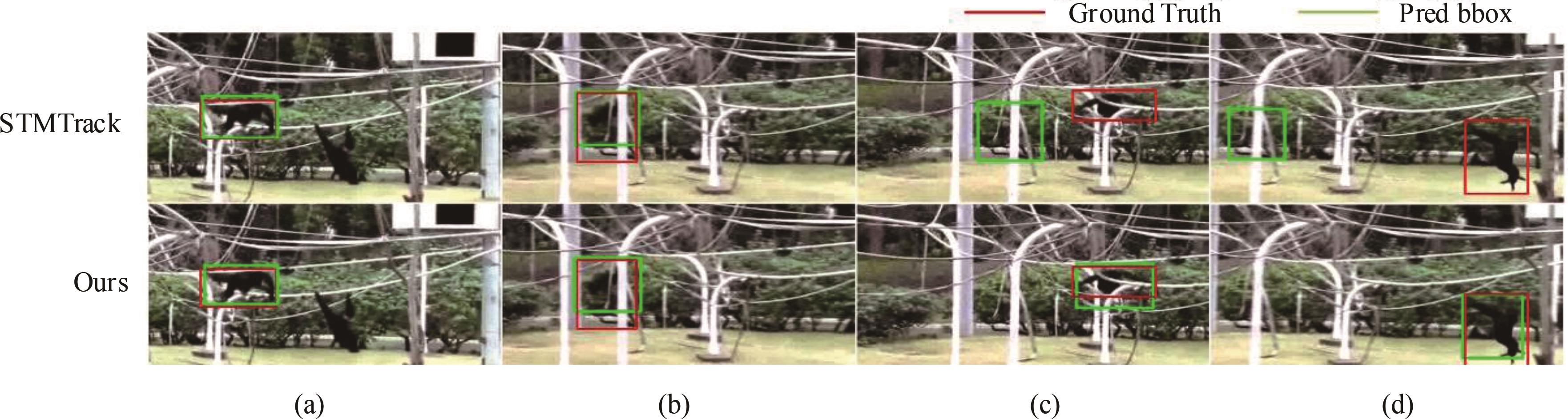
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3327-3337.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230003
Temporal salient attention siamese tracking network
Lin MAO( ),Hong-yang SU,Da-wei YANG(
),Hong-yang SU,Da-wei YANG( )
)
- School of Electromechanical Engineering,Dalian Minzu University,Dalian 116600,China
CLC Number:
- TP391
| 1 | Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]∥ European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 2016: 850-865. |
| 2 | Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 8971-8980. |
| 3 | Fan H, Ling H B. Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 7952-7961. |
| 4 | Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, et al. Siamrpn++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4282-4291. |
| 5 | Xu Y D, Wang Z Y, Li Z X, et al. Siamfc++: towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines[C]∥ Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12549-12556. |
| 6 | Gupta D K, Arya D, Gavves E. Rotation equivariant siamese networks for tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 12362-12371. |
| 7 | Yang T Y, Chan A B. Learning dynamic memory networks for object tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munichi, Germany, 2018: 152-167. |
| 8 | Yan B, Peng H W, Fu J L, et al. Learning spatio-temporal transformer for visual tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10448-10457. |
| 9 | Fu Z H, Liu Q J, Fu Z H, et al. Stmtrack: template-free visual tracking with space-time memory networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13774-13783. |
| 10 | Zhang Z P, Peng H W, Fu J L, et al. Ocean: object-aware anchor-free tracking[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 2020: 771-787. |
| 11 | Voigtlaender P, Luiten J, Torr P H, et al. Siam R-CNN: visual tracking by re-detection[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6578-6588. |
| 12 | Eom C, Lee G, Lee J, et al. Video-based person re-identification with spatial and temporal memory networks[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 12036-12045. |
| 13 | Oh S W, Lee J Y, Xu N, et al. Video object segmentation using space-time memory networks[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 9226-9235. |
| 14 | Xie H Z, Yao H X, Zhou S C, et al. Efficient regional memory network for video object segmentation[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 1286-1295. |
| 15 | Paul M, Danelljan M, Van G L, et al. Local memory attention for fast video semantic segmentation[C]∥ 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2021: 1102-1109. |
| 16 | Wang H, Wang W N, Liu J. Temporal memory attention for video semantic segmentation[C]∥ 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, USA, 2021: 2254-2258. |
| 17 | Yu F, Wang D Q, Shelhamer E, et al. Deep layer aggregation[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2403-2412. |
| 18 | Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818-2826. |
| 19 | Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, et al. Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]∥ 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 9626-9635. |
| 20 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 21 | Huang L H, Zhao X, Huang K Q. Got-10k: a large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis, Intelligence Machine, 2019, 43(5): 1562-1577. |
| 22 | Cui Y T, Jiang C, Wang L M, et al. Mixformer: end-to-end tracking with iterative mixed attention[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 13608-13618. |
| 23 | Xie F, Wang C Y, Wang G T, et al. Correlation-aware deep tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8751-8760. |
| 24 | Wang N, Zhou W G, Wang J, et al. Transformer meets tracker: exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 1571-1580. |
| 25 | Zhang Z P, Liu Y H, Wang X, et al. Learn to match: automatic matching network design for visual tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 13339-13348. |
| 26 | Cui Y T, Jiang C, Wang L M, et al. Fully convolutional online tracking[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2022, 224: 103547. |
