吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 46-52.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200502
随机载荷作用下的结构疲劳寿命区间分析
- 1.吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
2.中国科学院 光电技术研究所,成都 610041
Interval analysis of structural fatigue life under random load
Guang-wei MENG1( ),Chuan-xin REN2,Feng LI1(
),Chuan-xin REN2,Feng LI1( ),Tong-hui WEI1
),Tong-hui WEI1
- 1.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Institute of Optics and Electronics,Chinese Academy of Science,Chengdu 610041,China
摘要:
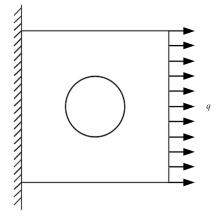
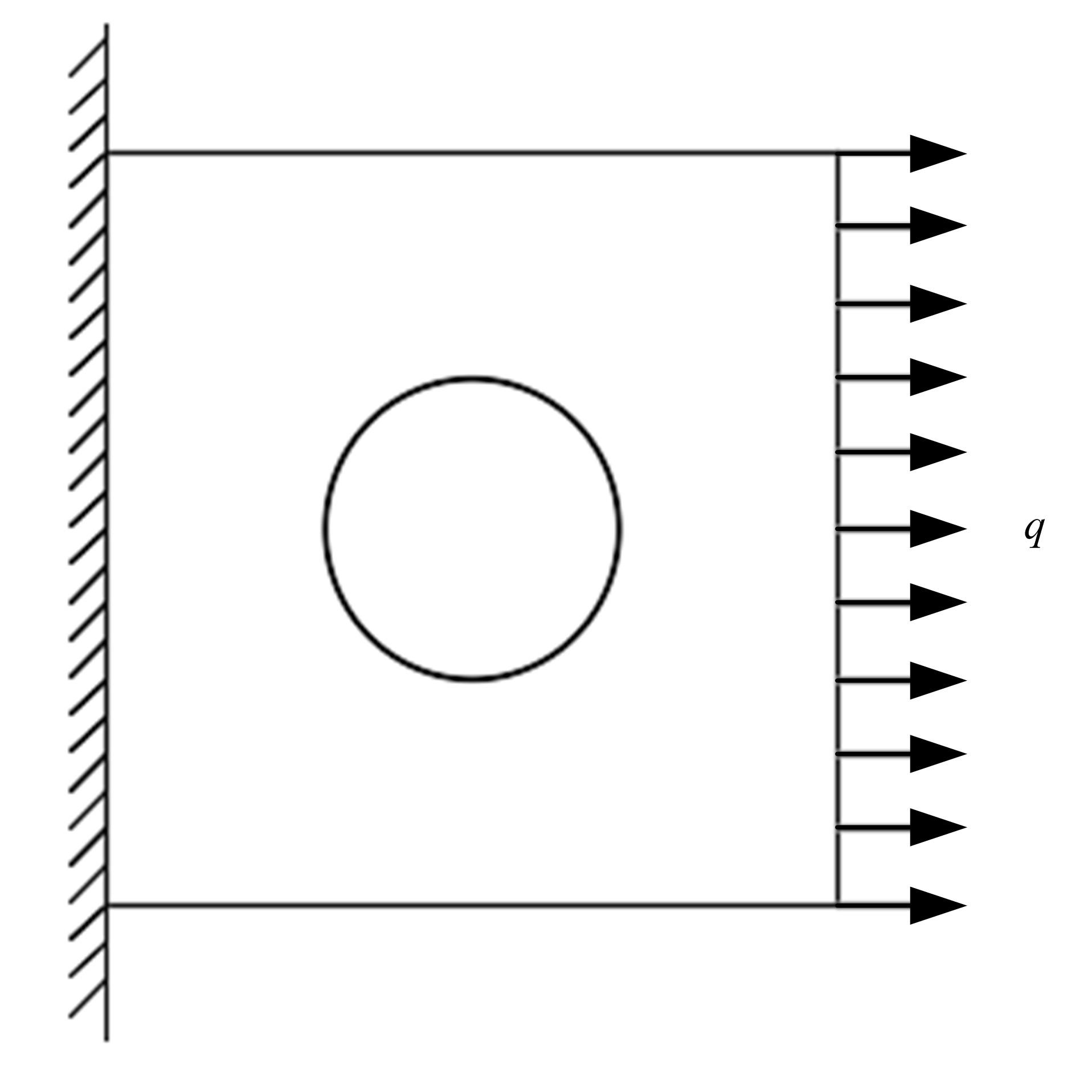
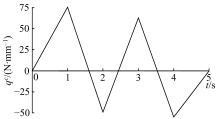
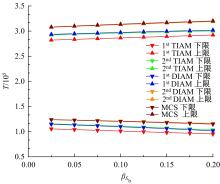
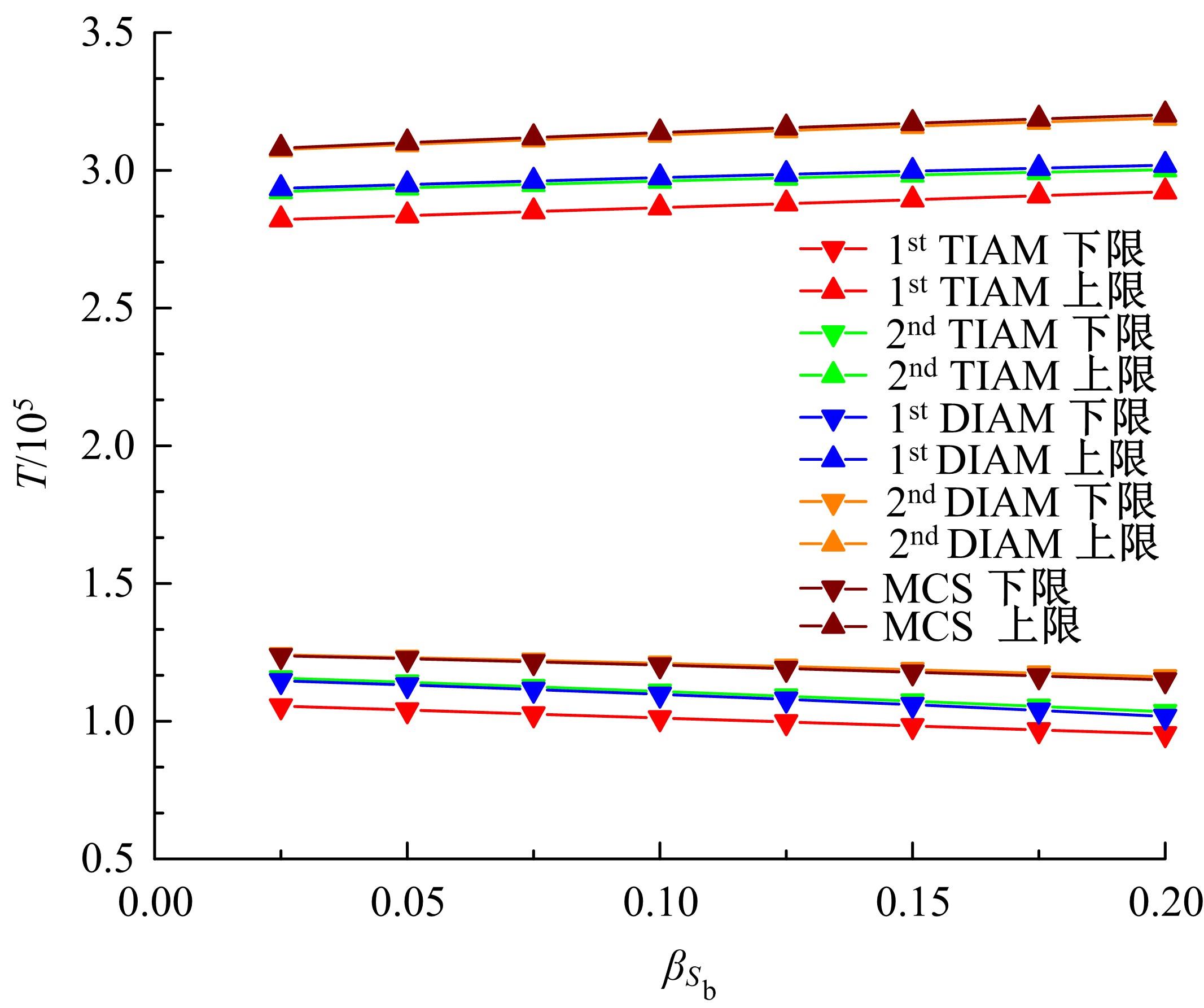
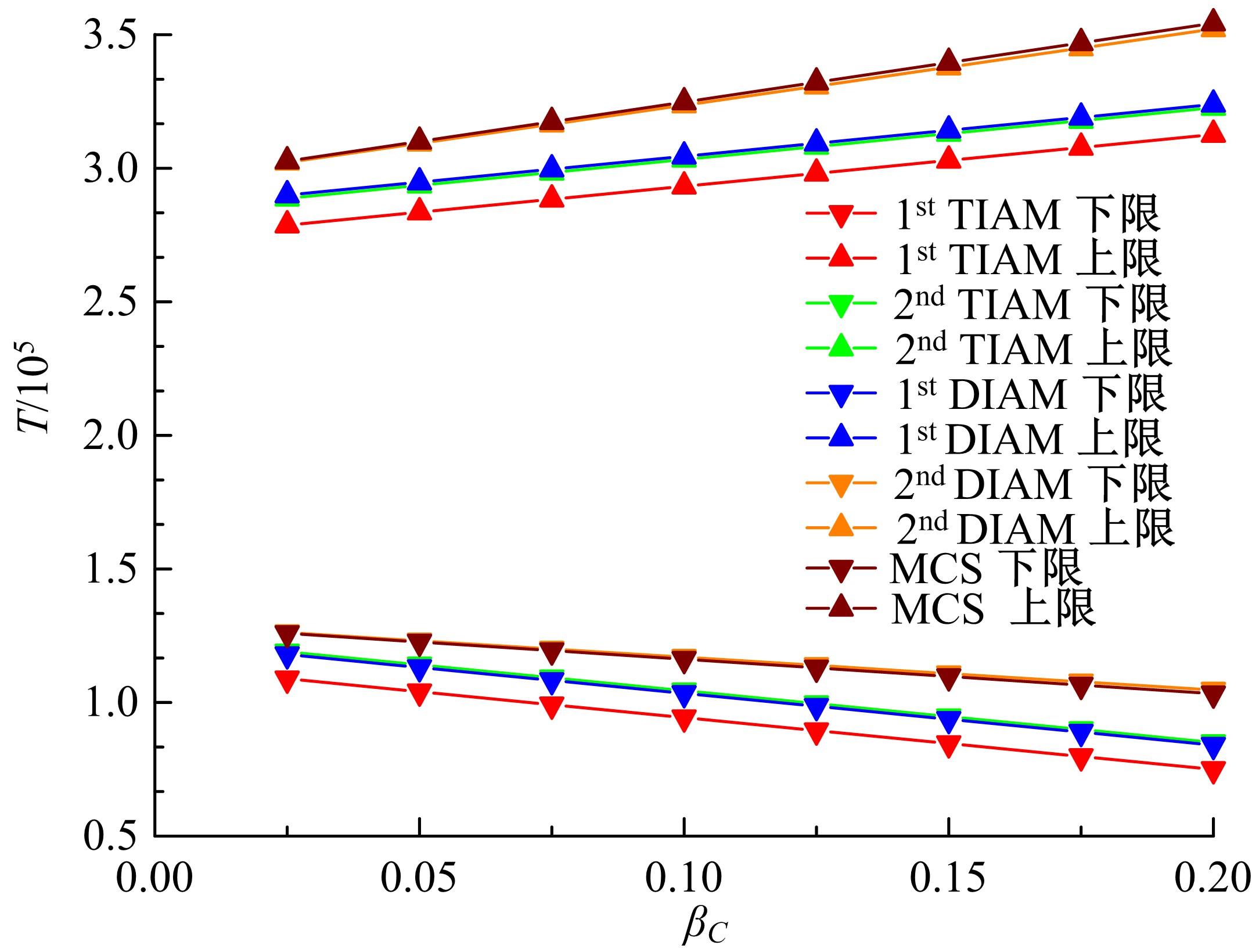
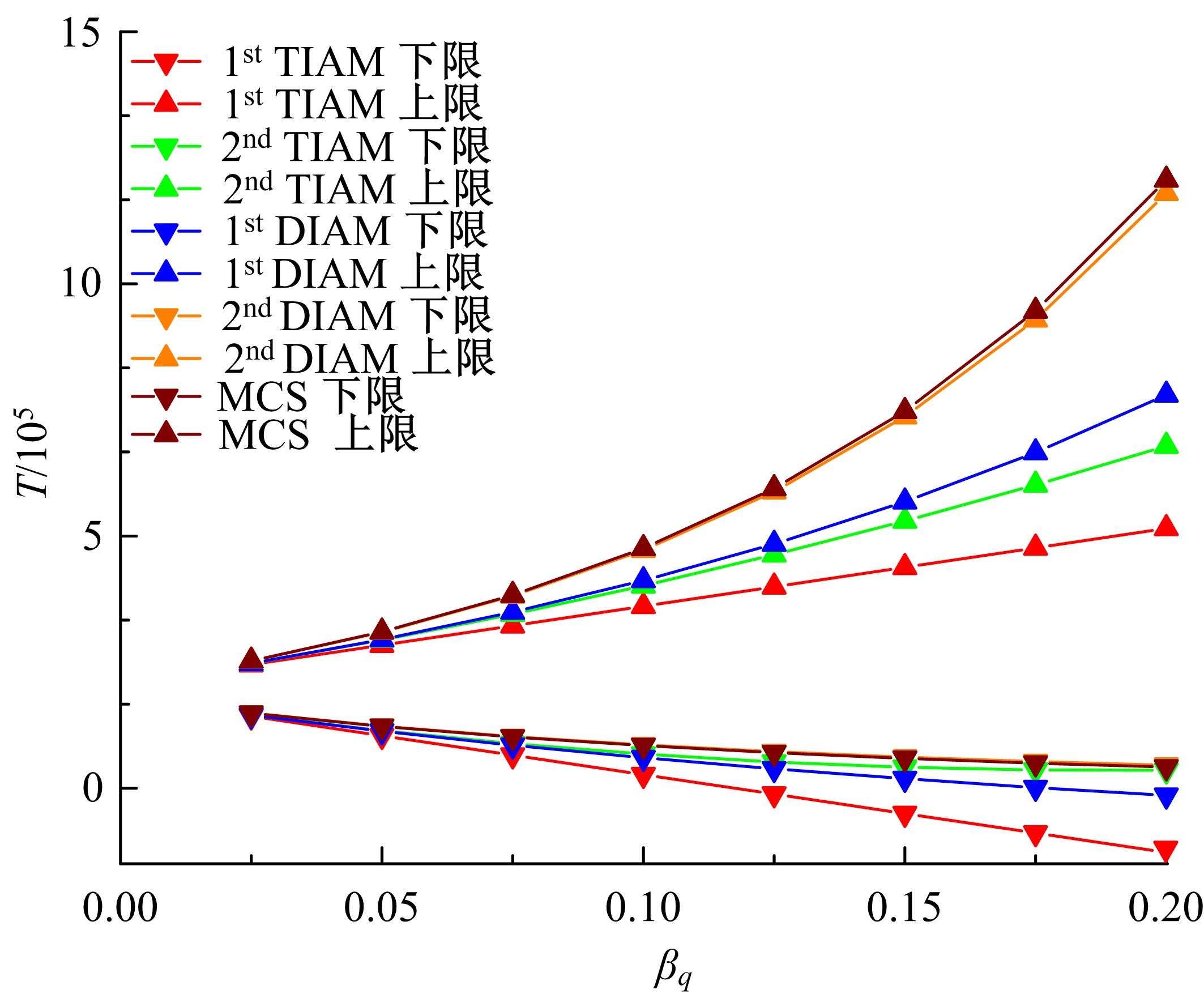
