吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 370-378.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190838
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于正交设计的协作机器人全域结构优化设计
- 1.中国科学院 沈阳自动化研究所机器人学国家重点实验室,沈阳 110016
2.中国科学院 机器人与智能制造创新研究院,沈阳 110169
3.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
Global structural optimization design of collaborative robots using orthogonal design
Ming-wei HU1,2,3( ),Hong-guang WANG1,2(
),Hong-guang WANG1,2( ),Xin-an PAN1,2
),Xin-an PAN1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Robotics,Shenyang Institute of Automation,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenyang 110016,China
2.Institutes for Robotics and Intelligent Manufacturing,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Shenyang 110169,China
3.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
摘要:
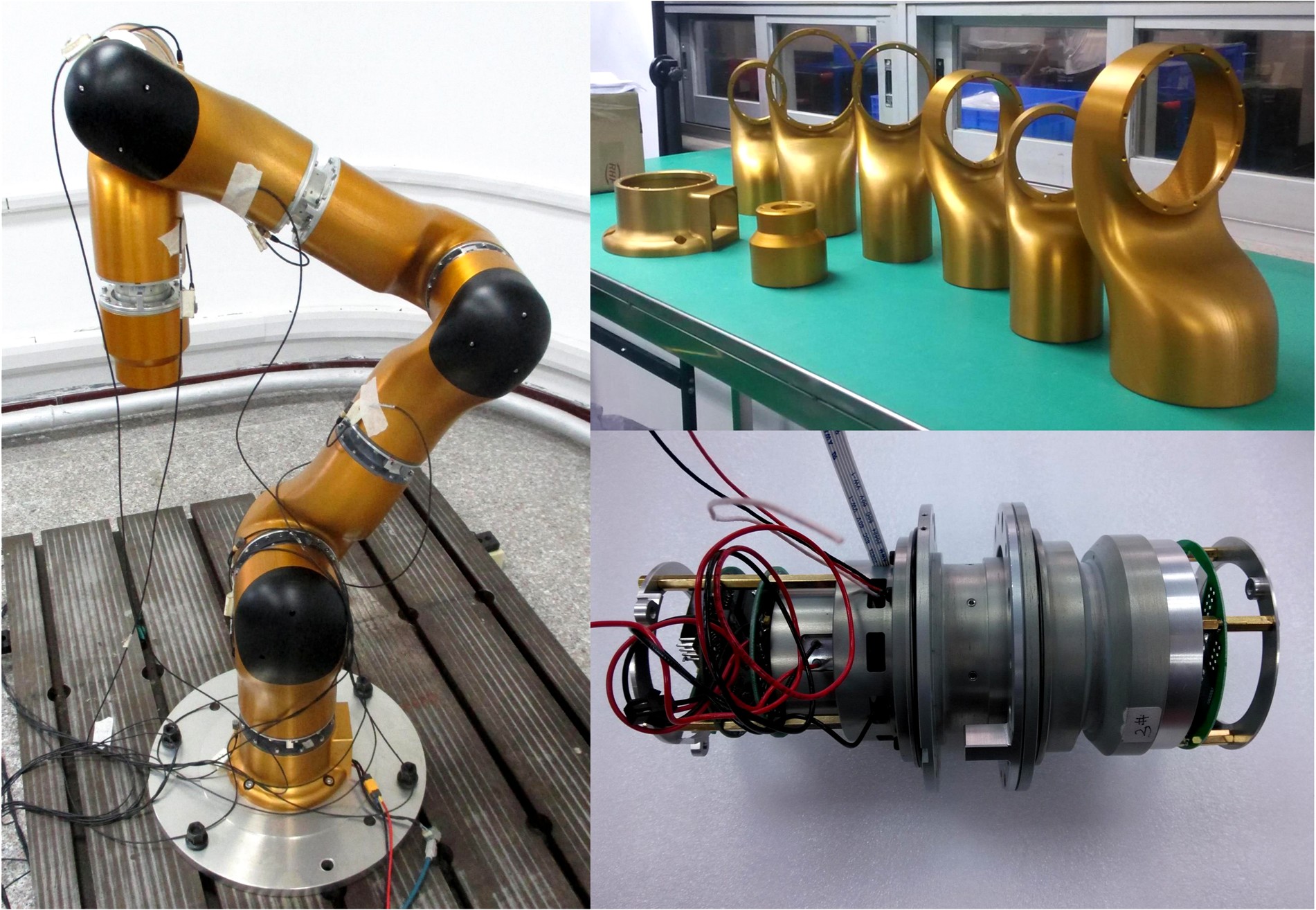
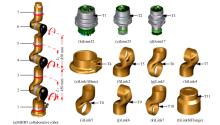
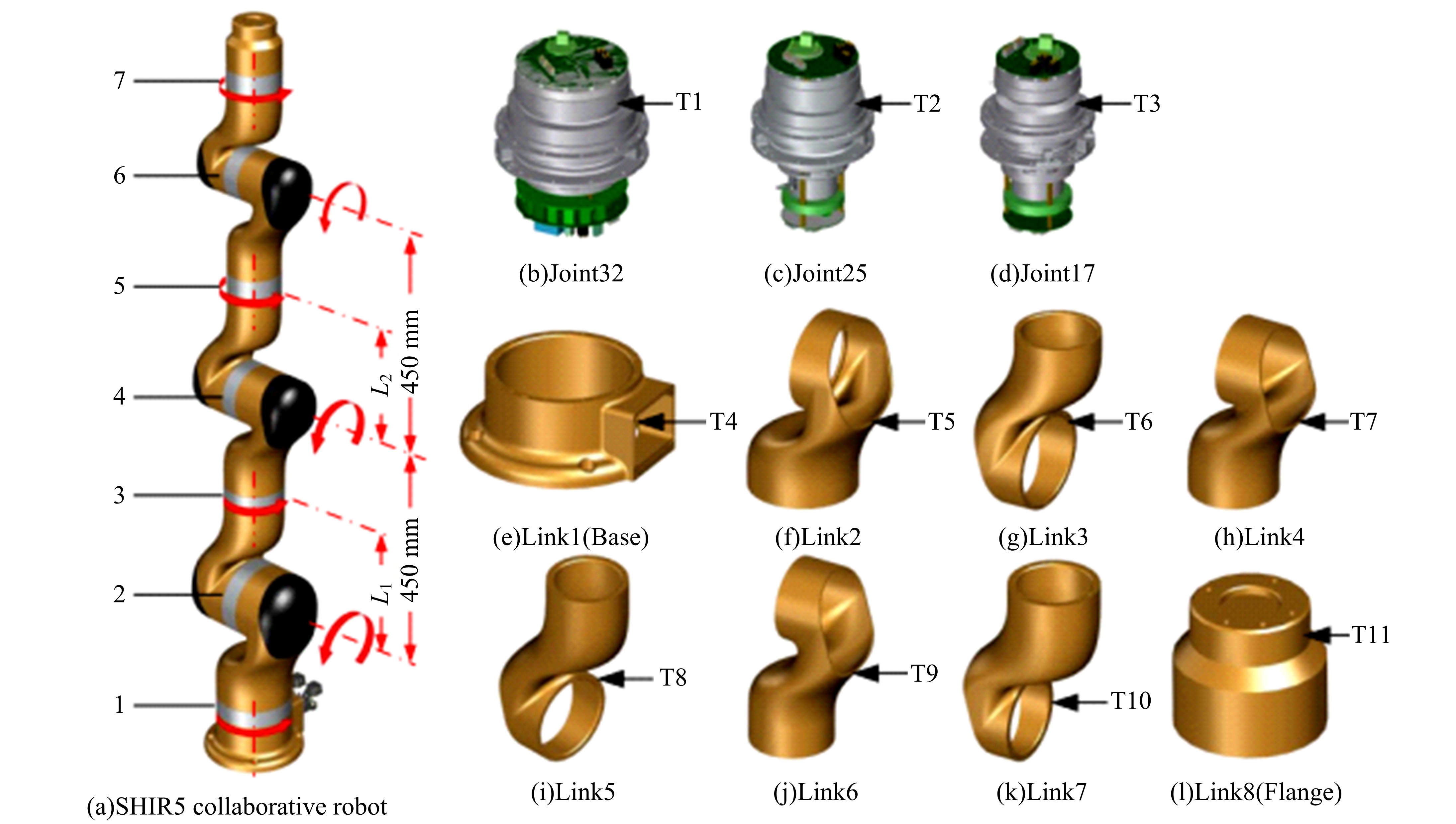
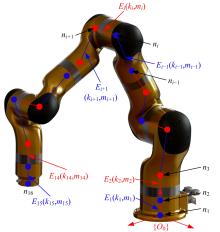
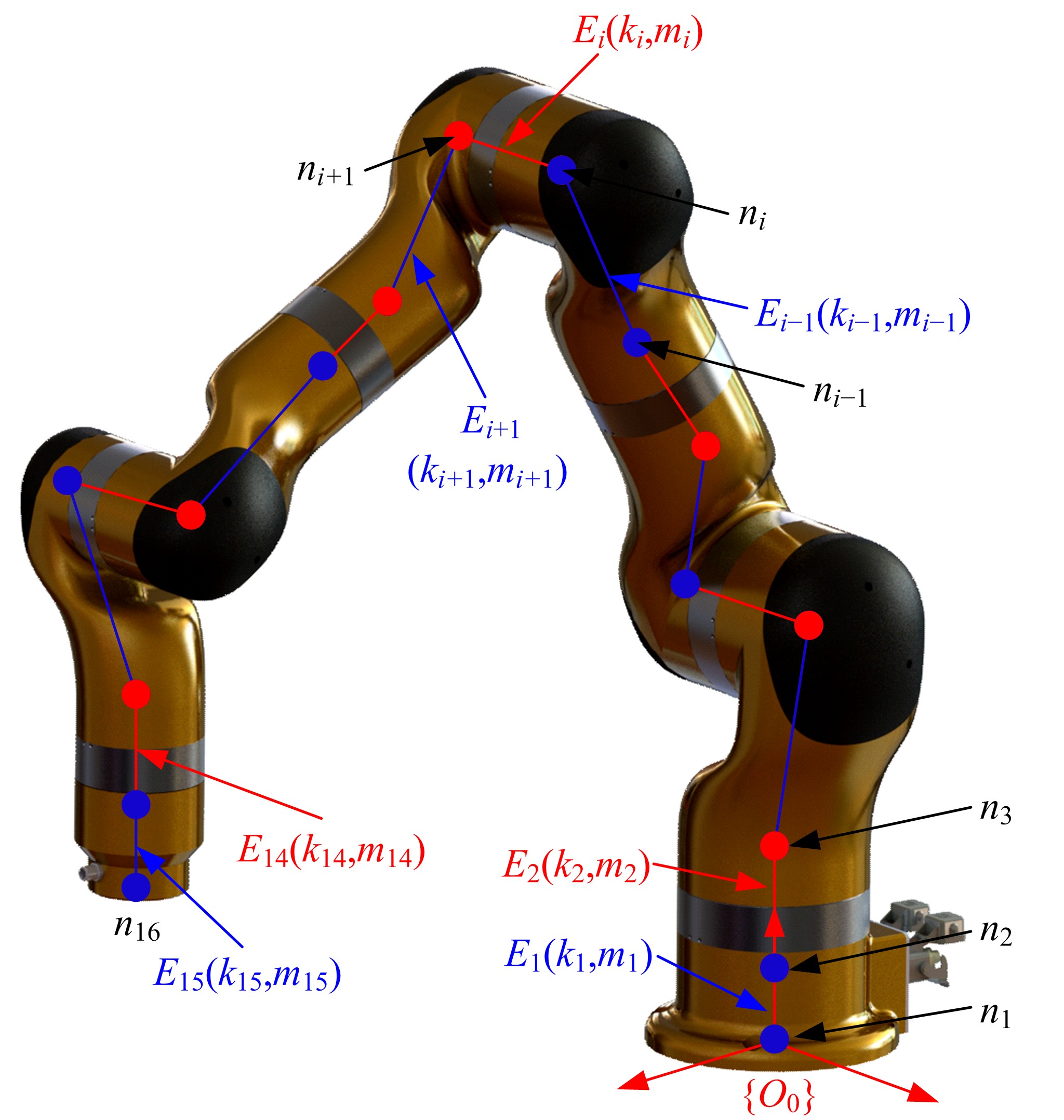
