吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 2076-2082.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180996
仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法
刘富1,2( ),权美静2,王柯2,刘云2,康冰2,韩志武3,侯涛2,3(
),权美静2,王柯2,刘云2,康冰2,韩志武3,侯涛2,3( )
)
- 1. 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室, 长春 130022
2. 吉林大学 通信工程学院, 长春 130022
3. 吉林大学 生物工程仿生教育部重点实验室, 长春 130022
Indoor positioning method based on location fingerprinting of imitating mechanism of scorpion vibration source
Fu LIU1,2( ),Mei-jing QUAN2,Ke WANG2,Yun LIU2,Bing KANG2,Zhi-wu HAN3,Tao HOU2,3(
),Mei-jing QUAN2,Ke WANG2,Yun LIU2,Bing KANG2,Zhi-wu HAN3,Tao HOU2,3( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
2. College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
3. Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering, Ministry of Education, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
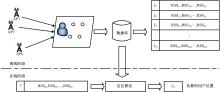
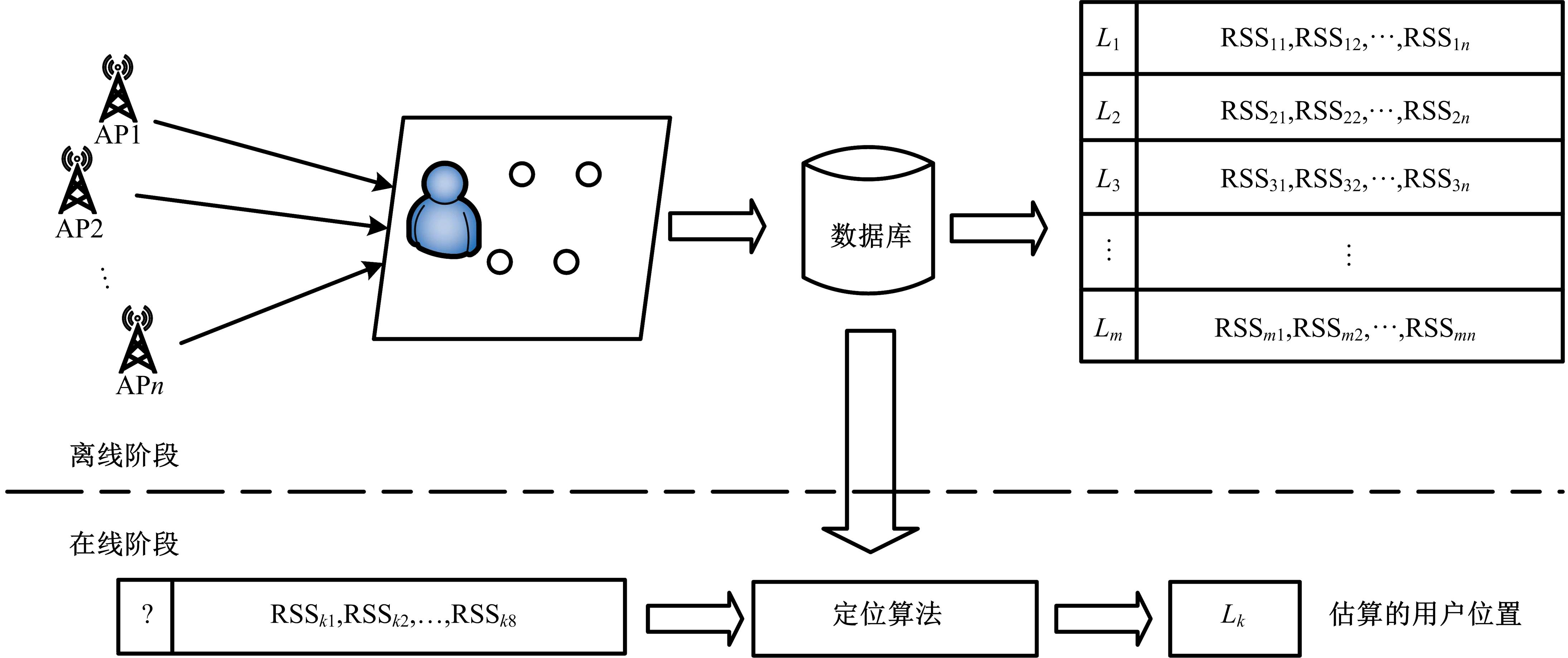
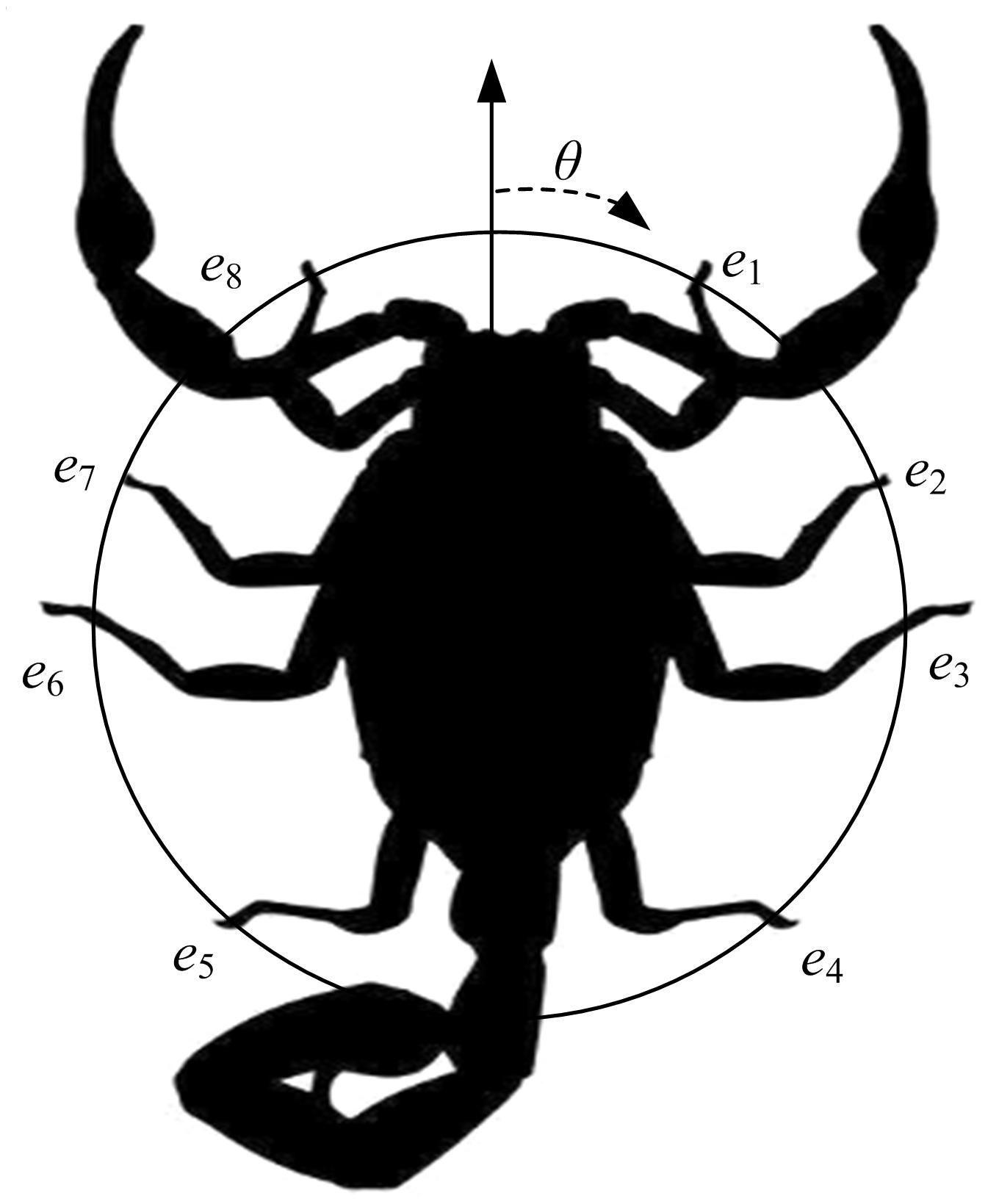
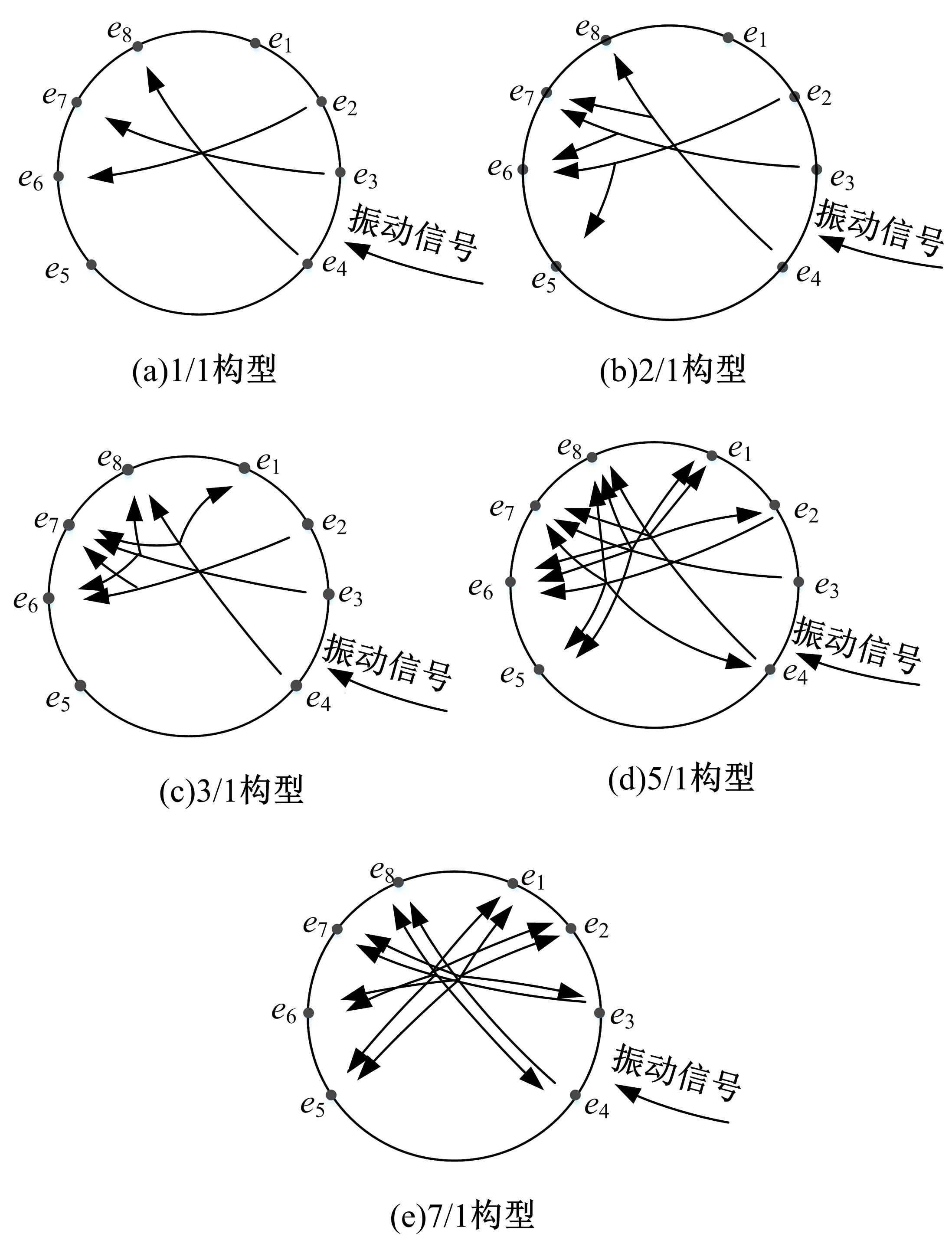
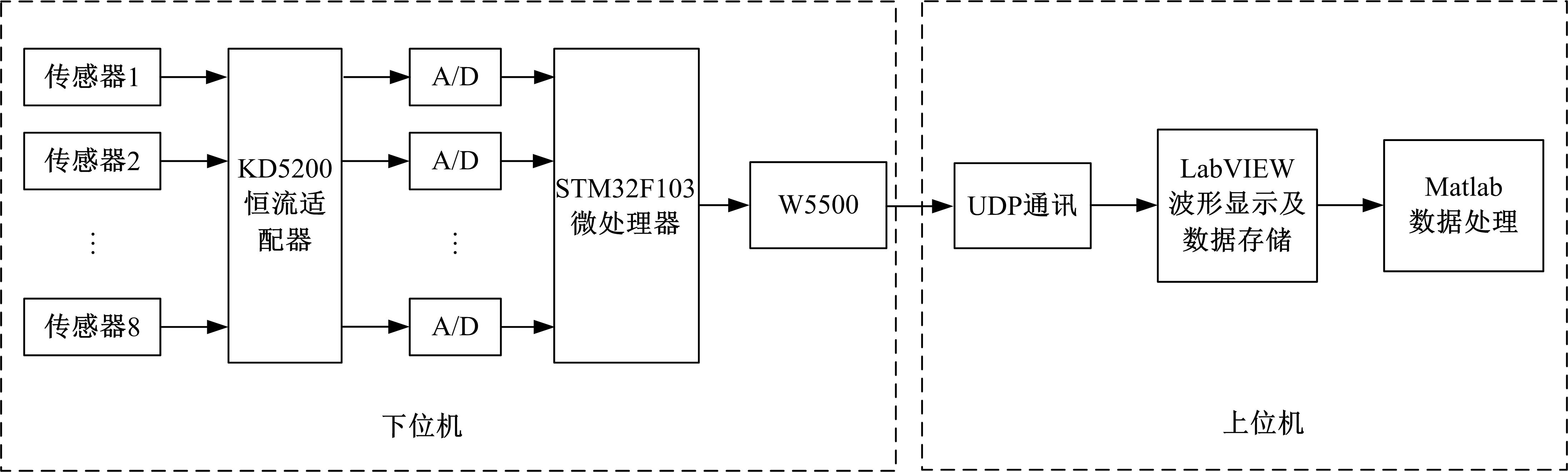
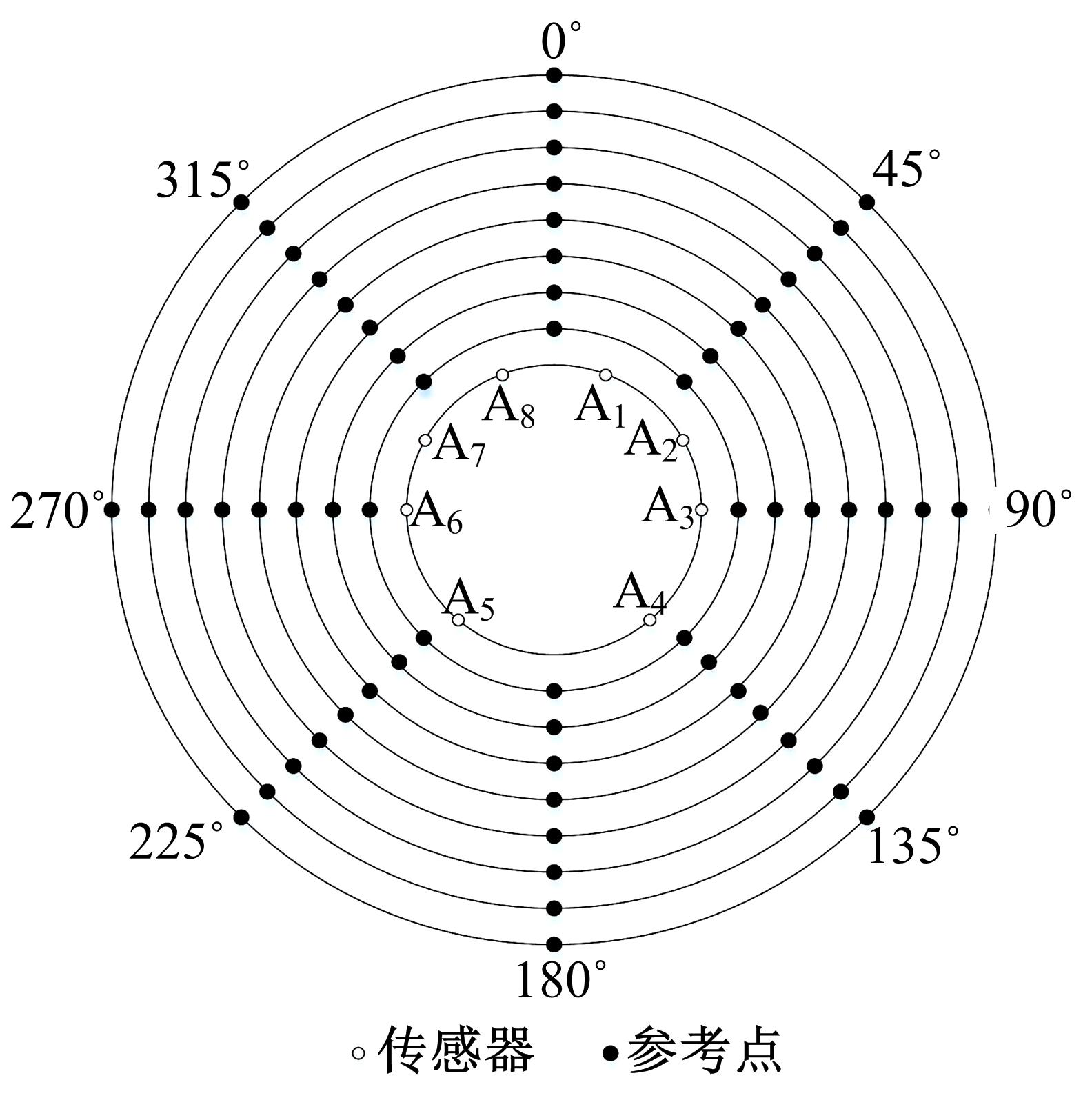
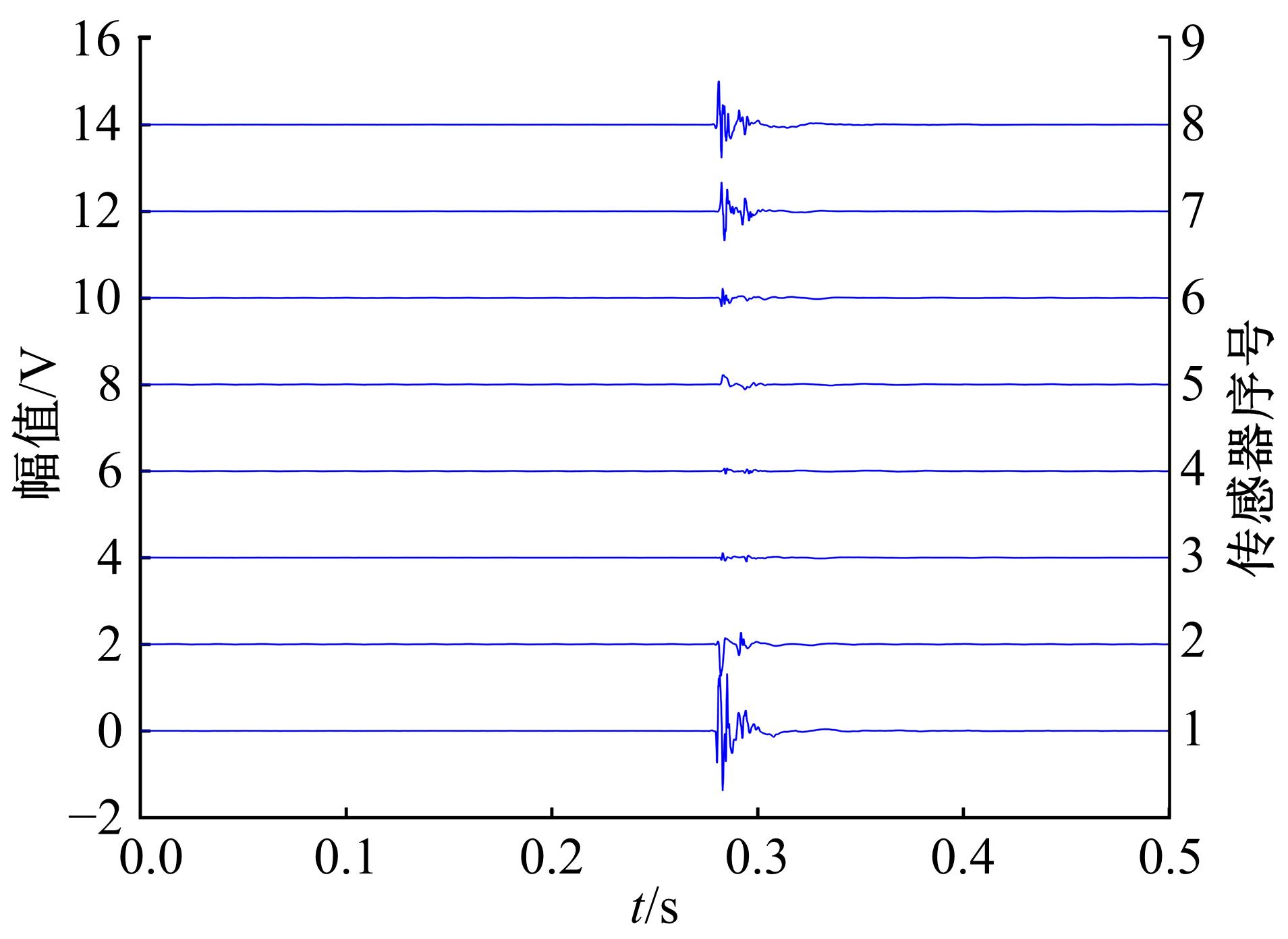
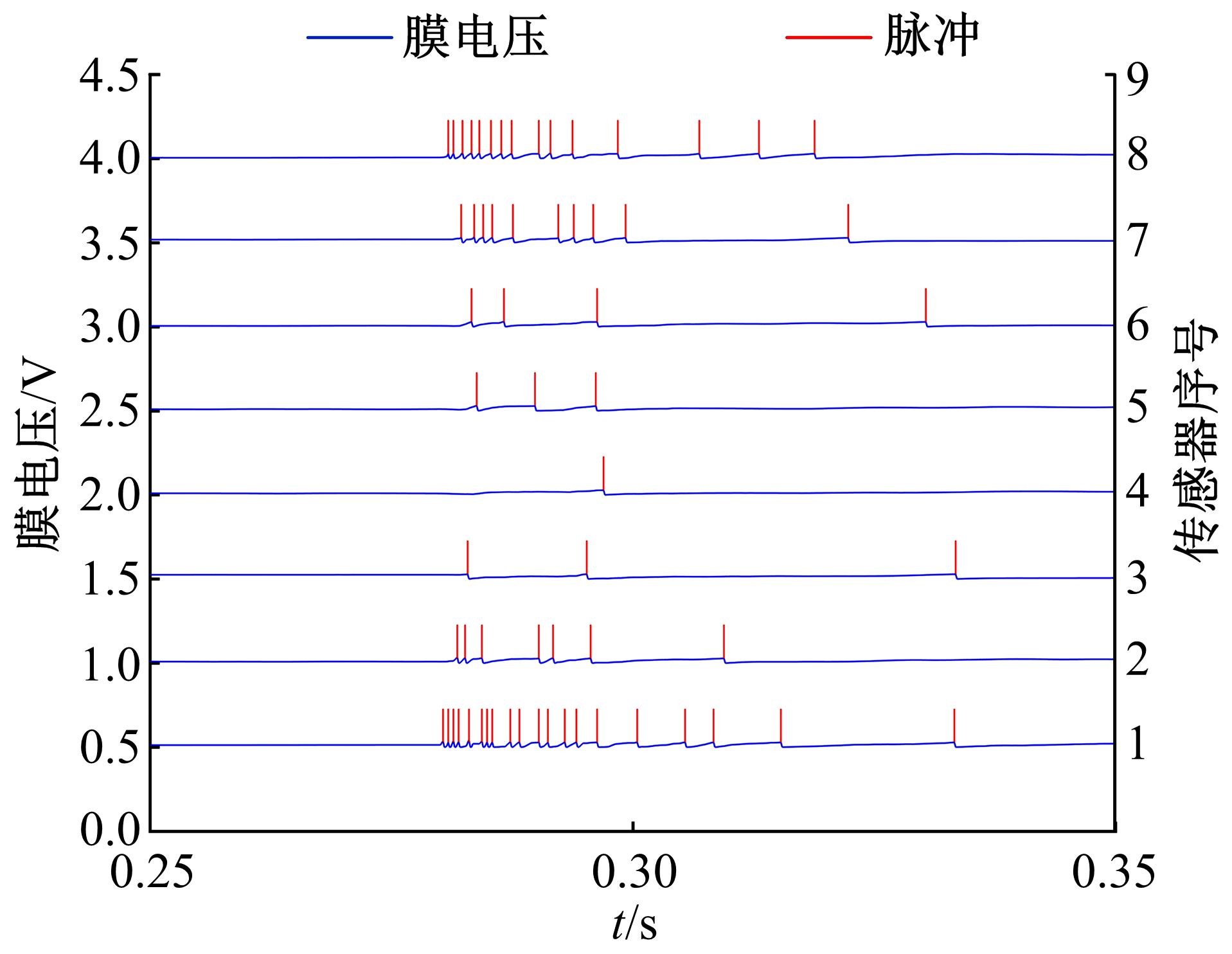
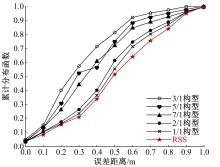