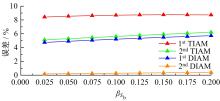
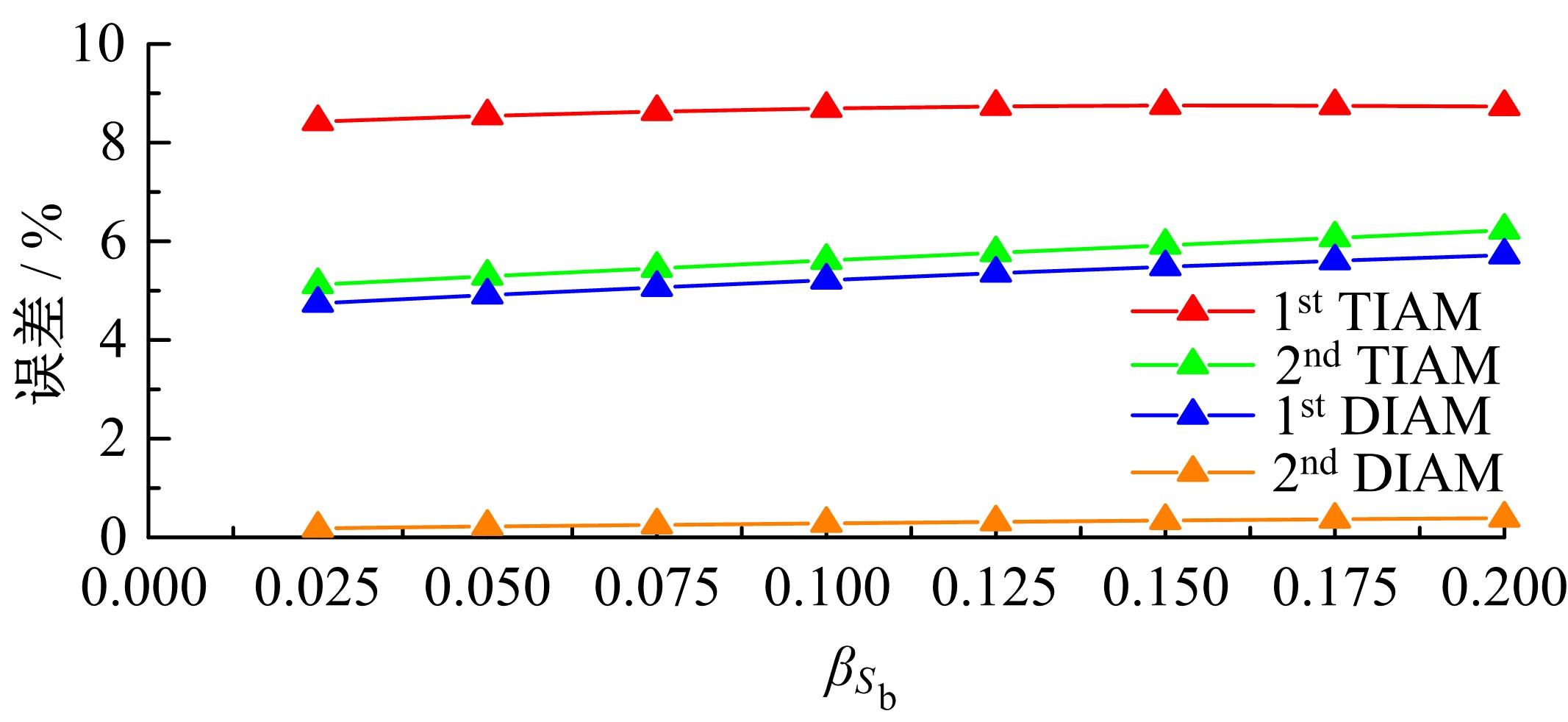
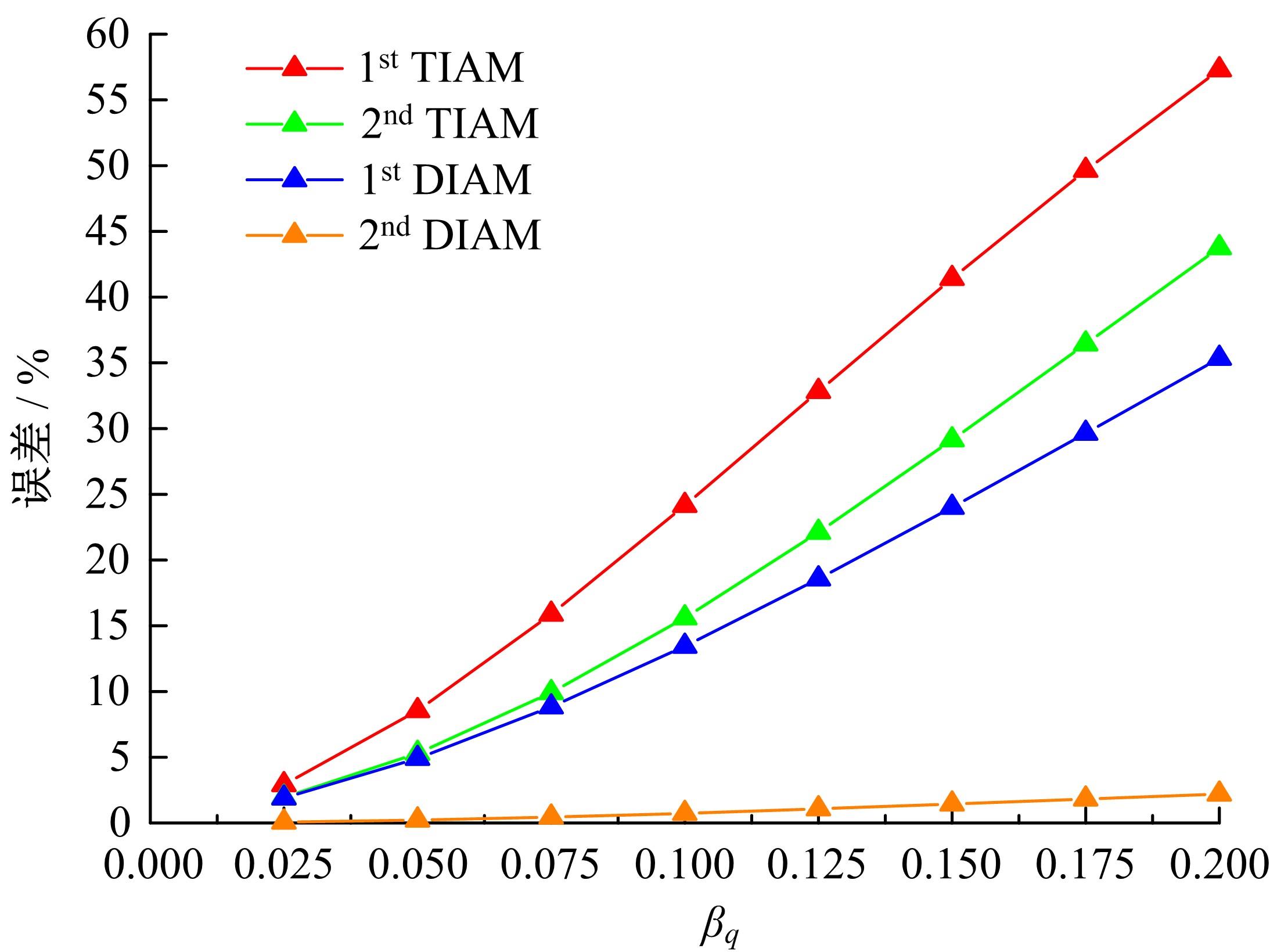
传统的概率方法分析结构疲劳寿命时,需要大量的样本以确定随变量的概率密度分布,而且概率密度函数较小的误差将会引起结构疲劳寿命较大的误差。针对这种情况,提出了一种随机载荷作用下结构疲劳寿命的区间分析模型。将影响结构疲劳寿命的不确定因素视为区间变量,给出了随机载荷作用下结构疲劳寿命的降维表达式,结合区间数学方法,得到了结构疲劳寿命的上限和下限。数值算例表明,与Taylor方法相比,基于降维算法的结构疲劳寿命区间分析方法具有较高的精度。对于强度极限和疲劳参数而言,一阶降维算法和二阶Taylor方法精度相当;而对于疲劳载荷,当其变化范围较大时,Taylor方法已经不能满足精度要求,而二阶降维算法仍然具有较高的计算精度和稳定性,其计算精度在一定范围内和遗传算法大致相当,但计算效率却远高于遗传算法。
中图分类号:
- TP202.1
| 1 | Karandikar J M, Kim N H, Schmitz T L. Prediction of remaining useful life for fatigue-damaged structures using Bayesian inference[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2012, 96: 588-605. |
