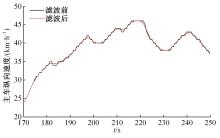
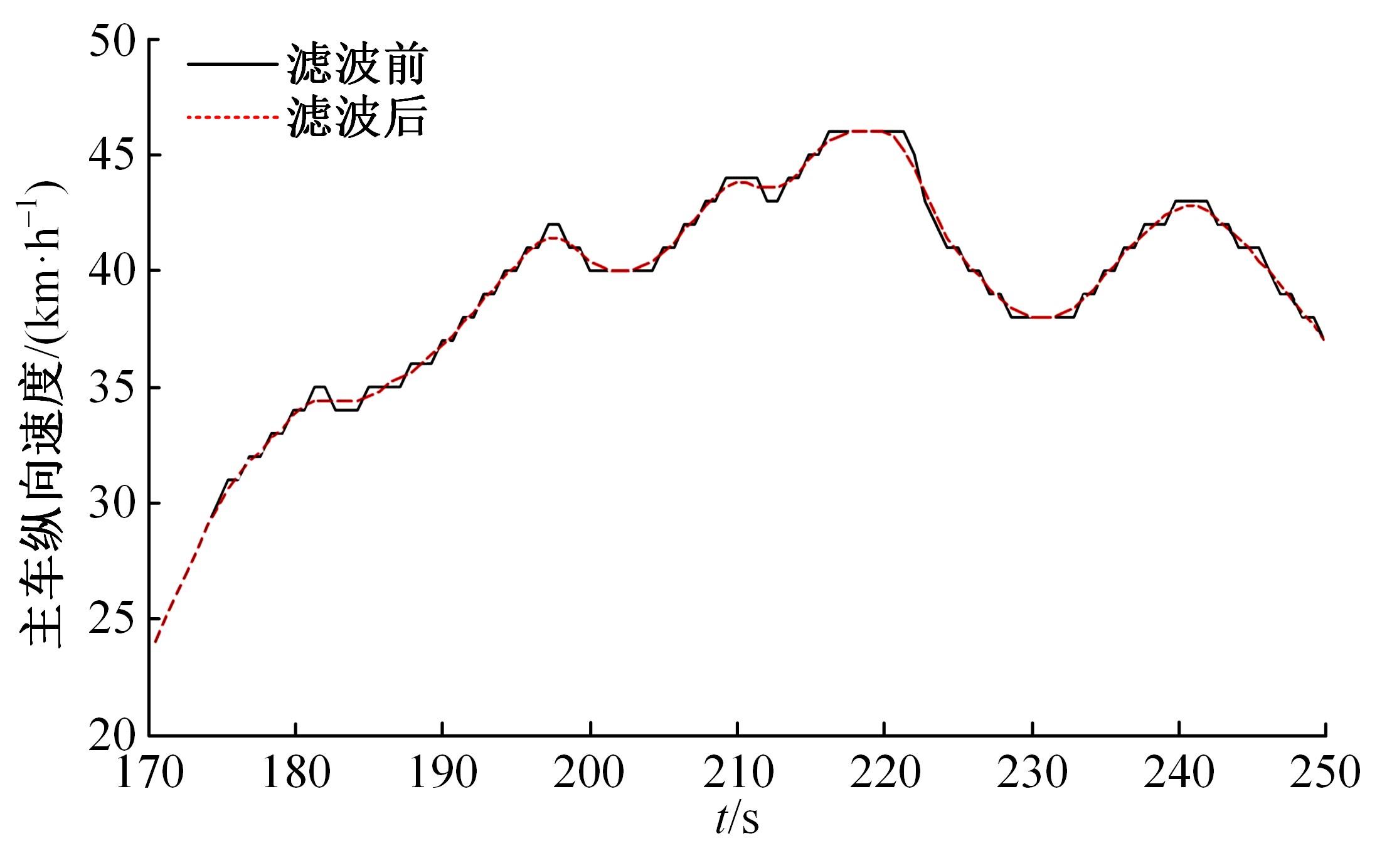
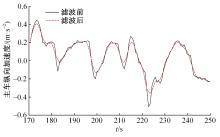
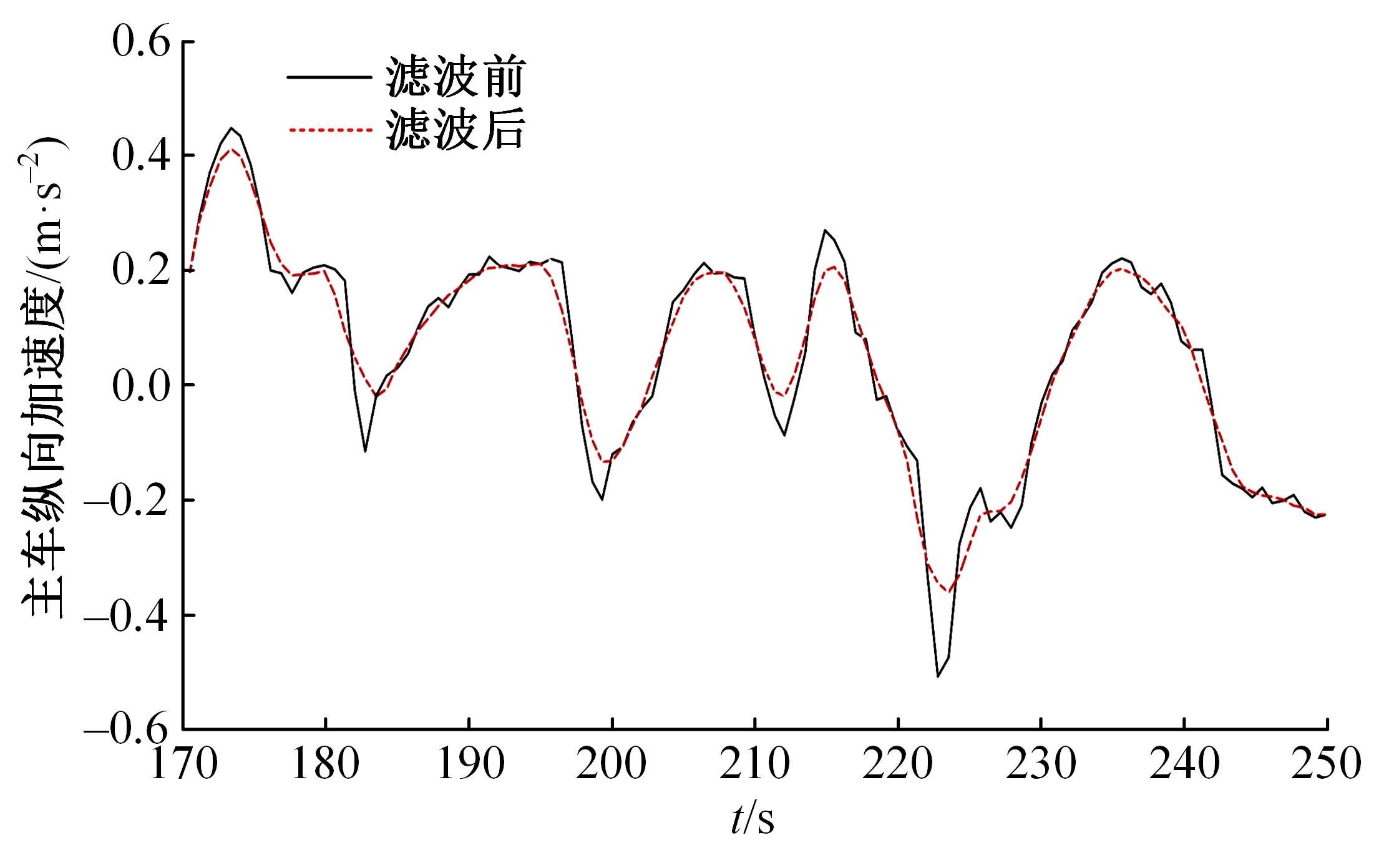
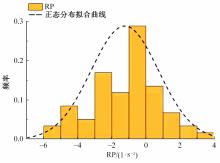
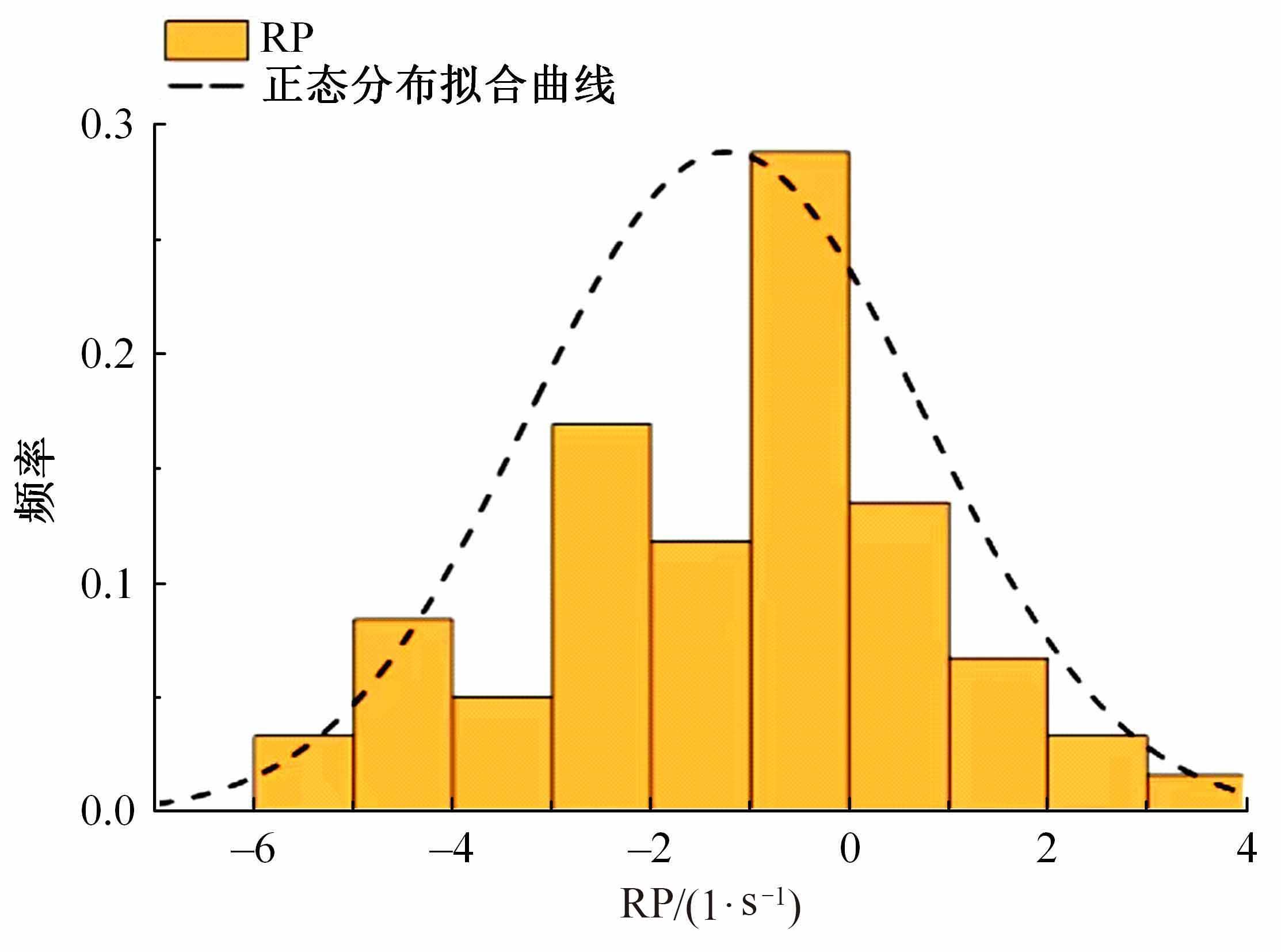
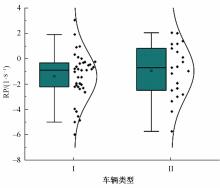
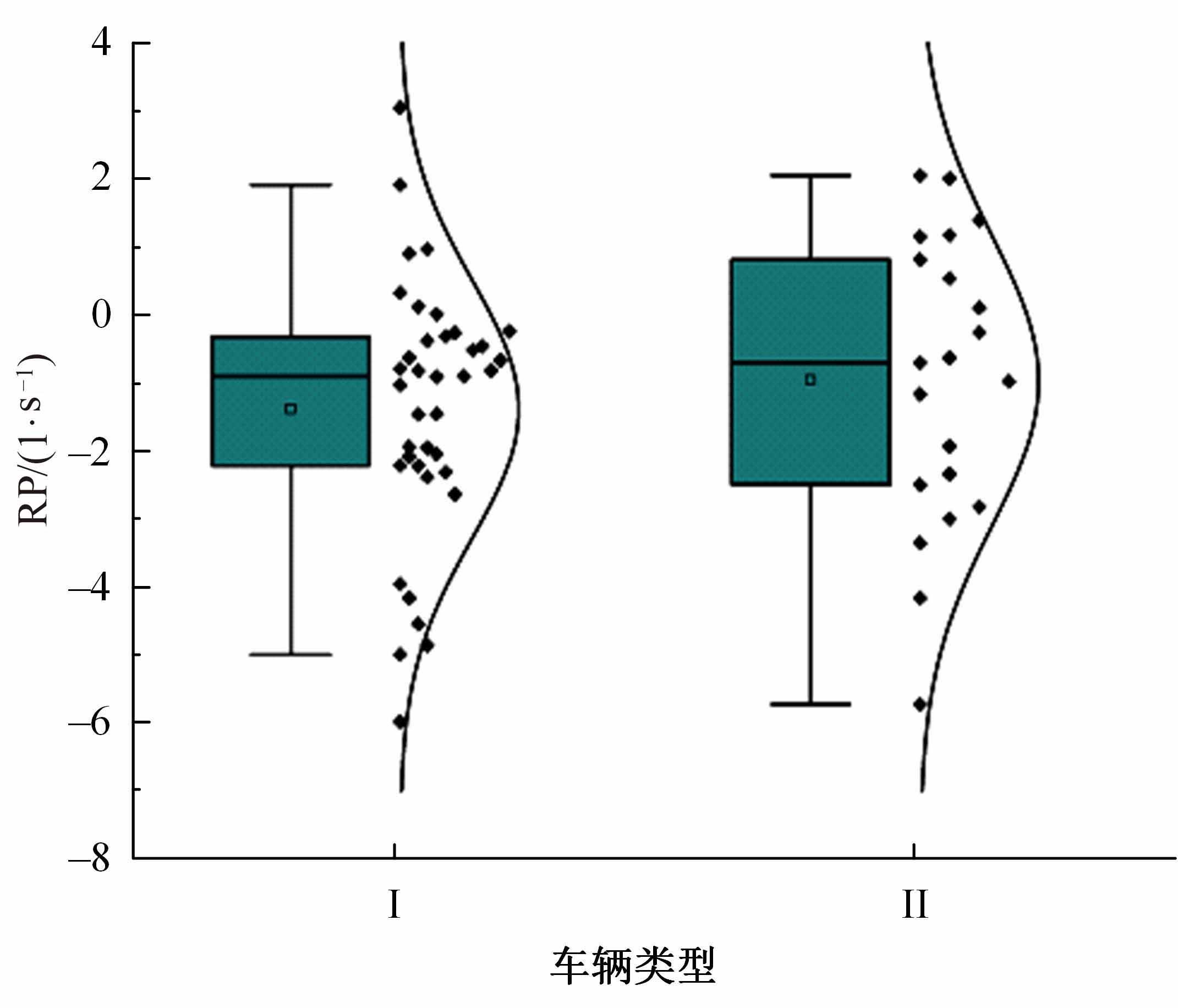
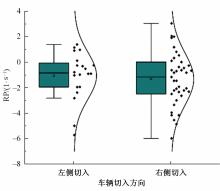
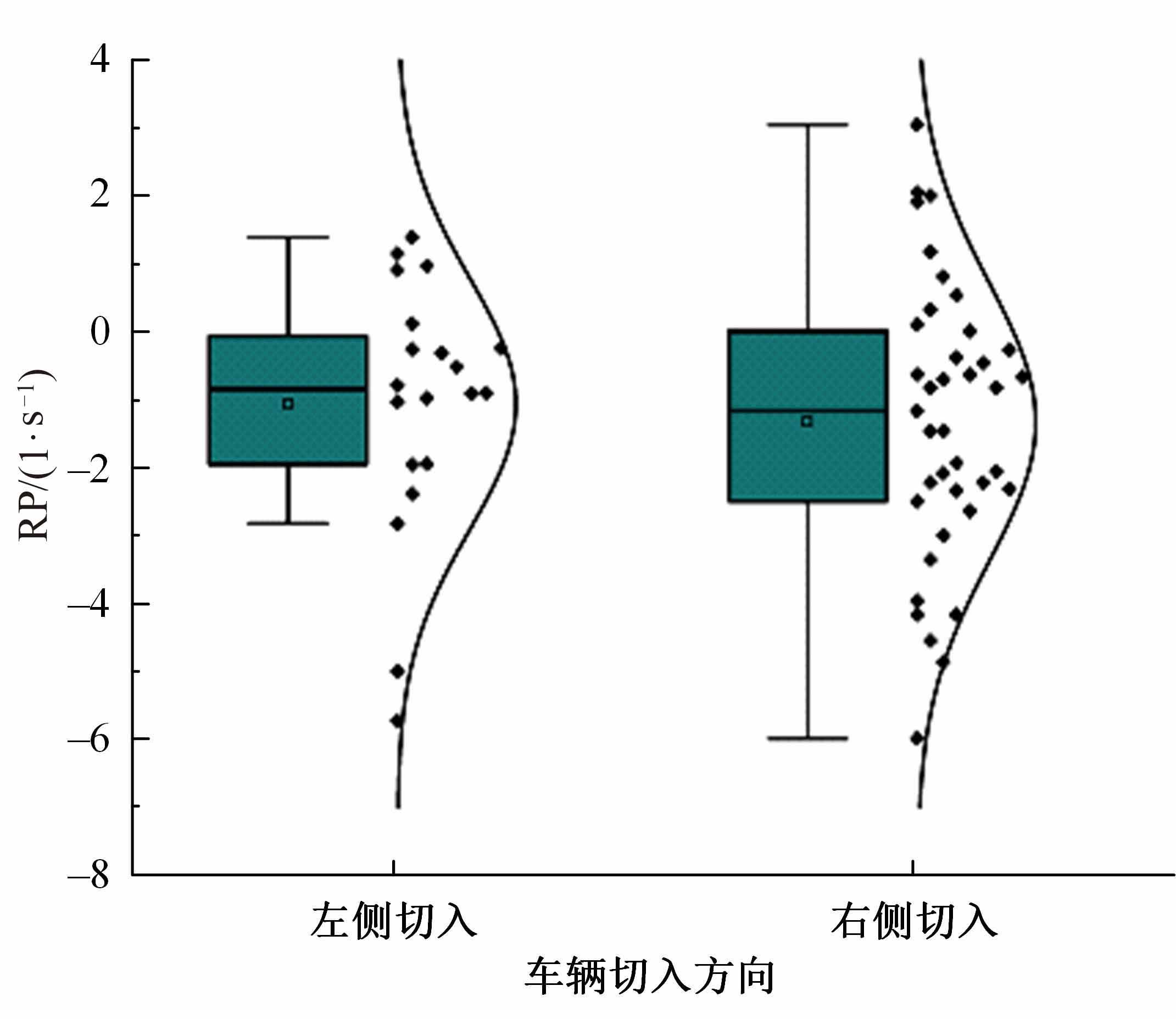
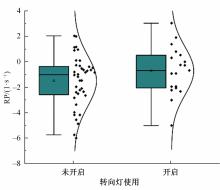
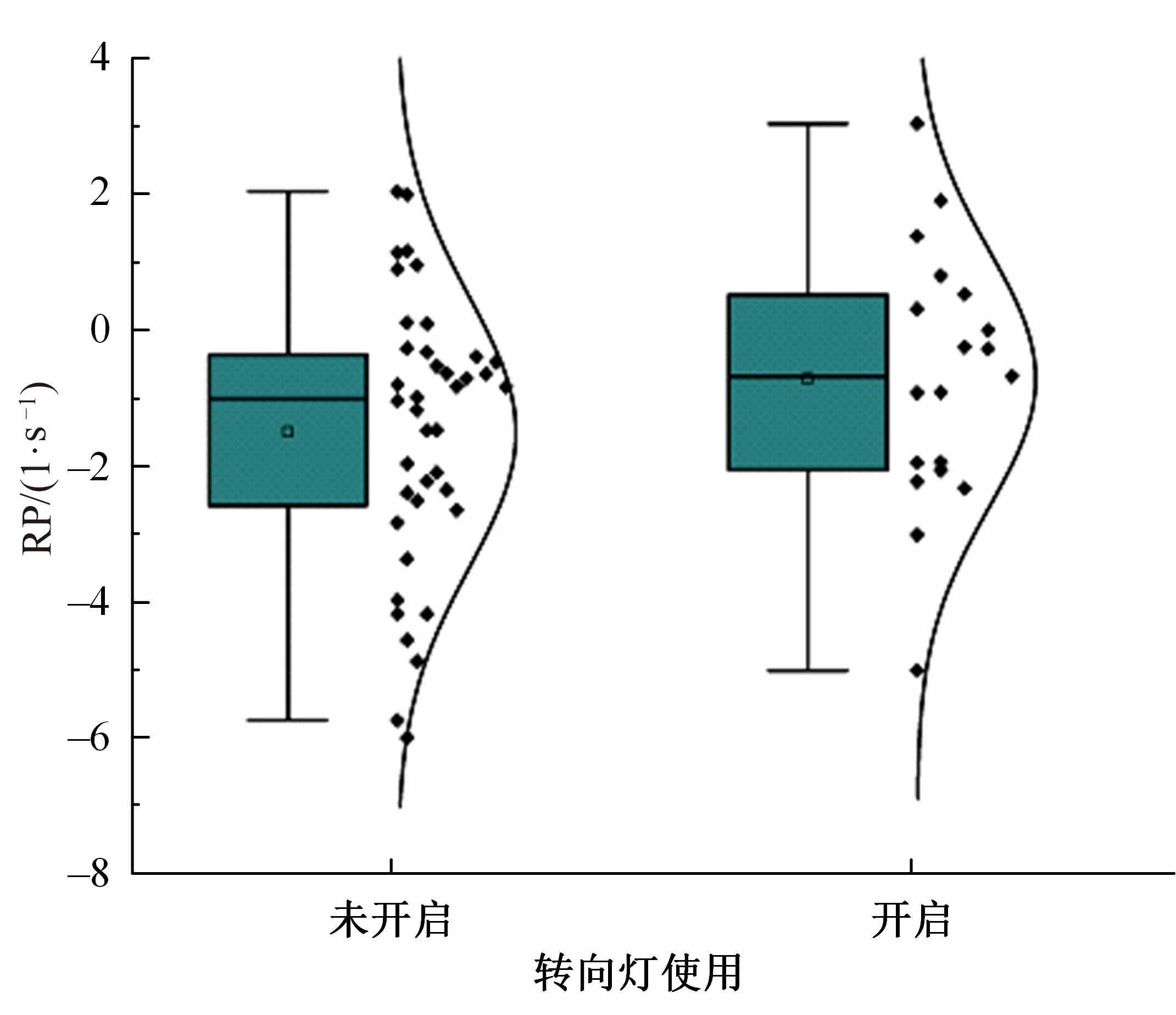
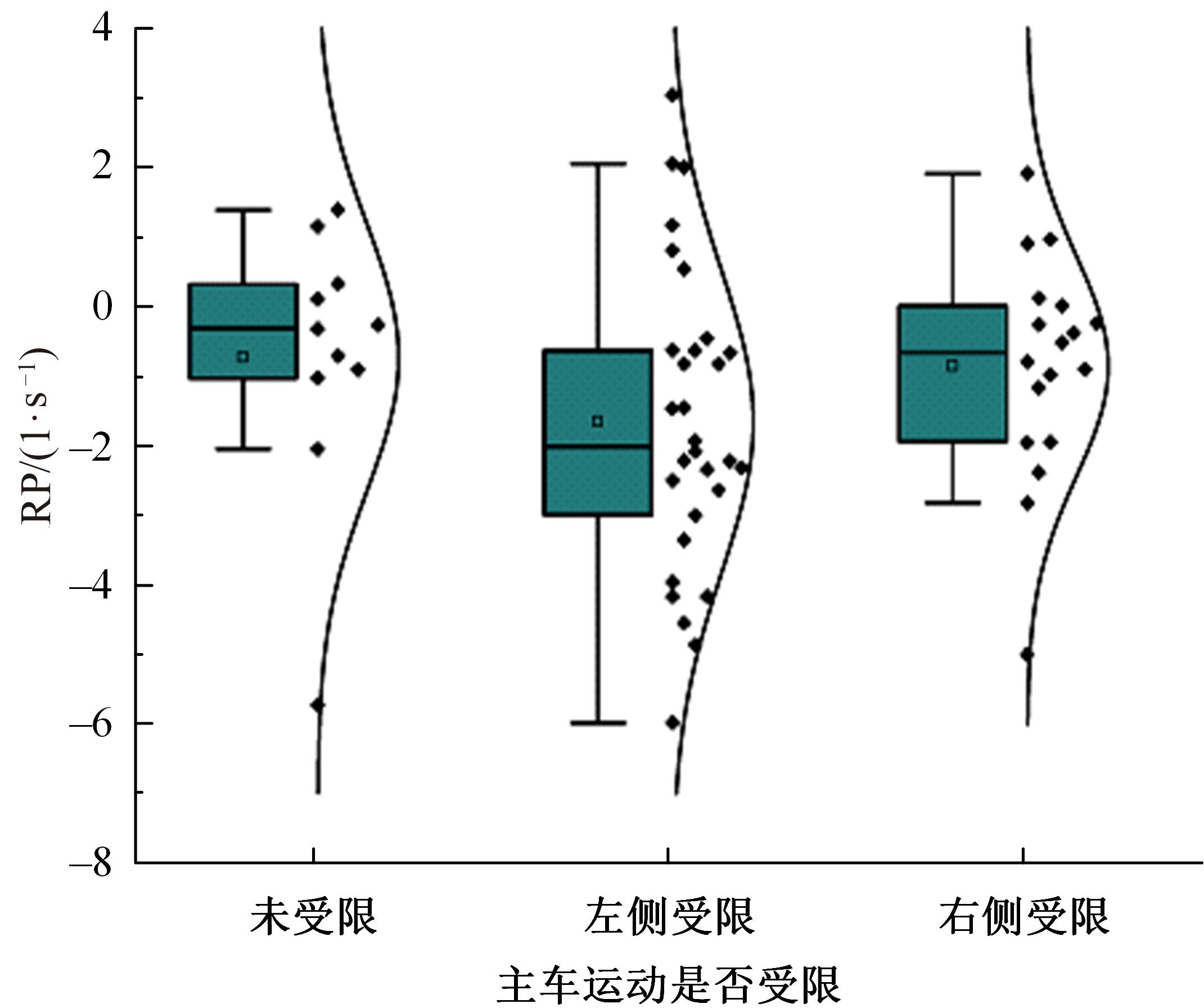
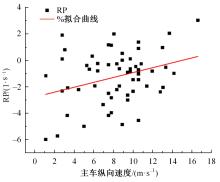
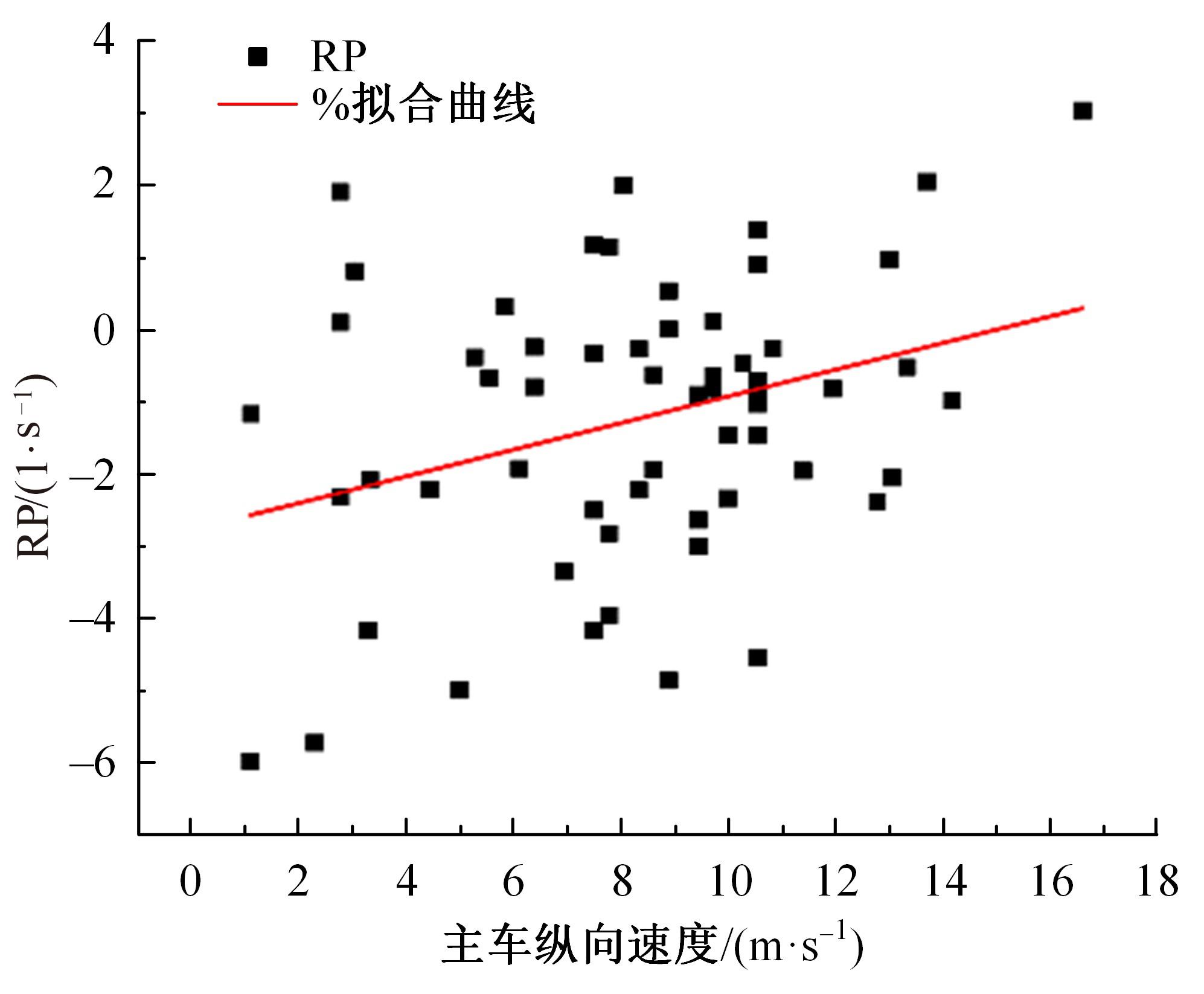
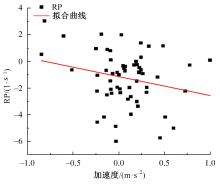
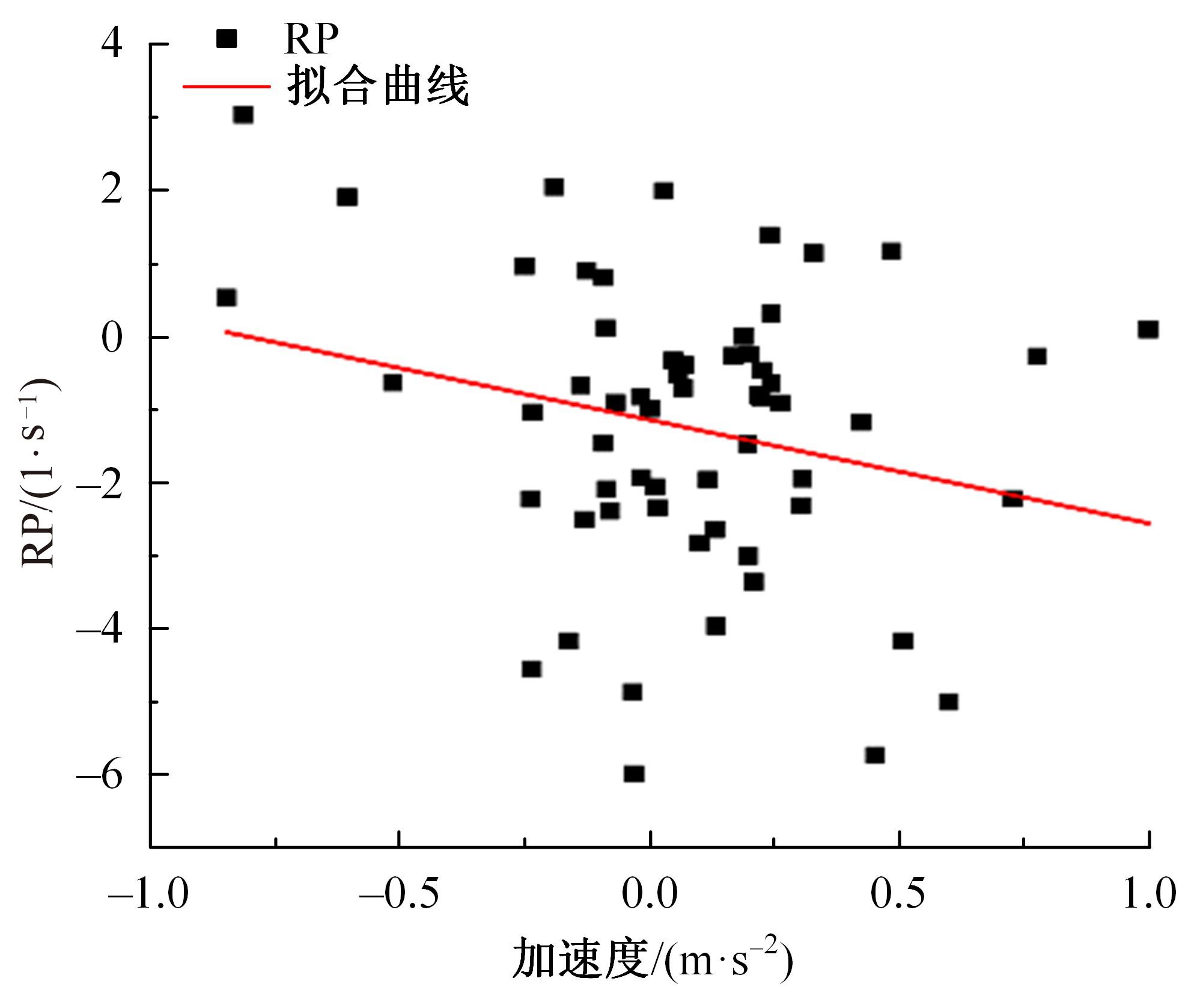
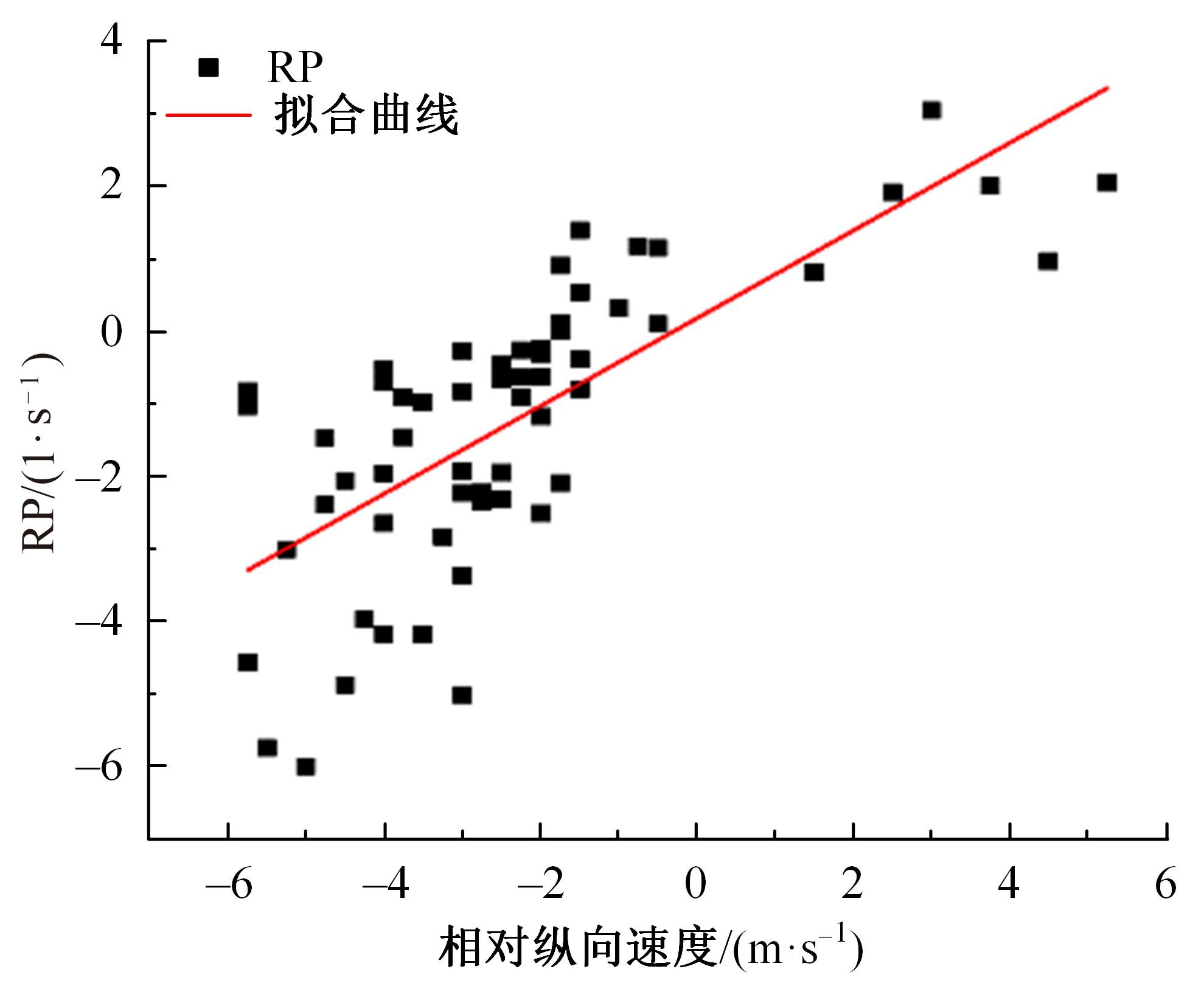
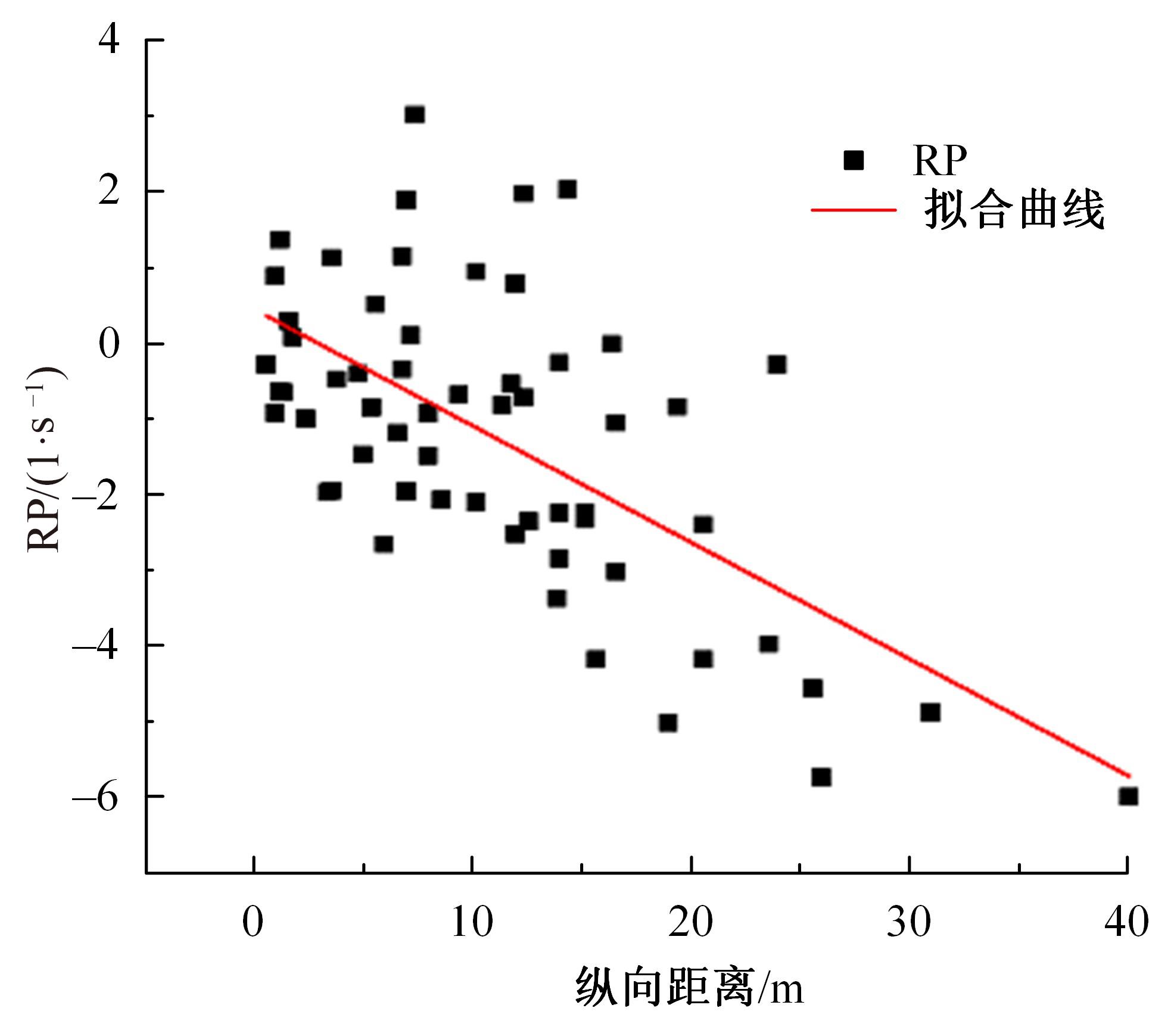
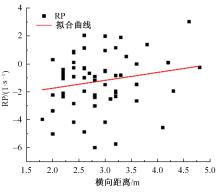
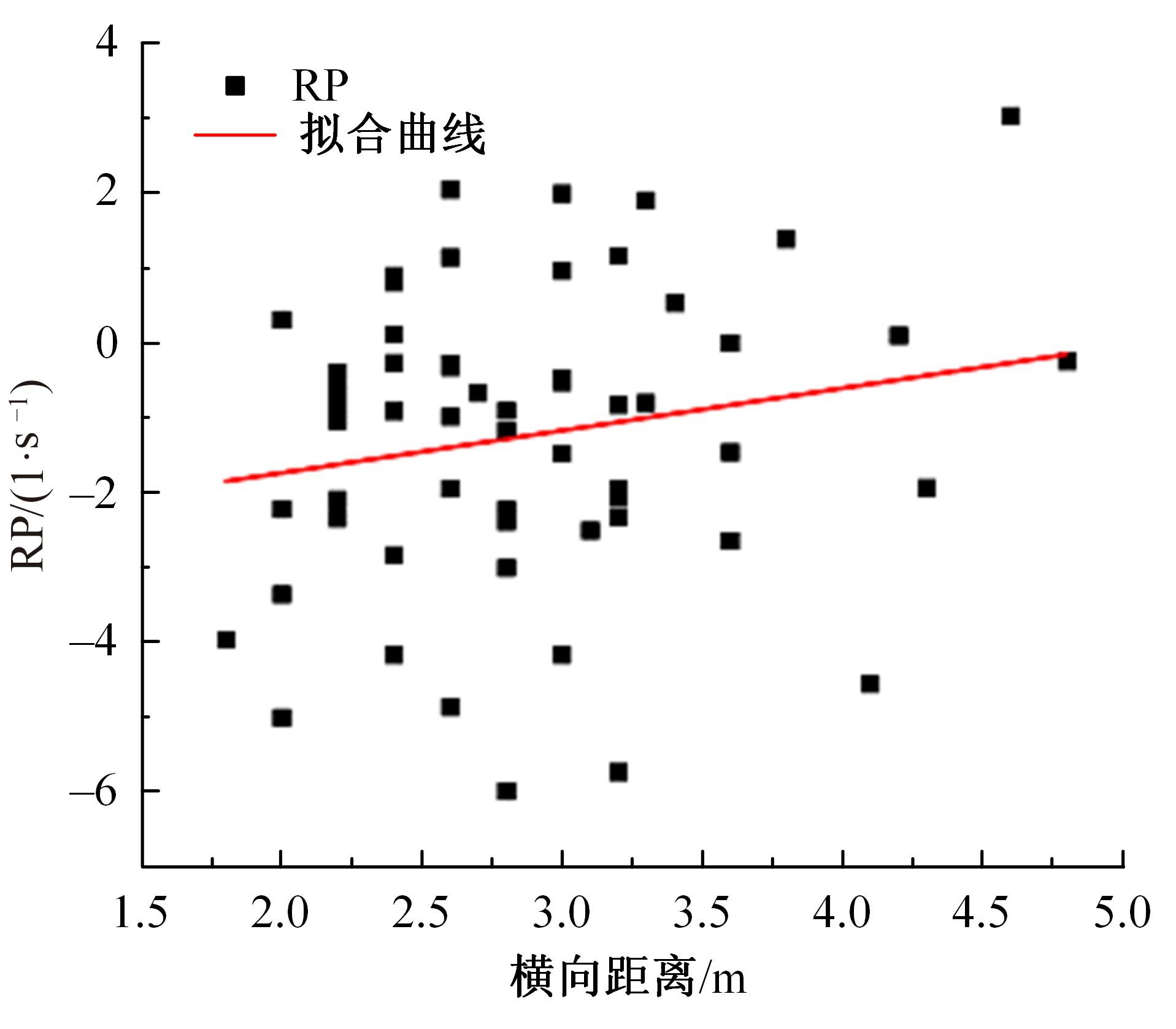
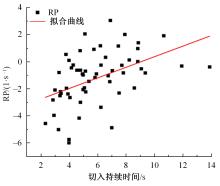
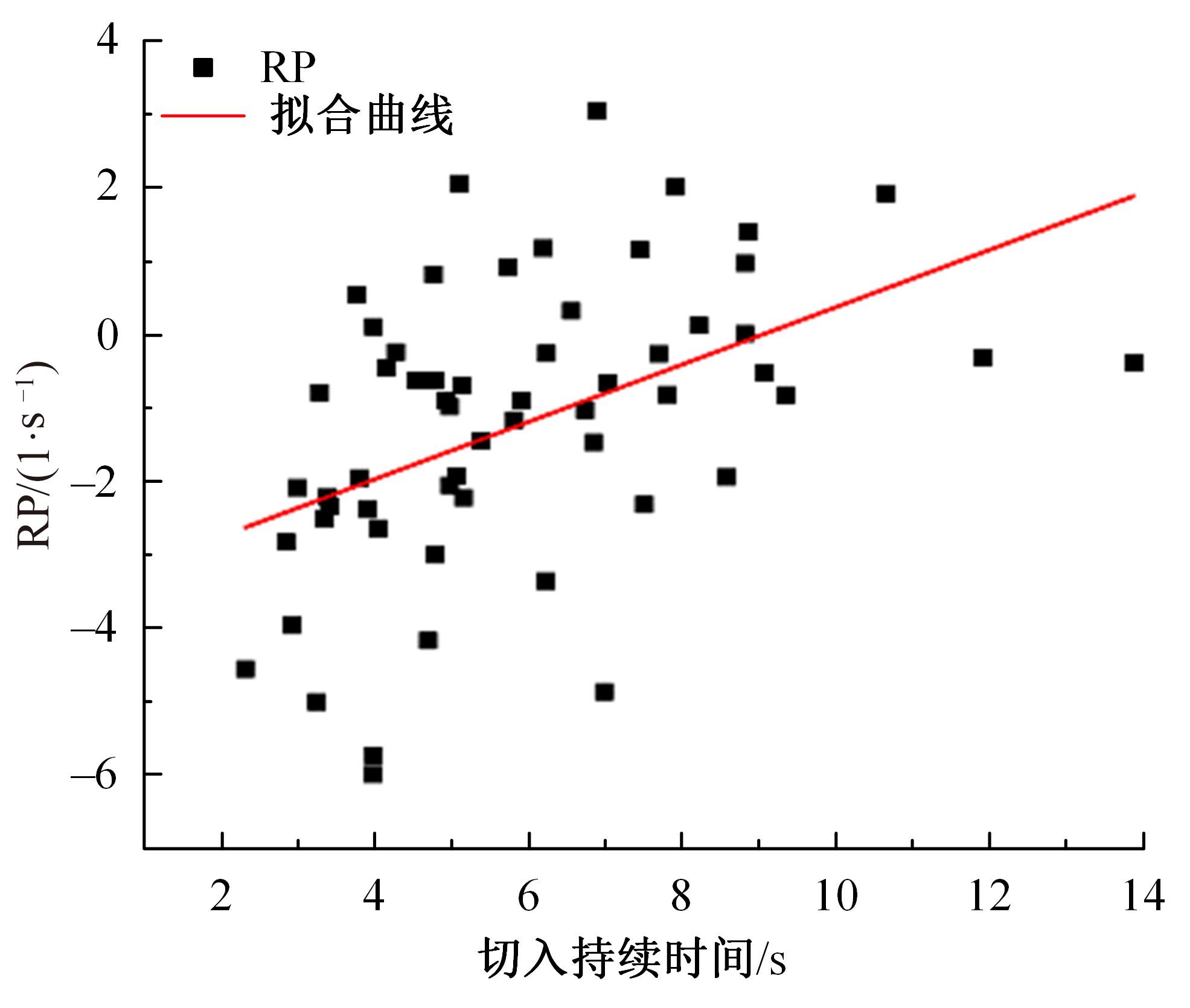
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (11): 3130-3140.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220029
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction method of cut-in scenario library for automatic driving virtual tests
Bai-cang GUO1( ),Guo-feng LUO1,Li-sheng JIN1(
),Guo-feng LUO1,Li-sheng JIN1( ),Xian-yi XIE1,Dong-xian SUN2
),Xian-yi XIE1,Dong-xian SUN2