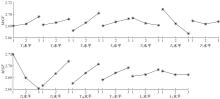
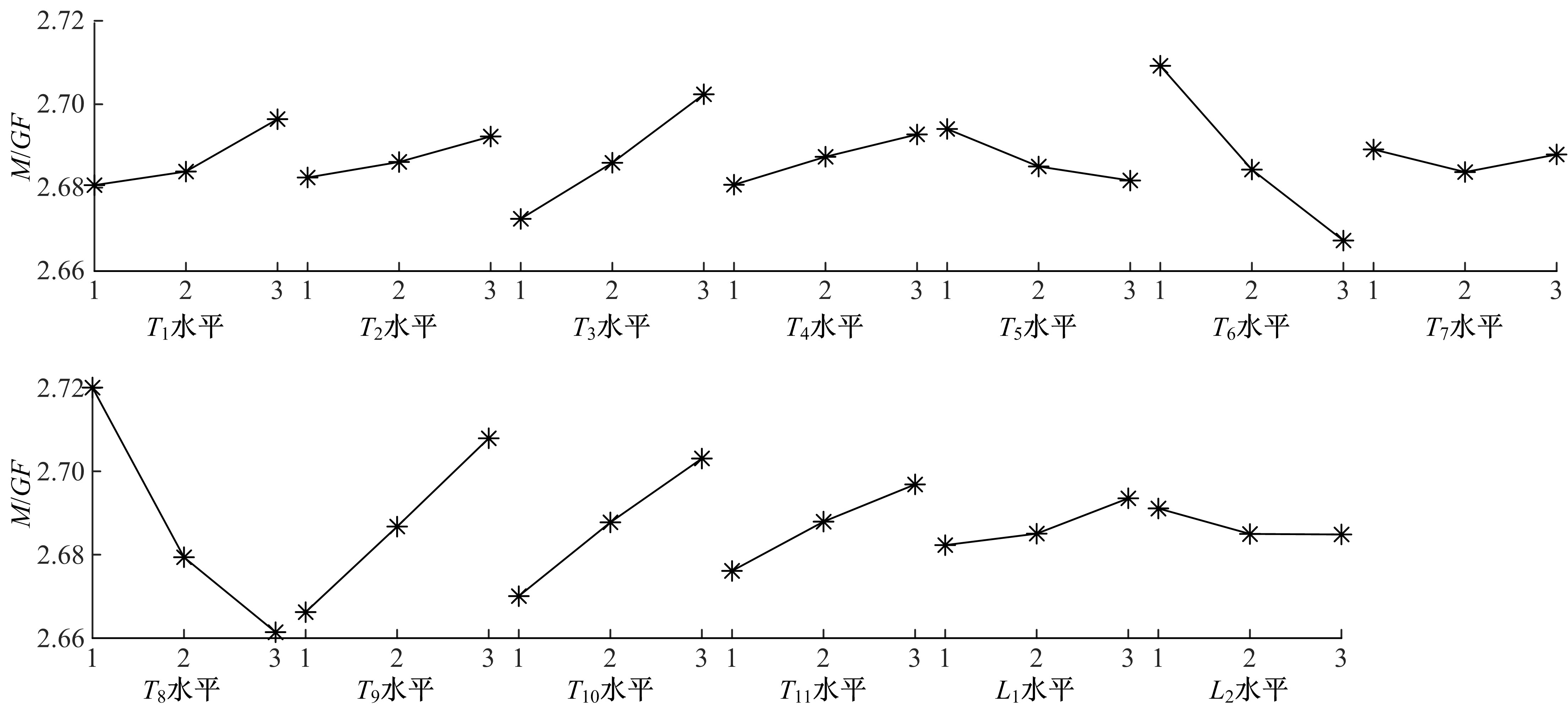
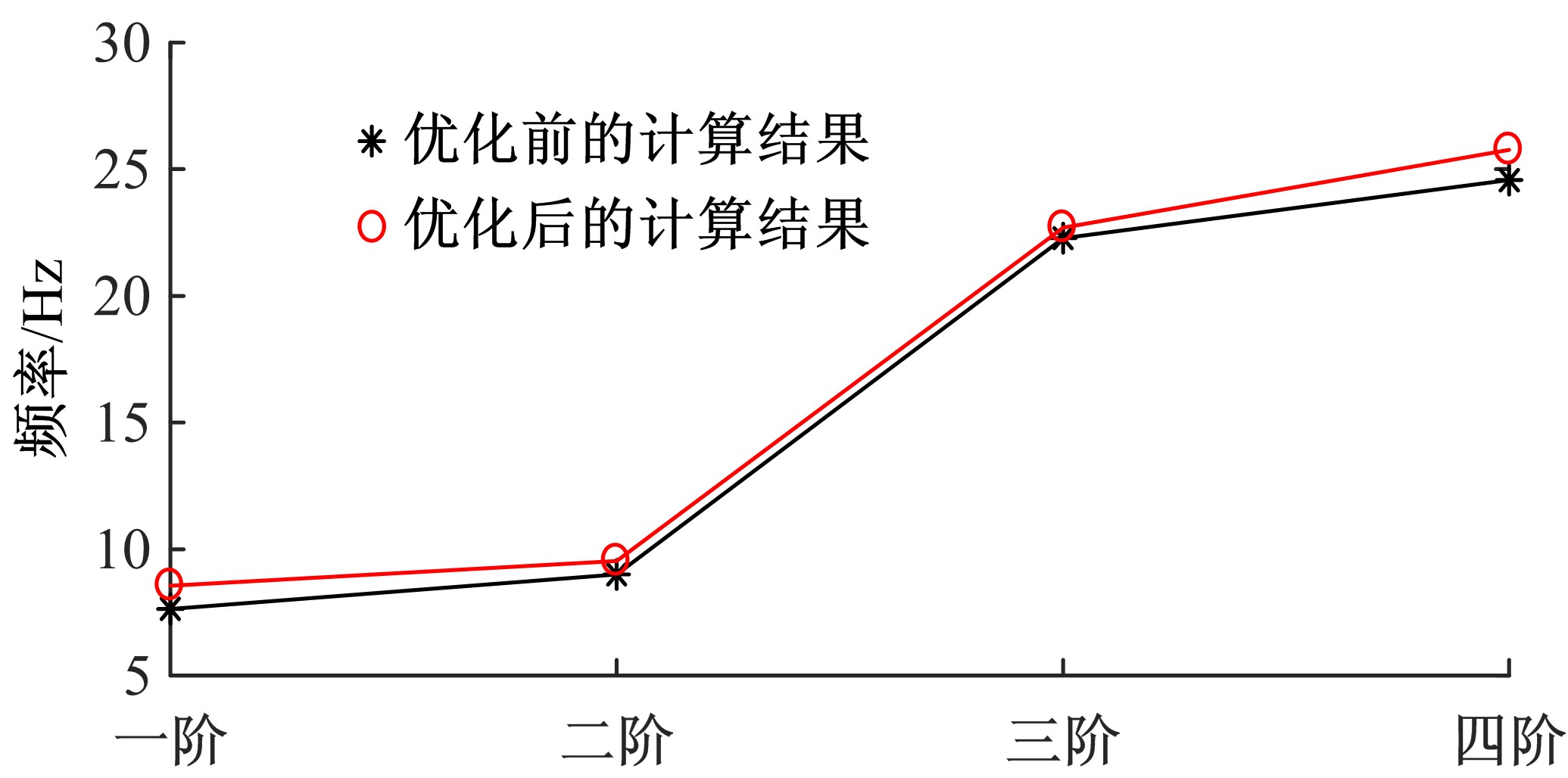
为解决时变位姿和建模精度对机器人结构优化的影响,提出了一种有限元与解析法相结合的机器人实时模态分析方法,能够实时、高效、高精度地获得机器人任意位姿下的固有频率和振型。同时为降低计算量,实现全域结构优化,基于正交设计提出了一种以机器人质量与全域一阶固有频率比(M/GF)为优化目标、以机器人结构尺寸为优化变量的全域动态性能结构优化设计方法。优化结果表明:优化后的M/GF指标比优化前提高了9.90%,优化后的全域一阶固有频率指标比优化前提高了0.91 Hz。
中图分类号:
- TP241
| 1 | ―2:2011. Robots and robotic devices—Safety requirements for industrial robots part 2: robot systems and integration[S]. |
| 2 | Alici G, Shirinzadeh B. Enhanced stiffness modeling, identification and characterization for robot manipulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(4): 554-564. |
| 3 | 胡明伟, 王洪光, 潘新安, 等. 一种协作型机器人运动性能分析与仿真[J]. 智能系统学报, 2017, 12(1): 75-81. |
| Hu Ming-wei,Wang Hong-guang,Pan Xin-an, et al. Analysis and simulation on kinematics performance of a collaborative robot[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2017, 12(1): 75-81. | |
| 4 | 刘延杰, 吴明月, 王刚, 等. 硅片传输机器人手臂结构优化设计方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(1): 1-9. |
