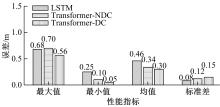
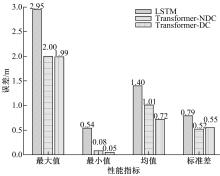
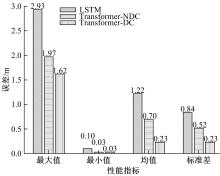
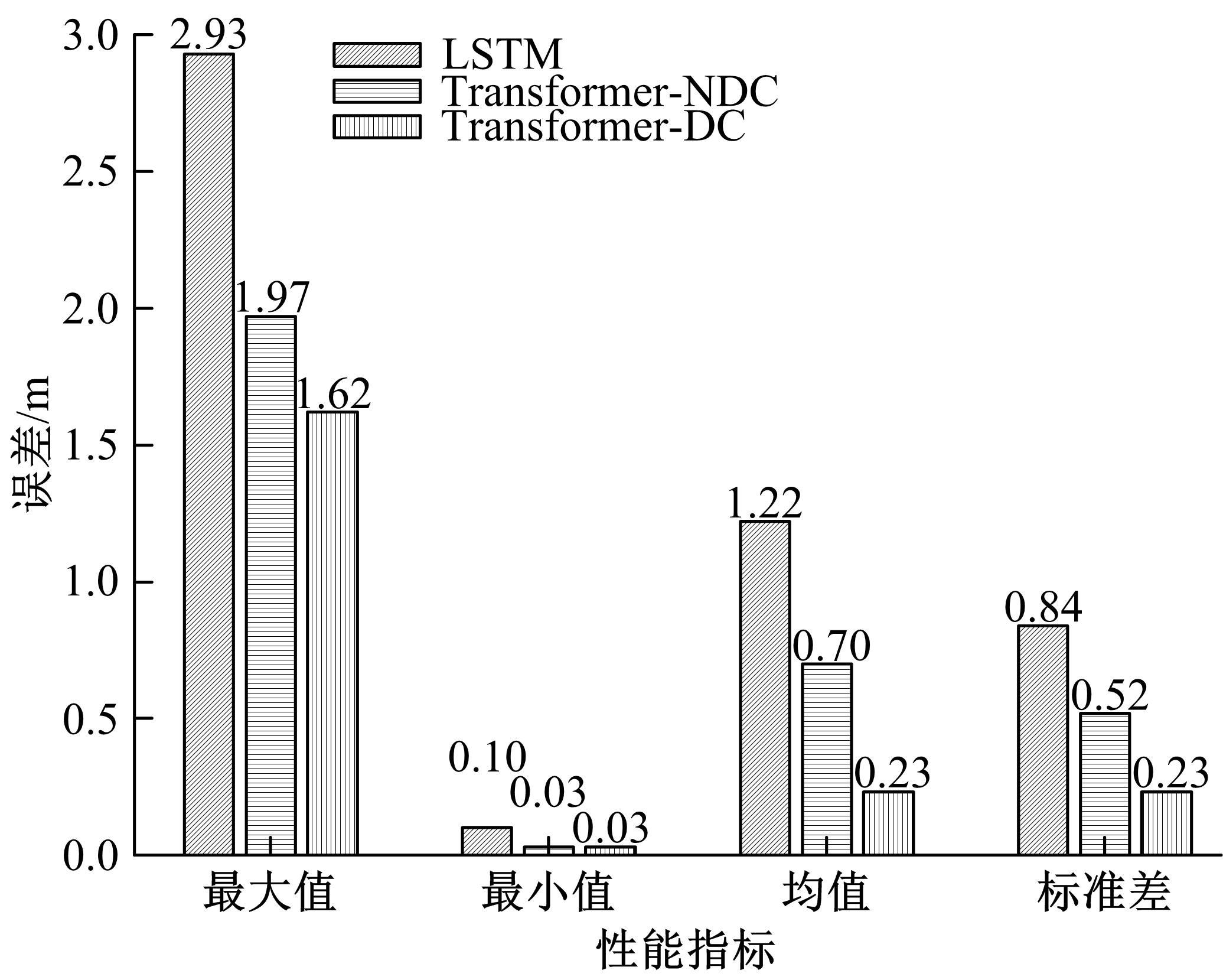
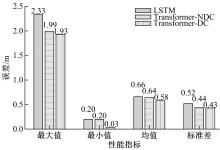
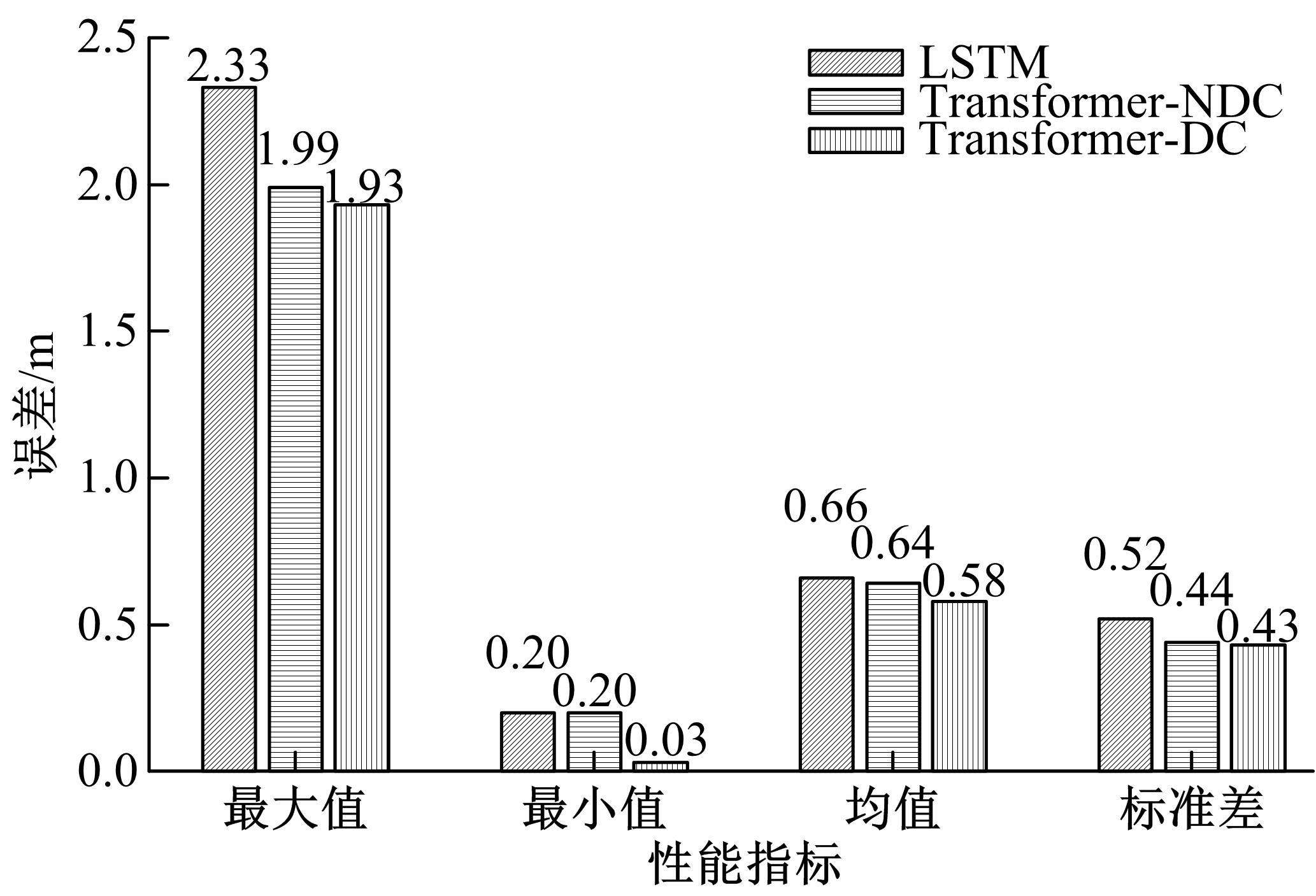
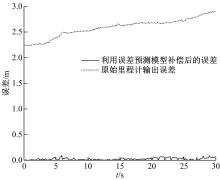
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 653-662.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221273
Wheel odometry error prediction model based on transformer
Ke HE( ),Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO
),Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO
- College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U469.79
| 1 | 高振海,孙天骏,何磊. 汽车纵向自动驾驶的因果推理型决策[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. |
| Gao Zhen-hai, Sun Tian-jun, He Lei. Causal reasoning decision⁃making for vehicle longitudinal automatic driving[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. | |
| 2 | Jo K, Kim J, Kim D, et al. Development of autonomous car—part I: distributed system architecture and development process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(12): 7131-7140. |
| 3 | Lu W, Rodríguez F S A, Seignez E, et al. Lane marking-based vehicle localization using low-cost GPS and open source map[J]. Unmanned Systems, 2015, 3(4): 239-251. |
| 4 | Xu L H, Hu S G, Luo Q. A new lane departure warning algorithm considering the driver's behavior characteristics[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015(1): No.412126. |
| 5 | Levinson J, Montemerlo M, Thrun S. Map-based precision vehicle localization in urban environments[C]∥Robotics: Science and Systems, Atlanta, Georgia, USA, 2007: No.16. |
| 6 | 秦晓辉, 王哲文, 庞涛, 等. 基于车辆模型紧耦合的封闭园区车辆定位方法[J]. 汽车工程,2021,43(9): 1328-1335. |
| Qin Xiao-hui, Wang Zhe-wen, Pang Tao, et al. Vehicle positioning method based on tight coupling of vehicle model in enclosed environments[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(9): 1328-1335. | |
| 7 | Kubo N, Suzuki T. Performance improvement of RTK-GNSS with IMU and vehicle speed sensors in an urban environment[J]. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences, 2016, 99(1): 217-224. |
| 8 | 何永明, 陈世升, 冯佳, 等. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J/OL]. [2022-02-15]. |
| 9 | Funk N, Alatur N, Deuber R, et al. Autonomous electric race car design[J/OL]. [2022-08-26]. |
