吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 681-686.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230384
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于因果特征学习的有权同构图分类算法
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning
Xiang-jiu CHE( ),Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU
),Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
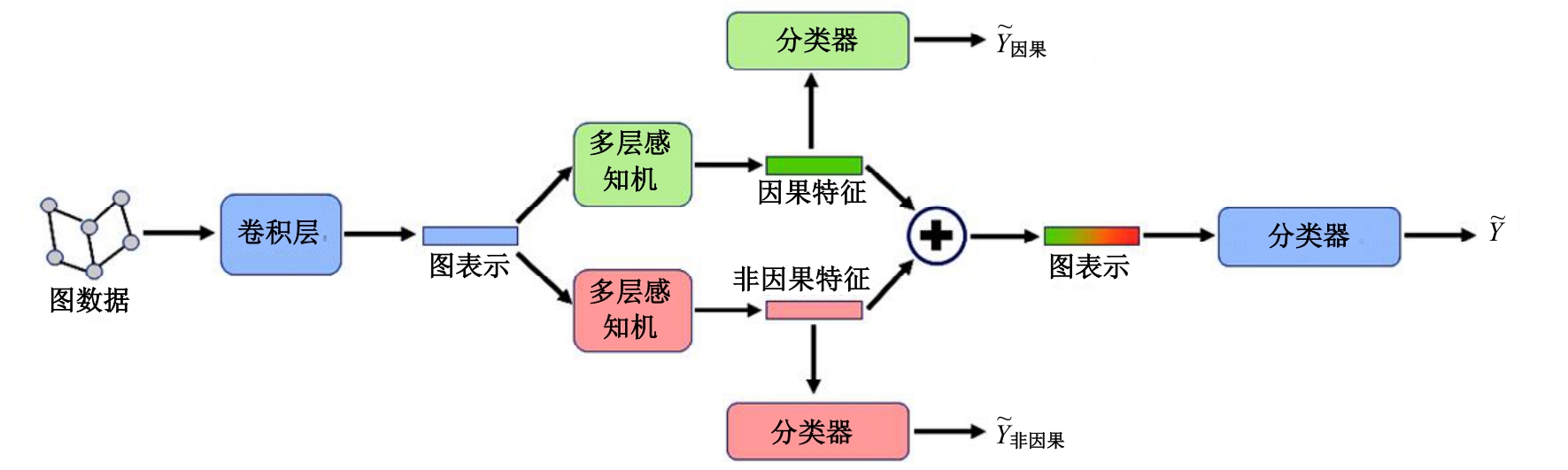
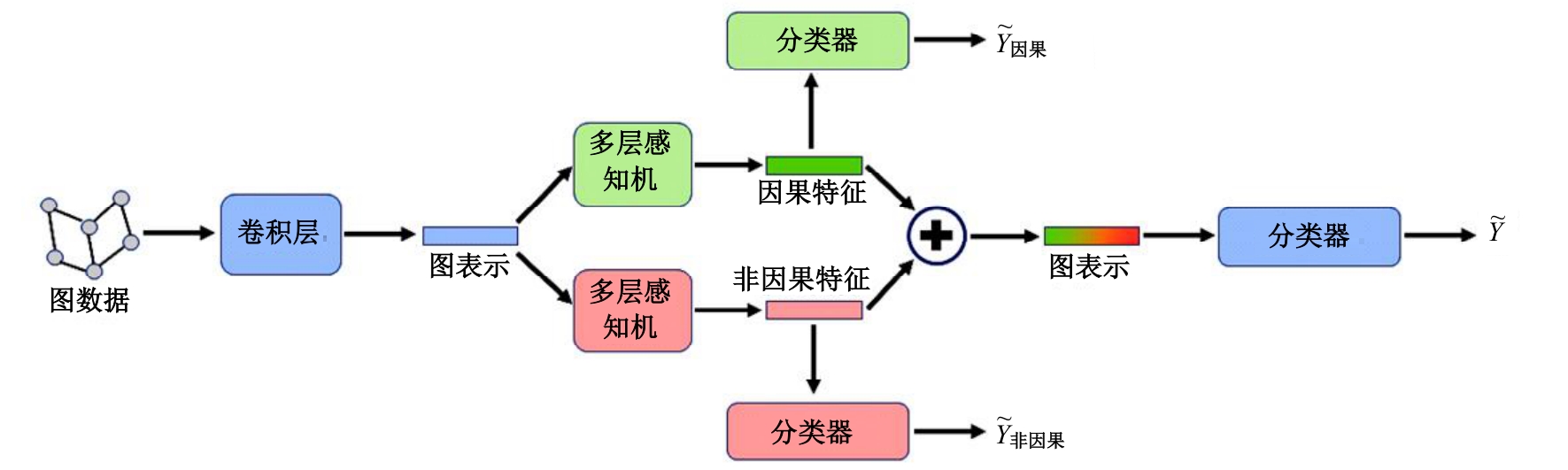
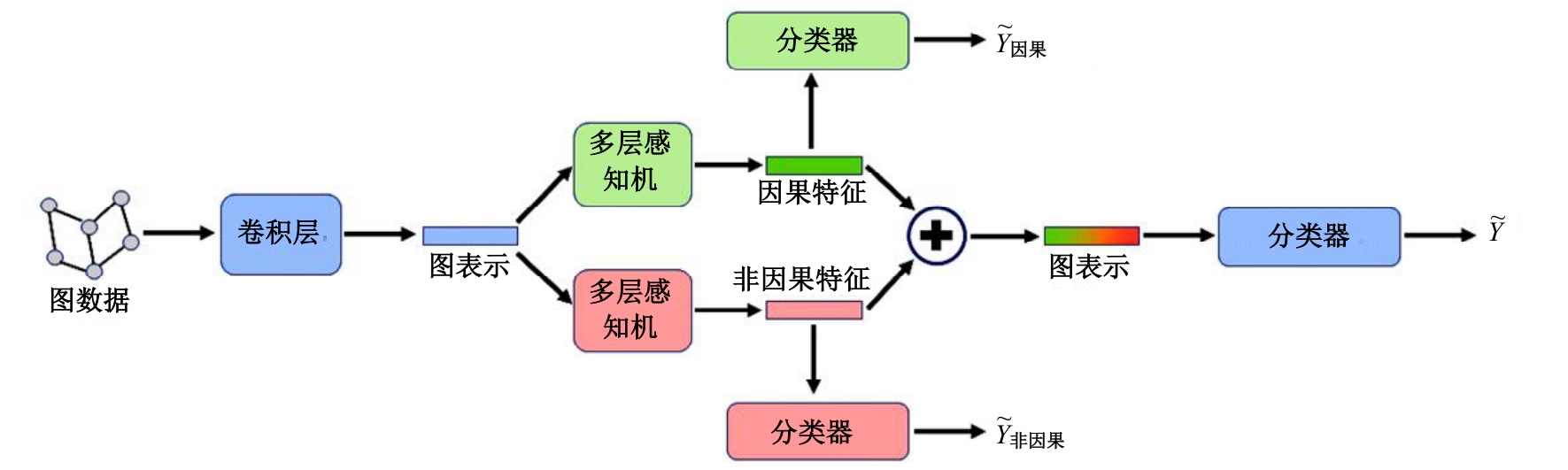
针对现有神经网络方法对心梗患者Killip分级预测精度不足的问题,提出了一种能够学习因果特征的有权同构图分类算法。使用差异化的学习目标来分离图表示中的因果相关特征和非因果相关特征,再使用因果推理中的后门调整方法,减小了非因果特征对分类结果的混淆影响。实验结果表明:在心梗患者Killip分级预测任务中,本文方法的平均准确度达到了80.52%,相比于非图神经网络方法提高了3.72%,而相比于未学习因果特征的图神经网络方法提高了0.72%,本文方法可以更好地完成心梗患者Killip分级预测的任务。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Kipf T N, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[J/OL].[2023-03-05]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 2 | Wu Y X, Wang X, Zhang A, et al. Discovering invariant rationales for graph neural networks[J/OL]. [2023-03-06].arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.12872v1 . |
| 3 | Sui Y, Wang X, Wu J, et al. Causal attention for interpretable and generalizable graph classification[C]∥ Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, USA, 2022: 1696-1705. |
| 4 | Fan S, Wang X, Mo Y, et al. Debiasing graph neural networks via learning disentangled causal substructure[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New York, USA, 2022: 3602078. |
| 5 | 徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. |
| Xu Bing-bing, Cen Ke-ting, Huang Jun-jie, et al. A survey on graph convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. | |
| 6 | 王兆慧, 沈华伟, 曹婍, 等. 图分类研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33(1): 171-192. |
| Wang Zhao-hui, Shen Hua-wei, Cao Qi, et al. Survey on graph classification[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33(1): 171-192. | |
| 7 | Geirhos R, Jacobsen J H, Michaelis C, et al. Shortcut learning in deep neural networks[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(11): 665-673. |