- 1.School of Vehicle and Energy,Yanshan University,Qinhuangdao 066004,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U461.91
| 1 | 徐向阳, 胡文浩, 董红磊,等. 自动驾驶汽车测试场景构建关键技术综述[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(4): 610-619. |
| Xu Xiang-yang, Hu Wen-hao, Dong Hong-lei, et al. Review of key technologies for autonomous vehicle test scenario construction[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(4): 610-619. | |
| 2 | 朱冰, 张培兴, 赵健,等. 基于场景的自动驾驶汽车虚拟测试研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 1-19. |
| Zhu Bing, Zhang Pei-xing, Zhao Jian, et al. Advances in scenario-based virtual testing of self-driving vehicles[J]. Chinese Journal of Highways, 2019, 32(6): 1-19. | |
| 3 | 朱冰,范天昕,赵健,等. 基于危险边界搜索的自动驾驶系统加速测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(1): 1-8. |
| Zhu Bing, Fan Tian-xin, Zhao Jian, et al. Accelerated test method of automatic driving system based on dangerous boundary search[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering Edition), 2022, 52(1): 1-8. | |
| 4 | Zhao D, Lam H, Peng H, et al. Accelerated evaluation of automated vehicles safety in lane-change scenarios based on importance sampling techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 18(3): 595-607. |
| 5 | Hou Y, Edara P, Sun C. Situation assessment and decision making for lane change assistance using ensemble learning methods[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(8): 2015-3875. |
