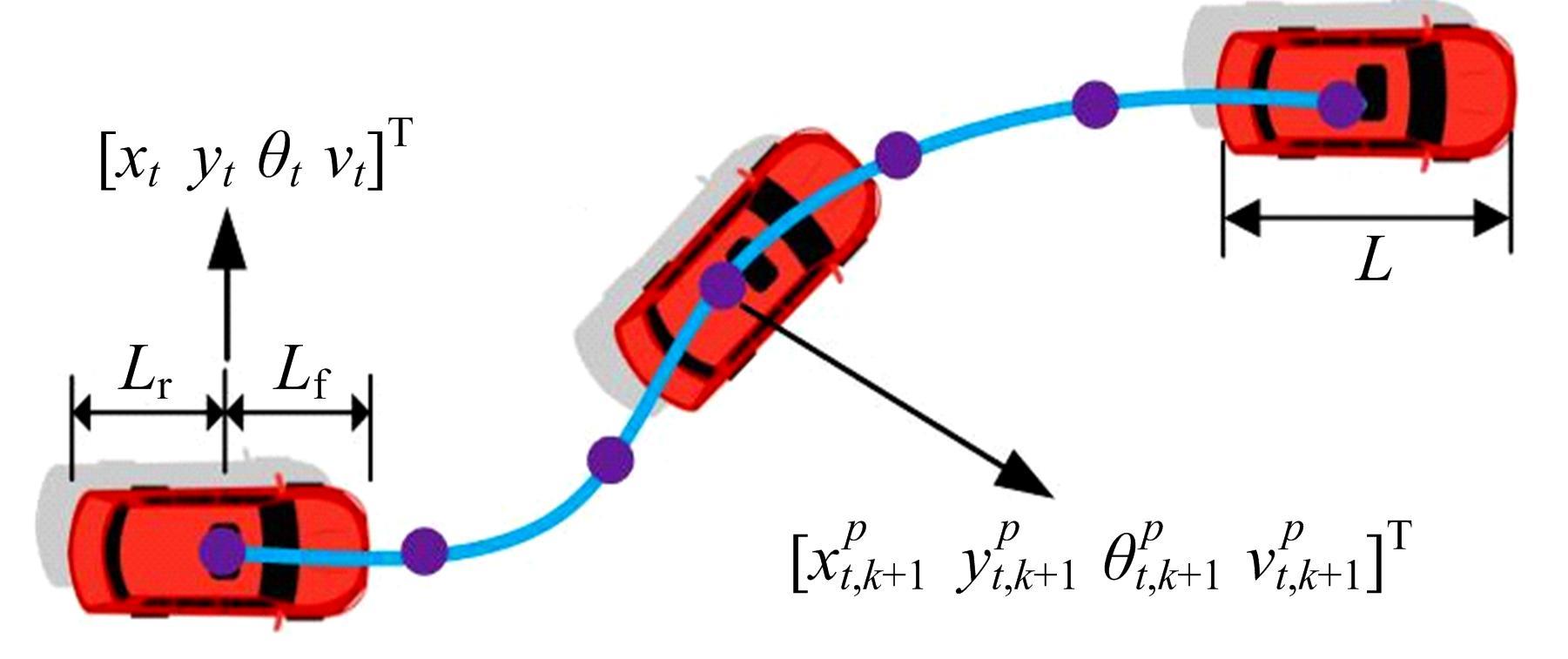
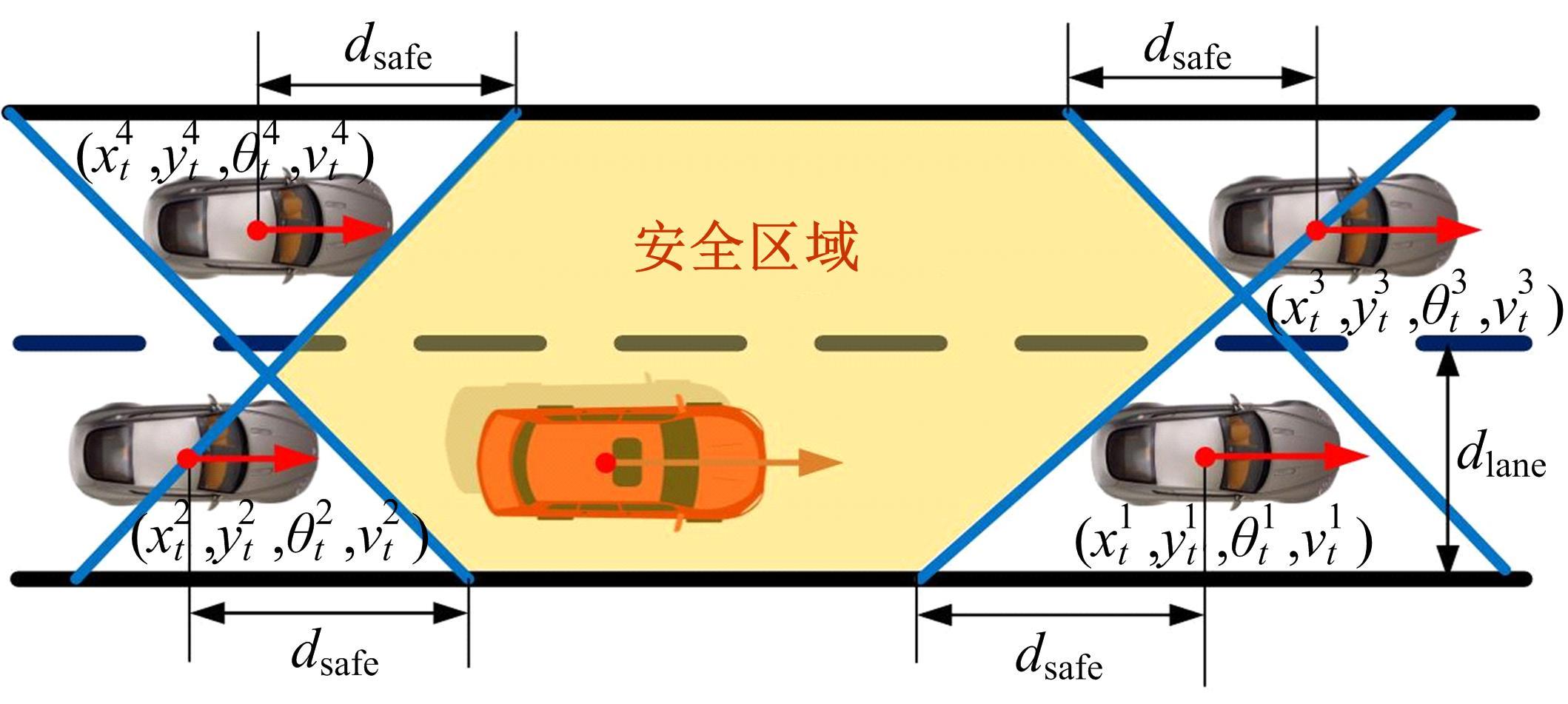
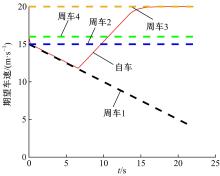
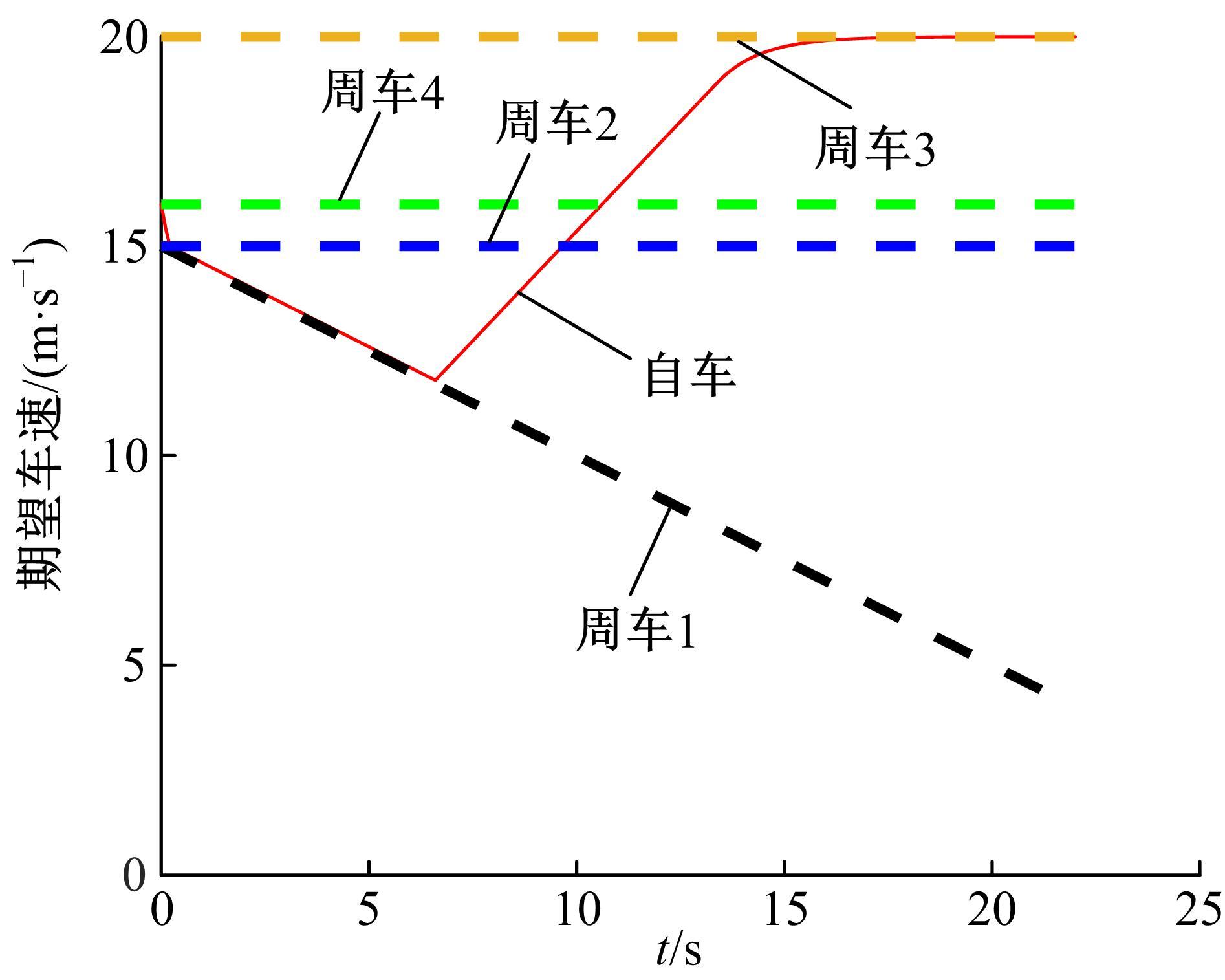
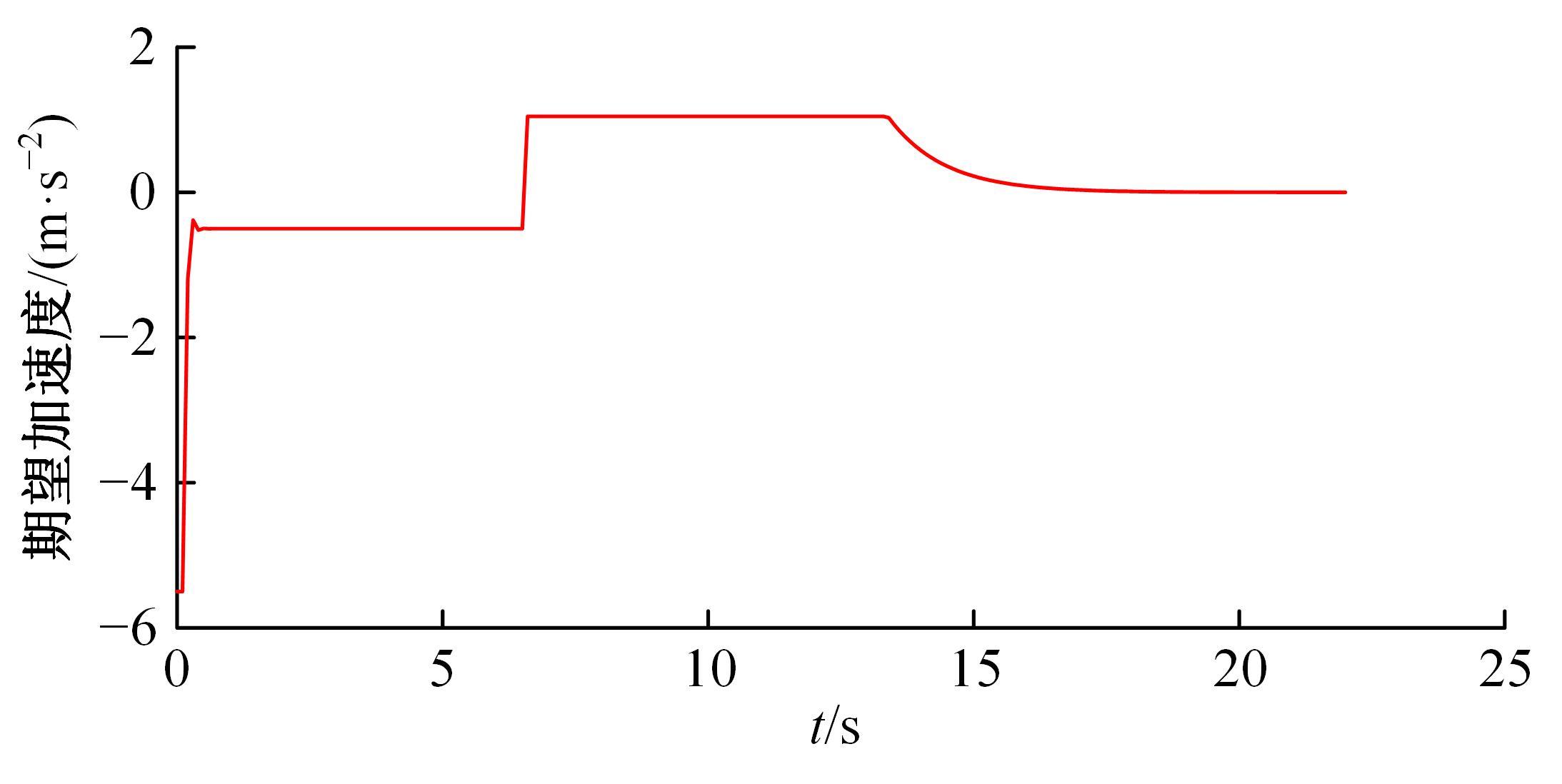
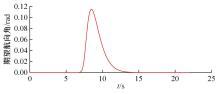
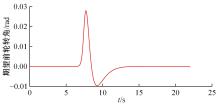
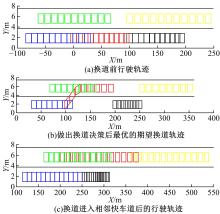
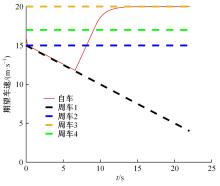
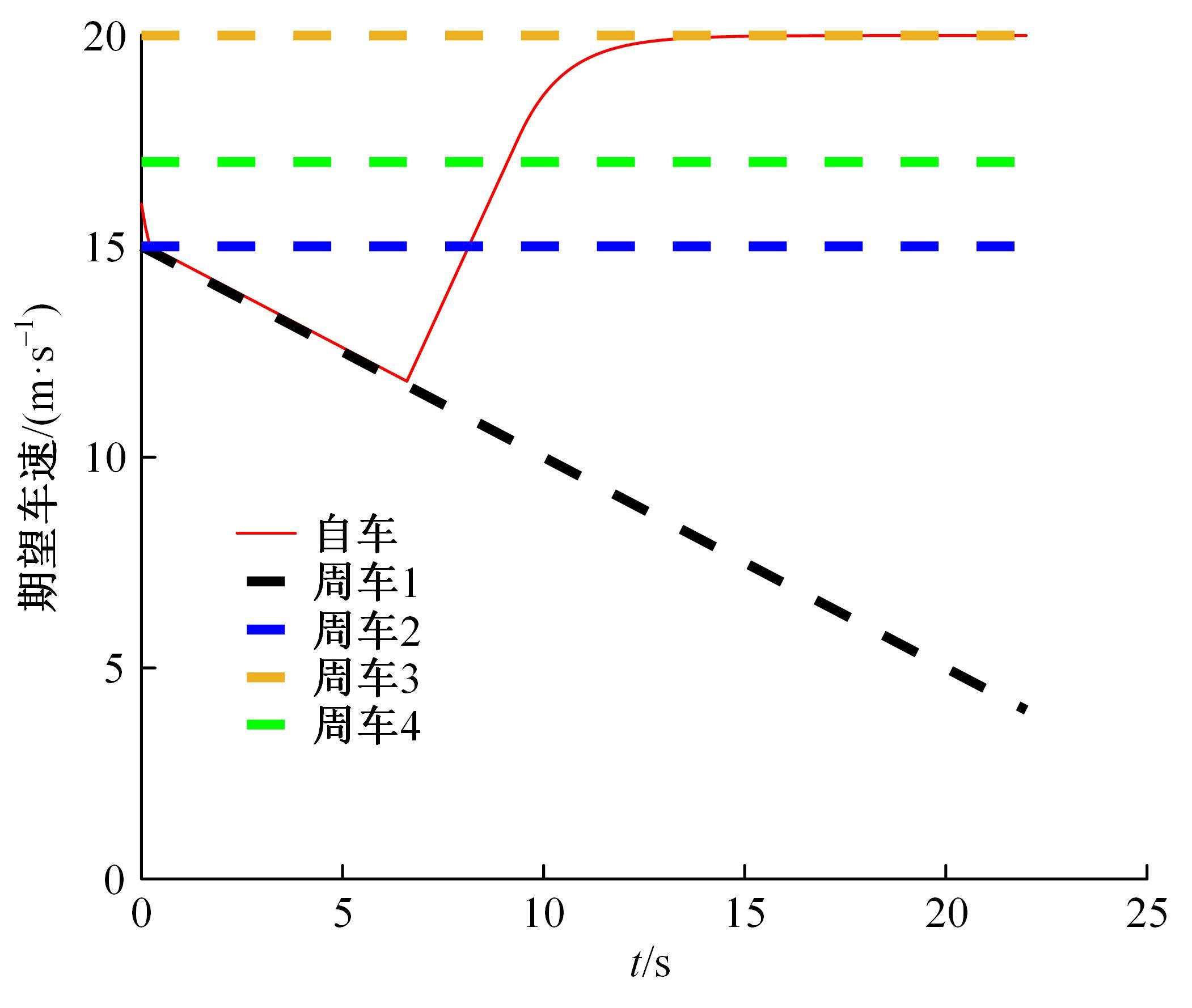
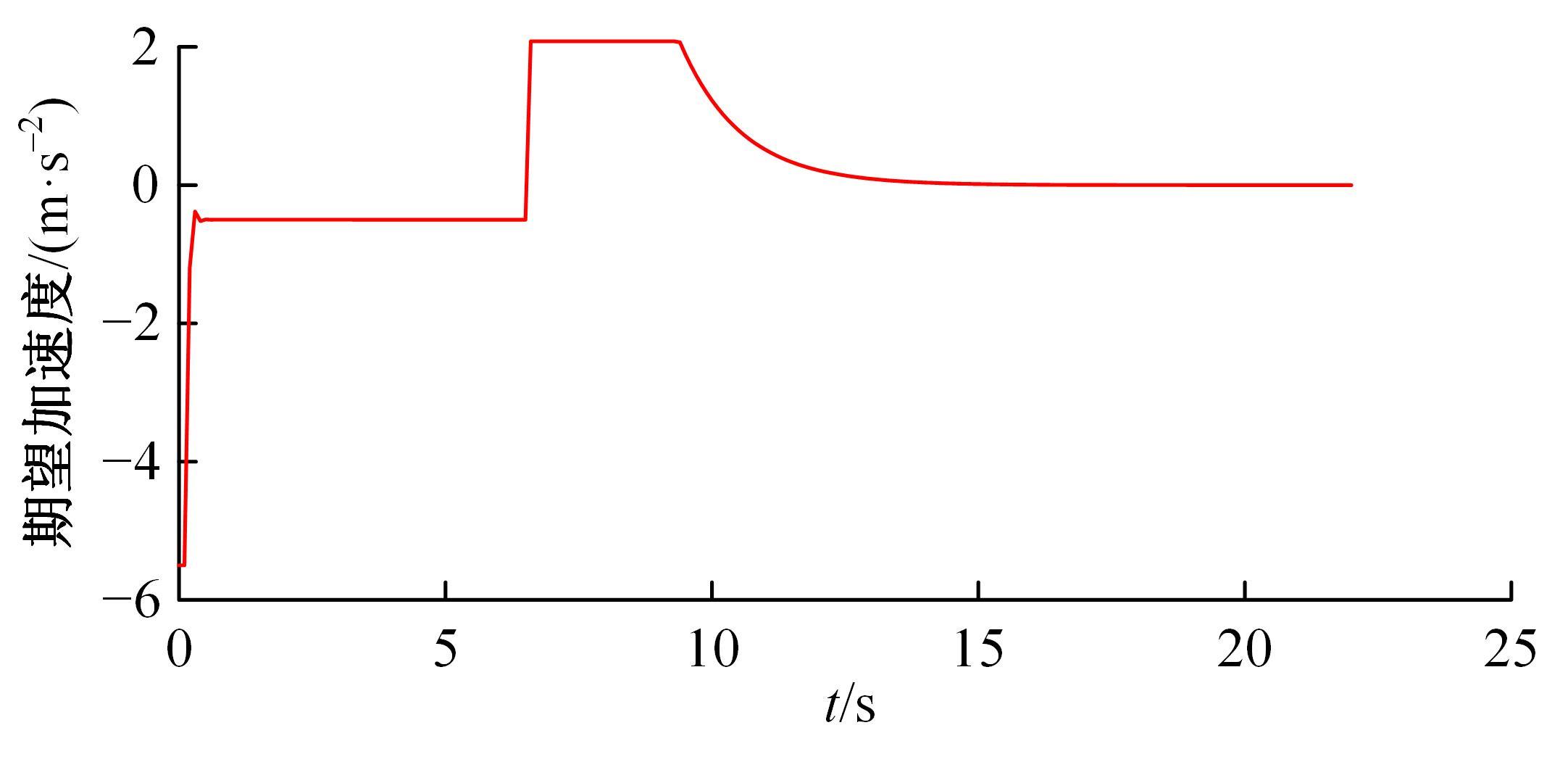
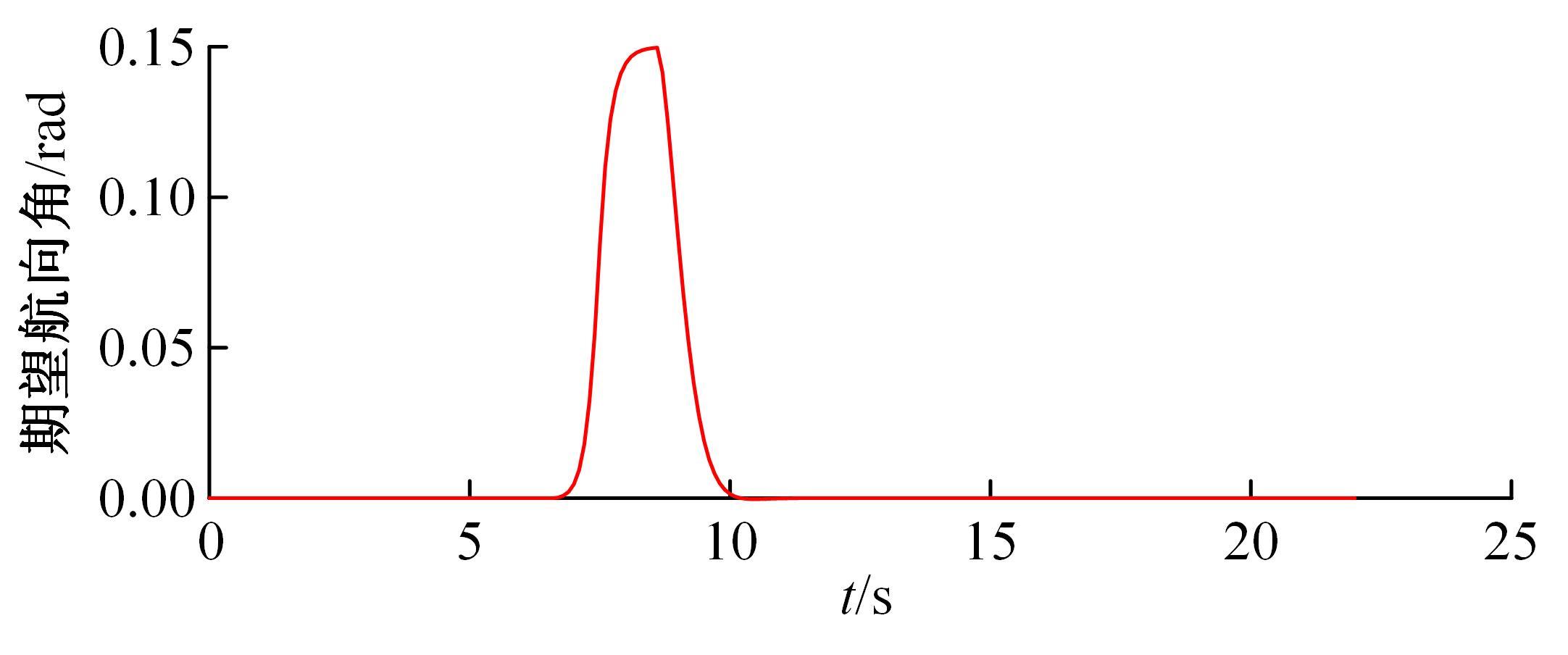
针对双车道公路交通场景,提出了自动驾驶汽车换道的决策和轨迹规划方法。首先,设计了基于贝叶斯概率理论的风险评估方法,得到当前场景车道安全性条件概率。然后,设计了基于安全效用的行为决策方法,根据风险评估贝叶斯网络和决策图做出此时的行为决策——车道保持或换道。在轨迹规划层提出了基于非线性模型预测控制(MPC)的轨迹规划方法,模仿优秀驾驶员给定各个优化目标函数的权重系数,求解最优期望换道轨迹。最后,通过仿真验证该决策和轨迹规划方法的有效性,结果表明,在不同风险场景中,所设计的风险评估、行为决策和轨迹规划方法能够使自动驾驶汽车做出安全的行为决策,并规划出最优的换道轨迹坐标和车速,使自动驾驶汽车安全、快速地换道行驶。
中图分类号:
- U461.1
