吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1935-1943.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221144
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于避险脱离的自动驾驶路测安全影响因素
- 同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804
Risk factors for autonomous vehicle road testing based on risk-avoiding disengagement
Hui-zhao TU( ),Chang LU,Miao-jia LU(
),Chang LU,Miao-jia LU( ),Hao LI
),Hao LI
- Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of the Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
摘要:
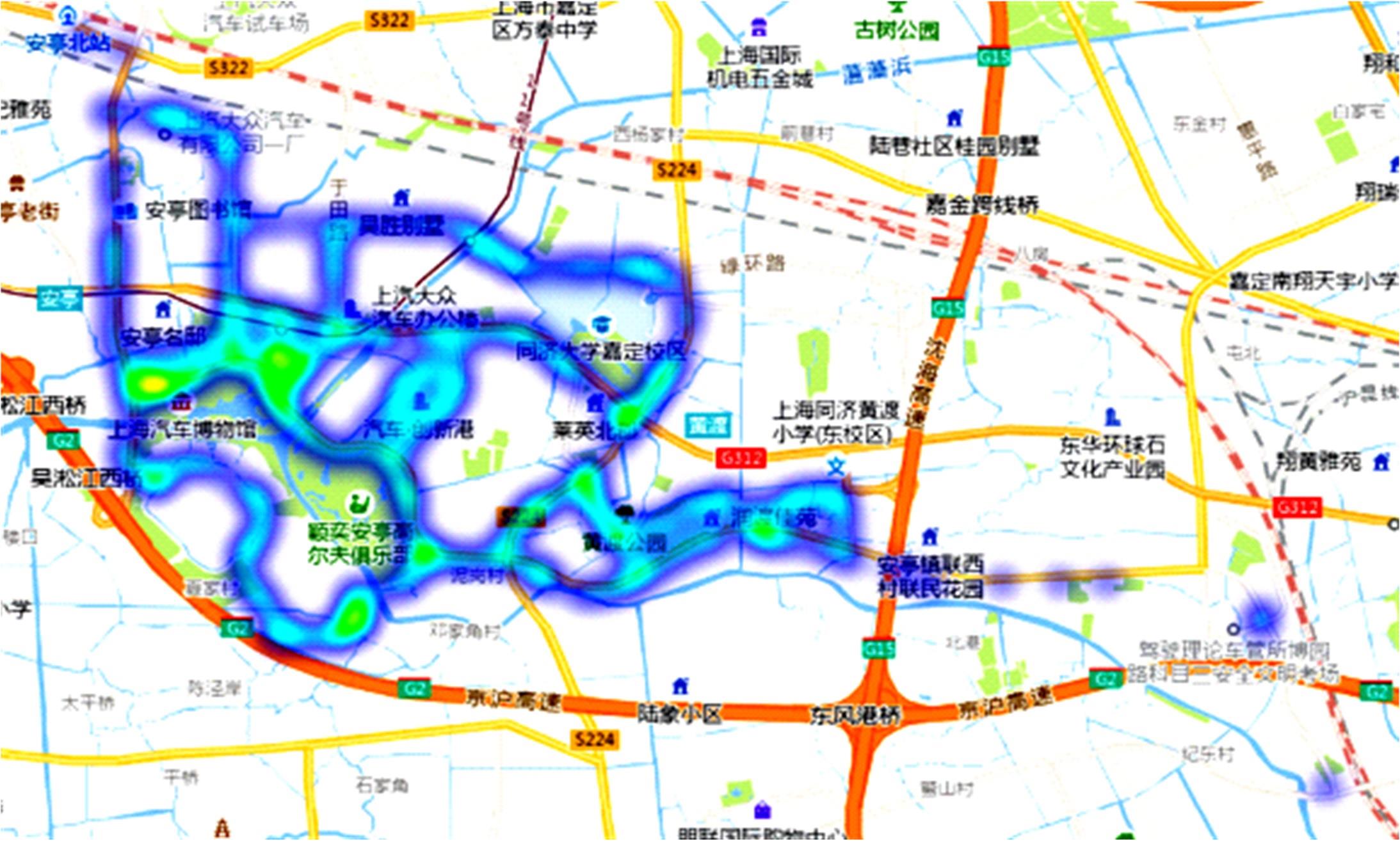
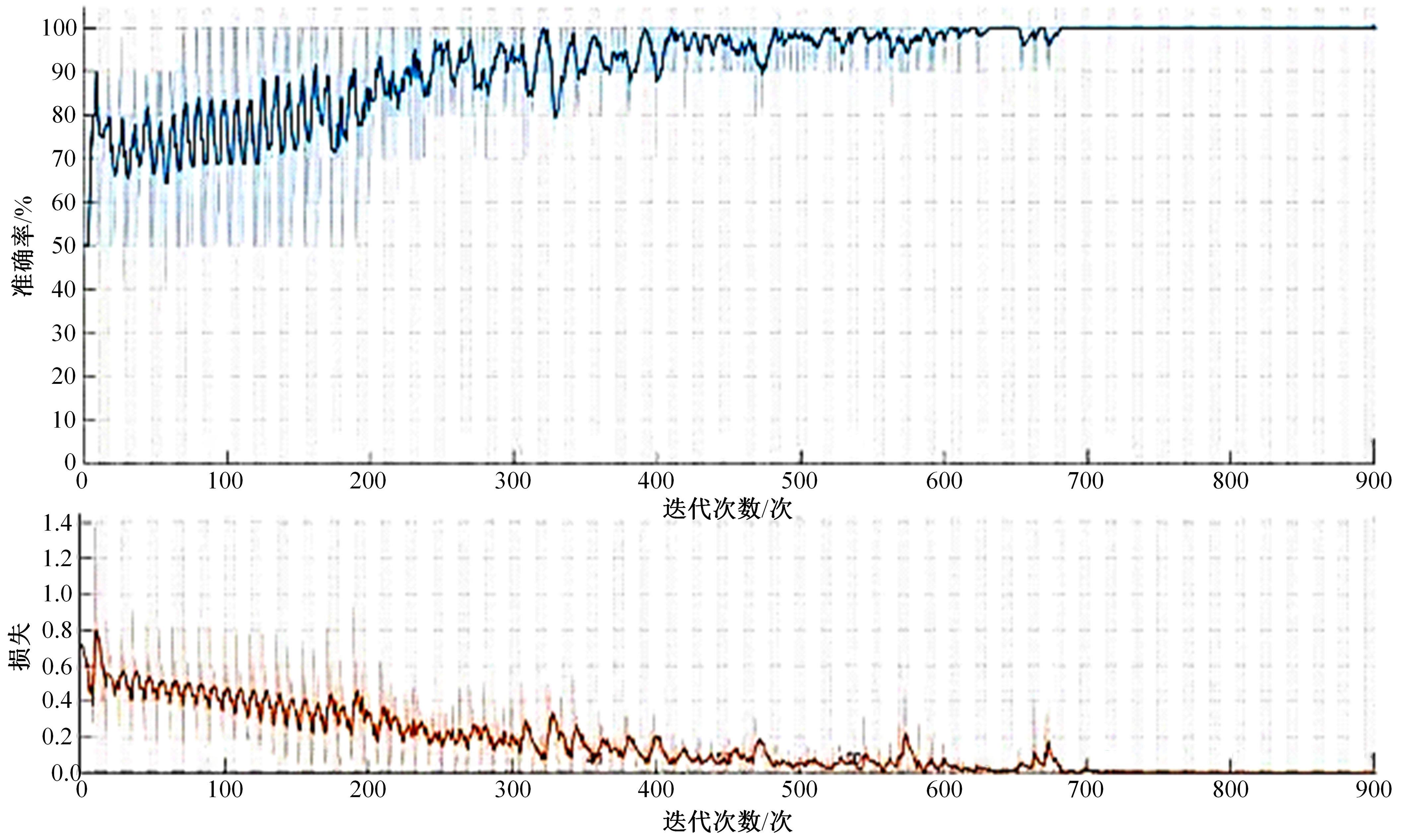
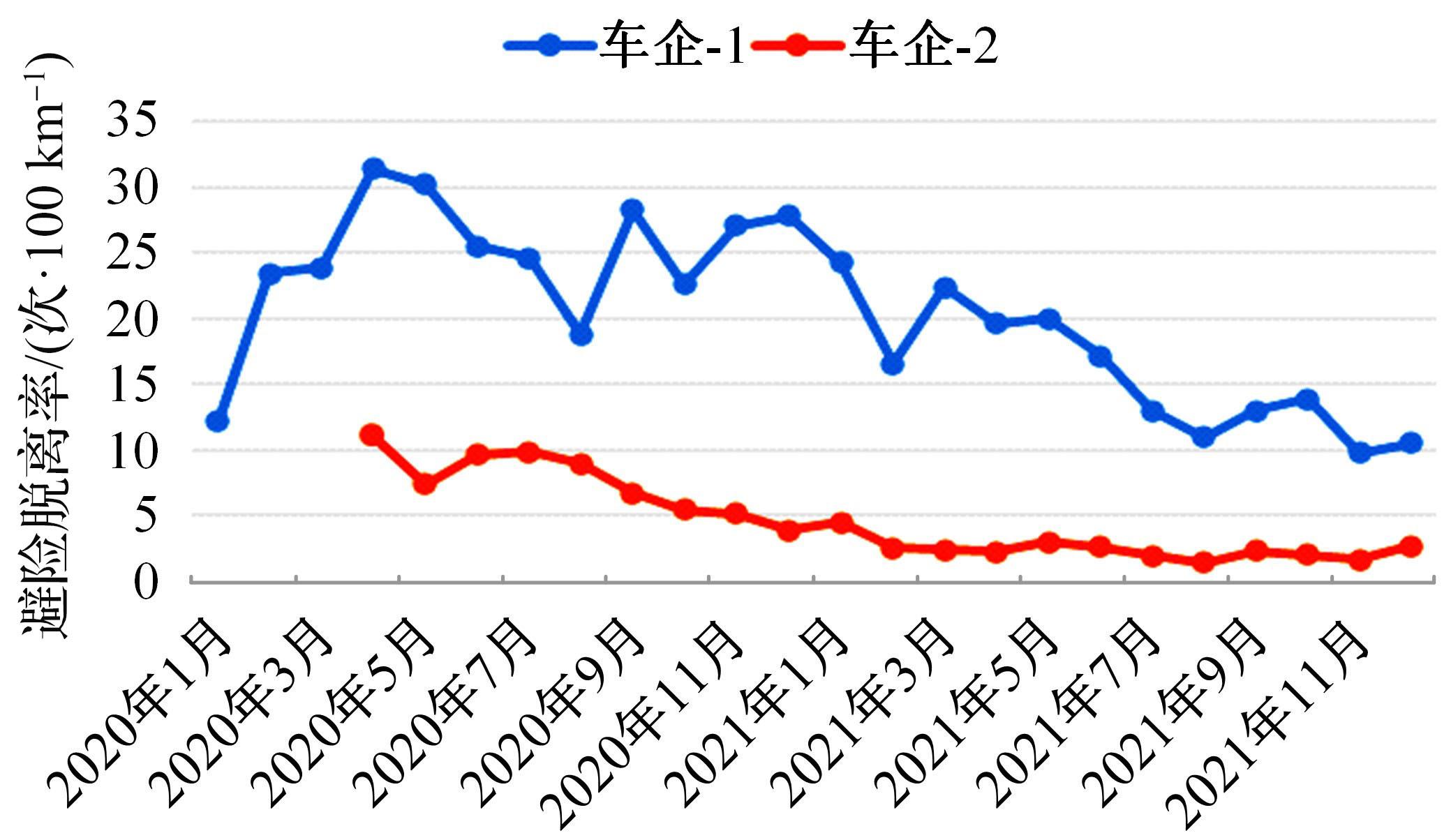
本文采用自动驾驶路测避险脱离率来表征自动驾驶路测风险。首先基于大量自动驾驶路测实测数据,采用LSTM方法辨识自动驾驶路测避险脱离,并基于Tobit模型分析车道宽度、天气等动静态因素对路测避险脱离率的影响,由此建立基于避险脱离的自动驾驶路测安全模型。本文安全模型从更为积极主动的角度来规避自动驾驶路测事故,保障自动驾驶路测安全有序地进行。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Saifuzzaman M, Zheng Z. Incorporating human-factors in car-following models: a review of recent developments and research needs[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 48: 379-403. |
| 2 | Hoogendoorn R, Van Arerm B, Hoogendoom S. Automated driving, traffic flow efficiency, and human factors: literature review[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014, 2422(1): 113-120. |
| 3 | Favarò F M, Nader N, Eurich S O, et al. Examining accident reports involving autonomous vehicles in California[J]. PLoS one, 2017, 12(9):No. e0184952. |
| 4 | Randazzo R. A slashed tire, a pointed gun, bullies on the road: why do Waymo self-driving vans get so much hate?[N]. Arizona Republic, 2018-07-12(5). |
| 5 | 王雪松, 宋洋, 黄合来, 等. 基于分层负二项模型的城郊公路安全影响因素研究[J]. 中国公路学报,2014(1): 100-106. |
| Wang Xue-song, Song Yang, Huang He-lai, et al. Analysis of risk factors for suburan highways using hierarchical negative binomial model[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014(1): 100-106. | |
| 6 | 殷炬元, 李铁男, 孙剑. 基于贝叶斯空间相关模型的城市快速路安全影响因素研究[J]. 交通信息与安全,2016,34(3): 27-33, 40. |