| 6 | 中华人民共和国公安部交通管理局. 2015中华人民共和国道路交通事故统计年报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国公安部交通管理局, 2016. |
| 7 | Feng Z, Ma X, Zhu X, et al. Analysis of driver brake behavior under critical cut-in scenarios[C]∥ IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, New York, USA, 2018: 2054-2059. |
| 8 | 王雪松, 杨敏明. 基于自然驾驶数据的变道切入行为分析[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 46(8): 1057-1063. |
| Wang Xue-song, Yang Min-ming. Analysis of lane change cut-in behavior based on natural driving data[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(8): 1057-1063. | |
| 9 | 朱西产, 张佳瑞, 马志雄. 安全切入场景下的驾驶人初始制动时刻分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 262-273. |
| Zhu Xi-chan, Zhang Jia-rui, Ma Zhi-xiong. Analysis of driver's initial braking moment under safety cut-in scenario[J]. Chinese Journal of Highways, 2019, 32(6): 262-273. | |
| 10 | Menzel T, Bagschik G, Maurer M. Scenarios for development, test and validation of automated vehicles[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, New York, USA, 2018: 1-7. |
| 11 | Menzel T, Bagschik G, Isensee L, et al. From functional to logical scenarios: detailing a keyword-based scenario description for execution in a simulation environment[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Paris, France, 2019: 2383-2390. |
