吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 891-901.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221288
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法
- 1.长春理工大学 机电工程学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 重庆研究院,重庆 401135
Anti⁃unmanned aerial vehicle system object detection algorithm under complex background
Shan XUE1,2( ),Ya-liang ZHANG1,Qiong-ying LYU1,Guo-hua CAO2
),Ya-liang ZHANG1,Qiong-ying LYU1,Guo-hua CAO2
- 1.College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.Chongqing Research Institute,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Chongqing 401135,China
摘要:
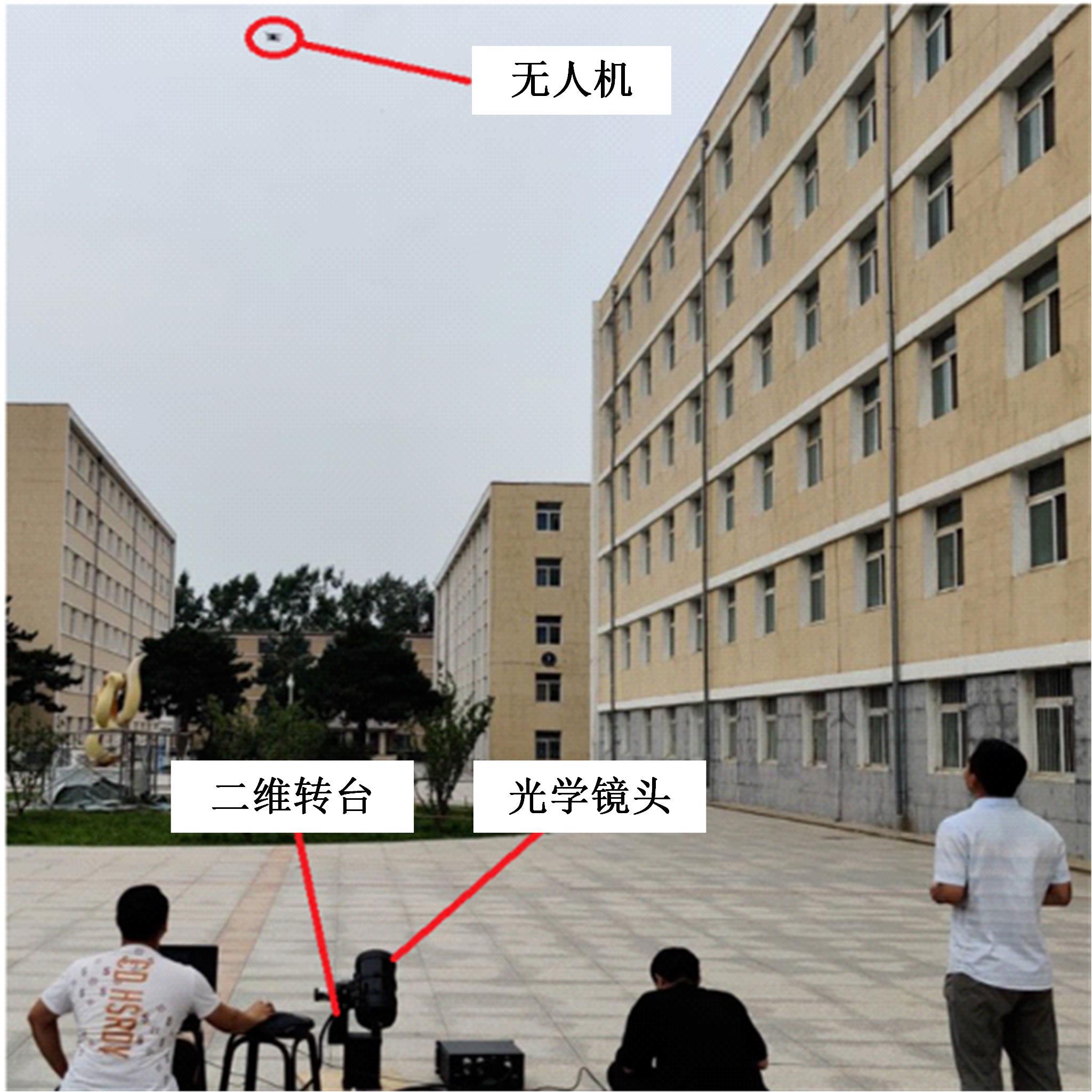
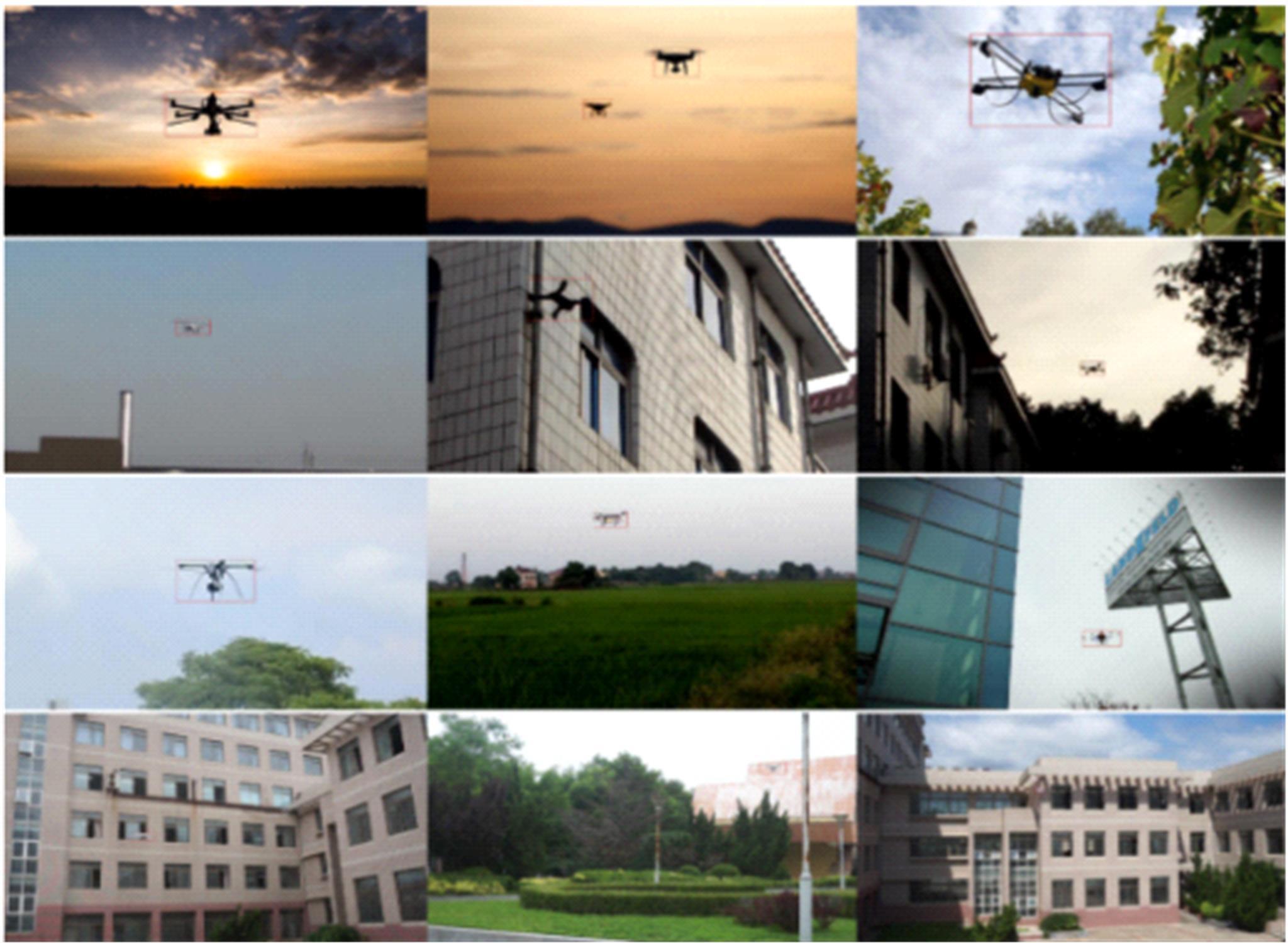
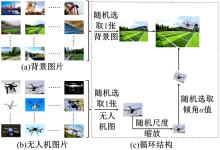
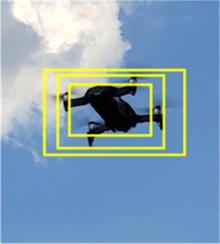
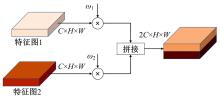
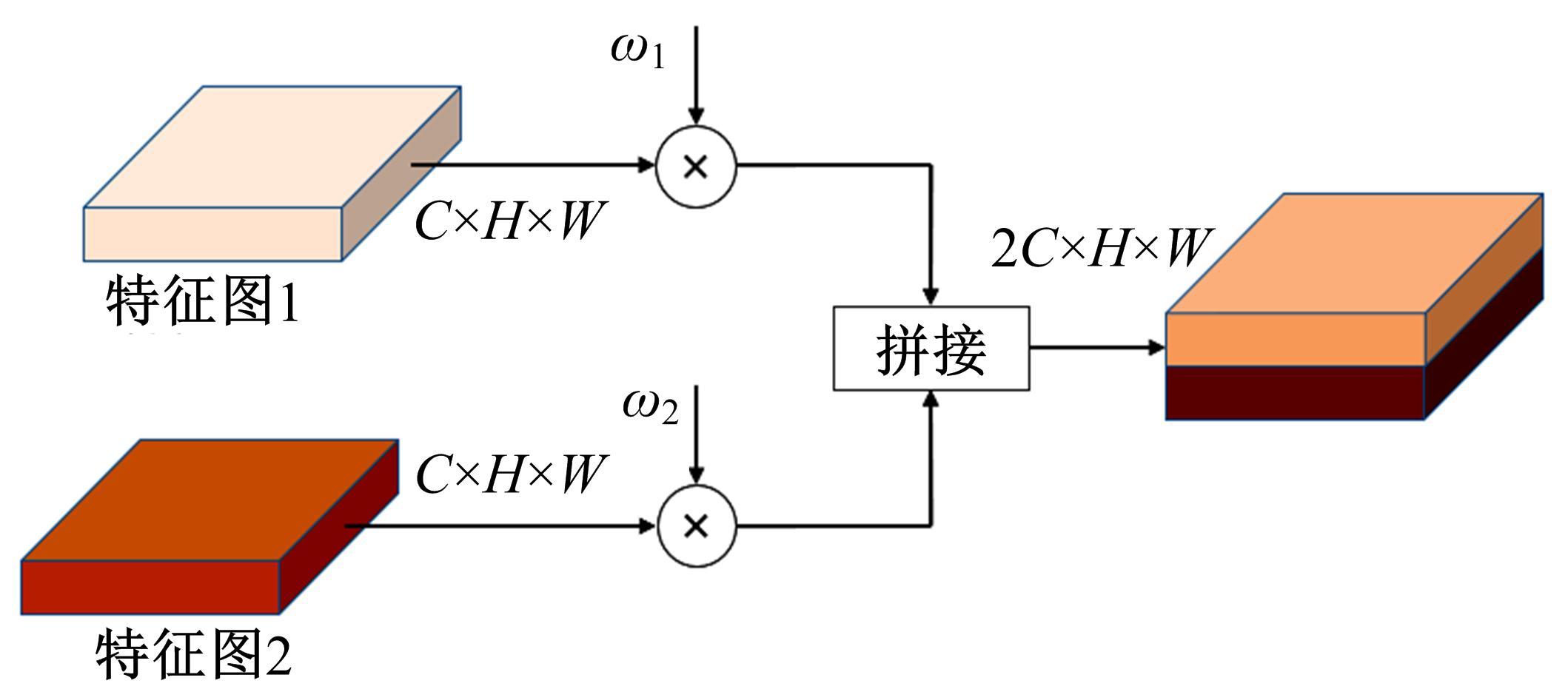
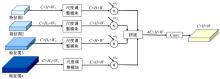
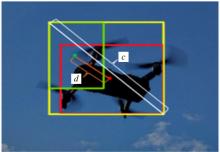
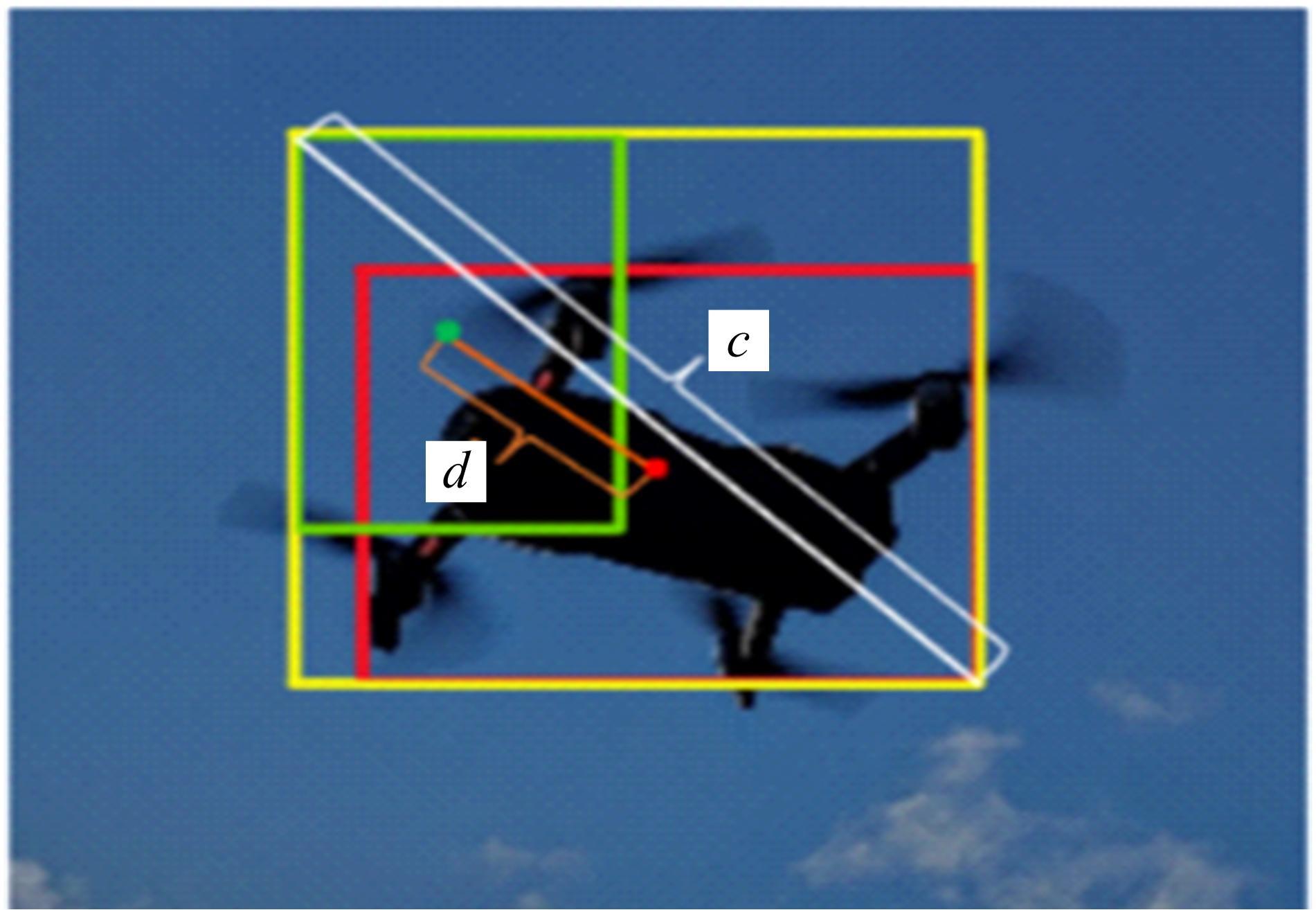
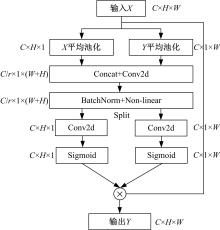
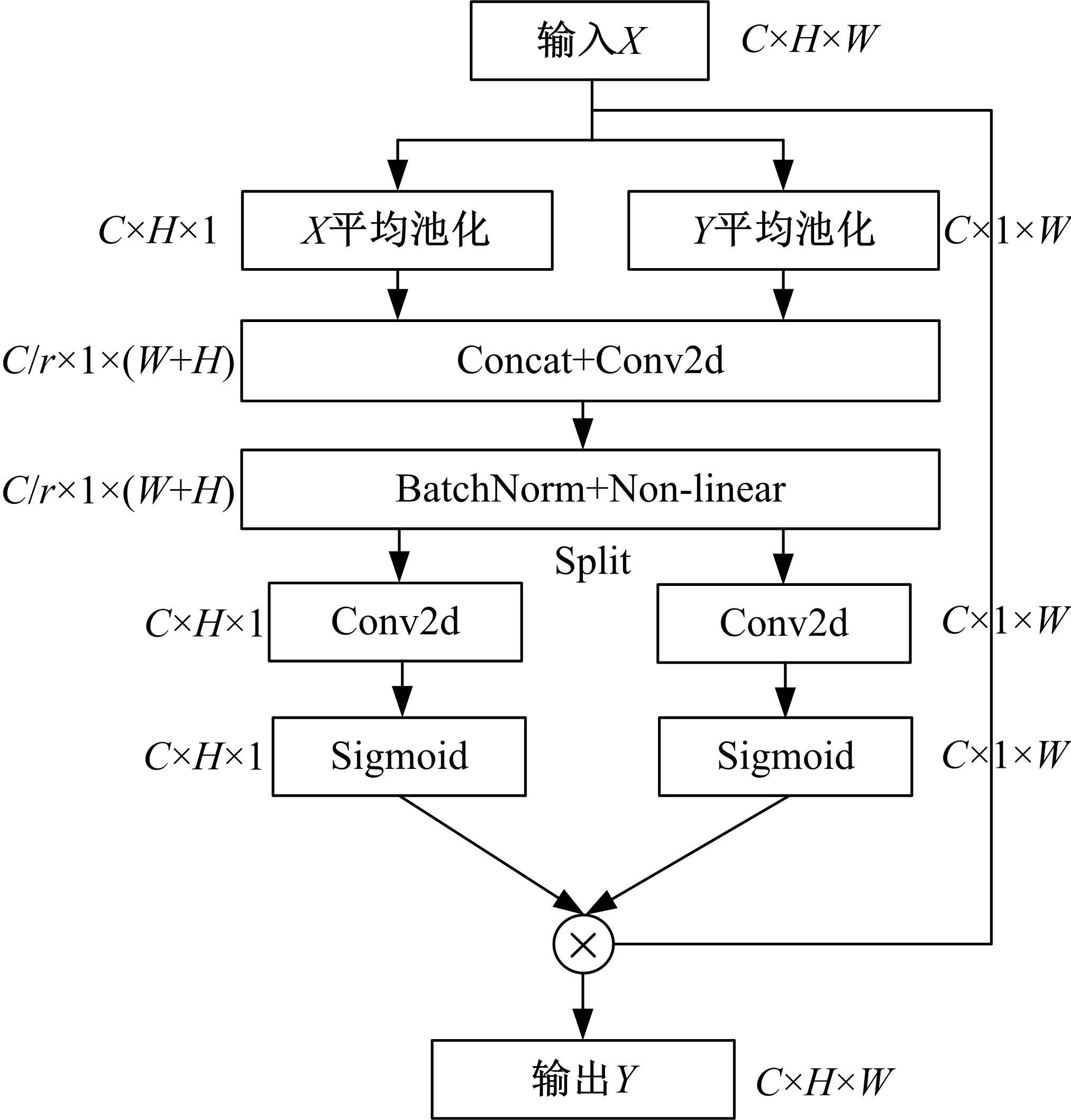
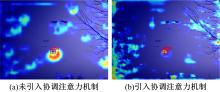