| 2 | Tsianika V, Geroulas V, Papadimitriou D, et al. A methodology of design for fatigue using an accelerated life testing approach with saddlepoint approximation[C]∥SAE International Paper, United States, 2019: 1-13. |
| 3 | 李亚波, 宋清源, 杨凯, 等. 试样疲劳性能尺度效应的概率控制体积方法[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(5): 1363-1371. |
| Li Ya-bo, Song Qing-yuan, Yang Kai, et al. Probabilistic control volume method for the size effect of specimen fatigue performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(5): 1363-1371. | |
| 4 | 孙祝岭. Birnbaum-Saunders疲劳寿命分布参数的回归估计方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2010, 31(9): 1259-1262. |
| Sun Zhu-ling. Regression estimation of the parameters of the Birnbaum-Saunders fatigue life distribution[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(9): 1259-1262. | |
| 5 | Moore R E. Methods and Applications of Interval Analysis[M]. Philadephia: SIAML, 1979. |
| 6 | Long X Y, Jiang C, Liu K, et al. An interval analysis method for fatigue crack growth life prediction with uncertainty [J]. Computers and Structures, 2018, 210(2018): 1-11. |
| 7 | 王军, 邱志平, 金延伟. 疲劳寿命的区间名义应力法及灵敏度分析[J]. 飞机设计, 2012, 32(6): 42-46. |
| Wang Jun, Qiu Zhi-ping, Jin Yan-wei. Nominal stress method of fatigue life and sensitivity analysis[J]. Aircraft Design, 2012, 32(6): 42-46. | |
| 8 | 陈小月, 文桂林, 刘杰,等. 基于泛灰数的结构疲劳寿命区间估计方法[J]. 计算机仿真, 2017, 34(4): 245-249. |
| Chen Xiao-yue, Wen Gui-lin, Liu Jie, et al. Estimation approach of structure fatigue life based on universal grey number[J]. Computer Simulation, 2017, 34(4): 245-249. | |
| 9 | 邱志平, 王晓军. 结构疲劳寿命的区间估计[J]. 力学学报, 2005(5): 653-657. |
| Qiu Zhi-ping, Wang Xiao-jun. Interval estimation for structural fatigue lifetime [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2005(5): 653-657. | |
