吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1872-1880.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210961
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别
白天1,2( ),徐明蔚3,刘思铭4,张佶安3,王喆1,2(
),徐明蔚3,刘思铭4,张佶安3,王喆1,2( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.吉林大学 软件学院,长春 130012
4.吉林大学 法学院,长春 130012
Dispute focus identification of pleading text based on deep neural network
Tian BAI1,2( ),Ming-wei XU3,Si-ming LIU4,Ji-an ZHANG3,Zhe WANG1,2(
),Ming-wei XU3,Si-ming LIU4,Ji-an ZHANG3,Zhe WANG1,2( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
4.School of Law,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
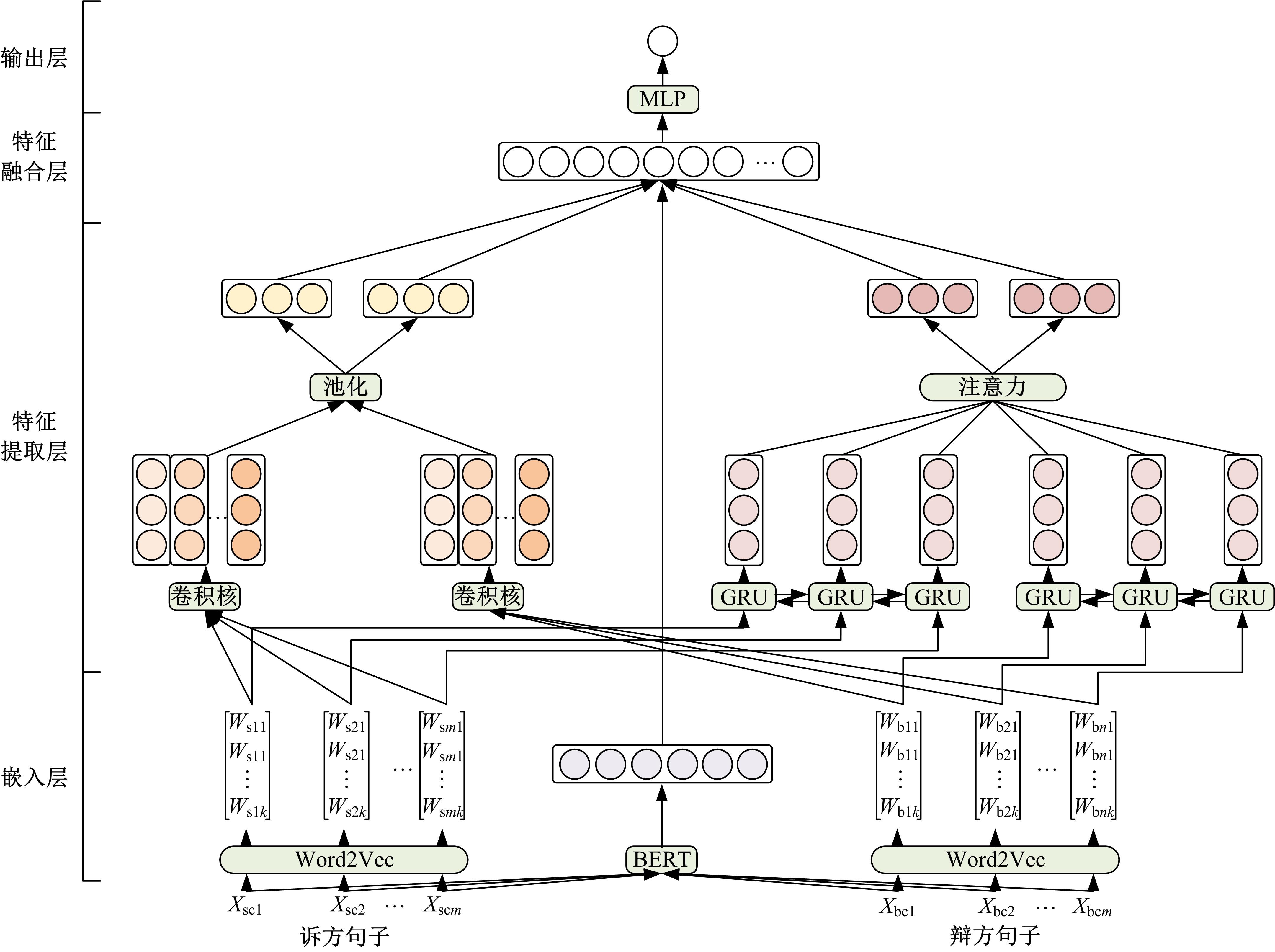
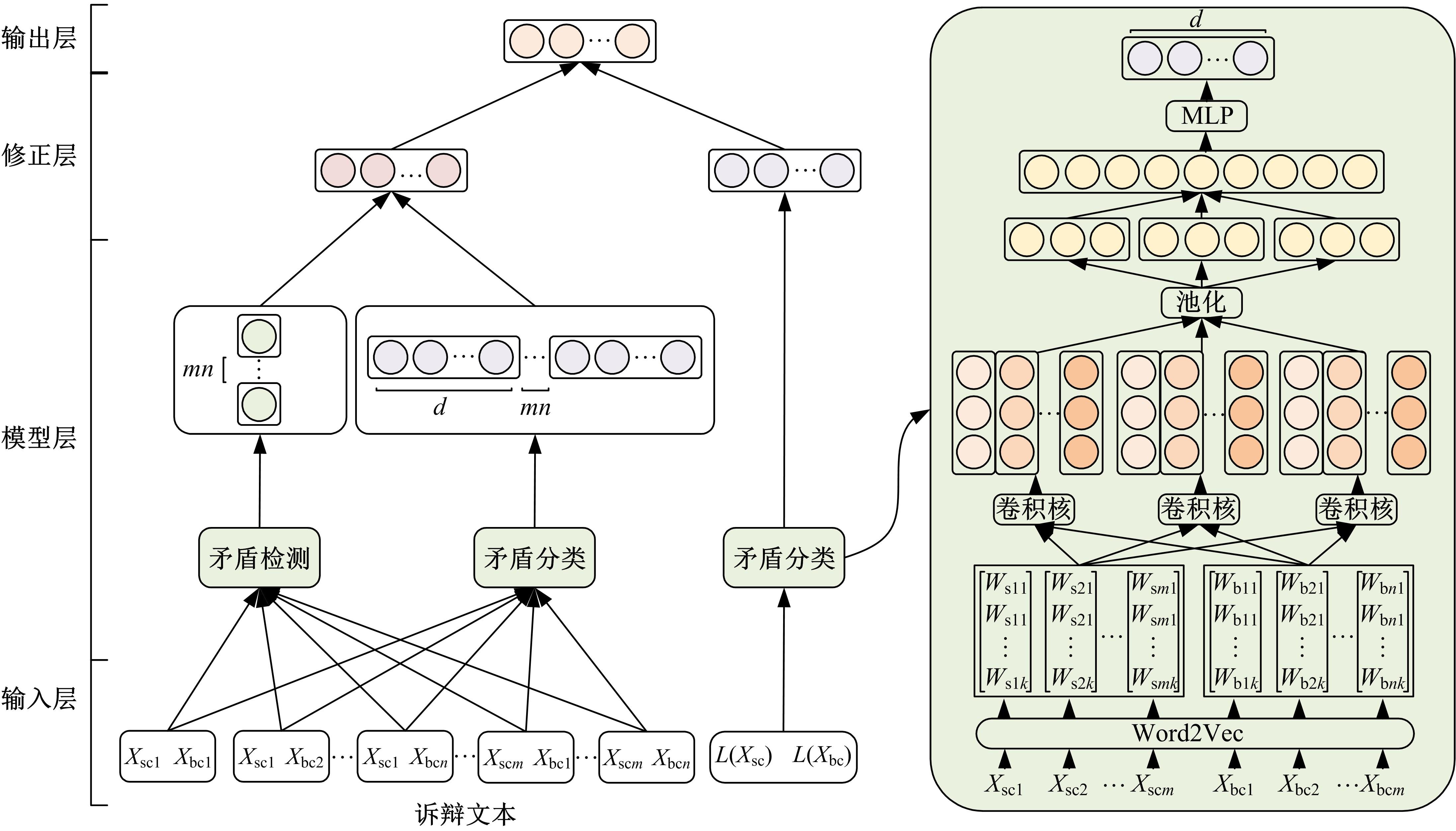
争议焦点是诉辩双方存在争议的焦点问题,是驱动案件审理、纠纷解决的主线和枢纽。准确快速地归纳争议焦点有利于提高庭审质量和效率,达到支撑“智慧司法”建设的效果。本文提出了一个端到端的模型来解决这个问题,模型基于深度神经网络对诉辩双方文本语义信息进行深层理解,通过结合字词级与句子级信息,同时进行句子级的矛盾检测、分类与完整诉辩文本的矛盾分类,通过基于规则的方法将二者结果融合,最终识别出诉辩文本中存在的全部争议焦点。在8个真实诉辩文本数据集上的实验结果表明:本文模型可以快速准确地识别出诉辩双方存在的争议焦点,与此领域当前主流方法相比,在识别准确率上有较大提升,对诉辩文本争议焦点的智能化识别提出了一个有效的新路径。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | 蔡立东. 智慧法院建设: 实施原则与制度支撑[J]. 中国应用法学, 2017(2): 19-28. |
| Cai Li-dong. Construction of intellectual court: principle of implementation and institutional support[J]. China Journal of Applied Jurisprudence, 2017(2): 19-28. | |
| 2 | 蔡立东. 信息技术创新开启法学研究新时代[J]. 中国社会科学文摘, 2018(6): 121-122. |
| Cai Li-dong. New era of jurisprudential research launched by information technology innovation[J]. Chinese Social Science Digest, 2018(6): 121-122. | |
| 3 | Zhong H, Xiao C, Guo Z, et al. Overview of CAIL2018: legal judgment prediction competition[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:. |
| 4 | Tran V, Nguyen M L, Satoh K. Building legal case retrieval systems with lexical matching and summarization using a pre-trained phrase scoring model[C]∥Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law, Montreal, Canada, 2019: 275-282. |
| 5 | Kim M Y, Goebel R. Two-step cascaded textual entailment for legal bar exam question answering[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th Edition of the International Conference on Articial Intelligence and Law, London, United Kingdom, 2017: 283-290. |
