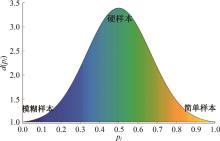
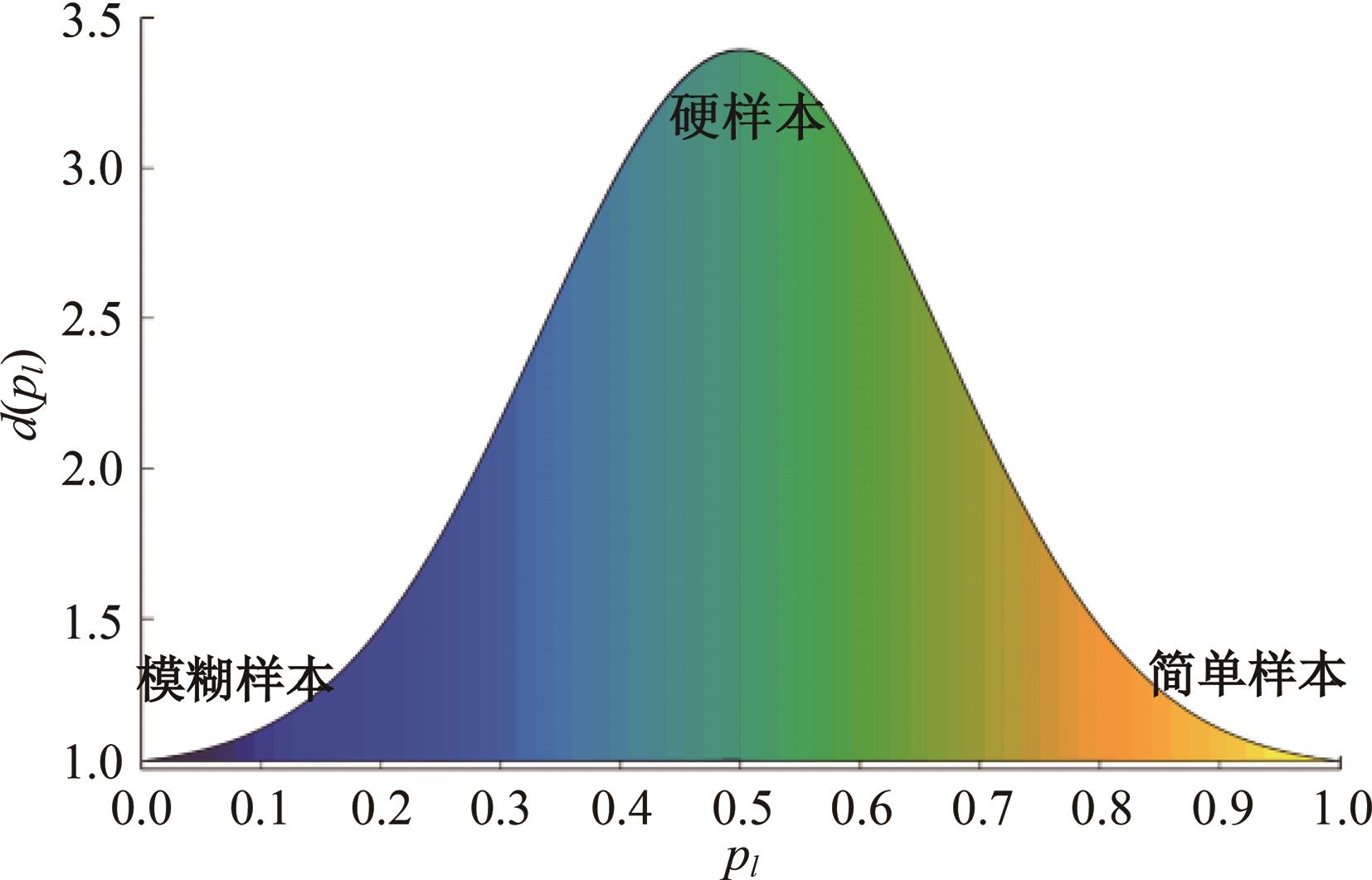
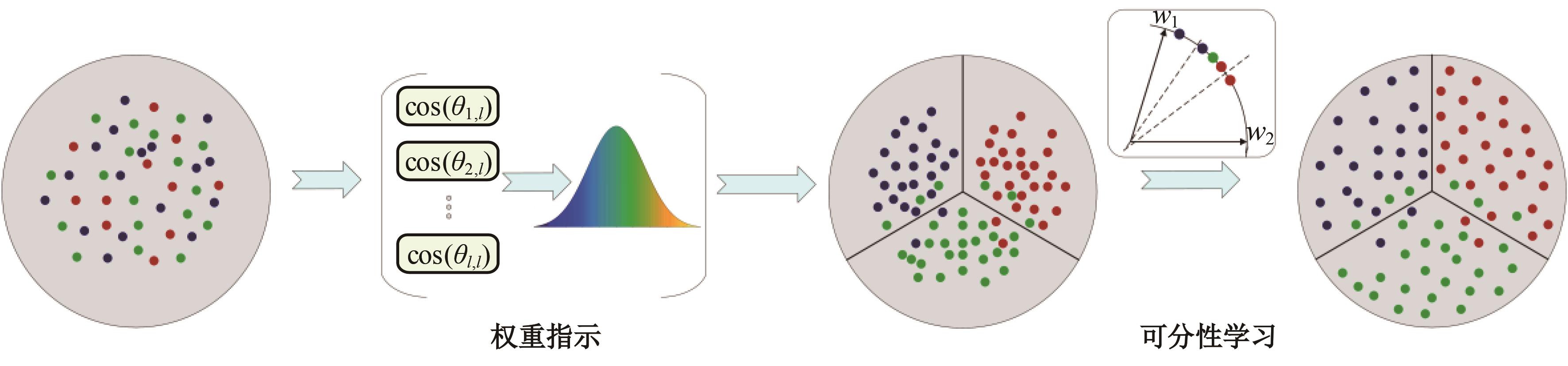