针对在公园、游乐场、体育场等具有复杂飞行背景的公共安全区域对无人机进行实时检测困难的问题,提出了一种基于注意力机制和尺度自适应特征融合的YOLOv5-UAV反无人机系统目标检测算法。首先,运用自拍图片和公共数据集DUT-Anti-UAV融合,构建了无人机数据集;其次,使用k-means方法重新设计先验框;再次,设计了尺度自适应特征融合模块;然后,采用CIoU损失函数作为算法的定位损失函数;最后,在主干网络引入协调注意力机制。在无人机航拍数据集VisDrone2019上进行对比实验,改进算法YOLOv5-UAV对所有类别的平均准确率(mAP@0.5)均高于原始算法YOLOv5s,且对复杂背景下的小目标检测效果较好,表明了改进算法的普适性。将改进的算法YOLOv5-UAV与基线算法YOLOv5s在建立的数据集上进行对比实验,实验结果表明,YOLOv5-UAV与YOLOv5s相比,在准确率、召回率、平均准确率(mAP@0.5)上分别提高了6.1%、5.8%、5.2%,检测速度为39 帧/s;在建立的数据集上,与YOLOv5m、YOLOv5l、YOLOX目标检测算法进行对比实验,改进算法的平均准确率(mAP@0.5)分别高于对比算法4.4%、3.6%、1.3%,表明了改进算法的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | 高明华, 杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2022, 52(6), 1353-1361. |
| Gao Ming-hua, Yang Can. Traffic target detection method based on improved convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. | |
| 2 | 薛珊, 卫立炜, 顾宸瑜, 等. 采用混合域注意力机制的无人机识别方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(10): 141-150. |
| Xue Shan, Wei Li-wei, Gu Chen-yu, et al. Drone identification method based on mixed domain attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(10): 141-150. | |
| 3 | 薛珊, 陈宇超, 吕琼莹, 等. 基于坐标注意力机制融合的反无人机系统图像识别方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2022, 51(9): 1-11. |