| 8 | Geirhos R, Rubisch P, Michaelis C, et al. Imagenet-trained CNNs are biased towards texture; increasing shape bias improves accuracy and robustness[J/OL].[2023-03-07]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 9 | Arjovsky M, Bottou L, Gulrajani I, et al. Invariant risk minimization[J/OL].[2023-03-08] .arXiv preprint, arXiv:. |
| 10 | Knyazev B, Taylor G W, Amer M. Understanding attention and generalization in graph neural networks[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 190502850. |
| 11 | Pearl J, Mackenzie D. The Book of Why: The New Science of Cause and Effect[M]. New York: Basic books, 2018. |
| 12 | Jia Z, Lin Y, Wang J, et al. Hetemotionnet: two-stream heterogeneous graph recurrent neural network for multi-modal emotion recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 2021: 1047-1056. |
| [1] | 张玺君,余光杰,崔勇,尚继洋. 基于聚类算法和图神经网络的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1593-1600. |
| [2] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [3] | 拉巴顿珠,扎西多吉,珠杰. 藏语文本标准化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3577-3588. |
| [4] | 车娜,朱奕明,赵剑,孙磊,史丽娟,曾现伟. 基于联结主义的视听语音识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2984-2993. |
| [5] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [6] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [7] | 王振,杨宵晗,吴楠楠,李国坤,冯创. 基于生成对抗网络的序列交叉熵哈希[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3536-3546. |
| [8] | 周丰丰,颜振炜. 基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
| [9] | 董立岩,梁伟业,王越群,李永丽. 基于会话的结合全局潜在信息的图神经网络推荐模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2964-2972. |
| [10] | 王俊杰,农元君,张立特,翟佩臣. 基于施工场景的视觉关系检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 226-233. |
| [11] | 朱冰,李紫薇,李奇. 基于改进SegNet的遥感图像建筑物分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 248-254. |
| [12] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [13] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [14] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [15] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
|
||