| 1 | Peng Hao-nan, Wang Wei-da, An Quan, et al. Path tracking and direct yaw moment coordinated control based on robust MPC with the finite time horizon for autonomous independent-drive vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6053-6066. |
| 2 | Xiang Chang-le, Peng Hao-nan, Wang Wei-da, et al. Path tracking coordinated control strategy for autonomous four in-wheel-motor independent-drive vehicles with consideration of lateral stability[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2021, 235(4): 1023-1036. |
| 3 | Sun L, Cheng P, Tomizuka M, et al. A Fast integrated planning and control framework for autonomous driving via imitation learning[C]∥Proceedings of the ASME 2018 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2018: 1-11. |
| 4 | Noh S. Decision-making framework for autonomous driving at road intersections: safeguarding against collision, overly conservative behavior, and violation vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(4): 3275-3286. |
| 5 | 宋威龙. 城区动态环境下智能车辆行为决策研究[D]. 北京:北京理工大学机械与车辆学院, 2016. |
| Song Wei-long. Research on behavioral decision making for intelligent vehicles in dynamic urban environments[D]. Beijing: School of Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. | |
| 6 | 何祥坤. 自动驾驶汽车紧急避撞系统的运动控制与决策方法研究[D]. 北京:清华大学车辆与运载学院, 2018. |
| He Xiang-kun, Research on motion control and decision-making method of emergency collision avoidance system for autonomous vehicle[D]. Beijing: School of Vehicle and Mobility, Tsinghua University, 2018. | |
| 7 | Furda A, Vlacic L. Enabling safe autonomous driving in real-world city traffic using multiple criteria decision making[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2011, 3(1): 4-17. |
| 8 | Huang Z, Xu X, He H, et al. Parameterized batch reinforcement learning for longitudinal control of autonomous land vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(4): 730-741. |