针对基于接受信号强度(RSS)的位置指纹室内定位方法易受到多径效应及噪声干扰而导致定位精度低这一问题,提出了一种仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法。该方法首先仿蝎子的
中图分类号:
- TN911.73
|
| [1] | 马子骥,卢浩,董艳茹. 双通道单图像超分辨率卷积神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2089-2097. |
| [2] | 于晓辉,张志成,李新波,孙晓东. 基于状态空间模型的指数衰减正弦信号参数估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2083-2088. |
| [3] | 卢洋,王世刚,赵文婷,赵岩. 基于离散Shearlet类别可分性测度的人脸表情识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1715-1725. |
| [4] | 郭继昌,吴洁,郭春乐,朱明辉. 基于残差连接卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1726-1734. |
| [5] | 曹运合,曾丽,王宇. 基于特征空间的子阵级自适应和差波束测角方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1735-1744. |
| [6] | 董超,刘晶红,徐芳,王仁浩. 光学遥感图像舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1369-1376. |
| [7] | 王柯俨,胡妍,王怀,李云松. 结合天空分割和超像素级暗通道的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. |
| [8] | 托乎提努尔,张海龙,王杰,王娜,冶鑫晨,王万琼. 基于图形处理器的高速中值滤波算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 979-985. |
| [9] | 付银娟,李勇,徐丽琴,张昆辉. NLFM⁃Costas射频隐身雷达信号设计及分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 994-999. |
| [10] | 苏寒松,代志涛,刘高华,张倩芳. 结合吸收Markov链和流行排序的显著性区域检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1887-1894. |
| [11] | 徐岩,孙美双. 基于卷积神经网络的水下图像增强方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1895-1903. |
| [12] | 李居朋,张祖成,李墨羽,缪德芳. 基于Kalman滤波的电容屏触控轨迹平滑算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1910-1916. |
| [13] | 黄勇,杨德运,乔赛,慕振国. 高分辨合成孔径雷达图像的耦合传统恒虚警目标检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1904-1909. |
| [14] | 应欢,刘松华,唐博文,韩丽芳,周亮. 基于自适应释放策略的低开销确定性重放方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1917-1924. |
| [15] | 陆智俊,钟超,吴敬玉. 星载合成孔径雷达图像小特征的准确分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1925-1930. |
|