吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1645-1656.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210127
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
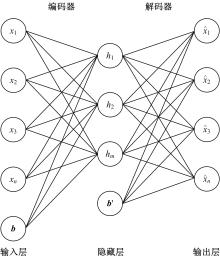
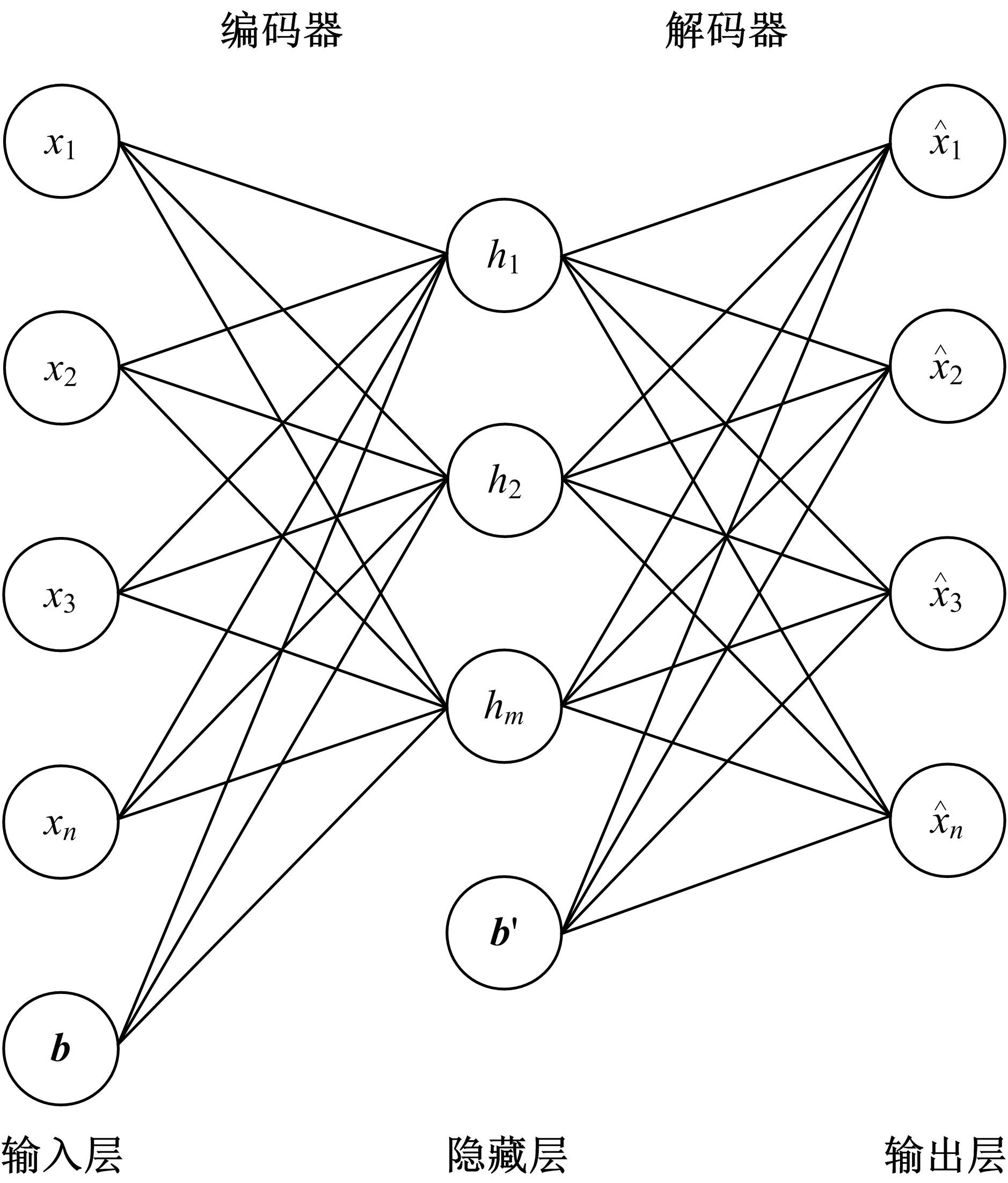
基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Unsupervised feature engineering algorithm BioSAE based on sparse autoencoder
Feng-feng ZHOU1,2( ),Yi-chi ZHANG1,2
),Yi-chi ZHANG1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
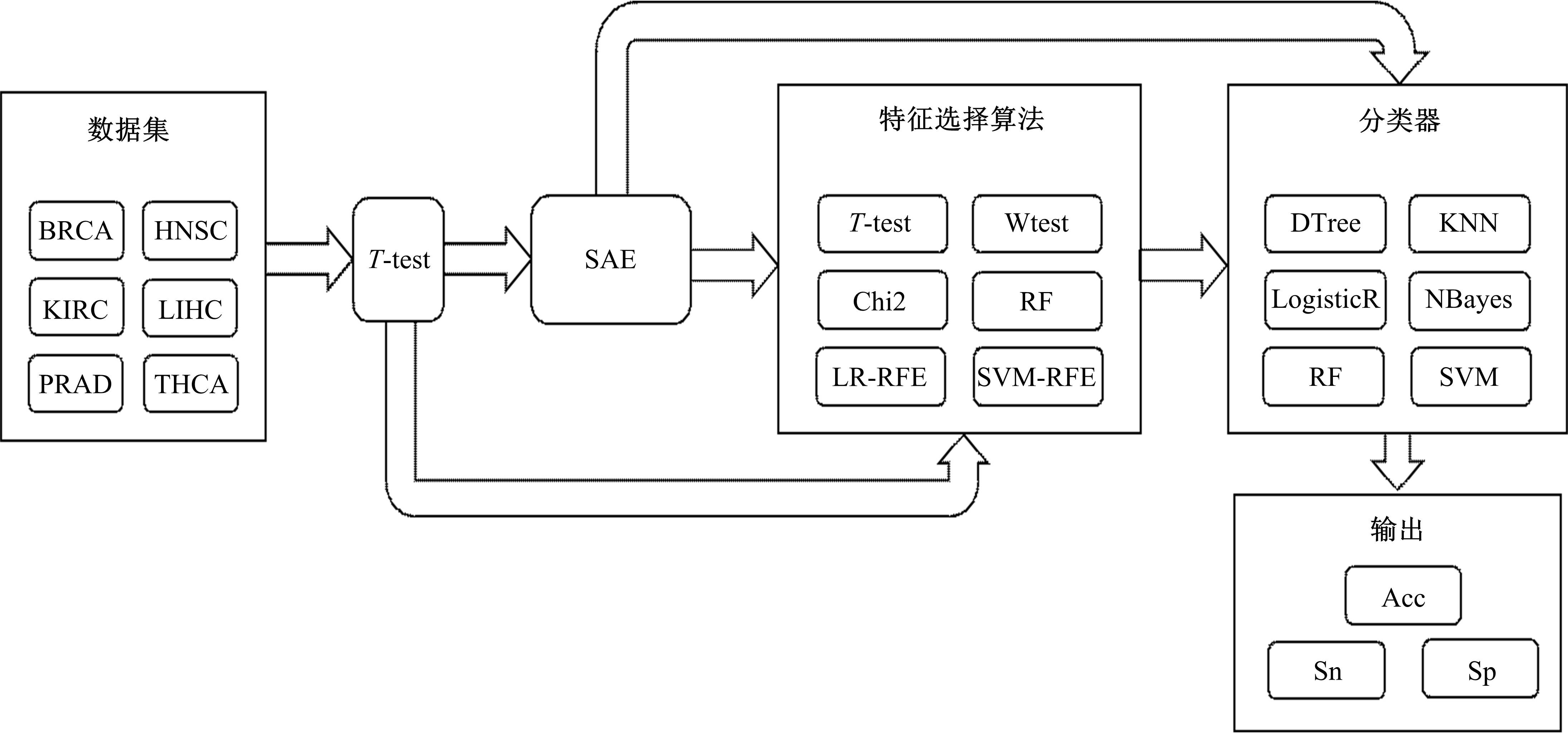
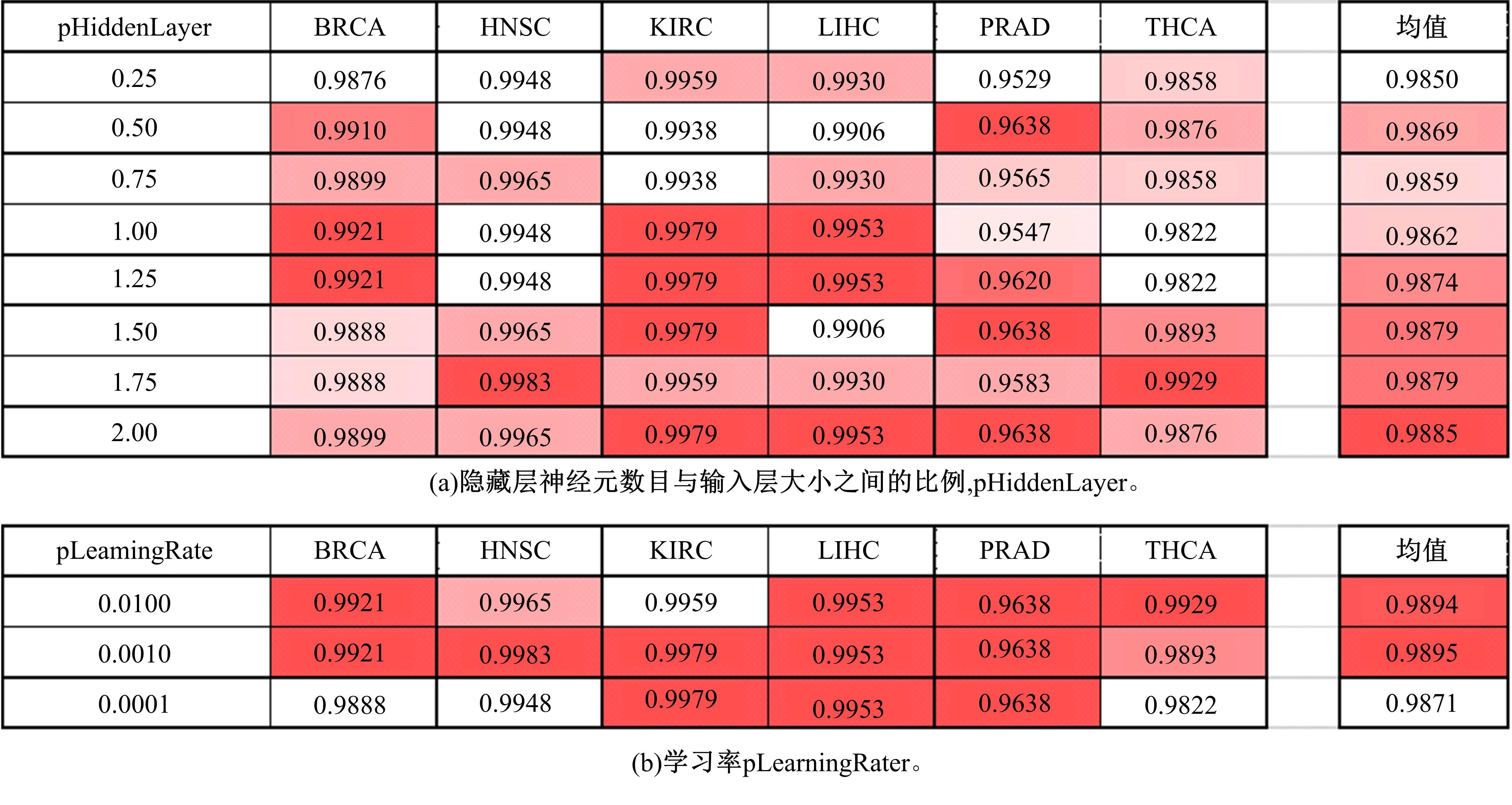
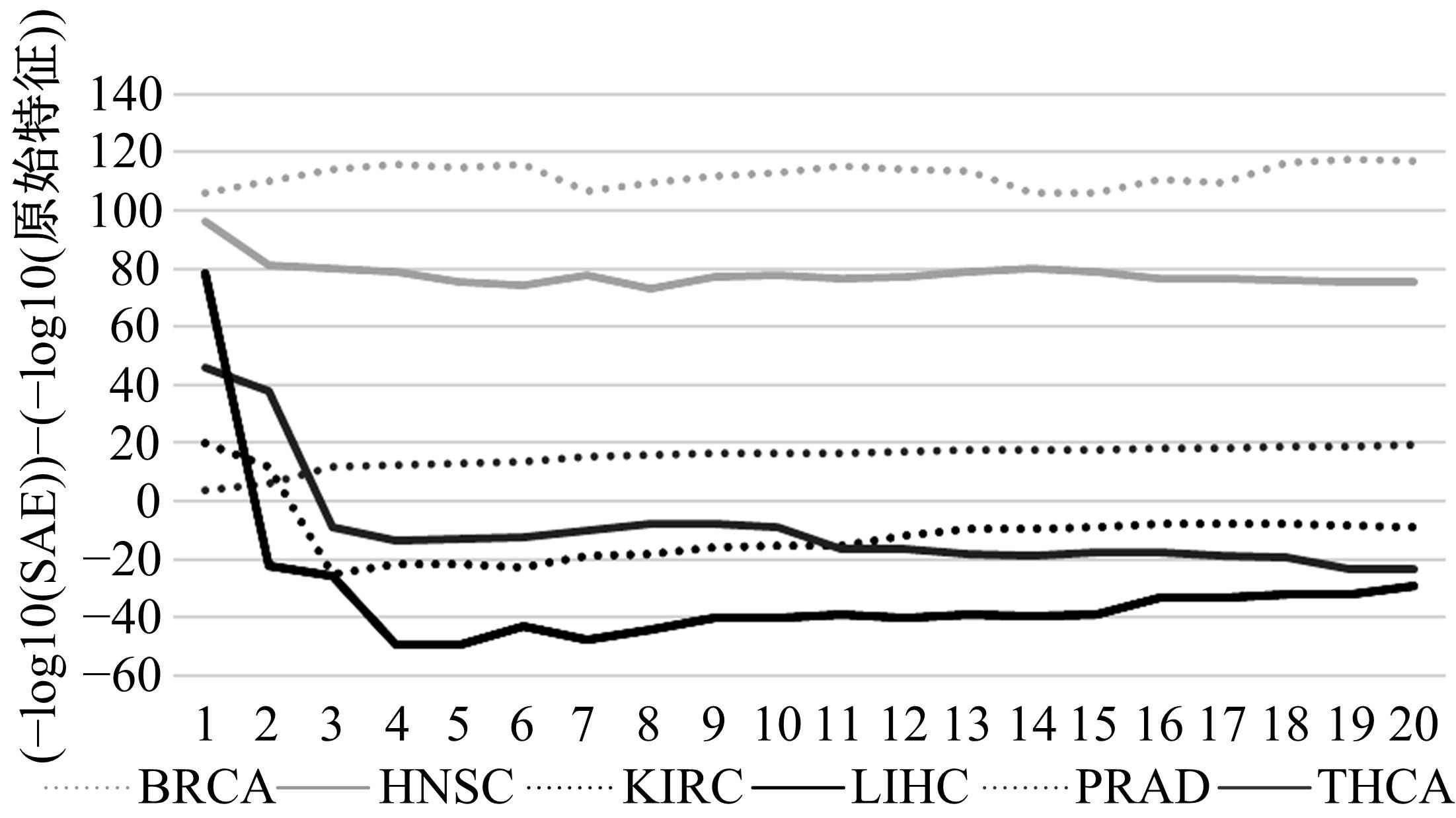
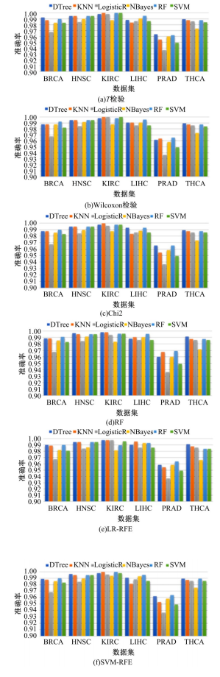
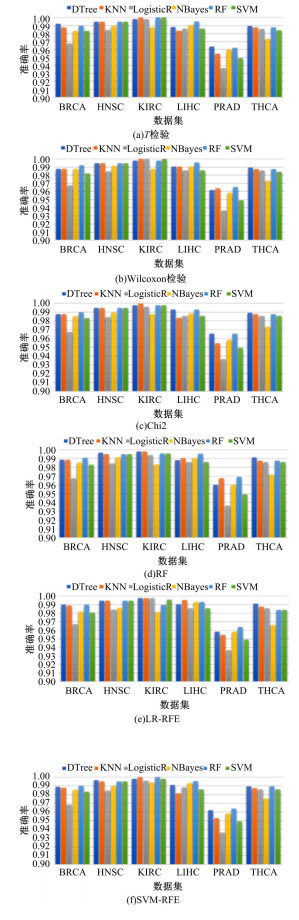
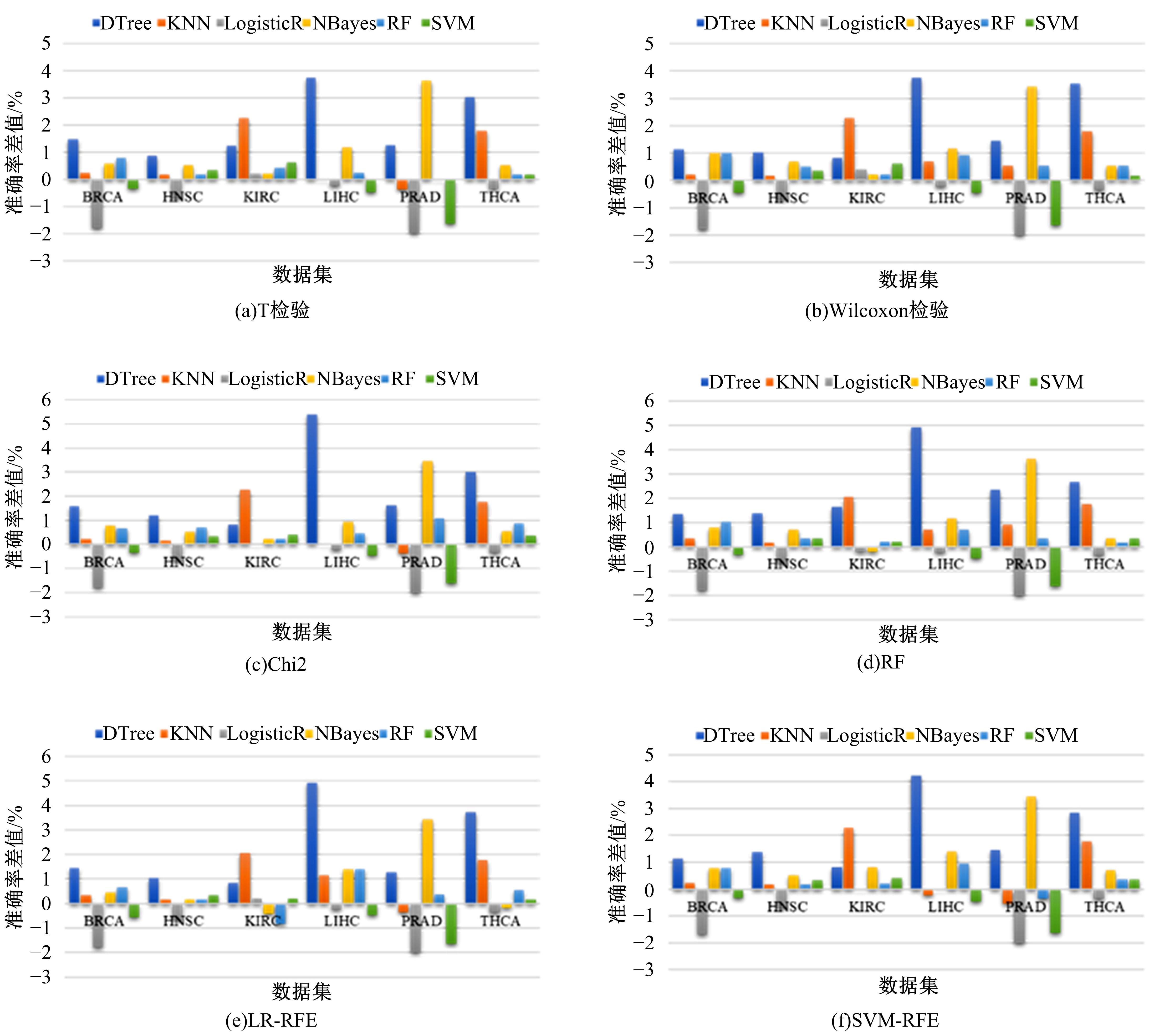
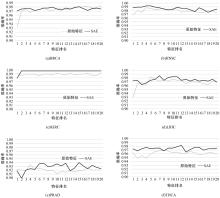
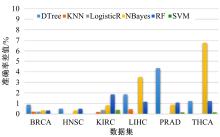
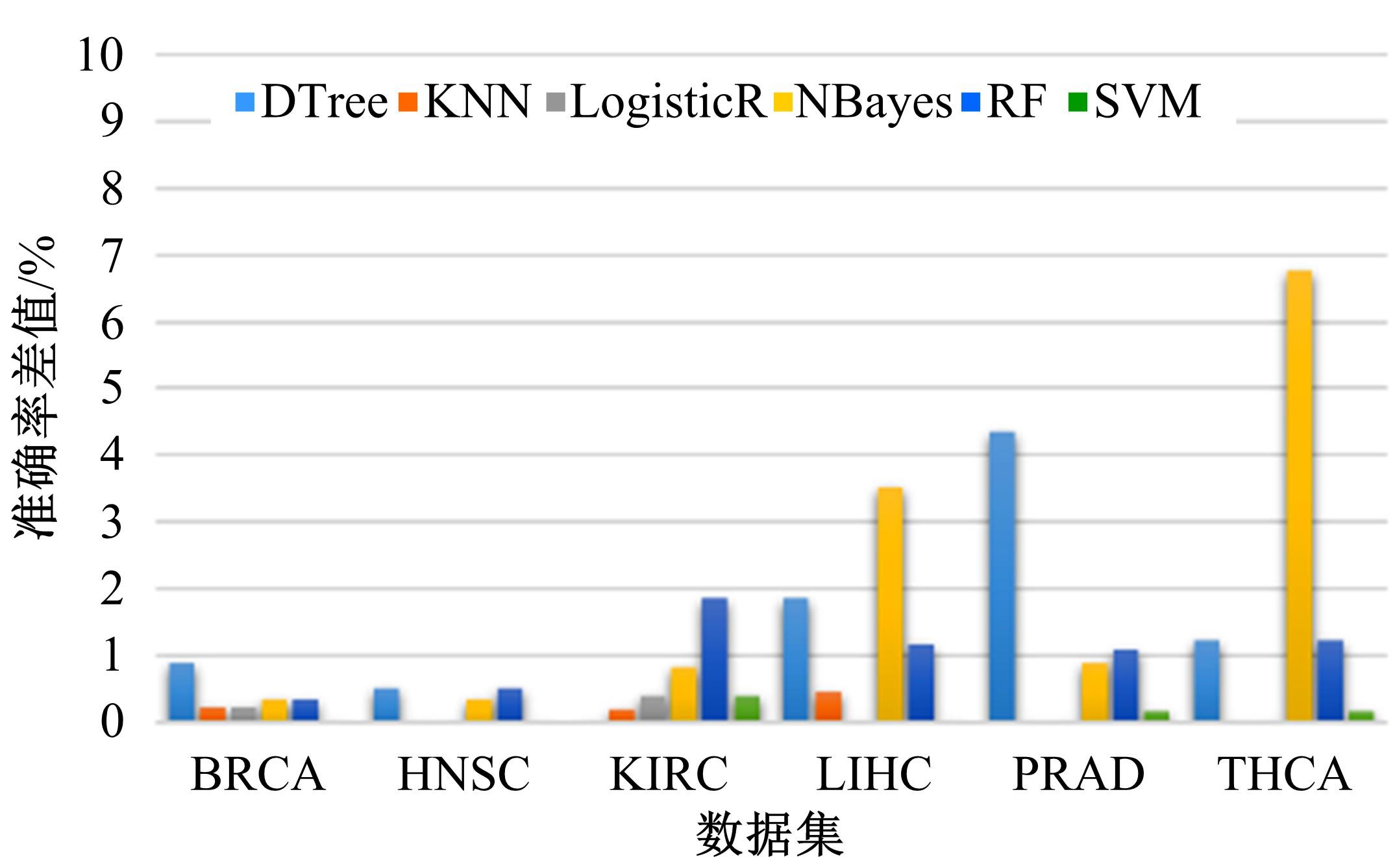
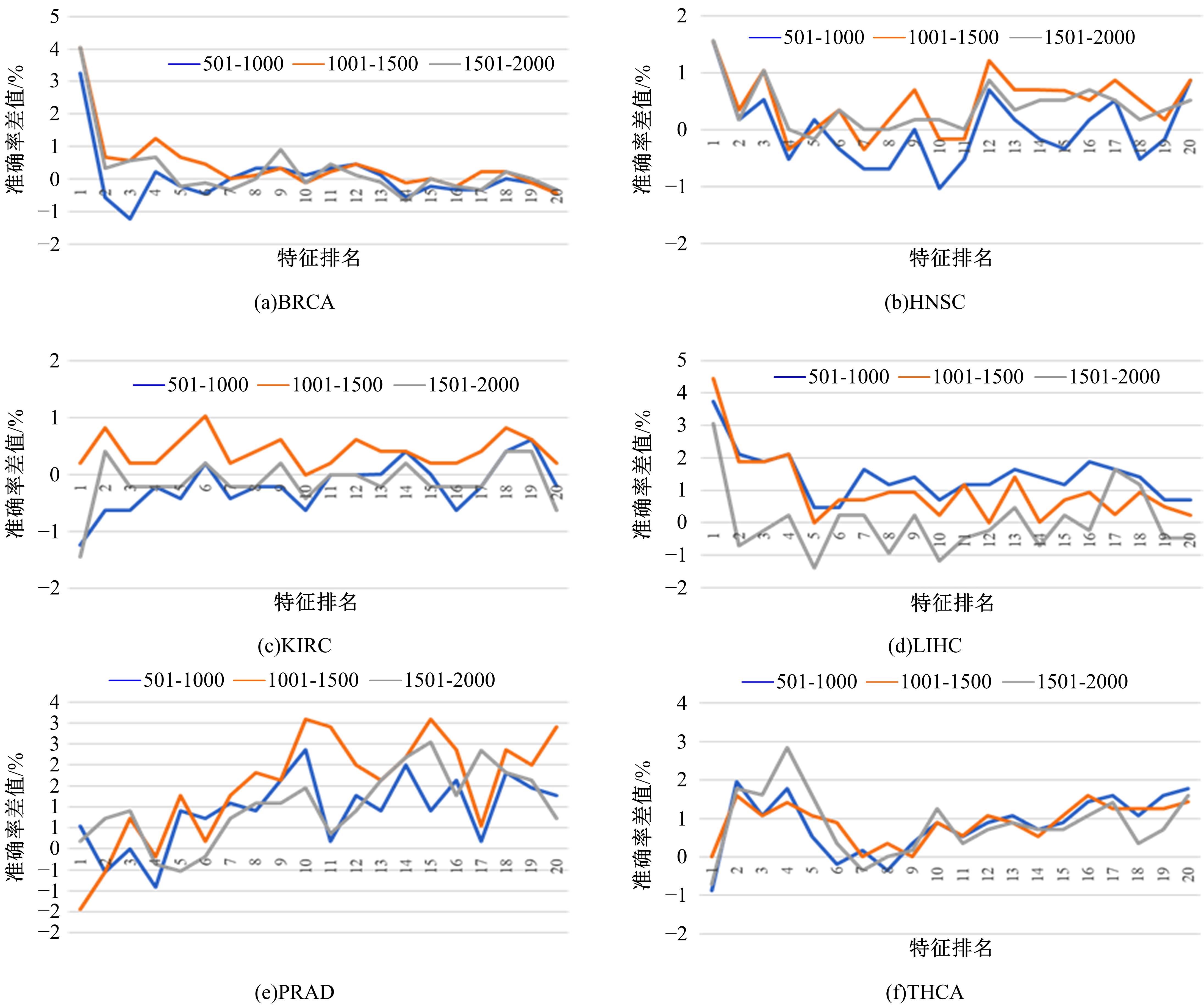
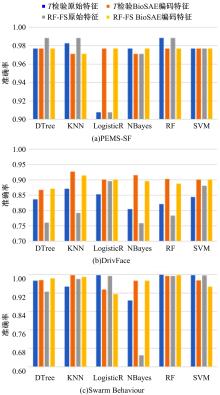
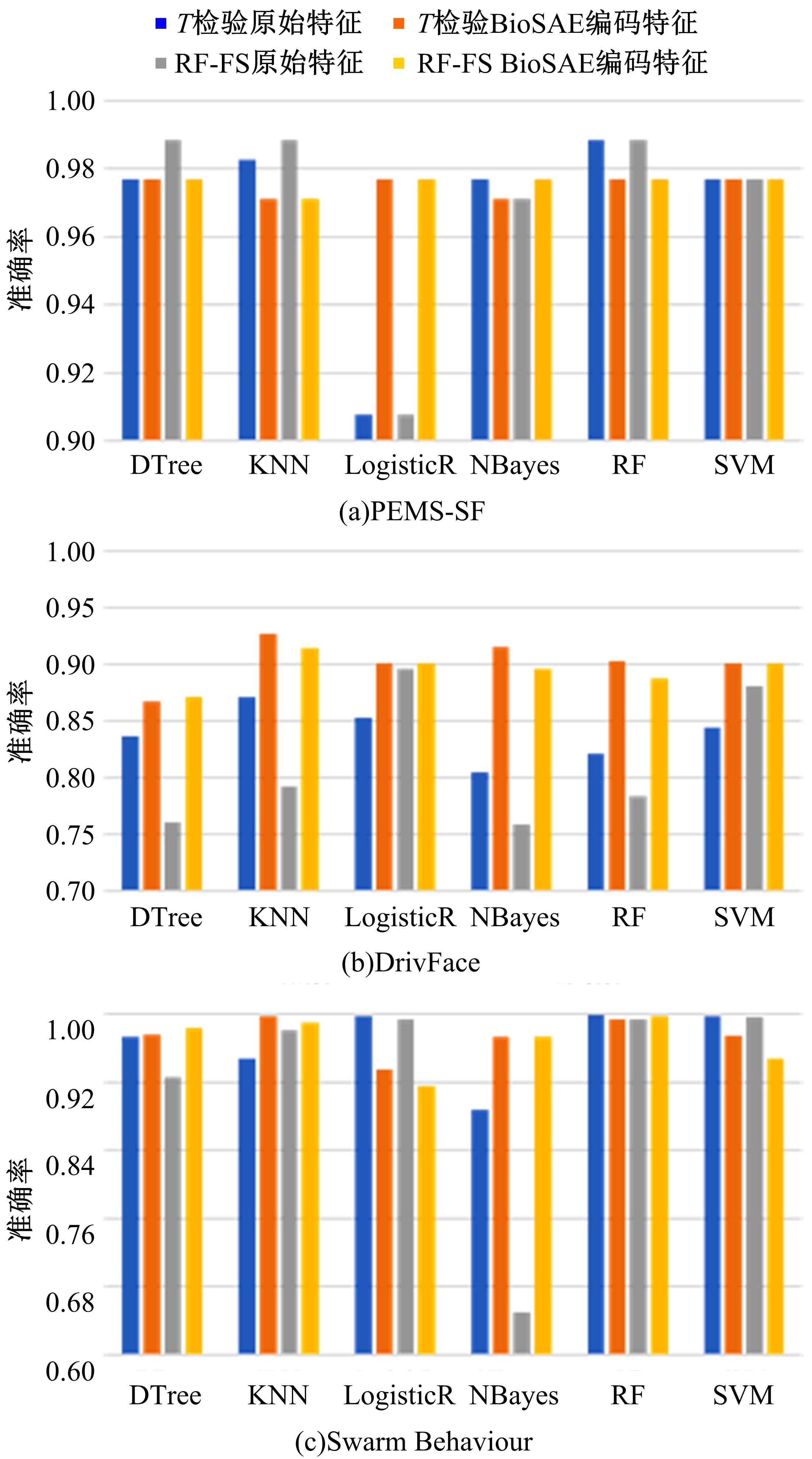
为了研究特征间的内在关系,提出了一种基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE对给定数据集进行编码,并猜想经过稀疏自编码器编码的新构造特征可以训练出更好的分类模型。使用来自TCGA的6种癌症类型的3494个甲基化样本进行了综合评估与实验,首先通过稀疏自编码器得到经过编码的特征,然后使用这些特征与原始的甲基化特征进行分析和对比。实验结果表明:在本研究进行的大多数建模实验中,经过BioSAE编码的特征均优于原始的甲基化特征。同时,将这一算法应用于一些其他领域数据集,如图像数据等,同样取得了相似的提升效果。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. |