| 10 | 孙作振, 孟广伟, 李锋, 等. 基于二阶区间摄动法的结构疲劳寿命估计[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 34(): 75-78. |
| Sun Zuo-zhen, Meng Guang-wei, Li Feng, et al. Structure fatigue life estimation based on the second-order interval perturbation method[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2013, 34(Sup.2): 75-78. | |
| 11 | 李锋, 孟广伟, 沙丽荣. 考虑模糊失效准则的结构疲劳寿命可靠性[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(12): 2316-2321. |
| Li Feng, Meng Guang-wei, Sha Li-rong. Reliability analysis of structural fatigue life under fuzzy failure criteria[J].Acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica, 2009, 30(12): 2316-2321. | |
| 12 | Rahman S. A dimensional decomposition method for stochastic fracture mechanics[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2006, 73(15): 2093-2109. |
| 13 | Li G, Zhang K. A combined reliability analysis approach with dimension reduction method and maximum entropy method[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2011, 43(1): 121-143. |
| 14 | 付酥昇.ANSYS ncode designlife: 疲劳分析基础与实例教程[M].北京:人民邮电出版社, 2020. |
| 15 | Ponticelli G S, Guarino S, Giannini O. An optimal genetic algorithm for fatigue life control of medium carbon steel in laser hardening process[J]. Applied Sciences-Basel, 2020, 10(1401): 1-14. |
| 16 | 闫楚良, 郝云霄, 刘克格. 基于遗传算法优化的BP神经网络的材料疲劳寿命预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1710-1715. |
| Yan Chu-liang, Hao Yun-xiao, Liu Ke-ge. Fatigue life prediction of materials based on BP neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1710-1715. |
