吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 648-656.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200813
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Dual⁃branch hybrid attention decision net for diabetic retinopathy classification
Ji-hong OUYANG( ),Ze-qi GUO,Si-guang LIU(
),Ze-qi GUO,Si-guang LIU( )
)
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
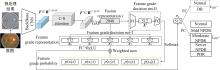
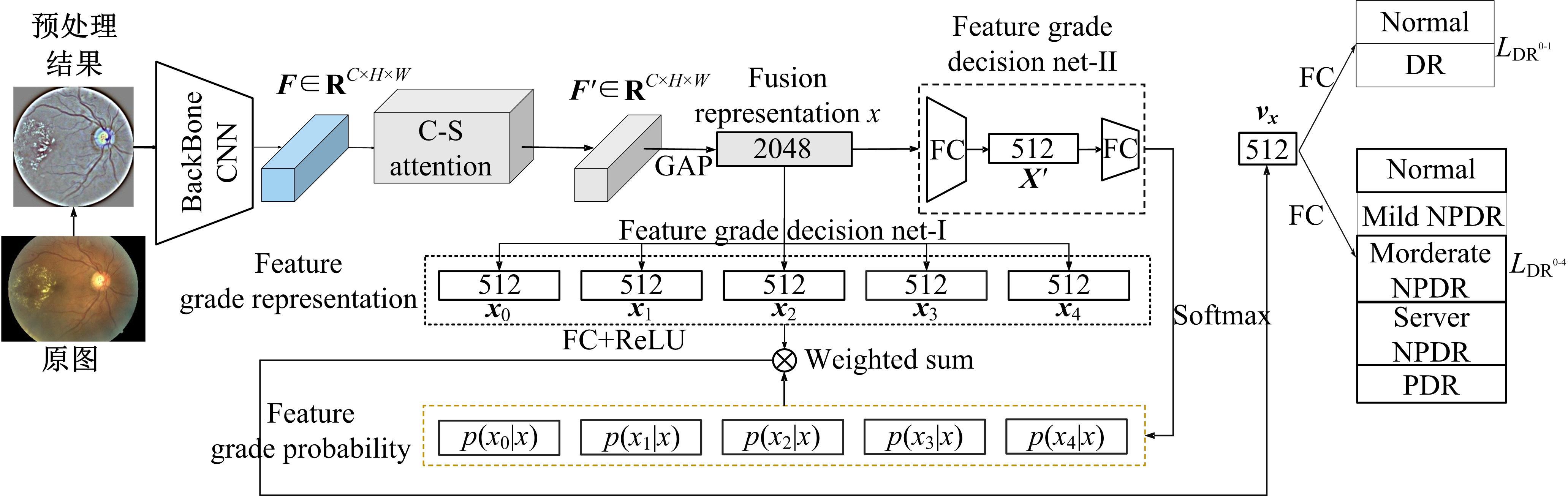
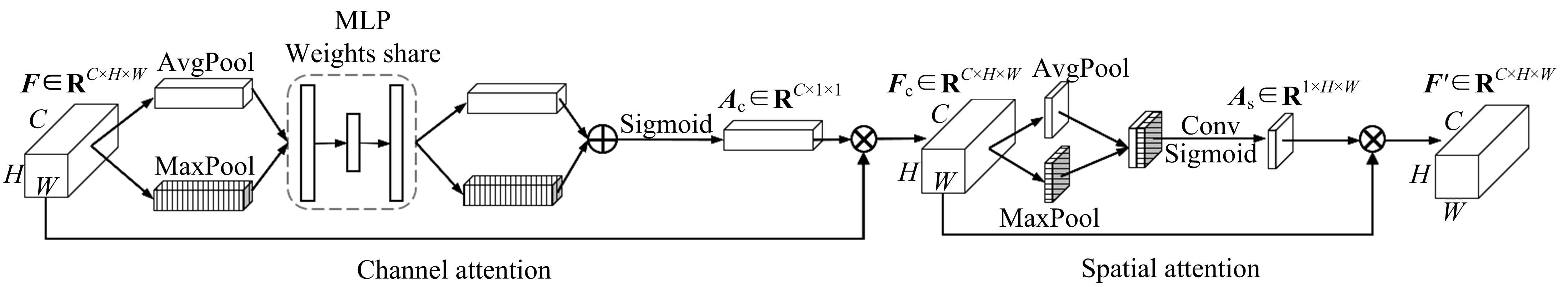
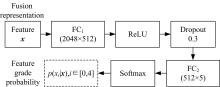
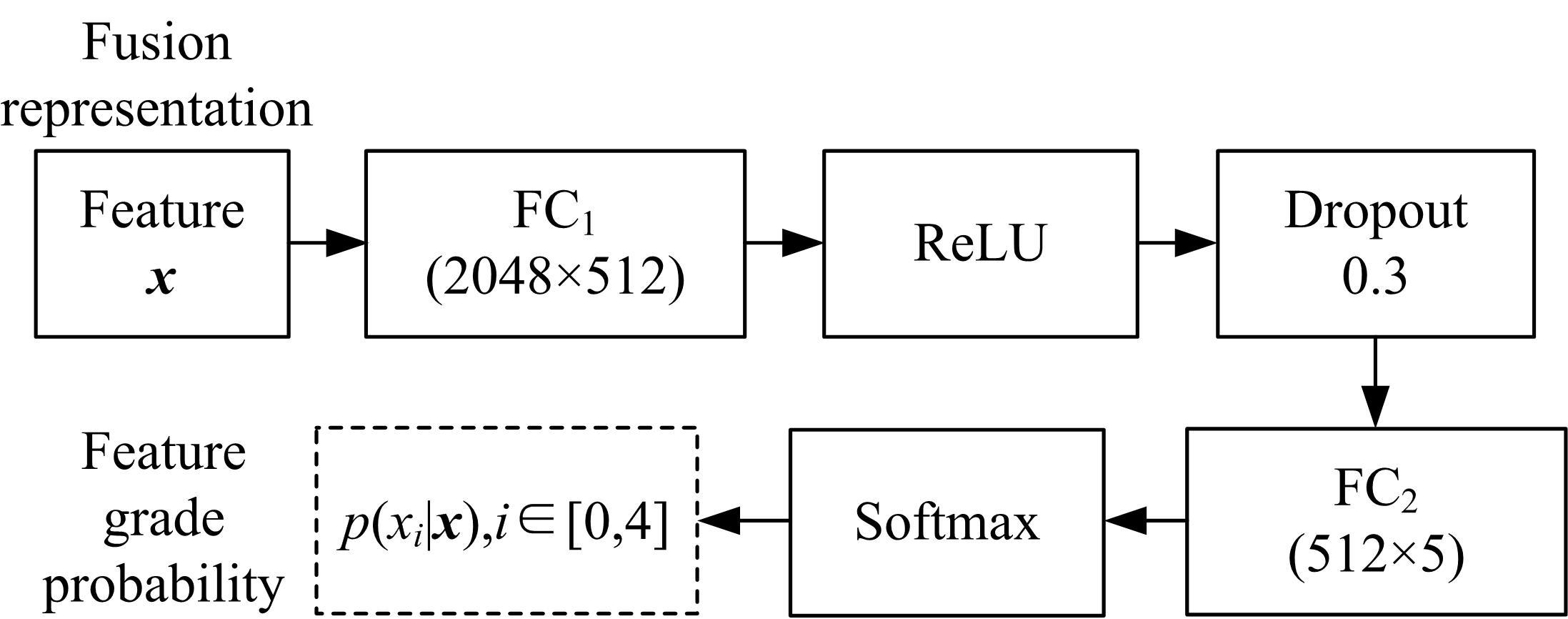
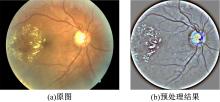
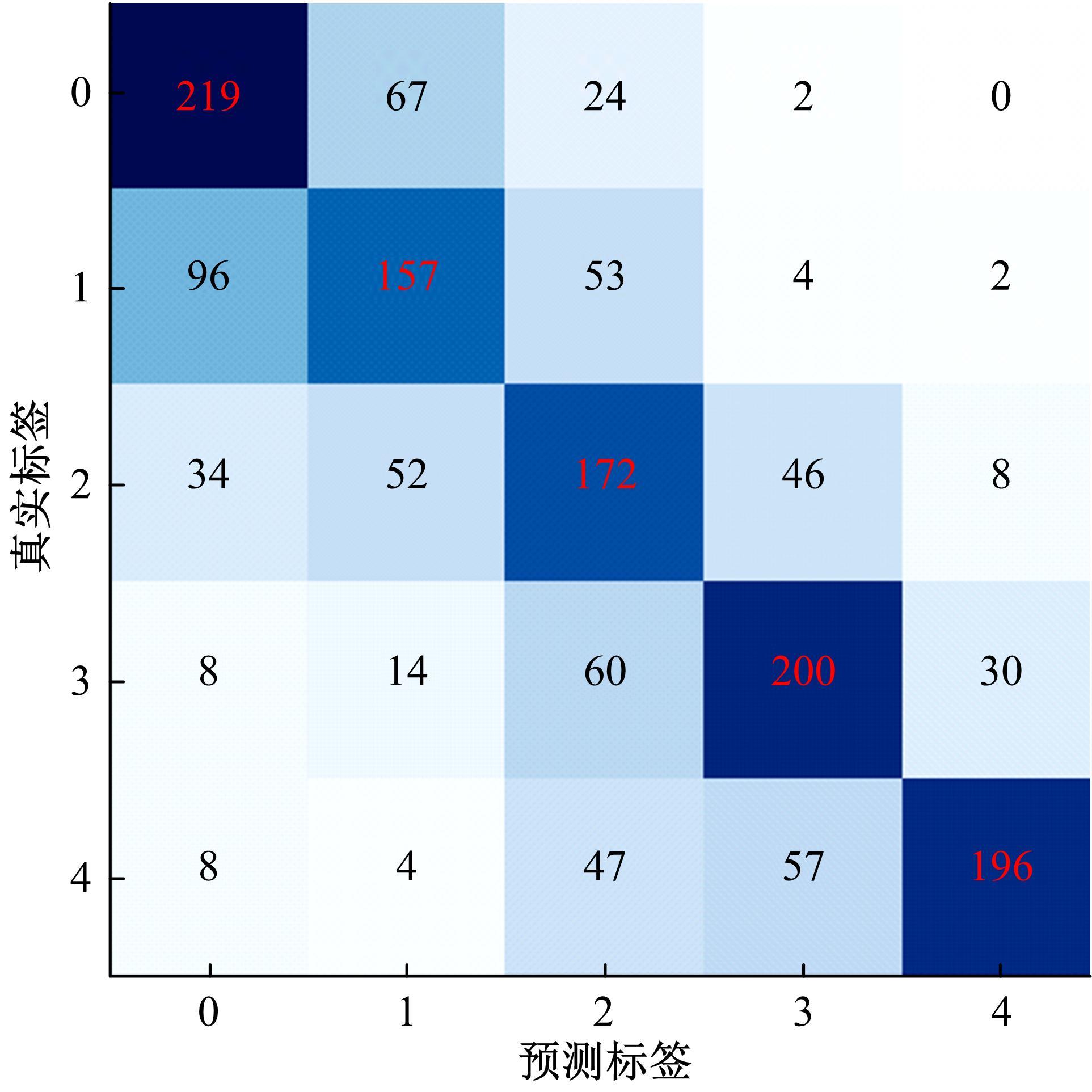
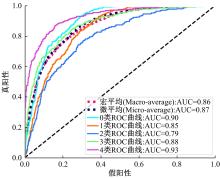
为了缓解大规模糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)筛查需求下医疗资源不足的问题,本文提出了糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络(BiRAD-Net)。该网络分为特征提取和分类两个阶段:在特征提取阶段,引入混合注意力机制抑制噪声,并设计了特征分级决策网络进一步优化特征质量;在特征分类阶段,设计了双分支分类器以及对应的损失,以减缓标签数据不足带来的影响,增强分类准确性。此外,在模型训练过程中应用迁移学习技术来提高模型的精度、降低训练所需数据量。在KAGGLE数据集上的实验结果表明:本文方法对糖尿病视网膜病变的各个阶段均具有较好的诊断能力,优于其他对比方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas(9th edition)[EB/OL]. [2019-12-01]. |
| 2 | Altaf F, Islam S M S, Akhtar N, et al. Going deep in medical image analysis: concepts, methods, challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 99540-99572. |
| 3 | Shen D G, Wu G R, Suk H. Deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 19(1):221-248. |