| 2 | Hanahan D, Weinberg R A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-674. |
| 3 | Martínez-Chantar M L, Avila M A, Lu S C. Hepatocellular carcinoma: updates in pathogenesis, detection and treatment[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(10): 1-4. |
| 4 | Kandaswamy R, Hannon E, Arseneault L, et al. DNA methylation signatures of adolescent victimization: analysis of a longitudinal monozygotic twin sample[J]. Epigenetics, 2021: 16(11):1169-1186. |
| 5 | Zafon C, Gil J, Pérez-González B, et al. DNA methylation in thyroid cancer[J]. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 2019, 26(7): 415-439. |
| 6 | Bilokapic S, Halic M. Nucleosome and ubiquitin position Set2 to methylate H3K36[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 1-9. |
| 7 | Champigny M J, Unda F, Skyba O, et al. Learning from methylomes: epigenomic correlates of Populus balsamifera traits based on deep learning models of natural DNA methylation[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(6): 1361-1375. |
| 8 | Levy J J, Titus A J, Petersen C L, et al. MethylNet: an automated and modular deep learning approach for DNA methylation analysis[J]. Bmc Bioinformatics, 2020, 21(1): 1-15. |
| 9 | Zhang M, Pan C, Liu H, et al. An attention-based deep learning method for schizophrenia patients classification using DNA methylation data[C]∥The 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Piscataway, USA, 2020: 172-175. |
| 10 | Shimobaba T, Endo Y, Hirayama R, et al. Autoencoder-based holographic image restoration[J]. Applied Optics, 2017, 56(13): 27-30. |
| 11 | Li F, Zurada J M, Wu W. Sparse representation learning of data by autoencoders with L1/2 regularization[J]. Neural Network, 2018, 28(2): 133-147. |
| 12 | Zhu Y, Qiu P, Ji Y. TCGA-Assembler: open-source software for retrieving and processing TCGA data[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(6): 599-600. |
| 13 | Wei L, Jin Z, Yang S, et al. TCGA-assembler 2: software pipeline for retrieval and processing of TCGA/CPTAC data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2018, 34(9): 1615-1617. |
| 14 | Cuturi M. UCI Machine Learning Repository[DB/OL]. [2011-07-24]. . |
| 15 | Diaz-Chito K, Hernández-Sabaté A, López A M. A reduced feature set for driver head pose estimation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2016, 45: 98-107. |