| 12 | 胡林, 易平, 黄晶, 等. 基于真实事故案例的自动紧急制动系统两轮车测试场景研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(12): 1436-1446. |
| Hu Lin, Yi Ping, Huang Jing, et al. Research on two-wheeled vehicle test scenarios of automatic emergency braking system based on real accident cases[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(12): 1436-1446. | |
| 13 | 郭景华, 李克强, 王进, 等. 基于危险场景聚类分析的前车随机运动状态预测研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(7): 847-853, 859. |
| Guo Jing-hua, Li Ke-qiang, Wang Jin, et al. Research on stochastic motion state prediction of front vehicle based on hazard scenario clustering analysis[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(7): 847-853, 859. | |
| 14 | Kondoh T, Yamamura T, Kitazaki S, et al. Identification of visual cues and quantification of drivers' perception of proximity risk to the lead vehicle in car-following situations[J]. Journal of Mechanical Systems for Transportation and Logistics, 2008, 1(2): 170-180. |
| 15 | 党睿娜. 具有换道辅助功能的车辆自适应巡航控制[D].北京: 清华大学车辆与运载学院, 2013. |
| Dang Rui-na. Adaptive cruise control for vehicles with lane change assist[D]. Beijing: School of Vehicles and Vehicles, Tsinghua University, 2013. | |
| 16 | Wu J, Du Y, Qi G, et al. Leveraging longitudinal driving behaviour data with data mining techniques for driving style analysis[J]. Iet Intelligent Transport Systems, 2015, 9(8): 792-801. |