| 4 | 郜峰利, 陶敏, 李雪妍, 等. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| Gao Feng-li, Tao Min, Li Xue-yan, et al. Accurate segmentation of stroke in CT image based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. | |
| 5 | 陈雪云, 许韬, 黄小巧. 基于条件生成对抗网络的医学细胞图像生成检测方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1414-1419. |
| Chen Xue-yun, Xu Tao, Huang Xiao-qiao. Detection method of medical cell image generation based on conditional generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1414-1419. | |
| 6 | Gargeya R, Leng T. Automated identification of diabetic retinopathy using deep learning[J]. Ophthalmology, 2017, 124(7): 962-969. |
| 7 | Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs[J]. JAMA, 2016, 316(22): 2402-2410. |
| 8 | Gondal W M, Kohler J M, Grzeszick R, et al. Weakly-supervised localization of diabetic retinopathy lesions in retinal fundus images[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Beijing, China, 2017: 2069-2073. |
| 9 | Pratt H, Coenen F, Broadbent D M, et al. Convolutional neural networks for diabetic retinopathy[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 90: 200-205. |
| 10 | Wang Z, Yin Y, Shi J, et al. Zoom-in-net: deep mining lesions for diabetic retinopathy detection[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cham, 2017: 267-275. |
| 11 | Bravo M A, Arbeláez P A. Automatic diabetic retinopathy classification[C]∥13th International Conference on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2017: No.105721E. |