| 16 | Abpeikar S, Kasmarik K, Barlow M, et al. UCI machine learning repository[DB/OL]. [2020-06-12]. . |
| 17 | Simon R. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV for predictive biomarkers[J]. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2015, 107(8): 1-3. |
| 18 | Ghimatgar H, Kazemi K, Helfroush M S, et al. Neonatal EEG sleep stage classification based on deep learning and HMM[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2020, 17(3): 1-17. |
| 19 | Ye Y, Zhang R, Zheng W, et al. RIFS: a randomly restarted incremental feature selection algorithm[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 1-11. |
| 20 | 李志军,杨楚皙,刘丹,等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的信息流增强图像压缩方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. |
| Li Zhi-jun, Yang Chu-xi, Liu Dan, et al. Deep convolutional networks based image compression with enhancement of information flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. | |
| 21 | Xu C, Liu Q, Ye M. Age invariant face recognition and retrieval by coupled auto-encoder networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 222: 62-71. |
| 22 | Yi B, Shen X, Zhang Z, et al. Expanded autoencoder recommendation framework and its application in movie recommendation[C]∥The 10th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management & Applications (SKIMA), Piscataway, USA, 2016: 298-303. |
| 23 | Sun W, Shao S, Zhao R, et al. A sparse auto-encoder-based deep neural network approach for induction motor faults classification[J]. Measurement, 2016, 89: 171-178. |
| 24 | 张根保,李浩,冉琰,等. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. |
| Zhang Gen-bao, Li Hao, Ran Yan, et al. A transfer learning model for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626. | |
| 25 | Chen Z, Li W. Multisensor feature fusion for bearing fault diagnosis using sparse autoencoder and deep belief network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(7): 1693-1702. |
| 26 | Stirzaker C, Taberlay P C, Statham A L, et al. Mining cancer methylomes: prospects and challenges[J]. Trends in Genetics, 2014, 30(2): 75-84. |
| 27 | Saeed S M U, Anwar S M, Khalid H, et al. EEG based classification of long-term stress using psychological labeling[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(7): 1-15. |
| 28 | Liao C, Li S, Luo Z. Gene selection for cancer classification using wilcoxon rank sum test and support vector machine[C]∥International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Piscataway, USA, 2007: 368-373. |
