吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 920-933.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180193
TPR⁃TF:基于张量分解的时间敏感兴趣点推荐模型
王楠1,2( ),李金宝1,2(
),李金宝1,2( ),刘勇1,2,张玉杰1,2,钟颖莉1,2
),刘勇1,2,张玉杰1,2,钟颖莉1,2
- 1. 黑龙江大学 计算机科学技术学院, 哈尔滨 150080
2. 黑龙江大学 数据库与并行计算重点实验室, 哈尔滨150080
TPR⁃TF: time⁃aware point of interest recommendation model based on tensor factorization
Nan WANG1,2( ),Jin⁃bao LI1,2(
),Jin⁃bao LI1,2( ),Yong LIU1,2,Yu⁃jie ZHANG1,2,Ying⁃li ZHONG1,2
),Yong LIU1,2,Yu⁃jie ZHANG1,2,Ying⁃li ZHONG1,2
- 1. School of Computer Science and Technology, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
2. Key Laboratory of Database and Parallel Computing, Heilongjiang University, Harbin 150080, China
摘要:
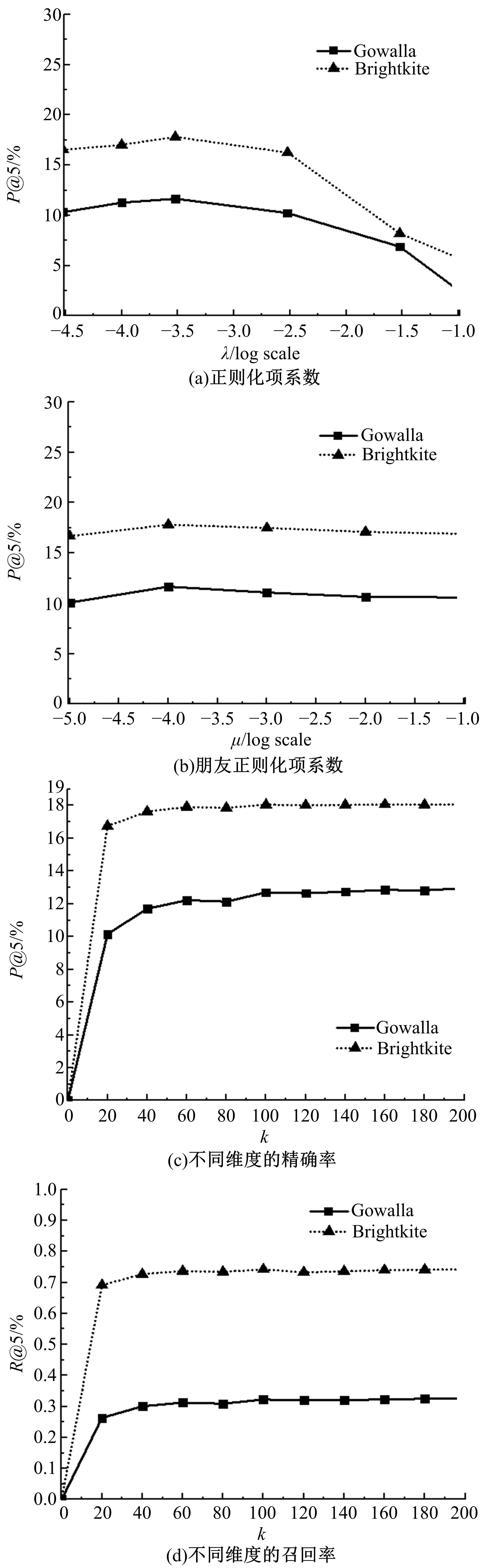
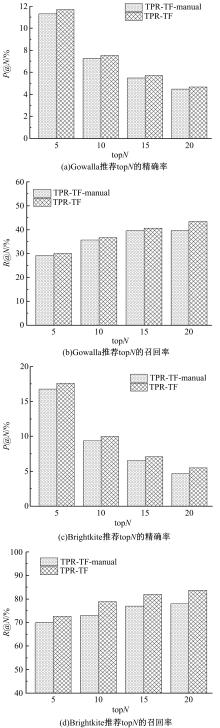
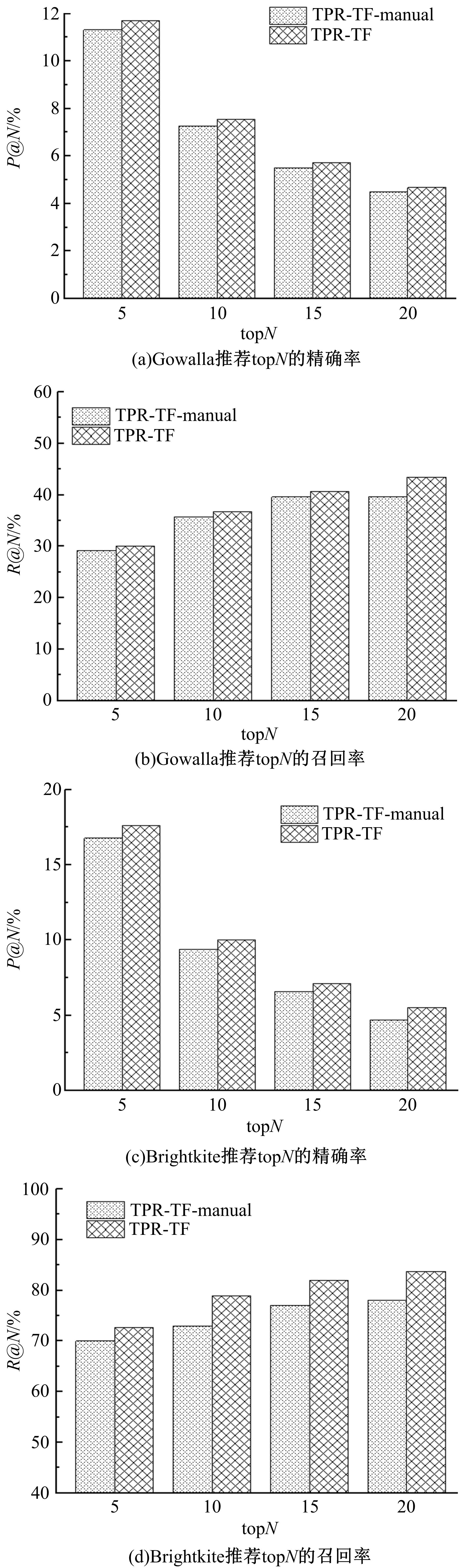
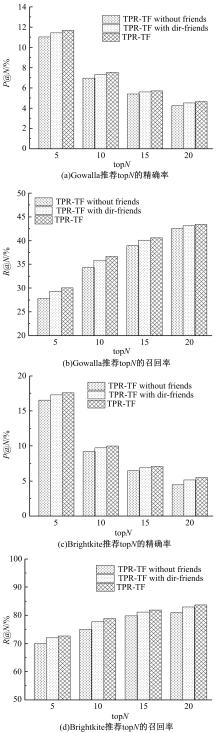
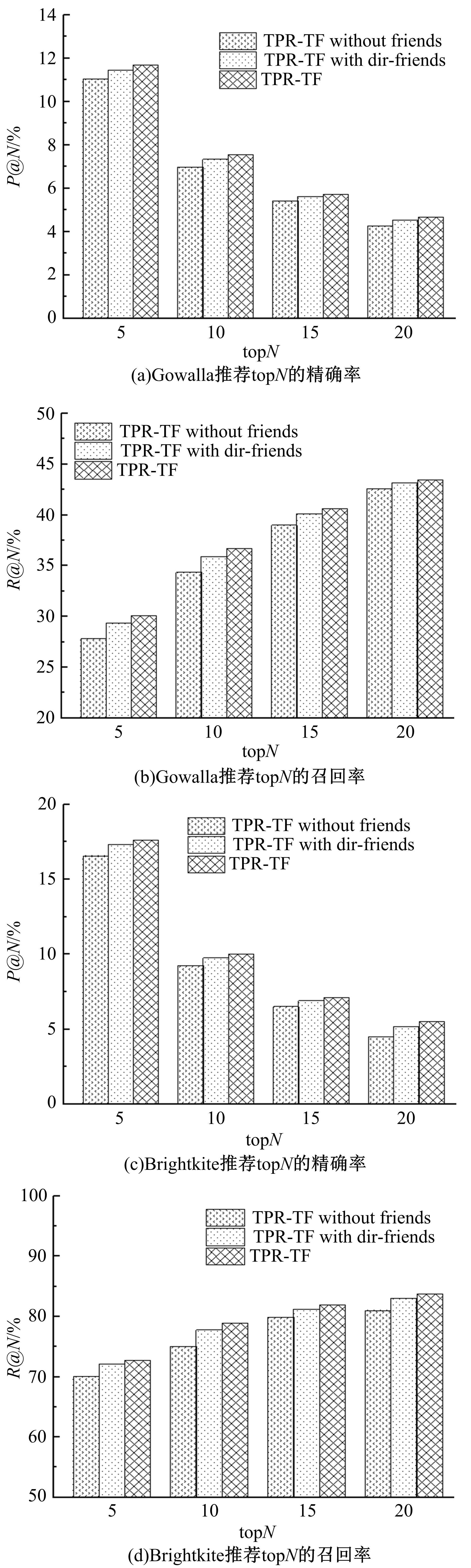
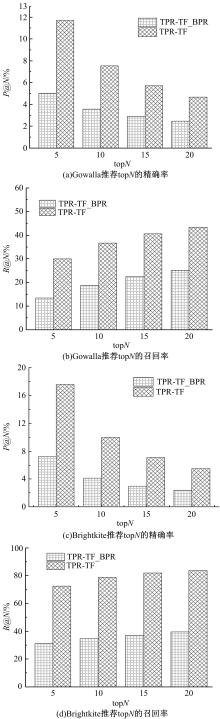
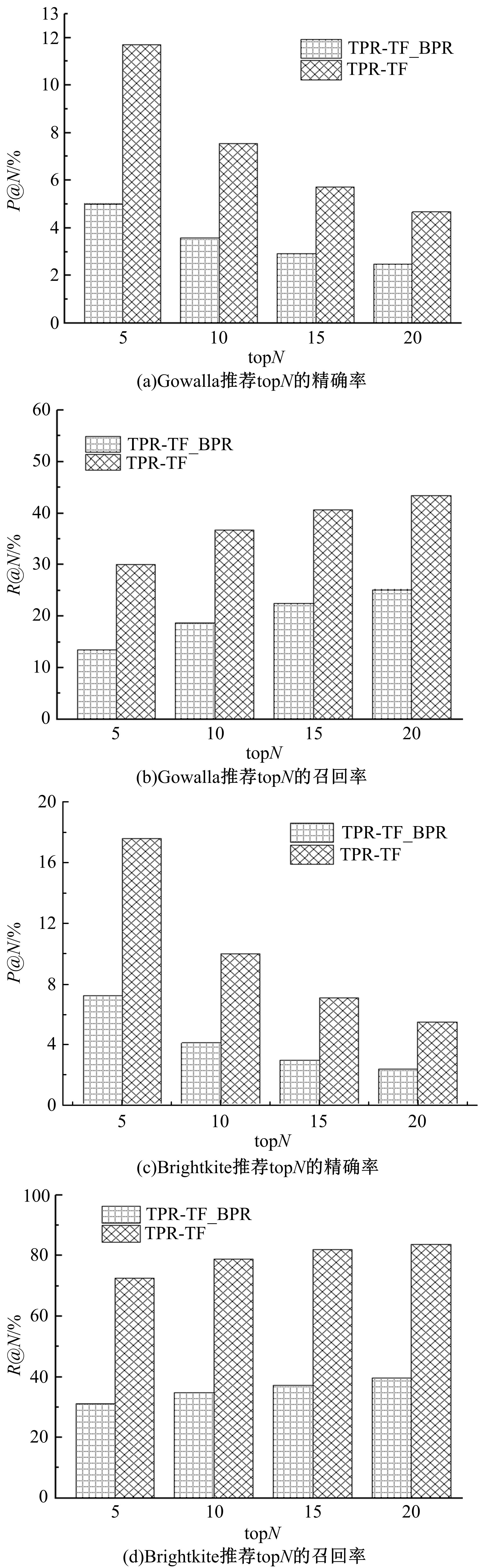
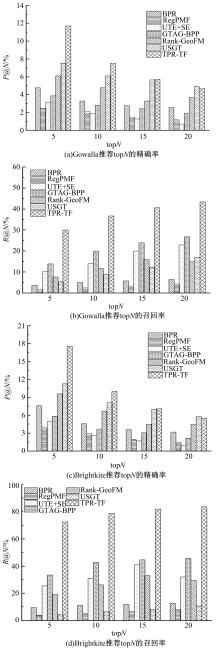
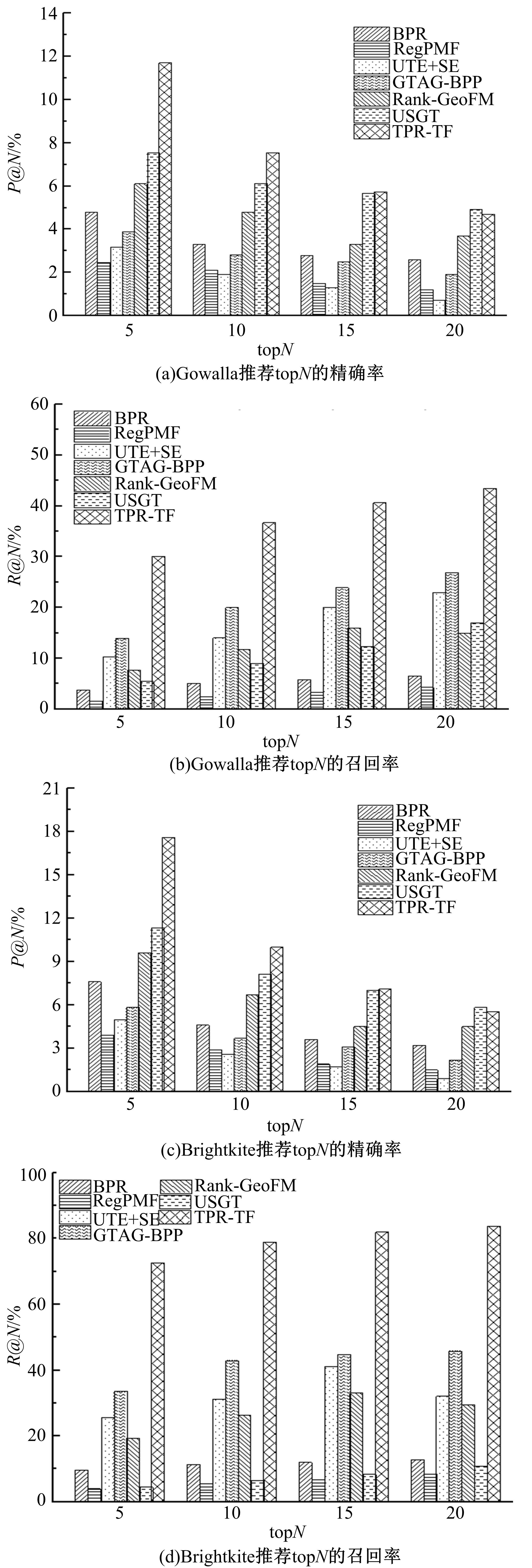
针对现有的兴趣点(POI)推荐研究没有合理地利用POI推荐的时间敏感性,对用户在不同时间段的行为偏好没有给予充分考虑,造成推荐效果较差的问题,提出了一种基于层次聚类的时间动态分段算法。把时间敏感的推荐和用户的直接朋友及潜在朋友影响相结合,扩充了用户的社交影响范围。在模型学习过程中采用按访问频次分布随机选择POI位置的方法,改善了经典的贝叶斯个性化排序(BPR)方法。实验结果表明,本文模型性能优于目前的主流POI推荐模型。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Ye M , Yin P F , Lee W , et al . Exploiting geographical influence for collaborative point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 34th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Beijing, China, 2011: 325⁃334. |