| Yin Ju-yuan, Li Tie-nan, Sun Jian. An analysis of effective factors of safety for urban expressways based on Bayesian spatial models[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety. 2016(3): 27-33, 40. | |
| 7 | Lord D, Mannering F. The statistical analysis of crash-frequency data: a review and assessment of methodological alternatives[J]. Transp Resarch Part A: Policy and Practice, 2010, 44(5): 291-305. |
| 8 | Miaou S P, Lum H. Modeling vehicle accidents and highway geometric design relationships[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 1993, 25(6): 689-709. |
| 9 | Miaou S P. The relationship between truck accidents and geometric design of road sections - poisson versus negative binomial regressions[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 1994, 26(4): 471-482. |
| 10 | Malyshkina N V, Mannering F. Empirical assessment of the impact of highway design exceptions on the frequency and severity of vehicle accidents[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2010, 42(1): 131-139. |
| 11 | Geedipally S R, Lord D, Dhavala S S. The negative binomial-Lindley generalized linear model: characteristics and application using crash data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2012, 45: 258-265. |
| 12 | Lord D, Miranda-Moreno L F. Effects of low sample mean values and small sample size on the estimation of the fixed dispersion parameter of Poisson-Gamma models for modeling motor vehicle crashes: a Bayesian perspective[J]. Safety Science, 2008, 46(5): 751-770. |
| 13 | Heydari S, Fu L P, Thakali L, et al. Benchmarking regions using a heteroskedastic grouped random parameters model with heterogeneity in mean and variance: applications to grade crossing safety analysis [J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2018, 19: 33-48. |
| 14 | Yu R, Wang Y, Quddus M, et al. A marginalized random effects hurdle negative binomial model for analyzing refined-scale crash frequency data[J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2019, 22:No. 100092. |
| 15 | Lord D, Washington S, Ivan J N. Further notes on the application of zero-inflated models in highway safety[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2007, 39(1): 53-57. |
