吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 692-699.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220606
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于公交线路运行稳定性的潜在公交专用道需求识别方法
- 1.同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804
2.同济大学 城市交通研究院,上海 201804
Identification method of potential public transportation lane demand based on bus line operation stability
Jiao-rong WU1,2( ),Qing-kai LIN1,Yong-qi DENG1
),Qing-kai LIN1,Yong-qi DENG1
- 1.Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Road and Transportation Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Urban Mobility Institution,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
摘要:
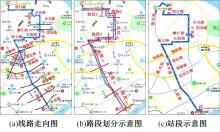
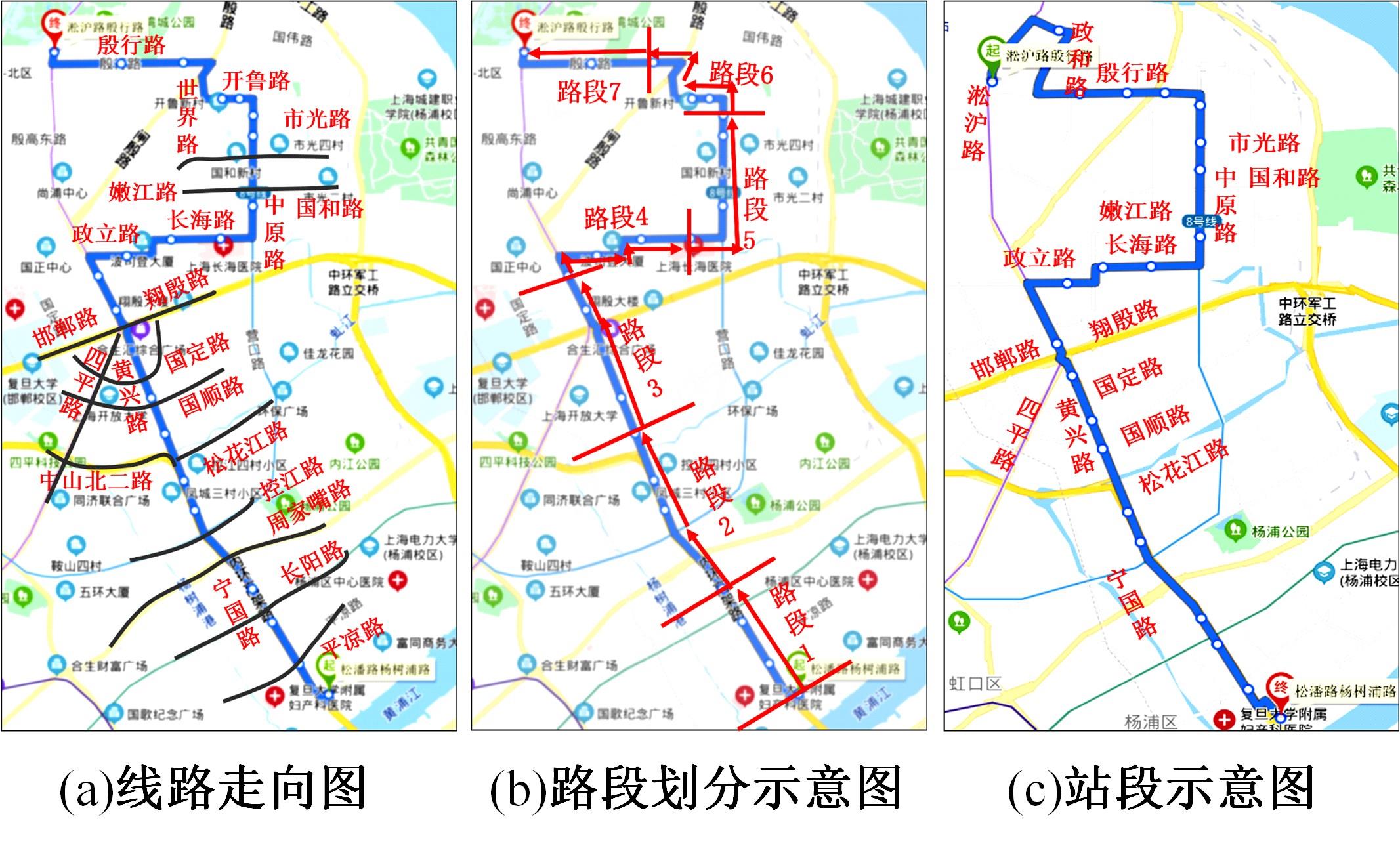
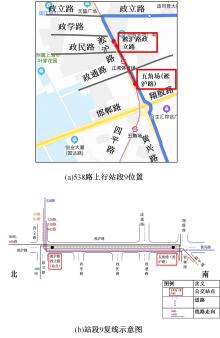
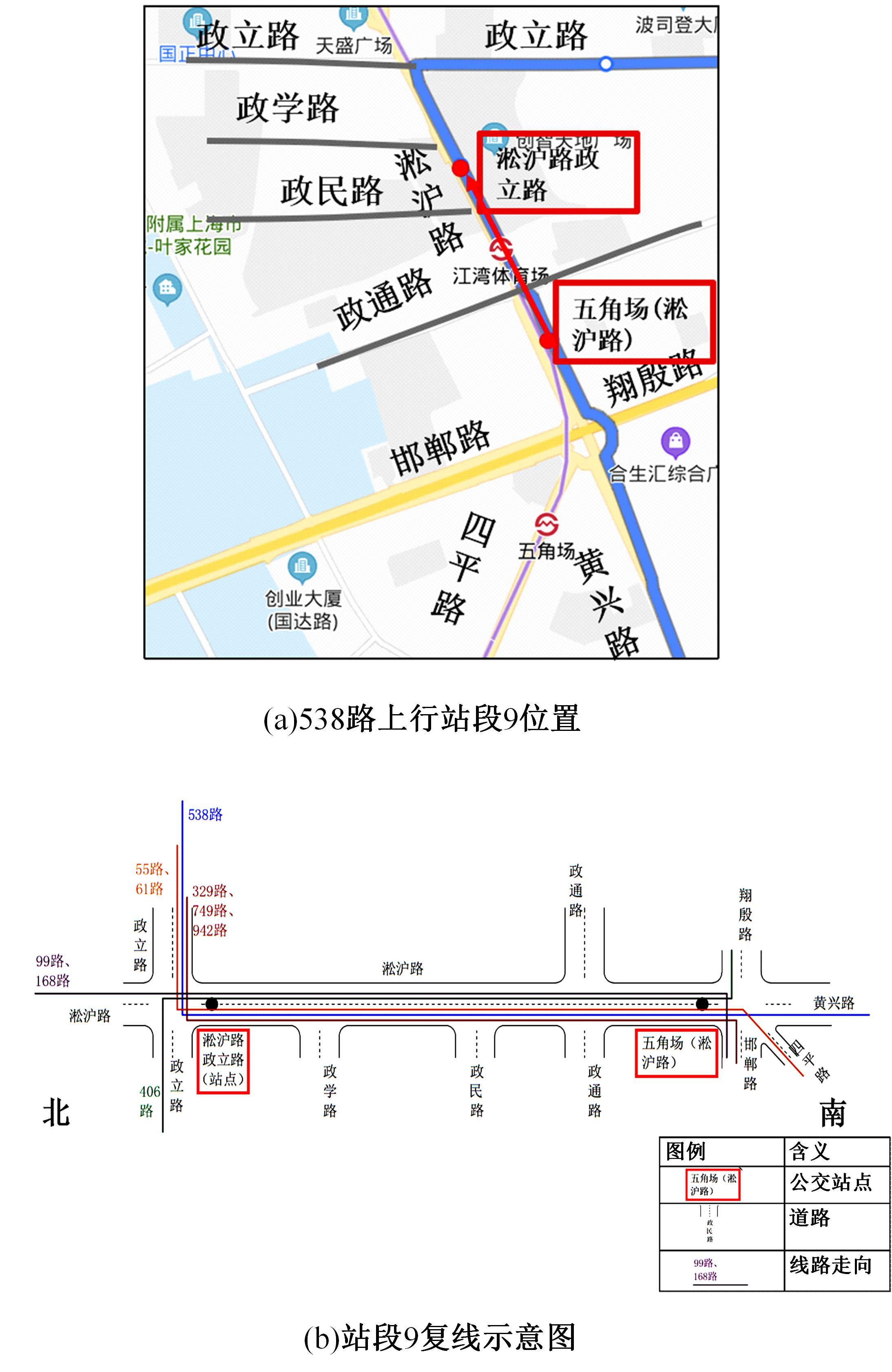
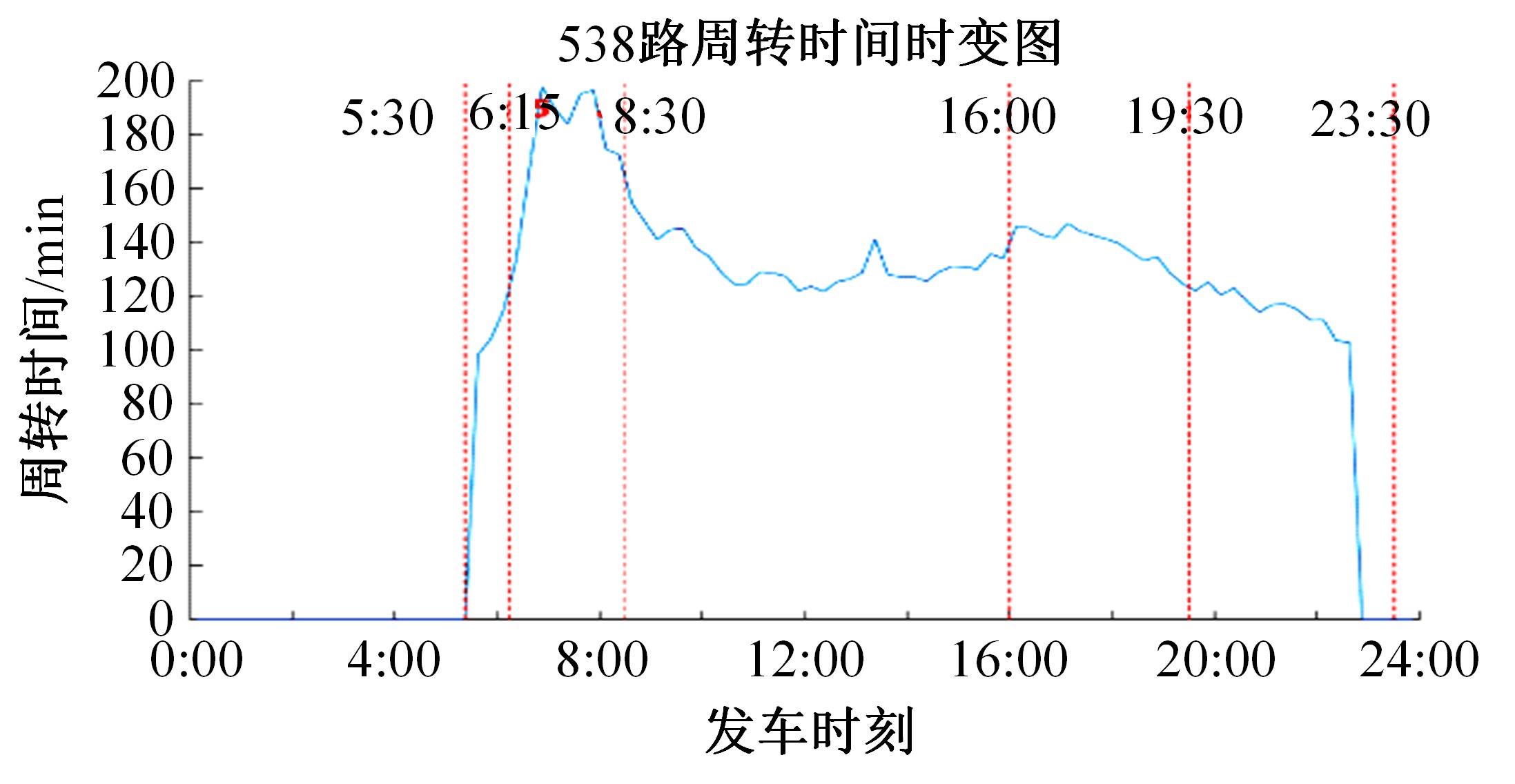
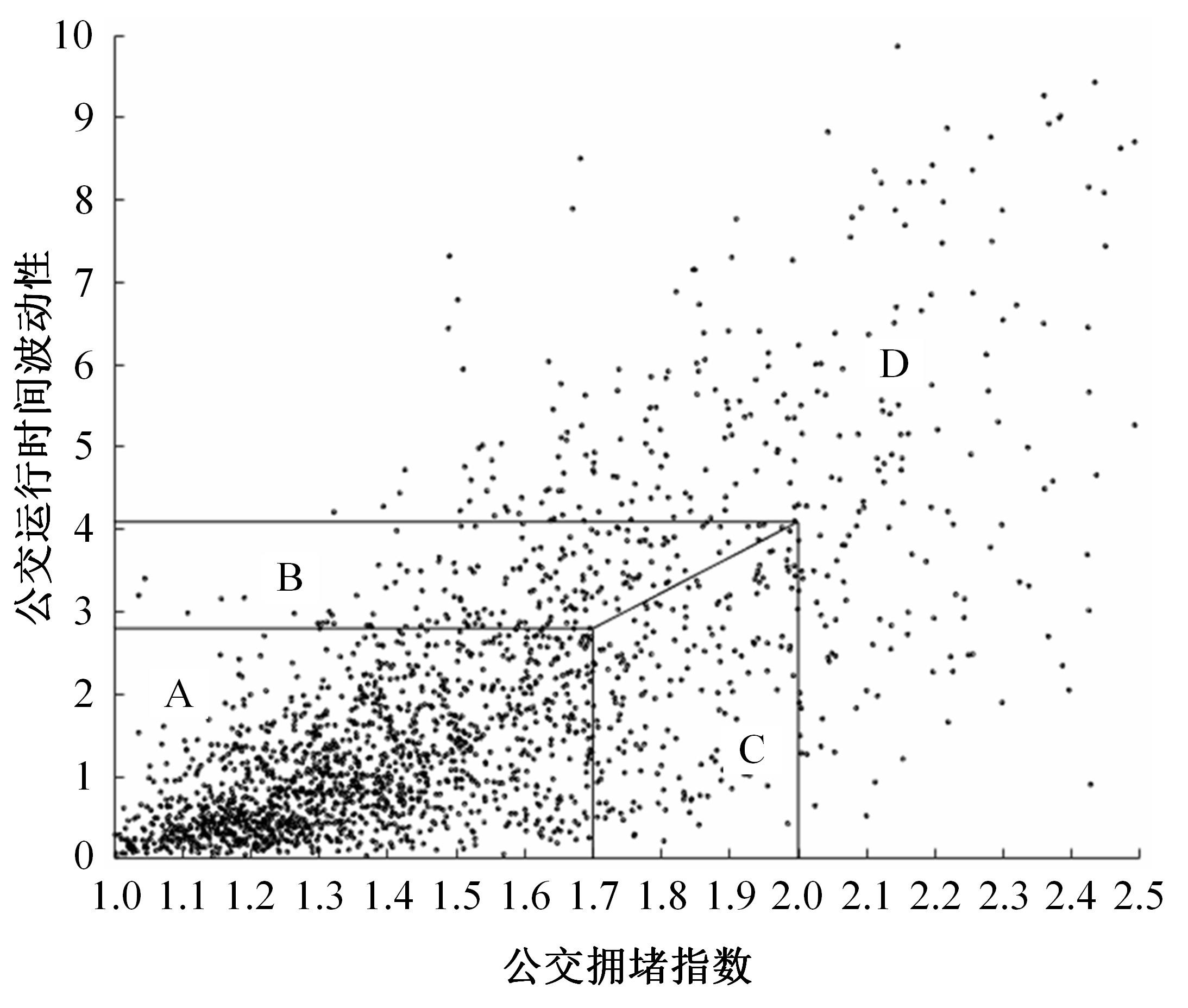
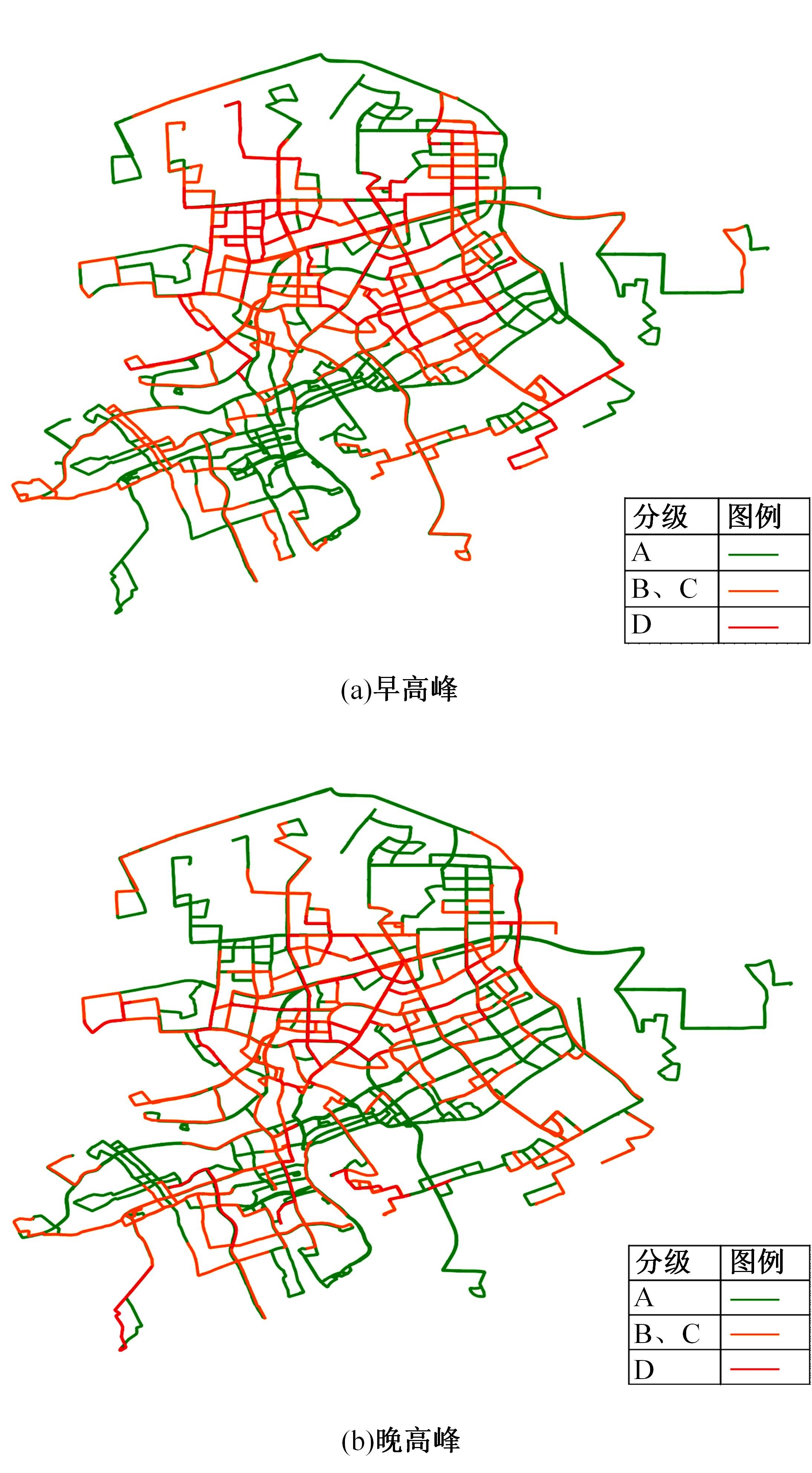
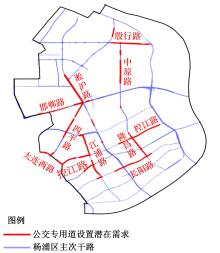
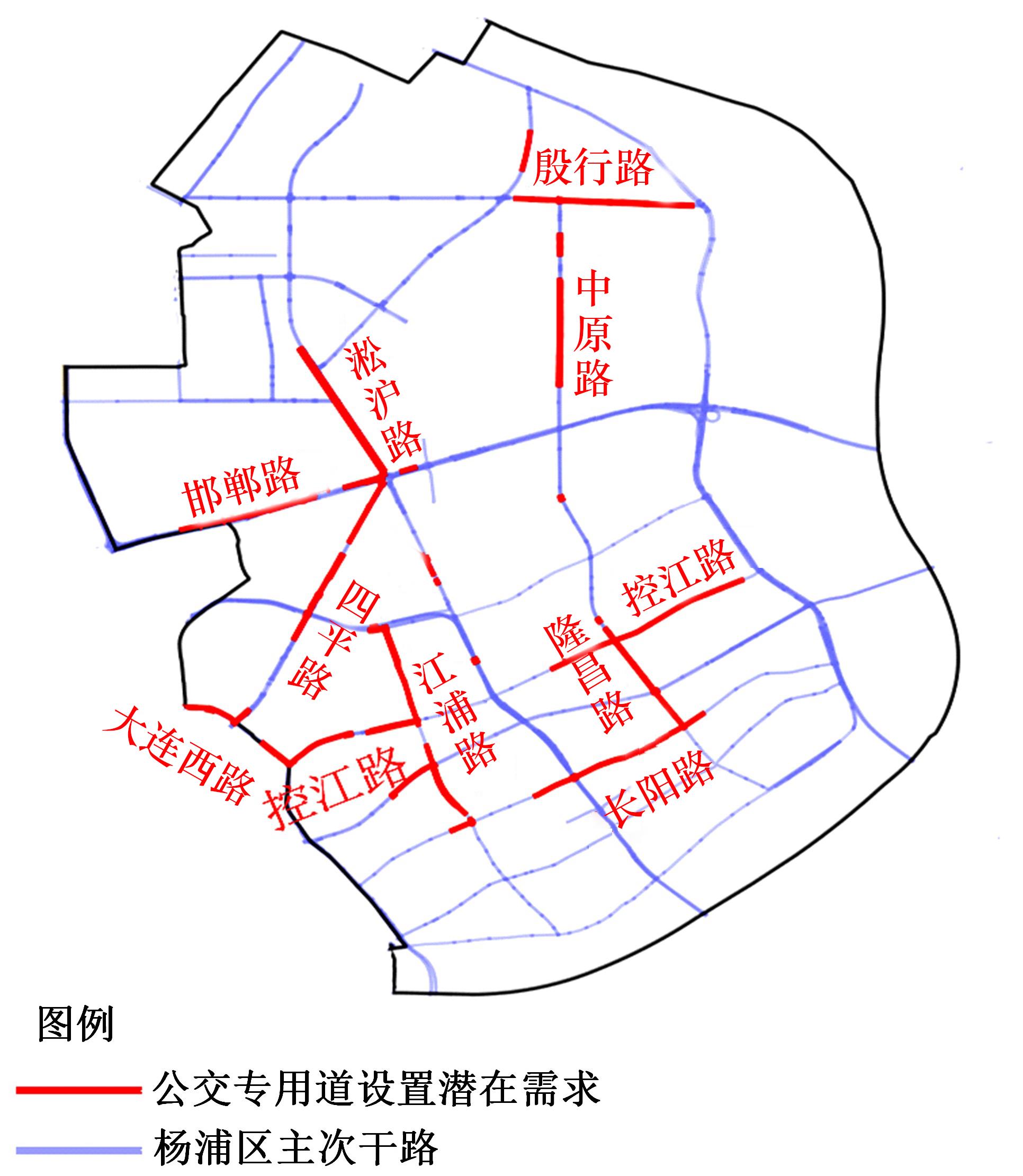
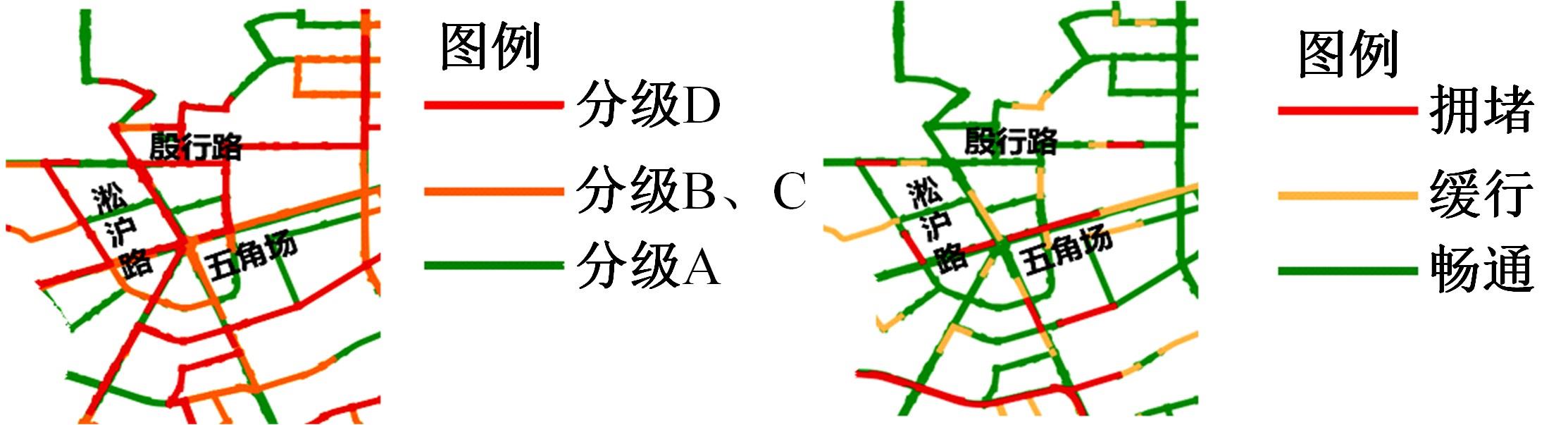
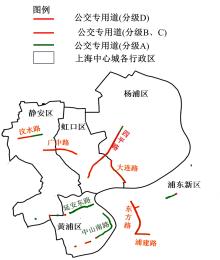
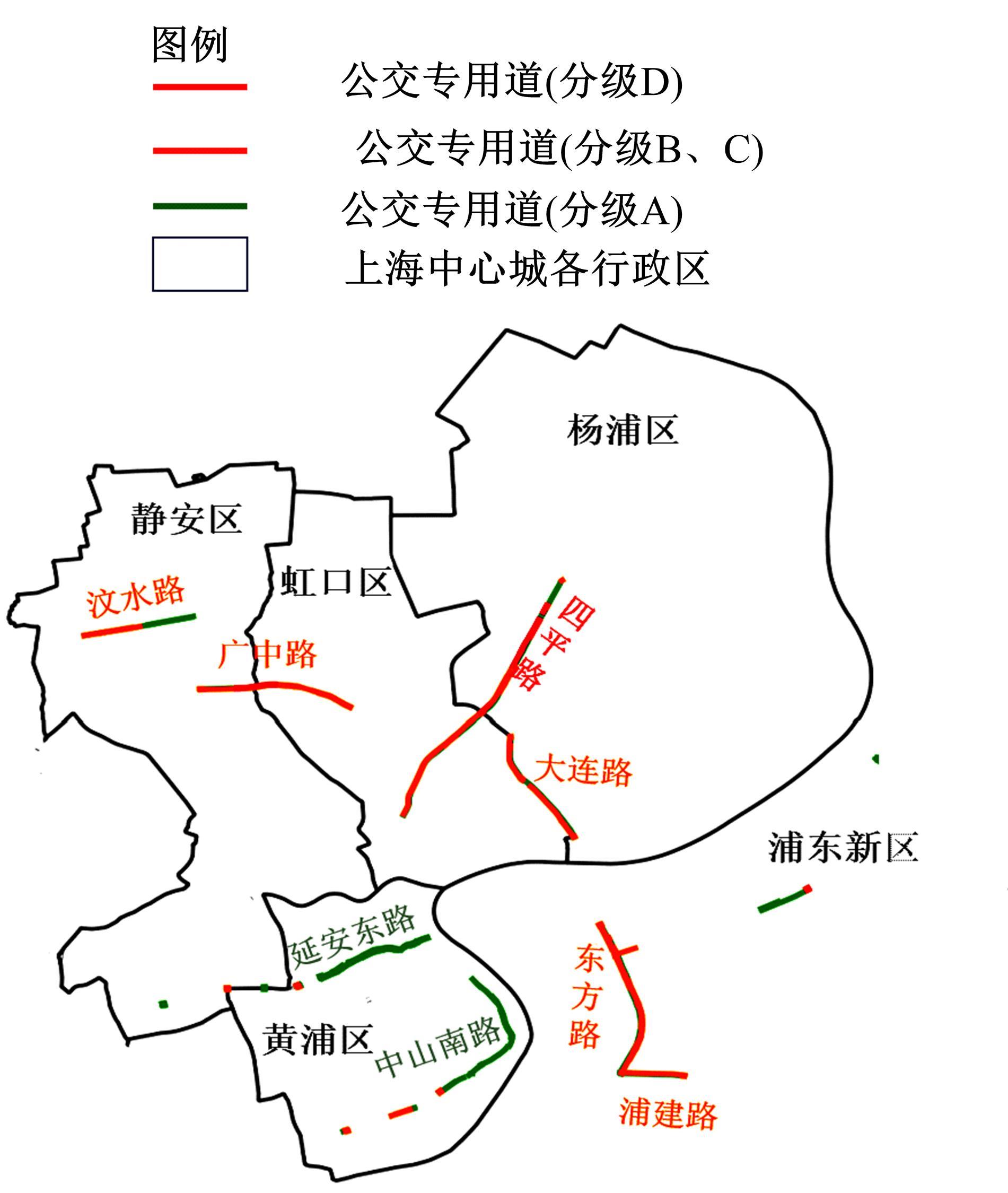
梳理了各地现行公交专用道设计规范,得出公交专用道的设置条件通常只考虑了高峰小时道路断面公交客运量、公交车流量、道路条件等客观指标,鲜有考虑道路上公交线路的运行稳定性及其对乘客公交服务可靠性体验提升的影响。针对公交专用道可靠性和效率评估中由于公交专用道设置条件的缺失,造成部分公交专用道运行效果不良、乘客体验感无提升的问题,本文考虑了乘客体验,提出了基于公交运行稳定性的潜在公交专用道需求识别方法。该方法基于实际路况和公交车辆全球定位系统(GPS)数据,分析了公交车辆在各路段或站段上偏离计划行车时刻表运行的情况,构建了公交拥堵指数和公交运送时间波动性两个指标。提出了基于公交运行稳定性的路段或站段分级方法,并将该方法用于上海中心城69条公交线路的途经道路,把识别出的公交运行稳定性为“差”的道路作为公交专用道潜在设置需求,同时,该方法也可锁定需要进一步优化改善的公交专用道。