| 2 | Yuan Q , Cong G , Ma Z Y , et al . Time⁃aware point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 36th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Dublin, Ireland, 2013: 363⁃372. |
| 3 | Bao J , Zheng Y , Mokbel M , et al . Location⁃based and preference⁃aware recommendation using sparse geo⁃social networking data[C]∥Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Redondo Beach, USA, 2012: 199⁃208. |
| 4 | Lian D , Zhao C , Xie X , et al . GeoMF: joint geographical modeling and matrix factorization for point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2014: 831⁃840. |
| 5 | Liu S D , Meng X W . Recommender systems in location⁃based social networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(2): 322⁃336. |
| 6 | Goodfellow I , Bengio Y , Courville A , et al . Deep Learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT press, 2016. |
| 7 | Yao Z , Fu Y , Liu B , et al . POI recommendation: a temporal matching between POI popularity and user regularity[C]∥Proceedings of International Conference on Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 2017: 549⁃558. |
| 8 | Cho E , Myers S A , Leskovec J . Friendship and mobility: user movement in location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, USA, 2011: 1082⁃1090. |
| 9 | Gao H , Tang J , Hu X , et al . Exploring temporal effects for location recommendation on location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 7th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Hong Kong, China, 2013: 93⁃100. |
| 10 | Yuan Q , Cong G , Sun A . Graph⁃based point⁃of⁃interest recommendation with geographical and temporal influences[C]∥Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Shanghai, China, 2014: 659⁃668. |