| 16 | Xie Y C, Zhang Y L. Crash frequency analysis with generalized additive models[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2008, 2061(1): 39-45. |
| 17 | Zhang Y L, Xie Y C, Li L H. Crash frequency analysis of different types of urban roadway segments using generalized additive model[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2012, 43(2): 107-114. |
| 18 | Quddus M A. Time series count data models: an empirical application to traffic accidents[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2008, 40(5): 1732-1741. |
| 19 | Guo F, Wang X S, Abdel-Aty M A. Modeling signalized intersection safety with corridor-level spatial correlations[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2010, 42(1): 84-92. |
| 20 | Zou Y J, Lin B, Yang X X, et al. Application of the Bayesian model averaging in analyzing freeway traffic incident clearance time for emergency management [J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2021, 2021: No.6671983. |
| 21 | Lao Y T, Wu Y J, Corey J, et al. Modeling animal-vehicle collisions using diagonal inflated bivariate Poisson regression[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2011, 43(1): 220-227. |
| 22 | Huang H L, Chang F R, Zhou H C, et al. Modeling unobserved heterogeneity for zonal crash frequencies: a Bayesian multivariate random-parameters model with mixture components for spatially correlated data [J]. Analytic Methods in Accident Research, 2019, 24: No.100105. |
| 23 | Wang K, Ivan J N, Ravishanker N, et al. Multivariate Poisson lognormal modeling of crashes by type and severity on rural two lane highways[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2017, 99: 6-19. |
| 24 | Lao Y T, Zhang G H, Wang Y H, et al. Generalized nonlinear models for rear-end crash risk analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2014, 62: 9-16. |
| 25 | Wu L T, Zou Y J, Lord D. Comparison of sichel and negative binomial models in hot spot identification [J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014, 2460(1): 107-116. |