| 12 | Zhao Z Y, Zhang K R, Hao X J, et al. Bira-net: bilinear attention net for diabetic retinopathy grading[C]∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, China, 2019: 1385-1389. |
| 13 | Luo D, Kamata S I. Diabetic retinopathy grading based on lesion correlation graph[J/OL]. [2020-09-28]. |
| 14 | Zhao Z Y, Chopra K, Zeng Z, et al. Sea-net: squeeze-and-excitation attention net for diabetic retinopathy grading[C]∥2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020: 2496-2500. |
| 15 | Zhou Y, He X D, Huang L, et al. Collaborative learning of semi-supervised segmentation and classification for medical images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 2074-2083. |
| 16 | Li X M, Hu X W, Yu L Q, et al. Canet: cross-disease attention network for joint diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema grading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 39(5): 1483-1493. |
| 17 | Wang Z G, Yang J B. Diabetic retinopathy detection via deep convolutional networks for discriminative localization and visual explanation[J/OL]. [2020-09-29]. |
| 18 | Jiang H Y, Yang K, Gao M D, et al. An interpretable ensemble deep learning model for diabetic retinopathy disease classification[C]∥2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Berlin, Germany, 2019: 2045-2048. |
| 19 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 20 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| 21 | Kim Y, Park W, Roh M C, et al. Groupface: Learning latent groups and constructing group-based representations for face recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020: 5621-5630. |