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | 吴娇蓉, 王宇沁, 魏明, 等. 路侧公交专用道设置长度对公交线路运行可靠性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(1): 82-91. |
| Wu Jiao-rong, Wang Yu-qin, Wei-ming, et al. Impact of length of road-side bus lane on bus operational reliability[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(1): 82-91. | |
| 2 | DG/TJ08-2172—2015. 公交专用道系统设计规范 [S]. |
| 3 | . 公交专用车道设置规范 [S]. |
| 4 | 苏建规[2012]76号. 江苏省城市规划管理规定 [S]. |
| 5 | 深圳市交通运输委员会.深圳市公交专用道设置标准及设计指引(试行)[J/OL]. [2017-03-01]. |
| 6 | 2013甬 SS—04.宁波市公交专用道设计导则 [S]. |
| 7 | 深圳市交通运输委员会. 佛山市公交专用道设置标准和设计指引(试行)[J/OL]. [2023-11-02]. |
| 8 | . 公交专用道设置 [S]. |
| 9 | 耿会灵. 基于轨迹与刷卡数据的公交运行可靠性评价[D]. 山东: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2018. |
| Geng Hui-ling. Bus operation reliability evaluation based on trajectory and smart card data[D]. Shandong: School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2018. | |
| 10 | Camus R, Longo G, Macorini C. Estimation of transit reliability level-of-service based on automatic vehicle location data[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2005, 1927(1): 277-286. |
| 11 | Bowman L A, Turnquist M A. Service frequency, schedule reliability and passenger wait times at transit stops[J]. Transportation Research Part A: General, 1981, 15(6): 465-471. |
| 12 | 杜雨威. 城市公共交通服务可靠性评价方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学交通运输工程学院, 2013. |