| 11 | Hosseini S , Li L T . Point⁃of⁃interest recommendation using temporal orientations of users and locations[C]∥Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications, Dallas, USA, 2016: 330⁃347. |
| 12 | Ma H , Zhou D , Liu C , et al . Recommender systems with social regularization[C]∥Proceedings of the Forth International Conference on Web Search and Web Data Mining, Kowloon, Hong Kong, 2011: 287⁃296. |
| 13 | Zhang J , Chow C . GeoSoCa: exploiting geographical, social and categorical correlations for point⁃of⁃interest recommendations[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 443⁃452. |
| 14 | Jamali M , Ester M . A matrix factorization technique with trust propagation for recommendation in social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Fourth ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2010:135⁃142. |
| 15 | Ma H , Zhou T C , Lyu M R , et al . Improving recommender systems by incorporating social contextual information[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2011, 29(2):1⁃23. |
| 16 | Cheng C , Yang H , King I , et al . Fused matrix factorization with geographical and social influence in location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, Canada, 2012: 17⁃23. |
| 17 | Rendle S , Freudenthaler C , Gantner Z , et al . BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback[C]∥Proceedings of the 25th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, Canada, 2009: 452⁃461. |
| 18 | Zhao S L , King I , Lyu M R . A survey of point⁃of⁃interest recommendation in location⁃based social networks[J/OL].[2018⁃02⁃26].https:∥⁃of⁃interest_Recommendation_in_Location⁃based_Social_Networks/links/5787365a08ae36ad40a6a4e8 /A⁃Survey⁃of⁃Point⁃of⁃interest⁃Recommendation⁃in⁃Location⁃based⁃Social⁃Networks.pdf?origin=publication_detail. |
| 19 | Ye M , Yin P , Lee W C . Location recommendation for location⁃based social networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA, 2010: 458⁃461. |
| 20 | Zhang W , Wang J . Location and time aware social collaborative retrieval for new successive point⁃of⁃interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Melbourne, Australia, 2015(19⁃23): 1221⁃1230. |
| 21 | Ye M , Liu X , Lee W C . Exploring social influence for recommendation: a generative model approach[C]∥Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Portland, USA, 2012: 671⁃680. |
| 22 | Li H , Ge Y , Zhu H , et al . Point⁃of⁃interest recommendations: learning potential check⁃ins from friends[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, USA, 2016(13⁃17): 975⁃984. |
| 23 | Zhang J , Chow C , Li Y , et al . LORE: exploiting sequential influence for location recommendations[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Dallas, Fort Worth, USA, 2014(4⁃7): 103⁃112. |
| 24 | Yao L , Sheng Q Z , Qin Y , et al . Context⁃aware point⁃of⁃interest recommendation using tensor factorization with social regularization[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1007⁃1010. |
| 25 | Li X , Cong G , Li X L , et al . Rank⁃GeoFM: a ranking based geographical factorization method for point of interest recommendation[C]∥Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 433⁃442. |