| Xue Shan, Chen Yu-chao, Lv Qiong-ying, et al. Image recognition method of anti drone system based on coordinate attention mechanism[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(9): 1-11. | |
| 4 | 朱孟真, 陈霞, 刘旭, 等. 战术激光武器反无人机发展现状和关键技术分析[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(7): 1-13. |
| Zhu Meng-zhen, Chen Xia, Liu Xu, et al. Situation and key technology of tactical laser anti-UAV[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(7): 1-13. | |
| 5 | 朱威, 王立凯, 靳作宝, 等. 引入注意力机制的轻量级小目标检测网络[J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(8): 998-1010. |
| Zhu Wei, Wang Li-kai, Jin Zuo-bao, et al. Lightweight small object detection network with attention mechanism[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(8): 998-1010. | |
| 6 | 严春满, 王钺. 基于特征增强的SAR图像舰船小目标检测算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(1): 239-247. |
| Yan Chun-man, Wang Yue. A ship small target detection algorithm based on feature enhancement in SAR image[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(1): 239-247. | |
| 7 | 陈欣, 万敏杰, 马超, 等. 采用多尺度特征融合SSD的遥感图像小目标检测[J]. 光学精密工程, 2021, 29(11): 2672-2682. |
| Chen Xin, Wan Min-jie, Ma Chao, et al. Recognition of small targets in remote sensing image using multi-scale feature fusion-based shot multi-box detector[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2021, 29(11): 2672-2682. | |
| 8 | 陈海燕, 甄霞军, 赵涛涛. 一种通道-空间注意力机制特征融合的小目标检测模型[J/OL]. [2022-09-23]. |
| 9 | 苏佳,贾欣雨,侯卫民. 基于YOLO-J的PCB缺陷检测算法[J/OL]. [2022-09-25]. |
| 10 | 邵盼愉. 基于视觉的无人机入侵检测与跟踪系统设计与实现[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院,2018. |
| Shao Pan-yu. Design and implementation of vision based drone intrusion detection and tracking system [D]. Hangzhou: College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2018. | |
| 11 | 王晓. 视频中无人机的实时检测与跟踪算法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学信息与通信工程学院,2019. |
| Wang Xiao. Research on real-time detection and tracking algorithm of UAV in video[D]. Harbin: College of Information and Communication Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, 2019. | |
| 12 | 王子哲. 基于视频的无人机目标检测算法研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学信息工程学院, 2019. |