| 27 | Lukezic A, Matas J, Kristan M. D3S-a discriminative single shot segmentation tracker[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 7133-7142. |
| 28 | Mayer C, Danelljan M, Bhat G, et al. Transforming model prediction for tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8731-8740. |
| 29 | Zhou Z K, Pei W J, Li X, et al. Saliency-associated object tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9866-9875. |
| 30 | Bhat G, Danelljan M, Gool L V, et al. Know your surroundings: exploiting scene information for object tracking[C]∥ European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 2020: 205-221. |
| 31 | Yu Y C, Xiong Y L, Huang W L, et al. Deformable siamese attention networks for visual object tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6728-6737. |
| 32 | Bhat G, Johnander J, Danelljan M, et al. Unveiling the power of deep tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munichi, Germany, 2018: 483-498. |
| 33 | Chen Z D, Zhong B E, Li G R, et al. SiamBAN: target-aware tracking with siamese box adaptive network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 45(4): 5158-5173. |
| 34 | Bhat G, Danelljan M, Gool L V, et al. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 6182-6191. |
| [1] | Yi CAO,Yu XIA,Qing-yuan GAO,Pei-tao YE,Fan YE. Skeleton-based action recognition based on hyper-connected graph convolutional network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 731-740. |
| [2] | Meng-xue ZHAO,Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Quan-le LIU. A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [3] | Hua CAI,Yan-yang ZHENG,Qiang FU,Sheng-yu WANG,Wei-gang WANG,Zhi-yong MA. Three-dimensional object detection algorithm based on multi-scale candidate fusion and optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 709-721. |
| [4] | Xiao-dong CAI,Qing-song ZHOU,Yan-yan ZHANG,Yun XUE. Social recommendation based on global capture of dynamic, static and relational features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 700-708. |
| [5] | Li-min ZHENG,Shuang CHEN,Gang LI. Multiple object detection of violated vehicles in traffic surveillance video based on YOLOv5 network algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 693-699. |
| [6] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU. A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [7] | Xiao-ran GUO,Tie-jun WANG,Yue YAN. Entity relationship extraction method based on local attention and local remote supervision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [8] | Hao WANG,Bin ZHAO,Guo-hua LIU. Temporal and motion enhancement for video action recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 339-346. |
| [9] | Xi ZHANG,Shao-ping KU. Facial super-resolution reconstruction method based on generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 333-338. |
| [10] | Jun-jie LIU,Jia-yi Dong,Yong YANG,Dan LIU,Fu-heng QU,Yan-chang LYU. Analysis of factors associated with online learning performance of students based on HM-OLS stepwise regression model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3755-3762. |
| [11] | Yu-ting SU,Meng-yao JING,Pei-guang JING,Xian-yi LIU. Deep photometric stereo learning framework for battery defect detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3653-3659. |
| [12] | Yao HU,Bi-bo TU. Dynamic access control algorithms for multi domain interoperability under advanced persistent threat attacks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3620-3625. |
| [13] | Xiao-yu YI,Mian-zhu YI. Network book resource recommendation based on deep fusion of interest information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3614-3619. |
| [14] | Xin CHENG,Sheng-xian LIU,Jing-mei ZHOU,Zhou ZHOU,Xiang-mo ZHAO. 3D object detection algorithm fusing dense connectivity and Gaussian distance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3589-3600. |
| [15] | Dondrub LHAKPA,Duoji ZHAXI,Jie ZHU. Tibetan text normalization method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3577-3588. |
|
||