| 10 | Schwesinger U, Bürki M, Timpner J, et al. Automated valet parking and charging for e-mobility[C]∥2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gothenburg, Sweden, 2016: 157-164. |
| 11 | Schanz A, Spieker A, Kuhnert K D. Autonomous parking in subterranean garages-a look at the position estimation[C]∥IEEE IV2003 Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, OH, USA, 2003: 253-258. |
| 12 | Malleswaran M, Vaidehi V, Manjula S, et al. Performance comparison of HONNs and FFNNs in GPS and INS integration for vehicular navigation[C]∥2011 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology (ICRTIT), Chennai, India, 2011: 223-228. |
| 13 | Malleswaran M, Vaidehi V, Saravanaselvan A, et al. Performance analysis of various artificial intelligent neural networks for GPS/INS integration[J]. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 27(5): 367-407. |
| 14 | Dai H, Bian H, Wang R, et al. An INS/GNSS integrated navigation in GNSS denied environment using recurrent neural network[J]. Defence Technology, 2020, 16(2): 334-340. |
| 15 | Fang W, Jiang J, Lu S, et al. A LSTM algorithm estimating pseudo measurements for aiding INS during GNSS signal outages[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(2): No.256. |
| 16 | Onyekpe U, Palade V, Kanarachos S, et al. Learning uncertainties in wheel odometry for vehicular localisation in GNSS deprived environments[C]∥2020 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Miami, FL, USA, 2020: 741-746. |
| 17 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[J/OL]. [2022-09-28]. |
| 18 | Onyekpe U, Kanarachos S, Palade V, et al. Vehicular localisation at high and low estimation rates during gnss outages: a deep learning approach[J]. Deep Learning Applications, 2021,2: 237-256. |
| 19 | Onyekpe U, Palade V, Kanarachos S, et al. IO-VNBD: inertial and odometry benchmark dataset for ground vehicle positioning[J]. Data in Brief, 2021, 35: No.106885. |
| 20 | Onyekpe U, Palade V, Kanarachos S. Learning to localise automated vehicles in challenging environments using Inertial Navigation Systems (INS)[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(3): No.1270. |
| [1] | Deng-feng WANG,Hong-li CHEN,Jing-xin NA,Xin CHEN. Failure comparison of single and double lap joints after high temperature aging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 346-354. |