| Du Yu-wei. Urban public transit service reliability evaluation method research[D]. Dalian: College of Transportation Engineering, Dalian Maritime University, 2013. | |
| 13 | 魏静. 蒙特卡洛法在公交到站间隔时间可靠性计算中的应用[C]∥上海市第七届世界华人交通运输学术大会论文集. 上海:人民交通出版社, 2007: 471-473. |
| 14 | 夏方林. 城市快速路偶发性交通拥堵持续时间分析[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2019. |
| Xia Fang-lin. Duration time analysis of non-recurrent traffic congestion on urban expressway[D]. Beijing: College of Transportation Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 15 | 张宇石. 大城市常规公共交通运行可靠性的研究与实例评价[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2008. |
| Zhang Yu-shi. Research and evaluation of public transportation operation reliability in metropolis[D] Beijing: College of Transportation Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2008. | |
| 16 | Bates O, Polak J, Jones P, Cook A. The valuation of reliability for personal travel[J]. Transportation Research Part E, 2001, 37(2): 191-229. |
| 17 | 王康. 城市交通拥堵中公交车辆调度模式研究[D]. 河南: 河南农业大学机电工程学院, 2018. |
| Wang Kang. Research on bus scheduling model in urban traffic[D] Henan: College of Mechanical & Electrical Engineering, Henan Agricultural University, 2018. | |
| 18 | 谭馨, 邓光明. 异方差White检验方法的改进[J]. 统计与决策, 2020, 36(19): 42-46. |
| Tan Xin, Deng Guang-ming. Improvement of White's test for heteroskedasticity[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2020, 36(19): 42-46. |