| Liu Yan-jie, Wu Ming-yue, Wang Gang, et al. Method for structural optimization design of wafer handling robot arms[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(1): 1-9. | |
| 5 | Hegde G S, Vinod M S, Shankar A, et al. Optimum dynamic design of flexible robotic manipulator[J]. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 2009, 5(4): 315-325. |
| 6 | Kim B J, Yun D K, Lee S H, et al. Topology optimization of industrial robots for system-level stiffness maximization by using part-level metamodels[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 54(4): 1061-1071. |
| 7 | Zhou L, Bai S. A new approach to design of a lightweight anthropomorphic arm for service applications[J]. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2015, 7(3): 1-12. |
| 8 | Luo H, Fu J, Wang P, et al. Design optimization of the ram structure of friction stir welding robot[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2019: 1-11. |
| 9 | 田野, 陈晓鹏, 贾东永, 等. 仿人机器人轻型高刚性手臂设计及运动学分析[J]. 机器人, 2011, 33(3): 332-339. |
| Tian Ye, Chen Xiao-peng, Jia Dong-yong, et al. Design and kinematic analysis of a light weight and high stiffness manipulator for humanoid robots[J]. Robot, 2011, 33(3): 332-339. | |
| 10 | Ning K P, Li D B, He F, et al. Research on the structural optimization design of ER300 palletizing robot[J]. The Open Automation and Control Systems Journal, 2015, 7(1): 1405-1414. |
| 11 | Nezhadali V. Multi-objective optimization of Industrial robots[D]. Linköping: Linköping University, 2015. |
| 12 | Yin H, Huang S, He M, et al. A unified design for lightweight robotic arms based on unified description of structure and drive trains[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2017, 14(4): 1-14. |
| 13 | Saravanan R, Ramabalan S, Ebenezer N G, et al. Evolutionary bi-criteria optimum design of robots based on task specifications[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 41(3): 386-406. |
| 14 | Zhu Y, Qiu J, Tani J. Simultaneous optimization of a two-link flexible robot arm[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2015, 18(1): 29-38. |