| 9 | 王娟, 朱庆保, 崔靖. 复杂环境下基于贝叶斯决策的机器人路径规划[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2012, 48(2): 245-248. |
| Wang Juan, Zhu Qing-bao, Cui Jing. Robot path planning based on Bayes decision in complex environment[J]. Computer Engineering and Application, 2012, 48(2): 245-248. | |
| 10 | 赵志成,华一丁,王文扬,等. 智能车辆驾驶行为决策方法研究[J]. 现代信息科技, 2019, 3(24): 191-193. |
| Zhao Zhi-cheng, Hua Yi-ding, Wang Wen-yang, et al. Research on intelligent vehicle driving behavior decision-making method[J]. Modern Information Technology, 2019, 3(24): 191-193. | |
| 11 | Zong X, Xu G, Yu G, et al. Obstacle avoidance for self-driving vehicle with reinforcement learning[J]. SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars-Electronic and Electrical Systems, 2017, 11(1): 28-37. |
| 12 | 惠飞, 穆柯楠, 赵祥模. 基于动态概率网格和贝叶斯决策网络的车辆变道辅助驾驶决策方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2018, 18(2): 148-158. |
| Hui Fei, Mu Ke-nan, Zhao Xiang-mo. Assistant driving decision method of vehicle lane change based on dynamic probability grid and Bayesian decision network[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 148-158. | |
| 13 | 孙浩, 邓伟文, 张素民, 等. 考虑全局最优性的汽车微观动态轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2014, 44(4): 918-924. |
| Sun Hao, Deng Wei-wen, Zhang Su-min, et al. Micro vehicle dynamic trajectory plan with global optimality[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(4): 918-924. | |
| 14 | 边明远. 基于紧急变道策略的汽车主动避障安全车距模型[J]. 重庆理工大学学报:自然科学, 2012, 26(4): 1-4. |
| Bian Ming-yuan. A vehicle safety distance model for collision avoidance system based on emergency lane change motion[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science), 2012, 26(4): 1-4. | |