| 6 | Kort F. Predicting supreme court decisions mathematically: a quantitative analysis of the "right to counsel" cases[J]. American Political Science Review, 1957, 51(1): 1-12. |
| 7 | Gardner A L. An artificial intelligence approach to legal reasoning[D]. San Francisco: Stanford Law School, Stanford University, 1984. |
| 8 | Zhong H, Xiao C, Tu C, et al. How does NLP benefit legal system: a summary of legal artificial intelligence[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: . |
| 9 | 欧阳丹彤, 肖君, 叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3):912-919. |
| Dan-tong Ou-yang, Xiao Jun, Ye Yu-xin. Distant supervision for relation extraction with weak constraints of entity pairs[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3):912-919. | |
| 10 | 刘桂霞,王沫沅,苏令涛,等.基于深度神经网络的蛋白质相互作用预测框架[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(2): 570-577. |
| Liu Gui-xia, Wang Mo-yuan, Su Ling-tao, et al. Prediction of protein-protein interactions based on deep neural networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(2): 570-577. | |
| 11 | Chen H, Cai D, Dai W, et al. Charge-based prison term prediction with deep gating network[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, HongKong, China, 2019: 6362-6367. |
| 12 | Luo B, Feng Y, Xu J, et al. Learning to predict charges for criminal cases with legal basis[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017: 2727-2736. |
| 13 | Zhong H, Guo Z, Tu C, et al. Legal judgment prediction via topological learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 2018: 3540-3549. |
| 14 | Deerwester S, Dumais S T, Furnas G W, et al. Indexing by latent semantic analysis[J]. Journal of the Association for Information Science & Technology, 2010, 41(6): 391-407. |
| 15 | Blei D M, Ng A Y, Jordan M I. Latent dirichlet allocation[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2013, 3(7): 993-1022. |
| 16 | Hu B T, Lu Z D, Hang L, et al. Convolutional neural network architectures for matching natural language sentences[C]∥Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 2042-2050. |
| 17 | Feng M, Xiang B, Glass M R, et al. Applying deep learning to answer selection: a study and an open task[C]∥EEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Scottsdale, USA, 2015: 813-820. |