| 15 | Alessandro C, Rosario S. Elastodynamic optimization of a 3T1R parallel manipulator[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2014, 73: 184-196. |
| 16 | Zhang L, Song Y. Optimal design of the Delta robot based on dynamics[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 2011, 43(9): 336-341. |
| 17 | Wang X, Zhang D, Zhao C, et al. Optimal design of lightweight serial robots by integrating topology optimization and parametric system optimization[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019, 132: 48-65. |
| 18 | Hu M W, Wang H G, Pan X A, et al. Research on elastic deformation modeling of collaborative robots[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Macau, China, 2017: 2462-2467. |
| 19 | 王新敏. ANSYS结构动力分析与应用[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2014. |
| 20 | Slamani M, Nubiola A, Bonev I A, et al. Assessment of the positioning performance of an industrial robot[J]. Industrial Robot——an International Journal, 2012, 39(1): 57-68. |
| 21 | Hu M W, Wang H G, Pan X A, et al. Optimal synthesis of pose repeatability for collaborative robots based on the ISO 9283 standard[J]. Industrial Robot, 2019, 46(6): 812-818. |
| [1] | 姜继海,赵存然,张冠隆,车明阳. 航空煤油柱塞泵摩擦副涂层材料摩擦性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 147-153. |
| [2] | 刘昌盛, 何清华, 张大庆, 李铁辉, 龚俊, 赵喻明. 混合动力挖掘机势能回收系统参数优化与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(2): 379-386. |
| [3] | 龚俊, 何清华, 张大庆, 张云龙, 刘昌盛, 唐中勇. 混合动力叉车节能效果评价及能量回收系统试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 29-34. |
| [4] | 张天霄, 刘昕晖, 张农. 液压溢流阀的振动分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 91-94. |
| [5] | 韩志武, 吕尤, 董立春, 张俊秋, 牛士超, 马荣峰, 任露泉. 仿生表面形态齿轮的模态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(06): 1604-1608. |
| [6] | 金文明,李华军,寇淑清,杨慎华. 装配式凸轮轴悬臂式数控装配机的机架模态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 319-0323. |
| [7] | 赵淑芝,赵贝,朱永刚. 基于SP调查的出行方式选择模型与公交优先政策[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 187-0190. |
| [8] | 苏铁坚, 管爱华, 麦莉. 受纵向分布压力的弹性薄板的动力分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2000, (3): 72-74. |
| [9] | 刘寒冰, 龚国庆, 魏媛. 改进的r-收敛和h-收敛自适应有限元方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2000, (3): 56-60. |
|
||