| 26 | Saha D, Alluri P, Dumbaugh E, et al. Application of the Poisson-Tweedie distribution in analyzing crash frequency data[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 137: No.100105. . |
| 27 | Wu L T, Meng Y, Kong X Q, et al. Incorporating survival analysis into the safety effectiveness evaluation of treatments: jointly modeling crash counts and time intervals between crashes[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2022, 14(2): 338-358. |
| 28 | Chang L Y, Chen W C. Data mining of tree-based models to analyze freeway accident frequency[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2005, 36(4): 365-375. |
| 29 | Xie Y C, Lord D, Zhang Y L. Predicting motor vehicle collisions using Bayesian neural network models: an empirical analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2007, 39(5): 922-933. |
| 30 | Li X G, Lord D, Zhang Y L, et al. Predicting motor vehicle crashes using support vector machine models [J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2008, 40(4): 1611-1618. |
| 31 | Abdel-Aty M, Haleem K. Analyzing angle crashes at unsignalized intersections using machine learning techniques[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2011, 43: 461-470. |
| 32 | Haleem K, Gan A, Lu J Y. Using multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) to develop crash modification factors for urban freeway interchange influence areas[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2013, 55: 12-21. |
| 33 | Zeng Q, Huang H L, Pei X, et al. Rule extraction from an optimized neural network for traffic crash frequency modeling[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2016, 97: 87-95. |
| 34 | Zhang X, Waller S T, Jiang P. An ensemble machine learning-based modeling framework for analysis of traffic crash frequency[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2020, 35(3): 258-76. |
| 35 | Pu Z Y, Li Z B, Ke R M, et al. Evaluating the nonlinear correlation between vertical curve features and crash frequency on highways using random forests [J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(10): No.4020115. |
