吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 2259-2267.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200577
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于强化学习的无人机吊挂负载系统轨迹规划
- 1.天津大学 电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072
2.天津航海仪器研究所,天津 300131
Trajectory planning for unmanned aerial vehicle slung⁃payload aerial transportation system based on reinforcement learning
Bin XIAN1( ),Shi-jing ZHANG1,Xiao-wei HAN1,Jia-ming CAI1,Ling WANG2
),Shi-jing ZHANG1,Xiao-wei HAN1,Jia-ming CAI1,Ling WANG2
- 1.School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.Tianjin Navigation Instrument Research Institute,Tianjin 300131,China
摘要:
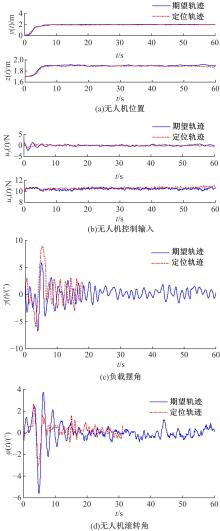
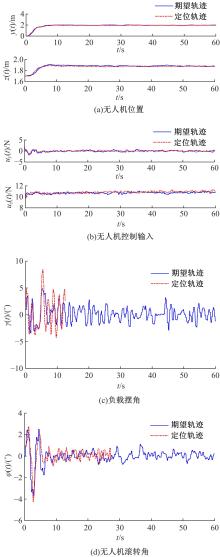
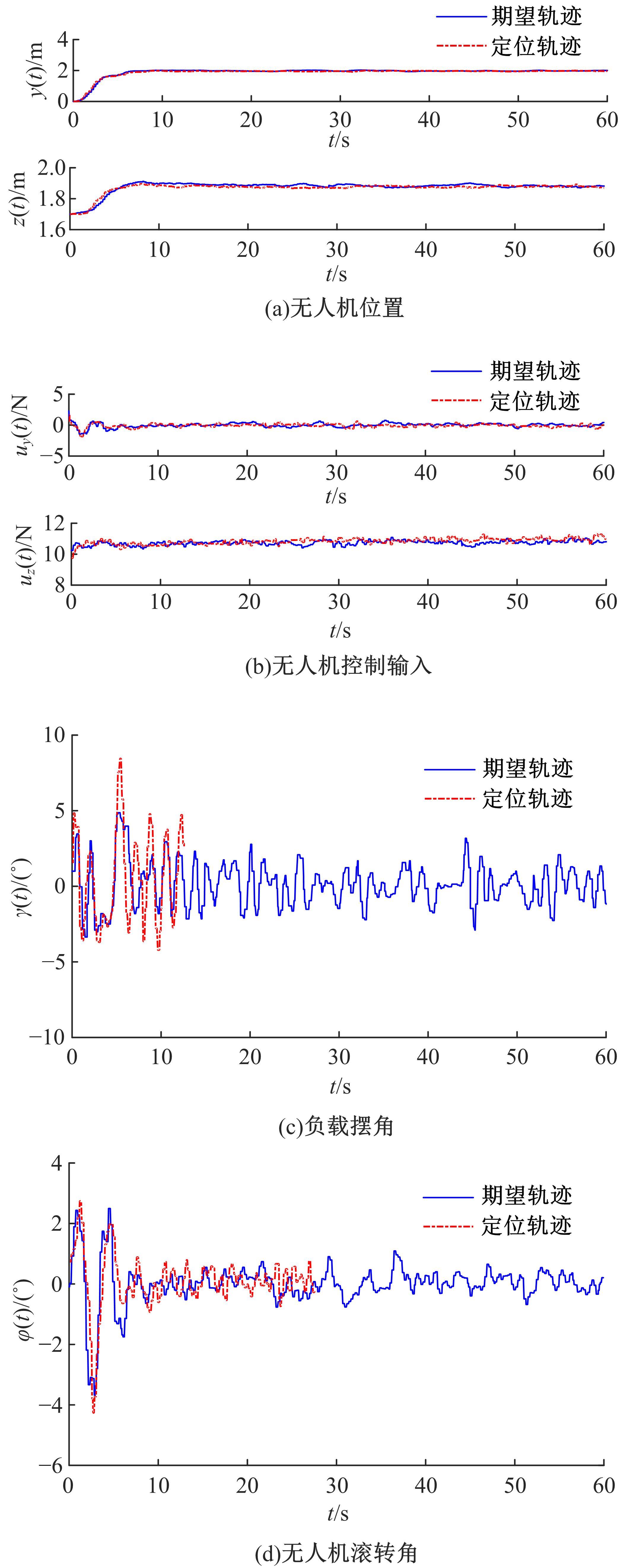
针对四旋翼无人机吊挂负载系统准确位置控制问题和吊挂负载的摆动抑制问题,提出了一种基于强化学习的在线轨迹规划方案。为补偿飞行过程中未知外界扰动的影响,本文首先将无人机的期望轨迹设计分为位置定位轨迹规划设计和抗扰动轨迹规划设计。其中,位置定位轨迹规划部分可预先设计,以引导无人机飞抵目标位置。抗扰动轨迹规划部分采用基于强化学习的在线更新策略,对外界未知扰动进行补偿,以达到抑制飞行过程中吊挂负载摆动的目的。然后,采用基于Lyapunov稳定性的分析方法,证明了闭环系统的稳定性,并证明了无人机位置跟踪误差和吊挂负载摆动运动的收敛。最后,通过飞行对比实验,验证了所提轨迹规划方法的有效性以及对外界干扰和负载质量变化的鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
- TP273
| 1 | 张琳, 章新杰, 郭孔辉, 等. 未知环境下智能汽车轨迹规划滚动窗口优化[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(3): 652-660. |
| Zhang Lin, Zhang Xin-jie, Guo Kong-hui, et al. Rolling window optimization for intelligent vehicle trajectory planning in unknown environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 652-660. | |
| 2 | 梁晓, 胡欲立. 基于微分平滑的四旋翼运输系统轨迹跟踪控制[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(4): 525-532. |
| Liang Xiao, Hu Yu-li. Trajectory control of a quadrotor with a cable-suspended load based on differential flatness[J]. Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 36(4): 525-532. | |
| 3 | Liang X, Fang Y, Sun N, et al. Dynamics analysis and time-optimal motion planning for unmanned quadrotor transportation systems[J]. Mechatronics, 2018, 50: 16-29. |
| 4 | Wang S, Xian B. An anti-swing trajectory approach for an unmanned aerial vehicle with a slung payload[C]∥Proc of 2018 37th Chinese Control Conference, Wuhan, China, 2018: 5560-5565. |
| 5 | Potdar N D, de Croon G C H E, Alonso-mora J. Online trajectory planning and control of a MAV payload system in dynamic environments[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2020, 44(7): 1065-1089. |
| 6 | 杨顺, 蒋渊德, 吴坚, 等. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| Yang Shun, Jiang Yuan-de, Wu Jian, et al. Autonomous driving policy learning based on deep reinforcement learning and multi-type sensor data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. | |
| 7 | 郭宪, 方勇纯. 深入浅出强化学习:原理入门[M]. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2018. |
| 8 | 董博, 刘克平, 李元春. 动态约束下可重构模块机器人分散强化学习最优控制[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2014, 44(5): 1375-1384. |