| Wang Zi-zhe. Research on UAV target detection algorithm based on video[D]. Zhengzhou: College of Information Engineering, Zhengzhou University, 2019. | |
| 13 | 崔艳鹏, 王元皓, 胡建伟. 一种改进YOLOv3的动态小目标检测方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(3): 1-7. |
| Cui Yan-peng, Wang Yuan-hao, Hu Jian-wei. Detection method for a dynamic small target using the improved YOLOv3[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2020, 47(3): 1-7. | |
| 14 | 吴曼佳. 基于视觉的多尺度低空小型无人机检测系统[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Wu Man-jia. Multi-scale target detection system for low-altitude small UAV based on vision[D]. Hangzhou: College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2020. | |
| 15 | 陶磊, 洪韬, 钞旭. 基于YOLOv3的无人机识别与定位追踪[J]. 工程科学学报, 2020, 42(4): 463-468. |
| Tao Lei, Hong Tao, Chao Xu. Drone identification and location tracking based on YOLOv3[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 463-468. | |
| 16 | Zhao J, Zhang J H, Li D D, et al. Vision-based anti-UAV detection and tracking[EB/OL]. [2022-09-28]. |
| 17 | He K, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. |
| 18 | Kalayeh M M, Shah M. Training faster by separating modes of variation in batch-normalized models[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2020, 42(6): 1483-1520. |
| 19 | Liu S, Qi L, Qin H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8759-8768. |
| 20 | Tan M X, Pang R M, Le Q V. Scalable and efficient object detection[EB/OL]. [2022-09-28]. |
| 21 | Liu S T, Huang D, Wang Y H. Learning spatial fusion for single-shot object detection[EB/OL]. [2022-09-29]. |
| 22 | Rezatofighi H, Tsoi N, Gwak J, et al. A metric and a loss for bounding box regression[EB/OL]. [2022-09-29]. |
| 23 | Zheng Z H, Wang P, Liu W, et al. Faster and better learning for bounding box regression[EB/OL]. [2022-09-29]. |
| 24 | Hou Q B, Zhou D Q, Feng J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, 2021: 13713-13722. |
| 25 | Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, et al. Learning Deep features for discriminative localization[EB/OL].[2022-10-01]. |
| 26 | Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1137-1149. |
| 27 | Ge Z, Liu S T, Wang F, et al. YOLOX: exceeding YOLO series in 2021[EB/OL]. [2022-09-30]. |
| 28 | Du D W, Zhu P F, Wen L Y, et al. VisDrone-Det2019: the vision meets drone object detection in image challenge resulted[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 213-226. |
| [1] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [2] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [4] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [5] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [6] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [7] | 刘铭,杨雨航,邹松霖,肖志成,张永刚. 增强边缘检测图像算法在多书识别中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 891-896. |
| [8] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [9] | 王生生,李晨旭,王翔宇,姚志林,刘一申,吴佳倩,杨晴然. 基于改进残差胶囊网络和麻雀搜索的脑瘤图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2653-2661. |
| [10] | 车翔玖,陈赫元. 基于改进YOLOv4的多目标光盘检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2662-2668. |
| [11] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [12] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [13] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [14] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [15] | 潘德伦,冀隽,张跃进. 基于运动矢量空间编码的视频监控动态目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1370-1374. |
|
||