| [2] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [3] | Ke-yong WANG,Da-tong BAO,Su ZHOU. Data-driven online adaptive diagnosis algorithm towards vehicle fuel cell fault diagnosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [4] | Qi-ming CAO,Hai-tao MIN,Wei-yi SUN,Yuan-bin YU,Jun-yu JIANG. Hydrothermal characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cell start⁃up at low temperature [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [5] | Hai-lin KUI,Ze-zhao WANG,Jia-zhen ZHANG,Yang LIU. Transmission ratio and energy management strategy of fuel cell vehicle based on AVL⁃Cruise [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [6] | Yan LIU,Tian-wei DING,Yu-peng WANG,Jing DU,Hong-hui ZHAO. Thermal management strategy of fuel cell engine based on adaptive control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [7] | Jin-wu GAO,Zhi-huan JIA,Xiang-yang WANG,Hao XING. Degradation trend prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on PSO⁃LSTM [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [8] | Cheng LI,Hao JING,Guang-di HU,Xiao-dong LIU,Biao FENG. High⁃order sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2203-2212. |
| [9] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [10] | Yao-wang PEI,Feng-xiang CHEN,Zhe HU,Shuang ZHAI,Feng-lai PEI,Wei-dong ZHANG,Jie-ran JIAO. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [11] | Guang-di HU,Hao JING,Cheng LI,Biao FENG,Xiao-dong LIU. Multi⁃objective sliding mode control based on high⁃order fuel cell model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
| [12] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Qi WU,Yuan-song LI,Tian-de MO,Yu LI,Li-ping HUANG,Jian-hong SU,Wei-dong ZHANG. Matching,simulation and optimization for 2.5 ton fuel cell/battery hybrid forklift [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [13] | Xiao-hua WU,Zhong-wei YU,Zhang-ling ZHU,Xin-mei GAO. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell buses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [14] | Qing GAO,Hao-dong WANG,Yu-bin LIU,Shi JIN,Yu CHEN. Experimental analysis on spray mode of power battery emergency cooling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1733-1740. |
| [15] | Kui-yang WANG,Ren HE. Recognition method of braking intention based on support vector machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1770-1776. |
|
||