| 18 | Mueller J, Thyagarajan A. Siamese recurrent architectures for learning sentence similarity[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, USA, 2016: 2786-2792. |
| 19 | Yin W, Schütze H, Xiang B, et al. ABCNN: attention-based convolutional neural network for modeling sentence pairs[J]. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016, 4: 259-272. |
| 20 | Wang Z, Hamza W, Florian R. Bilateral multi-perspective matching for natural language sentences[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 4144-4150. |
| 21 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: . |
| 22 | Chen Y. Convolutional neural network for sentence classification[D]. Waterloo: University of Waterloo, 2015. |
| 23 | Schuster M, Paliwal K K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(11): 2673-2681. |
| 24 | Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: . |
| 25 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]∥NIPS'17: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, California, USA,2017: 6000-6010. |
| 26 | Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. |
| 27 | Yang Z, Yang D, Dyer C, et al. Hierarchical attention networks for document classification[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, California, USA, 2016: 1480-1489. |
| [1] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [2] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [3] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [4] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [6] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [7] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [8] | 王春波,底晓强. 基于标签分类的云数据完整性验证审计方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1364-1369. |
| [9] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [10] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [11] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [12] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [13] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [14] | 周炫余, 刘娟, 邵鹏, 罗飞, 刘洋. 基于层次过滤模型的中文指代消解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1209-1215. |
| [15] | 胡冠宇, 乔佩利. 基于云群的高维差分进化算法及其在网络安全态势预测上的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 568-577. |
|
||