| 22 | Kaggle: diabetic retinopathy detection[EB/OL]. [2019-05-01]. |
| 23 | Graham B. Kaggle diabetic retinopathy detection competition report[D]. Coventry, UK: University of Warwick, 2015. |
| [1] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [2] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [3] | 宋林,王立平,吴军,关立文,刘知贵. 基于信息物理融合和数字孪生的可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 439-449. |
| [4] | 曹洁,马佳林,黄黛麟,余萍. 一种基于多通道马尔可夫变迁场的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [5] | 刘桂霞,裴志尧,宋佳智. 基于深度学习的蛋白质⁃ATP结合位点预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 187-194. |
| [6] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [7] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [8] | 张杰,景雯,陈富. 基于被动分簇算法的即时通信网络协议漏洞检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2253-2258. |
| [9] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [10] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [11] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [12] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
| [13] | 任丽莉,王志军,闫冬梅. 结合黏菌觅食行为的改进多元宇宙算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2190-2197. |
| [14] | 姚引娣,贺军瑾,李杨莉,谢荡远,李英. 自构建改进型鲸鱼优化BP神经网络的ET0模拟计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1798-1807. |
| [15] | 董丽丽,杨丹,张翔. 基于深度学习的大规模语义文本重叠区域检索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1817-1822. |
|
||