吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 925-933.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200912
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测
- 广西大学 电气工程学院,南宁 530004
Pedestrian segmentation and detection in multi-scene based on G-UNet
Xue-yun CHEN( ),Xue-yu BEI,Qu YAO,Xin JIN
),Xue-yu BEI,Qu YAO,Xin JIN
- School of Electrical Engineering,Guangxi University,Nanning 530004,China
摘要:
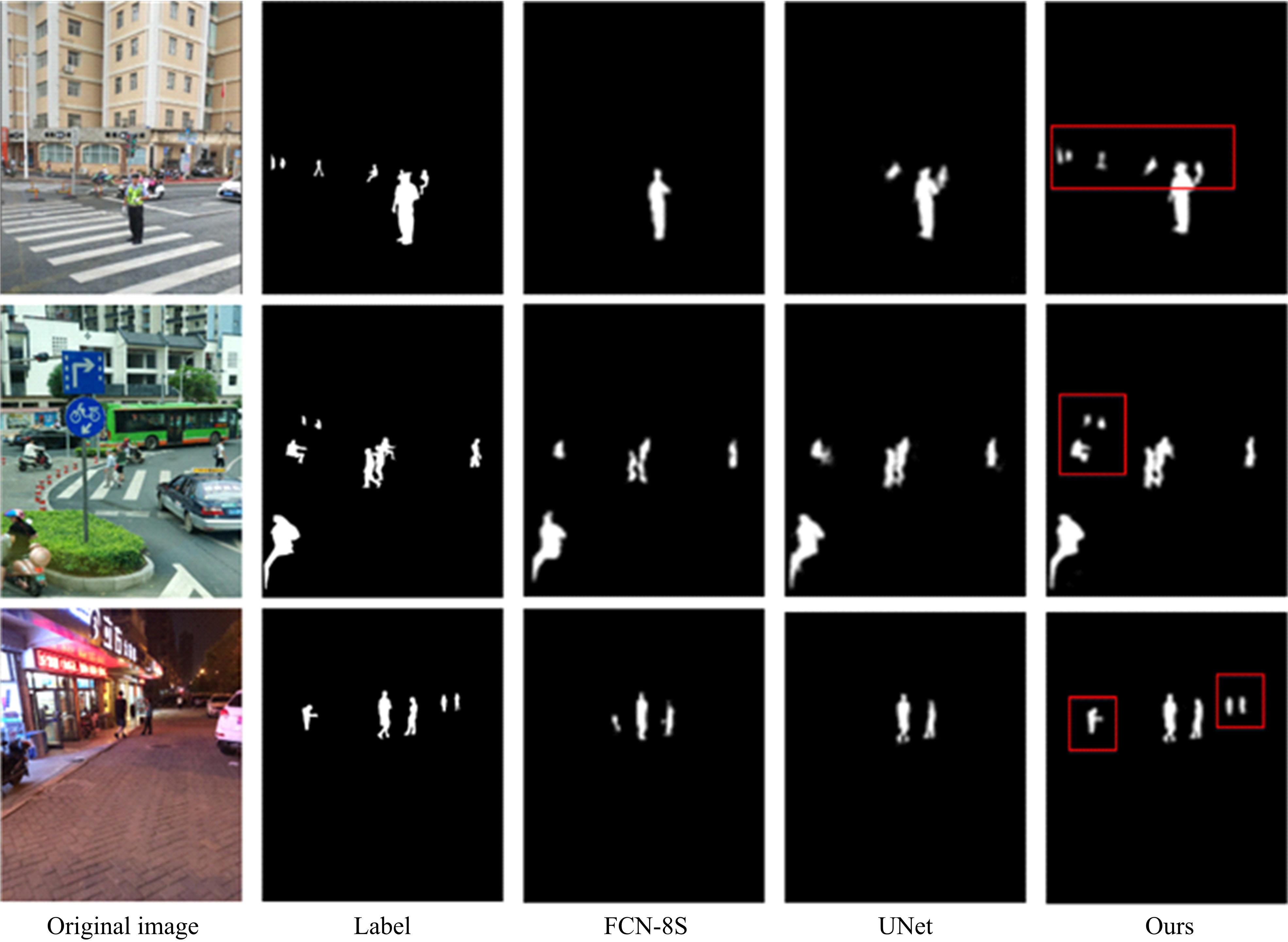
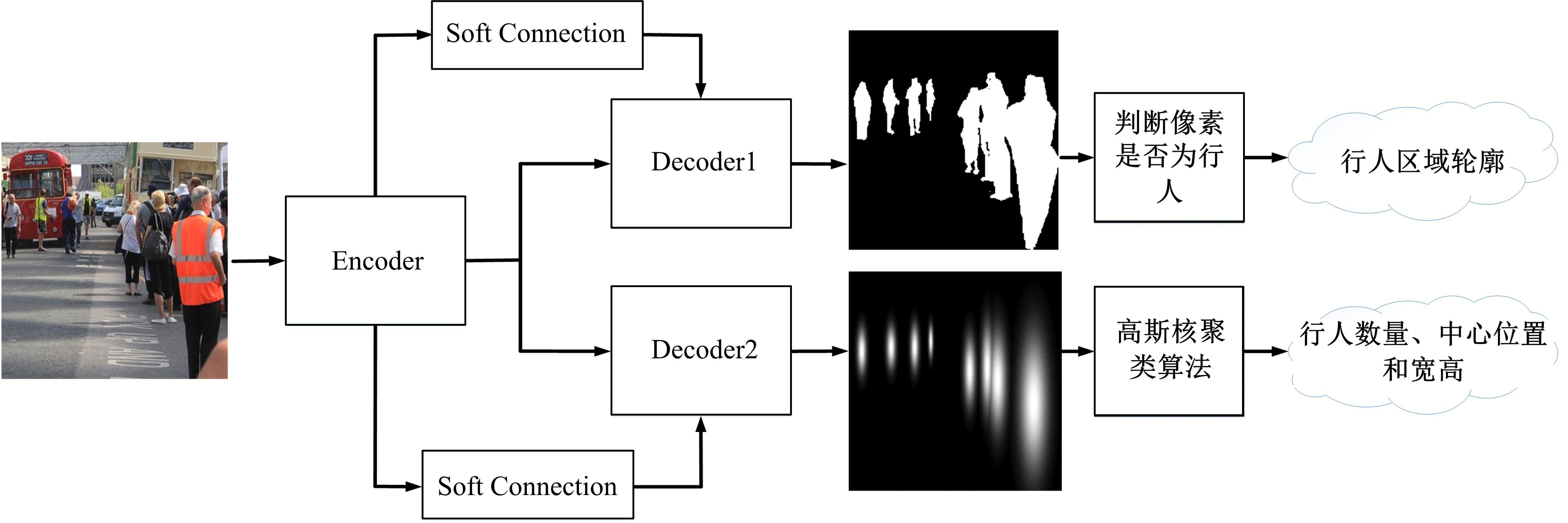
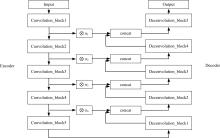
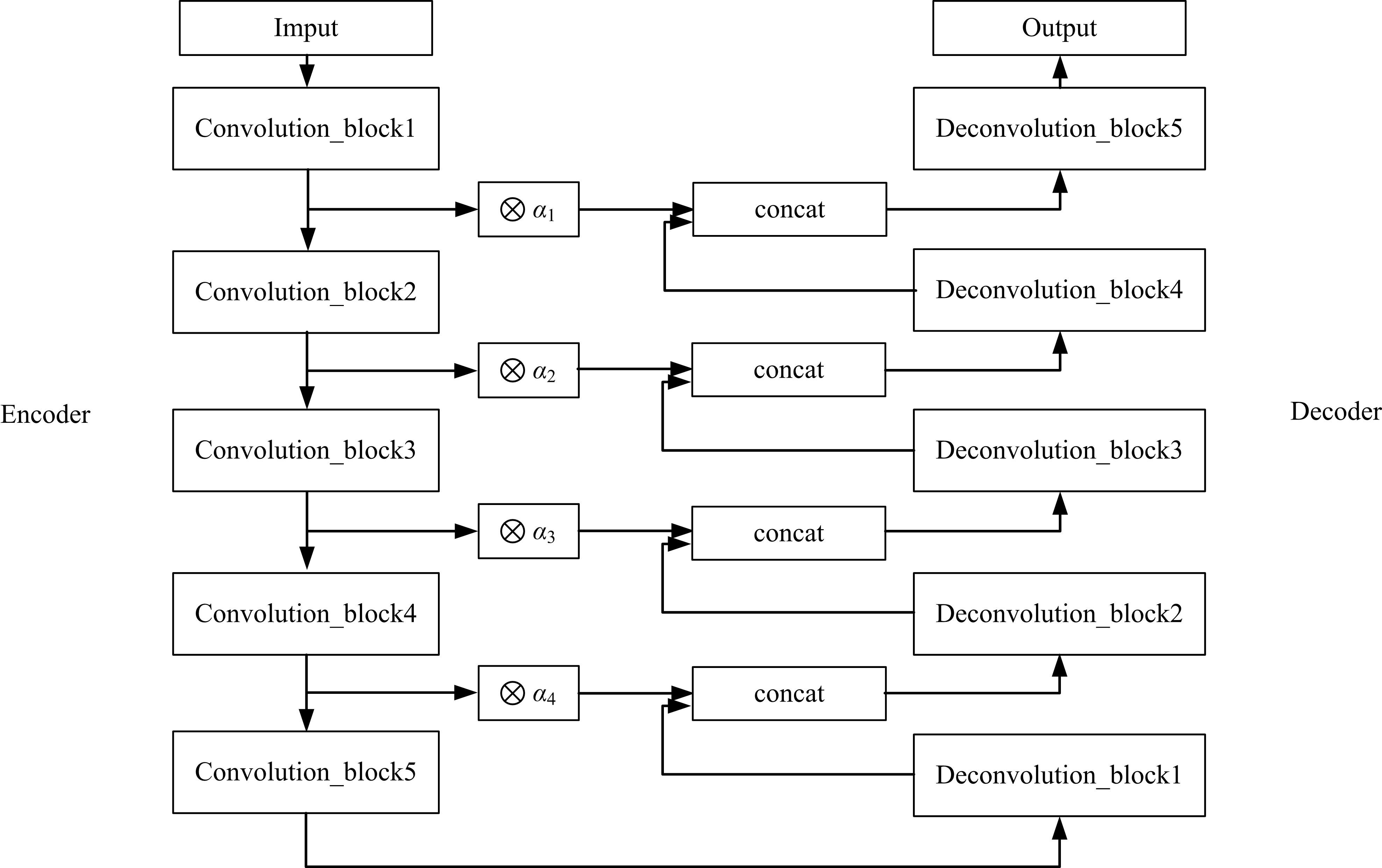
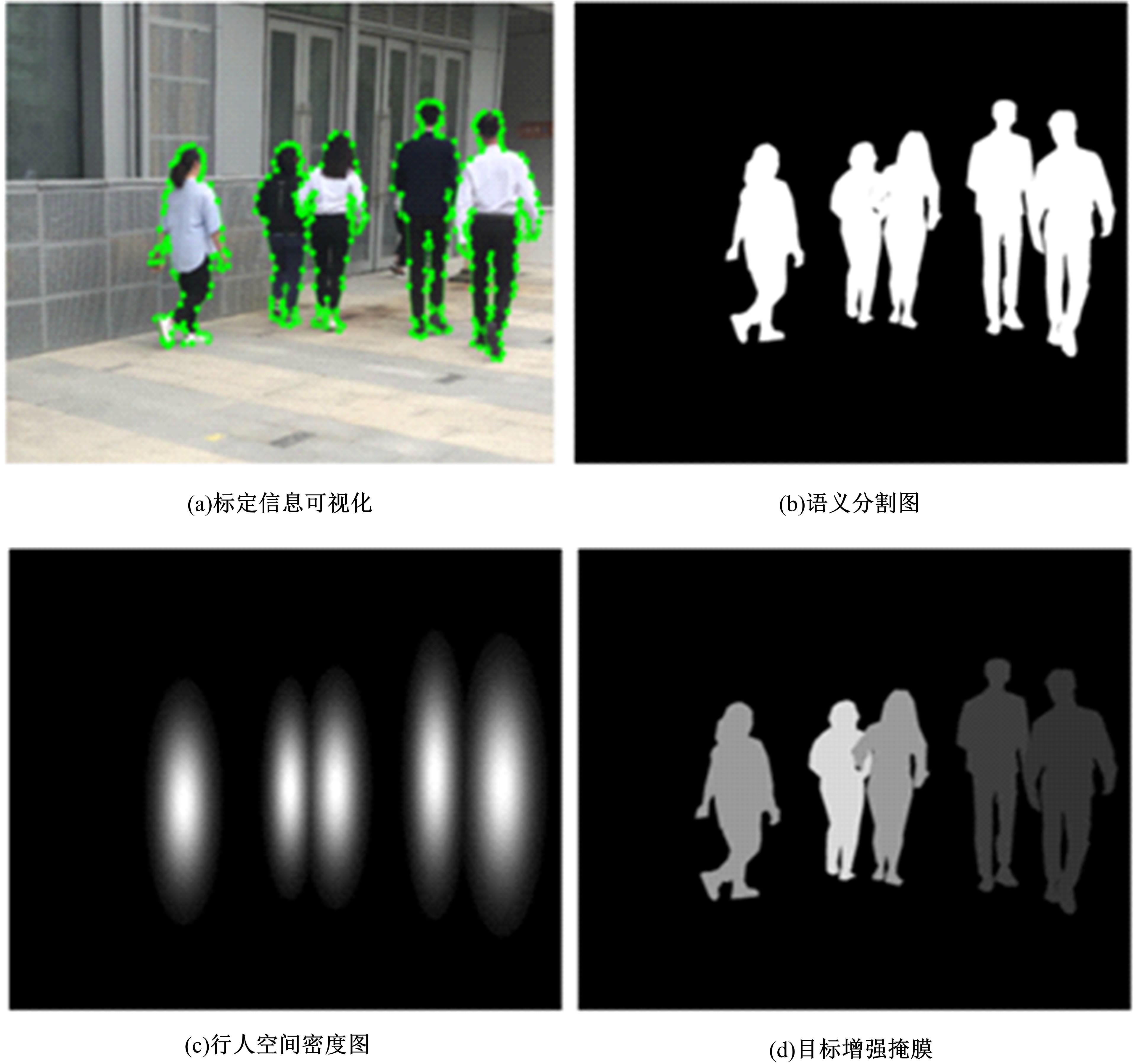
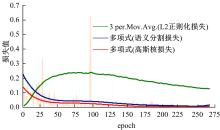
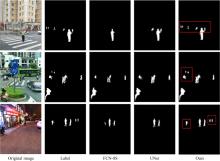
目前的语义分割方法可以得到行人的轮廓,但在行人相互遮挡时,无法直接得到图中行人的数量、身高和中心位置等信息。针对这一缺陷,提出了G-UNet模型算法:在语义分割主干之外,增加一个行人区域的高斯椭圆密度核检测分支,通过核的极大值点、垂直和水平轴尺度,分别检测行人的中心位置、高度和宽度,并由密度核极大值点的唯一性,解决了行人遮挡的检测难题。另外,UNet以空间对称的方式将底层和高层特征进行硬性的拼接,使得50%的固定误差直接传播到底层。本文提出可训练的柔性系数拼接方式,可以得到最优的误差分配传播方式。