| 17 | 金立生, 谢宪毅, 司法, 等. 考虑驾驶人特性的智能驾驶路径跟踪算法[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(4): 553-561. |
| Jin Li-sheng, Xie Xian-yi, Si Fa, et al. Intelligent driving path tracking algorithm considering driver characteristics[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(4): 553-561. | |
| 18 | Lv N, Wen J, Duan Z, et al. Vehicle trajectory prediction and cut-in collision warning model in a connected vehicle environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(2): 966-981. |
| 19 | Wang X, Yang M, Hurwitz D. Analysis of cut-in behavior based on naturalistic driving data[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 124: 127-137. |
| 20 | 王雪松, 徐晓妍. 基于自然驾驶数据的危险事件识别方法[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(1): 51-59. |
| Wang Xue-song, Xu Xiao-yan. Hazardous event identification method based on natural driving data[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(1): 51-59. | |
| 21 | Lv N, Duan Z, Ma C, et al. Safety margins-a novel approach from risk homeostasis theory for evaluating the impact of advanced driver assistance systems on driving behavior in near-crash events[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020(1): 1-14. |
| 22 | 丁洁云, 党睿娜, 王建强, 等. 驾驶人换道决策分析及意图识别算法设计[J]. 清华大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 55(7): 769-774. |