| [1] | 庄焱,董春娇,米雪玉,张小雨,王菁. 基于随机参数Logit的中小城市居民出行方式选择建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 461-468. |
| [2] | 张文会,伊静. 考虑通行能力和排队延误的公交停靠系统优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 146-154. |
| [3] | 邝先验,陈自如. 基于CA的无信号灯控制路段行人过街横道处动态博弈礼让行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 837-846. |
| [4] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [5] | 董春娇,董黛悦,诸葛承祥,甄理. 电动自行车出行特性及骑行决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
| [6] | 杨世军,裴玉龙,潘恒彦,程国柱,张文会. 城市公交车辆驻站时间特征分析及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2031-2039. |
| [7] | 宋现敏,张明业,李振建,王鑫,张亚南. 动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [8] | 孙宝凤,姜源,郑黎黎,崔万坤,任欣欣. 变覆盖半径下城市轨道交通维护保障网络设计模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 526-534. |
| [9] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [10] | 吴娇蓉, 王宇沁, 魏明, 林彬. 路侧公交专用道设置长度对公交线路运行可靠性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 82-91. |
| [11] | 于德新,杨兆升,高鹏. 动态限制搜索区域的带约束K则最优路径算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 172-0176. |
| [12] | 杨兆升,于悦,杨薇. 基于固定型检测器和浮动车的路段行程时间获取技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(增刊2): 168-0171. |
| [13] | 李霞,邵春福,贾洪飞 . 土地利用与居民出行生成模型及其参数标定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2007, 37(06): 1300-1303. |
| [14] | 卢守峰,杨兆升,刘喜敏. 基于复杂性理论的城市交通系统研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊1): 153-0156. |
| [15] | 季常煦,杨楠,胡娟娟,陈昕. 城市交通流诱导系统与交通控制系统集成中的信息处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊1): 140-0143. |
|
||