| 36 | Wen X, Xie Y, Wu L, et al. Quantifying and comparing the effects of key risk factors on various types of roadway segment crashes with LightGBM and SHAP[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 159: No.106261. |
| 37 | Anastasopoulos P C, Tarko A P, Mannering F L. Tobit analysis of vehicle accident rates on interstate highways[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2008, 40: 768-775. |
| 38 | Guo Y, Li Z, Liu P, et al. Modeling correlation and heterogeneity in crash rates by collision types using full Bayesian random parameters multivariate Tobit model[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 128: 164-174. |
| 39 | Zeng Q, Wen H, Huang H, et al. A Bayesian spatial random parameters Tobit model for analyzing crash rates on roadway segments[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2017, 100: 37-43. |
| 40 | Xu C, Ding Z, Wang C, et al. Statistical analysis of the patterns and characteristics of connected and autonomous vehicle involved crashes[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 71: 41-47. |
| 41 | Chen H, Chen H, Liu Z, et al. Analysis of factors affecting the severity of automated vehicle crashes using XGBoost model combining POI data[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 2020:No.8881545. |
| 42 | Boggs A M, Wali B, Khattak A J. Exploratory analysis of automated vehicle crashes in California: a text analytics & hierarchical Bayesian heterogeneity-based approach[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 135:No. 105354. |
| 43 | 涂辉招, 崔航, 鹿畅, 等. 面向自动驾驶路测驾驶能力评估的避险脱离率模型 [J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版,2020,48(11): 1562-1569. |
| Tu Hui-zhao, Cui Hang, Lu Chang, et al. A risk-avoiding disengagement frequency model for assessing driving ability of autonomous vehicles in road testing[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2020,48(11):1562-1569. | |
| 44 | Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2014. |