| 29 | Feng G, An B, Yang F, et al. Relevance popularity: a term event model based feature selection scheme for text classification[J]. Plos One, 2017, 12(4): 1-15. |
| 30 | Cai J, Xu Y, Zhang W, et al. A comprehensive comparison of residue-level methylation levels with the regression-based gene-level methylation estimations by ReGear[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2021,22(4): 1-18. |
| 31 | Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, et al. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines[J]. Machine Learning, 2002, 46(1-3): 389-422. |
| 32 | Parikh S A, Gomez R, Thirugnanasambandam M, et al. Decision tree based classification of abdominal aortic aneurysms using geometry quantification measures[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 46(12): 2135-2147. |
| 33 | Hu L-Y, Huang M-W, Ke S-W, et al. The distance function effect on k-nearest neighbor classification for medical datasets[J]. Springerplus, 2016, 5(1): 1-9. |
| 34 | Zhu Y, Fang J. Logistic regression-based trichotomous classification tree and its application in medical diagnosis[J]. Medical Decision Making, 2016, 36(8): 973-989. |
| 35 | Ontivero-Ortega M, Lage-Castellanos A, Valente G, et al. Fast gaussian naïve bayes for searchlight classification analysis[J]. Neuroimage, 2017, 163: 471-479. |
| 36 | Sarica A, Cerasa A, Quattrone A. Random forest algorithm for the classification of neuroimaging data in alzheimer's disease: a systematic review[J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 2017, 9: 1-12. |
| 37 | Huang S, Cai N, Pacheco P P, et al. Applications of support vector machine (SVM) learning in cancer genomics[J]. Cancer Genomics & Proteomics, 2018, 15(1): 41-51. |
| 38 | Hatfield G W, Hung S P, Baldi P. Differential analysis of DNA microarray gene expression data[J]. Molecular Microbiology, 2003, 47(4): 871-877. |
| 39 | King B H, Robinson C D. Differential analysis of the angle of incidence response of utility-grade PV modules[C]∥The IEEE 46th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (Pvsc), Piscataway, USA, 2019: 77-81. |
| 40 | Liu T, Wang F, Zhu J, et al. Differential analysis on deep web data sources[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops,Piscataway, USA, 2010: 33-40. |
| 41 | Rosenberg T, Kisliouk T, Cramer T, et al. Embryonic heat conditioning induces TET-dependent cross-tolerance to hypothalamic inflammation later in life[J]. Frontiers in Genetics, 2020, 11: 1-20. |
| 42 | Wan P, Long E, Li Z, et al. TET-dependent GDF7 hypomethylation impairs aqueous humor outflow and serves as a potential therapeutic target in glaucoma[J]. Molecular Therapy, 2021, 29: 1-19. |
| [1] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [2] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [4] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [5] | 李大湘,陈梦思,刘颖. 基于STA⁃LSTM的自发微表情识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 897-909. |
| [6] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [7] | 魏晓辉,苗艳微,王兴旺. Rhombus sketch:自适应和准确的流数据sketch[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 874-884. |
| [8] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [9] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [10] | 毛琳,任凤至,杨大伟,张汝波. 双向特征金字塔全景分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 657-665. |
| [11] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [12] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [13] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [14] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [15] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
|
||