| Dong Bo, Liu Ke-ping, Li Yuan-chun. Decentralized reinforcement learning optimal control for time varying constrained reconfigurable modular robot[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(5): 1375-1384. | |
| 9 | Alothman Y, Jasim W, Gu D. Quad-rotor lifting transporting cable-suspended payloads control[C]∥Proc of 2015 21st International Conference on Automation and Computing, Glasgow, England, 2015: 299-304. |
| 10 | Abu-khalaf M, Lewis F L. Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach[J]. Automatica, 2005, 41(5): 779-791. |
| 11 | Song R, Lewis F, Wei Q, et al. Multiple actor-critic structures for continuous-time optimal control using input-output data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(4): 851-865. |
| 12 | Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L. Online actor-critic algorithm to solve the continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control problem[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(5): 878-888. |
| 13 | Bhasin S, Kamalapurkar R, Johnson M, et al. A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(1): 82-92. |
| 14 | Fan Q, Yang G. Adaptive actor-critic design-based integral sliding-mode control for partially unknown nonlinear systems with input disturbances[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 27(1): 165-177. |
| 15 | Sun N, Fang Y. An efficient online trajectory generating method for underactuated crane systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2014, 24(11): 1653-1663. |
| [1] | 韩光信,赵聚乐,胡云峰. 控制输入受限的板球系统滚动线性二次型调节器控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1982-1989. |
| [2] | 吕帅,刘京. 基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1420-1426. |
| [3] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [4] | 于树友,常欢,孟凌宇,郭洋,曲婷. 基于扰动观测器的轮式移动机器人滚动时域路径跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1097-1105. |
| [5] | 李丽娜,魏晓辉,郝琳琳,王兴旺,王储. 大规模流数据处理中代价有效的弹性资源分配策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1832-1843. |
| [6] | 吴爱国,韩俊庆,董娜. 基于极局部模型的机械臂自适应滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1905-1912. |
| [7] | 王伟,赵健廷,胡宽荣,郭永仓. 基于快速非奇异终端滑模的机械臂轨迹跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 464-471. |
| [8] | 刘富,安毅,董博,李元春. 基于ADP的可重构机械臂能耗保代价分散最优控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 342-350. |
| [9] | 曲兴田,王学旭,孙慧超,张昆,闫龙威,王宏一. 熔融沉积成型技术3D打印机加热系统的模糊自适应PID控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 77-83. |
| [10] | 马常友, 高海波, 丁亮, 于海涛, 邢宏军, 邓宗全. 机器人末端执行器自更换机构设计及对接策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2027-2037. |
| [11] | 马苗苗,潘军军,刘向杰. 含电动汽车的微电网模型预测负荷频率控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1644-1652. |
| [12] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [13] | 于树友,谭雷,王伍洋,陈虹. 基于三步法的汽车主动四轮转向控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 934-942. |
| [14] | 温海营,任翔,徐卫良,丛明,秦文龙,胡书海. 咀嚼机器人颞下颌关节仿生设计及试验测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 943-952. |
| [15] | 顾万里,王萍,胡云峰,蔡硕,陈虹. 具有H∞性能的轮式移动机器人非线性控制器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1811-1819. |
|
||