| 45 | Ordóñez F J, Roggen D. Deep convolutional and lstm recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(1): No.e115. |
| 46 | Hou Q, Meng X, Leng J, et al. Application of a random effects negative binomial model to examine crash frequency for freeways in China[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 509: 937-944. |
| 47 | Hair J F, Black W C, Babin B J, et al. Multivariate Data Analysis[M].London: Pearson Education Limited, 2013. |
| [1] | 胡钊政,孙勋培,张佳楠,黄戈,柳雨婷. 基于时空图模型的车-路-图协同定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1246-1257. |
| [2] | 涂辉招,王万锦,乔鹏,郭静秋,鹿畅,吴海飞. 自动驾驶卡车路测安全员接管干预行为解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 727-740. |
| [3] | 李津,孙雨彤,魏小忠,焦玉玲. 考虑柔性车道设置的公交优先信号设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 448-456. |
| [4] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [5] | 李文勇,马从若,胡清玮,刘承堃,廉冠,顾国斌,周旦. 基于站台容量限制和路段绿波控制的公交速度引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3088-3103. |
| [6] | 徐洪峰, 高霜霜, 郑启明, 章琨. 信号控制交叉口的复合动态车道管理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 430-439. |
| [7] | 王海玮, 温惠英, 刘敏. 夜间环境驾驶员精神负荷的生理特性评估与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 420-428. |
| [8] | 姜桂艳, 刘彬, 隋晓艳, 马明芳. 基于IC卡收费系统的公交客流信息实时采集方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1076-1082. |
| [9] | 宗芳, 王占中, 贾洪飞, 焦玉玲, 吴杨. 基于支持向量机的通勤日活动-出行持续时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 406-411. |
| [10] | 李世武, 徐艺, 孙文财, 王琳虹, 郭梦竹, 柴萌. 基于瞳孔直径的撞固定物冲突自反馈识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 418-425. |
| [11] | 潘义勇, 马健霄, 孙璐. 基于可靠度的动态随机交通网络耗时最优路径[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 412-417. |
| [12] | 赵淑芝, 梁士栋, 马明辉, 刘华胜, 朱永刚. 信号交叉口实时排队长度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 85-91. |
| [13] | 刘华胜,赵淑芝,朱永刚,李晓玉. 基于有效路径的轨道交通接运线路设计模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [14] | 祝进城,肖峰,帅斌,刘晓波. 城市出租车拥挤收费[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 89-96. |
| [15] | 游峰, 张荣辉, 王海玮, 徐建闽, 温惠英. 欠驱动半挂汽车列车的运动建模与跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1296-1302. |
|
||