最后,传统的损失函数的误差值与行人标定面积成正比,导致小尺度行人容易漏检,本文提出目标增强损失函数提高网络检测小尺度行人的能力。在自建行人分割数据库中,实验结果证明了本文方法的有效性且优于其他方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Saeidi M, Ahmadi A. Deep learning based on CNN for pedestrian detection: an overview and analysis[C]∥The 9th International Symposium on Telecommunications (IST), Tehran, Iran, 2018: 108-112. |
| 2 | Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]∥IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,San Diego, USA, 2005 . |
| 3 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014. |
| 4 | Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015. |
| 5 | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. |
| 6 | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016. |
| 7 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),Honolulu,USA, 2017: 6517-6525. |
| 8 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement[EB/OL].[2018-02-08].. |
| 9 | Tayara H, Kim G S. Vehicle detection and counting in high-resolution aerial images using convolutional regression neural network[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 6: 2220-2230. |
| 10 | Chen X Y, Lin J Y, Xiang S M, et al. Detecting maneuvering target accurately based on a two-phase approach from remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Geoence and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(5): 849-853. |
| 11 | 罗会兰, 张云. 基于深度网络的图像语义分割综述[J].电子学报, 2019, 47(10): 2211-2220. |
| Luo Hui-lan, Zhang Yun. A survey of image semantic segmentation based on deep network[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(10): 2211-2220. | |
| 12 | Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Computer Society, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. |
| 13 | Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230-6239. |
| 14 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2015, 9351: 234-241. |
| 15 | Chen L C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[DB/OL].[2017-02-05].. |
| [1] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [2] | 魏晓辉,苗艳微,王兴旺. Rhombus sketch:自适应和准确的流数据sketch[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 874-884. |
| [3] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [4] | 李大湘,陈梦思,刘颖. 基于STA⁃LSTM的自发微表情识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 897-909. |
| [5] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [6] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [7] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [8] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [9] | 毛琳,任凤至,杨大伟,张汝波. 双向特征金字塔全景分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 657-665. |
| [10] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [11] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [12] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [13] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [14] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [15] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
|
||