| [1] | 刘富,宗宇轩,康冰,张益萌,林彩霞,赵宏伟. 基于优化纹理特征的手背静脉识别系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1844-1850. |
| [2] | 王利民,刘洋,孙铭会,李美慧. 基于Markov blanket的无约束型K阶贝叶斯集成分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1851-1858. |
| [3] | 金顺福,王宝帅,郝闪闪,贾晓光,霍占强. 基于备用虚拟机同步休眠的云数据中心节能策略及性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1859-1866. |
| [4] | 赵东,孙明玉,朱金龙,于繁华,刘光洁,陈慧灵. 结合粒子群和单纯形的改进飞蛾优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1867-1872. |
| [5] | 刘恩泽,吴文福. 基于机器视觉的农作物表面多特征决策融合病变判断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1873-1878. |
| [6] | 欧阳丹彤, 范琪. 子句级别语境感知的开放信息抽取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1563-1570. |
| [7] | 刘富, 兰旭腾, 侯涛, 康冰, 刘云, 林彩霞. 基于优化k-mer频率的宏基因组聚类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1593-1599. |
| [8] | 桂春, 黄旺星. 基于改进的标签传播算法的网络聚类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1600-1605. |
| [9] | 刘元宁, 刘帅, 朱晓冬, 陈一浩, 郑少阁, 沈椿壮. 基于高斯拉普拉斯算子与自适应优化伽柏滤波的虹膜识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1606-1613. |
| [10] | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [11] | 赵宏伟, 刘宇琦, 董立岩, 王玉, 刘陪. 智能交通混合动态路径优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1214-1223. |
| [12] | 黄辉, 冯西安, 魏燕, 许驰, 陈慧灵. 基于增强核极限学习机的专业选择智能系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1224-1230. |
| [13] | 傅文博, 张杰, 陈永乐. 物联网环境下抵抗路由欺骗攻击的网络拓扑发现算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1231-1236. |
| [14] | 曹洁, 苏哲, 李晓旭. 基于Corr-LDA模型的图像标注方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1237-1243. |
| [15] | 侯永宏, 王利伟, 邢家明. 基于HTTP的动态自适应流媒体传输算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1244-1253. |
|