| 15 | Ardakani M K, Tavana M. A decremental approach with the A* algorithm for speeding-up the optimization process in dynamic shortest path problems[J]. Measurement, 2015, 60: 299-307. |
| 16 | Kuwata Y, Teo J, Fiore G, et al. Real-time motion planning with applications to autonomous urban driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2009, 17(5): 1105-1118. |
| 17 | Madås D, Nosratinia M, Keshavarz M, et al. On path planning methods for automotive collision avoidance[C]∥2013 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Gold Coast City, QLD, Australia, 2013: 931-937. |
| 18 | Ali M, Gray A, Gao Y, et al. Multi-objective collision avoidance[C]∥ASME 2013 Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, Palo Alto, California, USA, 2013: No. V003T47A004. |
| 19 | Ji J, Khajepour A, Melek W W, et al. Path planning and tracking for vehicle collision avoidance based on model predictive control with multiconstraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 66(2): 952-964. |
| 20 | Dixit S, Montanaro U, Dianati M,et al. Trajectory planning for autonomous high-speed overtaking in structured environments using robust MPC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(6): 2310-2323. |
| 21 | Rajamani R. Vehicle Dynamics and Control[M]. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. |
| [1] | 胡云峰,于彤,杨惠策,孙耀. 低温环境下燃料电池启动优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2034-2043. |
| [2] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [3] | 鲜斌,张诗婧,韩晓薇,蔡佳明,王岭. 基于强化学习的无人机吊挂负载系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2259-2267. |
| [4] | 贾超,徐洪泽,王龙生. 基于多质点模型的列车自动驾驶非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1913-1922. |
| [5] | 张琳, 章新杰, 郭孔辉, 王超, 刘洋, 刘涛. 未知环境下智能汽车轨迹规划滚动窗口优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 652-660. |
| [6] | 曲兴田, 闫龙威, 孙慧超, 周伟, 李光辉. 工作平台可翻转的3D打印机装置结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1489-1497. |
| [7] | 曹福成, 邢笑雪, 李元春, 赵希禄. 下肢康复机器人轨迹自适应滑模阻抗控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1602-1608. |
| [8] | 管成,王飞,张登雨. 基于NURBS的挖掘机器人时间最优轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 540-546. |
| [9] | 缪东晶,吴聊,徐静,陈恳,谢颖,刘志. 飞机表面自动喷涂机器人系统与喷涂作业规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 547-553. |
| [10] | 孙浩, 邓伟文, 张素民, 吴梦勋. 考虑全局最优性的汽车微观动态轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 918-924. |
| [11] | 石屹然, 田彦涛, 史红伟, 张立. 基于Modified Volterra模型的SI发动机空燃比非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 538-547. |
| [12] | 任园园, 李显生, 席建锋. 驾驶行为决策风险的多维结构模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(02): 343-0348. |
| [13] | 于树友, 陈虹, 赵海艳. 非线性离散时间系统的准无限时域NMPC[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(04): 1002-1006. |
|