| Ding Jie-yun, Dang Rui-na, Wang Jian-qiang, et al. Driver lane change decision analysis and intention recognition algorithm design[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 55(7): 769-774. | |
| 23 | 李洪雪, 李世武, 孙文财, 等. 重型危险品半挂列车行驶工况的构建[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1700-1707. |
| Li Hong-xue, Li Shi-wu, Sun Wen-cai, et al. Construction of working conditions of heavy dangerous goods semi-trailer train[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1700-1707. | |
| 24 | 李航. 统计学习方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019. |
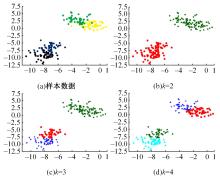
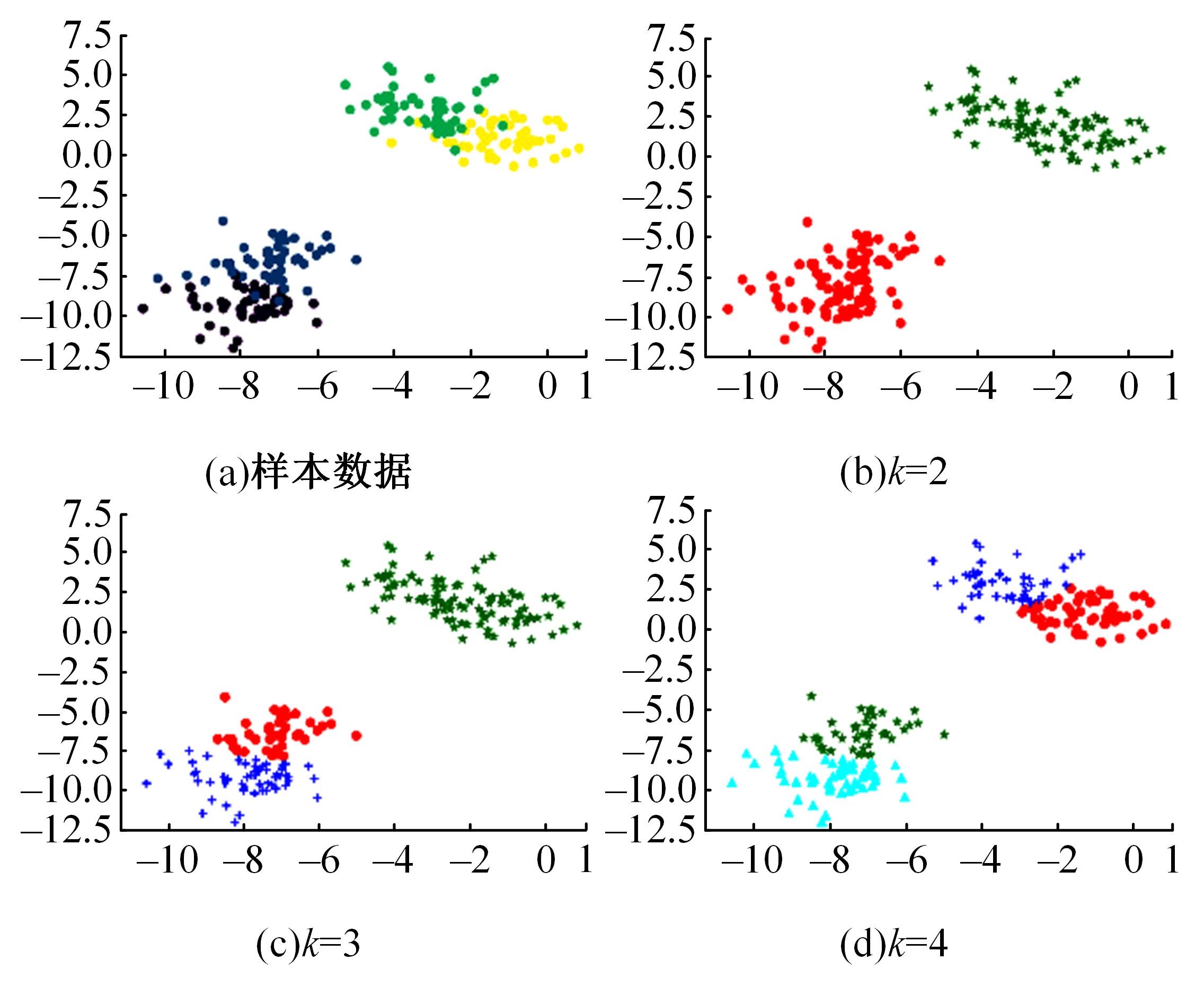
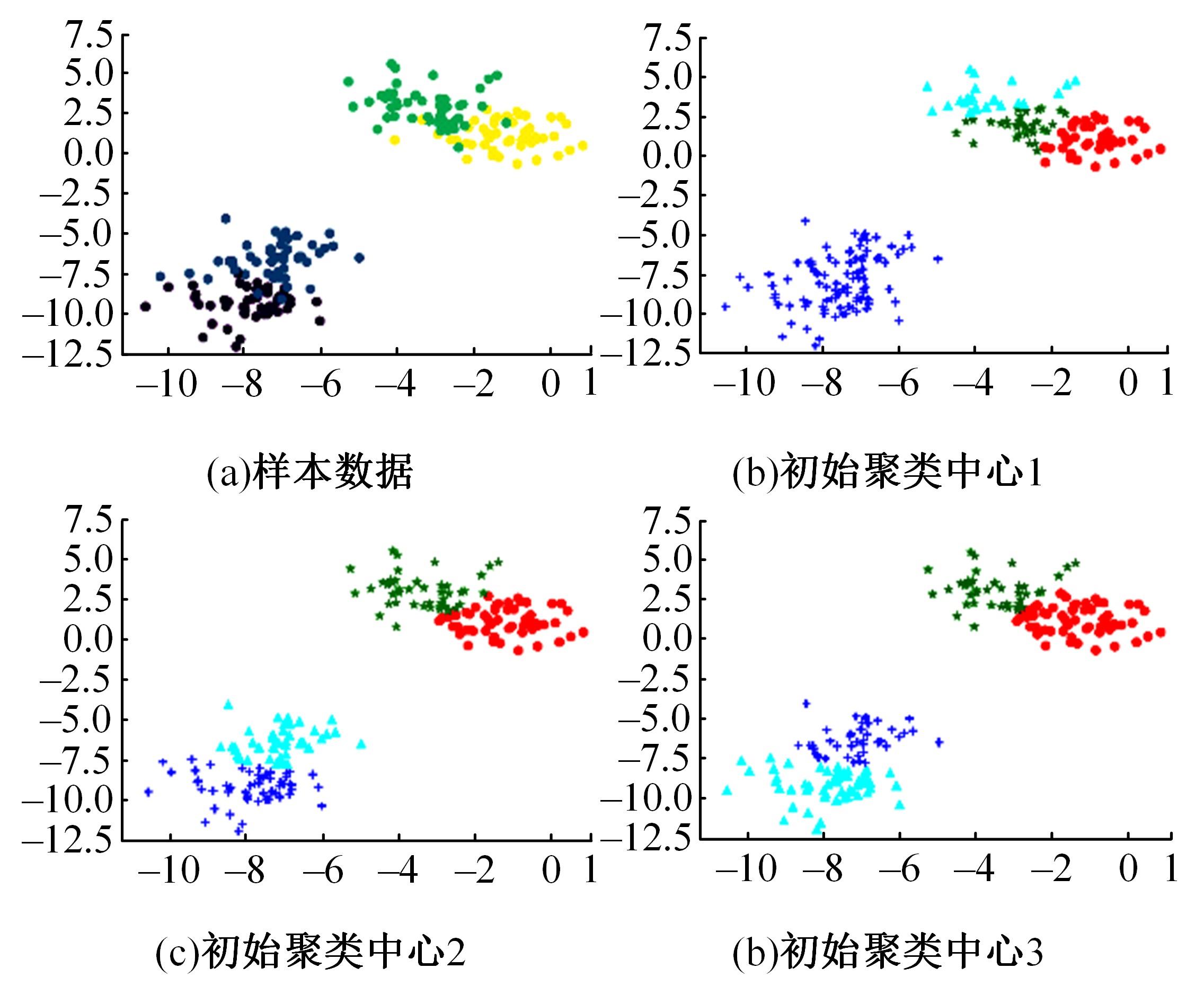
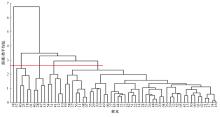
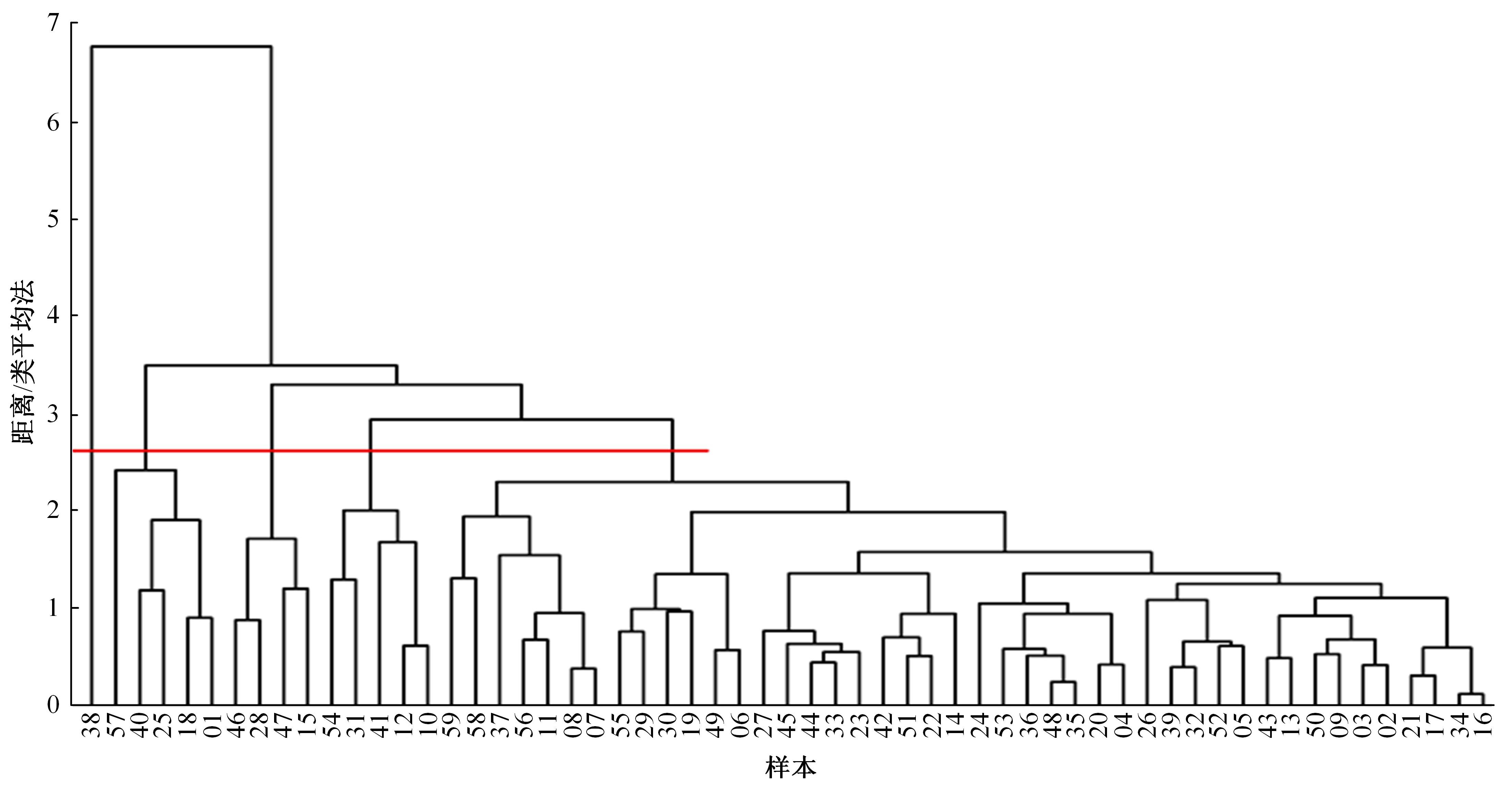
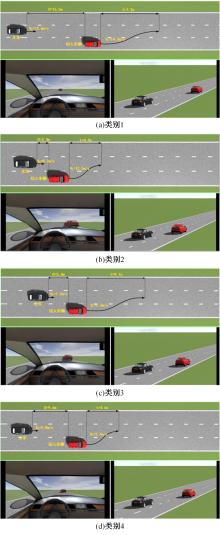
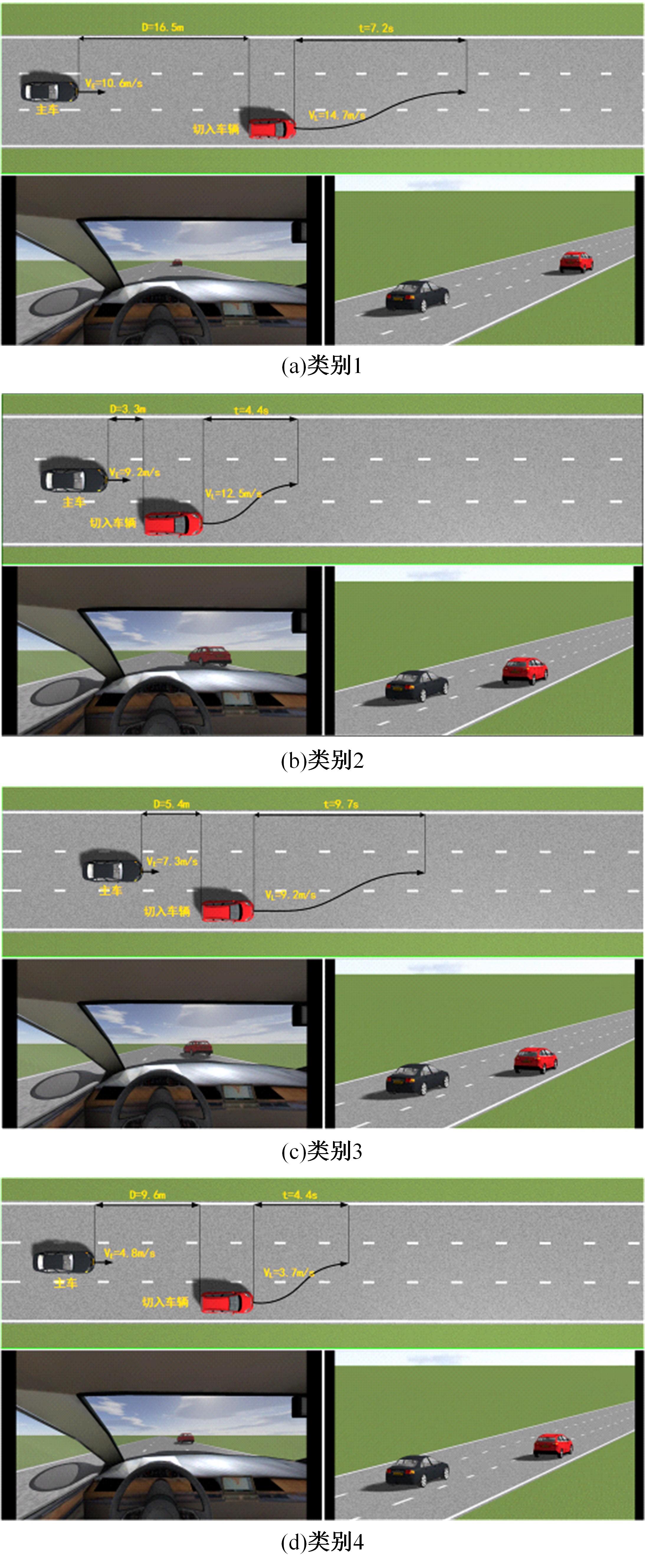
| 25 | 孙栋先. 基于自然驾驶数据的变道切入场景库构建研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2021. |
| Sun Dong-xian. Research on construction of cut-in scenario library based on naturalistic driving data[D]. Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2021. | |
| 26 | 彭涛, 方锐, 刘兴亮, 等. 基于典型事故场景的雪天高速换道自动驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(11): 2558-2567. |