| [1] | 彭勇,杨汉铎,陆学元,李彦伟. 基于离散元法的空隙特征对沥青混合料虚拟剪切疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 956-964. |
| [2] | 李碧雄,廖桥,章一萍,周练,隗萍,刘侃. 超高强钢筋工程用水泥基复合材料梁受弯计算理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1153-1161. |
| [3] | 尼颖升,孙启鑫,马晔,徐栋,刘超. 基于空间网格分析的多箱室波形钢腹板组合梁腹板剪力分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1735-1746. |
| [4] | 毛宇泽, 王黎钦. 鼠笼支撑一体化结构对薄壁球轴承承载性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
| [5] | 王春生, 邹丽, 杨鑫华. 基于邻域粗糙集的铝合金焊接接头疲劳寿命影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1848-1853. |
| [6] | 闫亚宾, 王晓媛, 万强. 纳米尺度界面低周疲劳破坏行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1201-1206. |
| [7] | 王国林, 孙砚田, 梁晨, 杨建, 周海超. 应用满应力理论的轮胎轮廓设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 365-372. |
| [8] | 陈江义, 刘保元. 纤维断裂损伤对复合材料板中导波频散特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 180-184. |
| [9] | 孟广伟, 冯昕宇, 周立明, 李锋. 基于降维算法的结构可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 174-179. |
| [10] | 曹珊珊, 雷俊卿. 考虑区间不确定性的钢结构疲劳寿命分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 804-810. |
| [11] | 蒋荣超, 王登峰, 秦民, 蒋永峰. 基于疲劳寿命的轿车后悬架扭转梁轻量化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 35-42. |
| [12] | 邢保英, 何晓聪, 王玉奇, 邓成江. 多铆钉自冲铆接头力学性能机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1488-1494. |
| [13] | 杨慧艳, 何晓聪, 周森. 压印接头强度的有限元模型及理论计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 864-871. |
| [14] | 邓成江,何晓聪,邢保英,王玉奇,曾凯,丁燕芳. 铝与铜异质板材自冲铆搭接接头的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 473-480. |
| [15] | 闫楚良, 郝云霄, 刘克格. 基于遗传算法优化的BP神经网络的材料疲劳寿命预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1710-1715. |
|
||