| Peng Tao, Fang Rui, Liu Xing-liang, et al. Automatic lane-changing driving strategy based on typical accident scenarios in snowy days[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2558-2567. |
| [1] | Xing-tao LIU,Xiao-jian LIU,Ji WU,Yao HE,Xin-tian LIU. State of health estimation method for lithium⁃ion battery based on curve compression and extreme gradient boosting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1273-1280. |
| [2] | Xing-tao LIU,Si-yuan LIN,Ji WU,Yao HE,Xin-tian LIU. Regenerative braking optimization strategy considering battery state of power [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2796-2805. |
| [3] | Ming LIU,Xue-wen RONG,Yi-bin LI,Shuai-shuai ZHANG,Yan-fang YIN,Jiu-hong RUAN. Speed adaptive control of mobile robot based on terrain clustering analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1496-1505. |
| [4] | Cai-hua ZHU,Xiao-li SUN,Yan LI. Forecast of urban public bicycle traffic demand by station classification [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| [5] | WANG Jun-nian, YE Tao, SUN Wen, WANG Qing-nian. Vibration isolation performance of energy-regenerative semi-active suspension with variable stiffness and damping [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 701-708. |
| [6] | LIU Yang, SUN Ze-chang, WANG Meng. Brake force cooperative control and test for integrated electro-hydraulic brake system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 718-724. |
| [7] | WANG Zhe, YANG Bai-ting, LIU Xin, LIU Qun, SONG Xian-min. Discriminant analysis of driving decisions based on fuzzy clustering [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. |
| [8] | LIU Shu-fen, MENG Dong-xue, WANG Xiao-yan. DBSCAN algorithm based on grid cell [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(4): 1135-1139. |
| [9] | HAN Fei, ZHANG Su-min, LIU Jia-yi. Estimation of probability of blind zone of vehicle rearview mirror based on eyellipse [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 521-525. |
| [10] | WANG Qing-nian, QU Xiao-dong, YU Yuan-bin. Optimal matching of HEV with composite electric power supply [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(05): 1153-1159. |
| [11] | LI Qi, JIANG Gui-yan, YANG Ju-fen. Automatic incident detection algorithms fusion method based on factor analysis and cluster analysis [J]. , 2012, 42(05): 1191-1197. |
| [12] | JIN Liqiang, WANG Qingnian, SONG Chuanxue. Simulation of 4-wheel independent driving electric vehicle dynamics control system [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (4): 547-553. |
| [13] | SONG Chuanxue, CAI Zhanglin. Modeling and simulation of double wishbone suspension based on ADAMS/CAR [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (4): 554-558. |
|