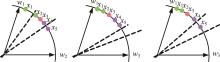
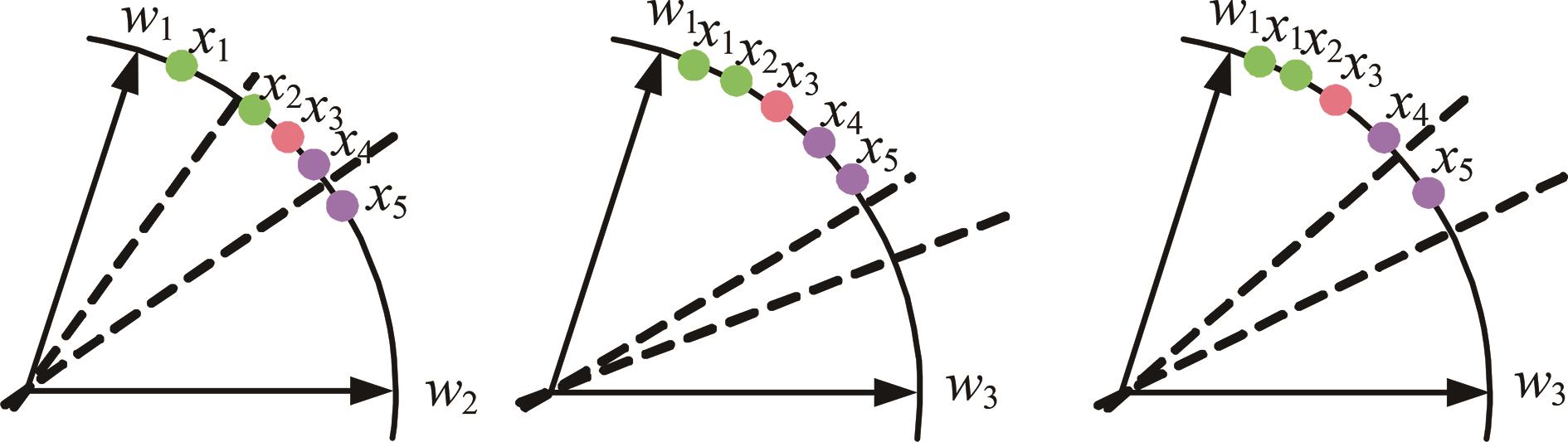
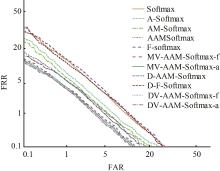
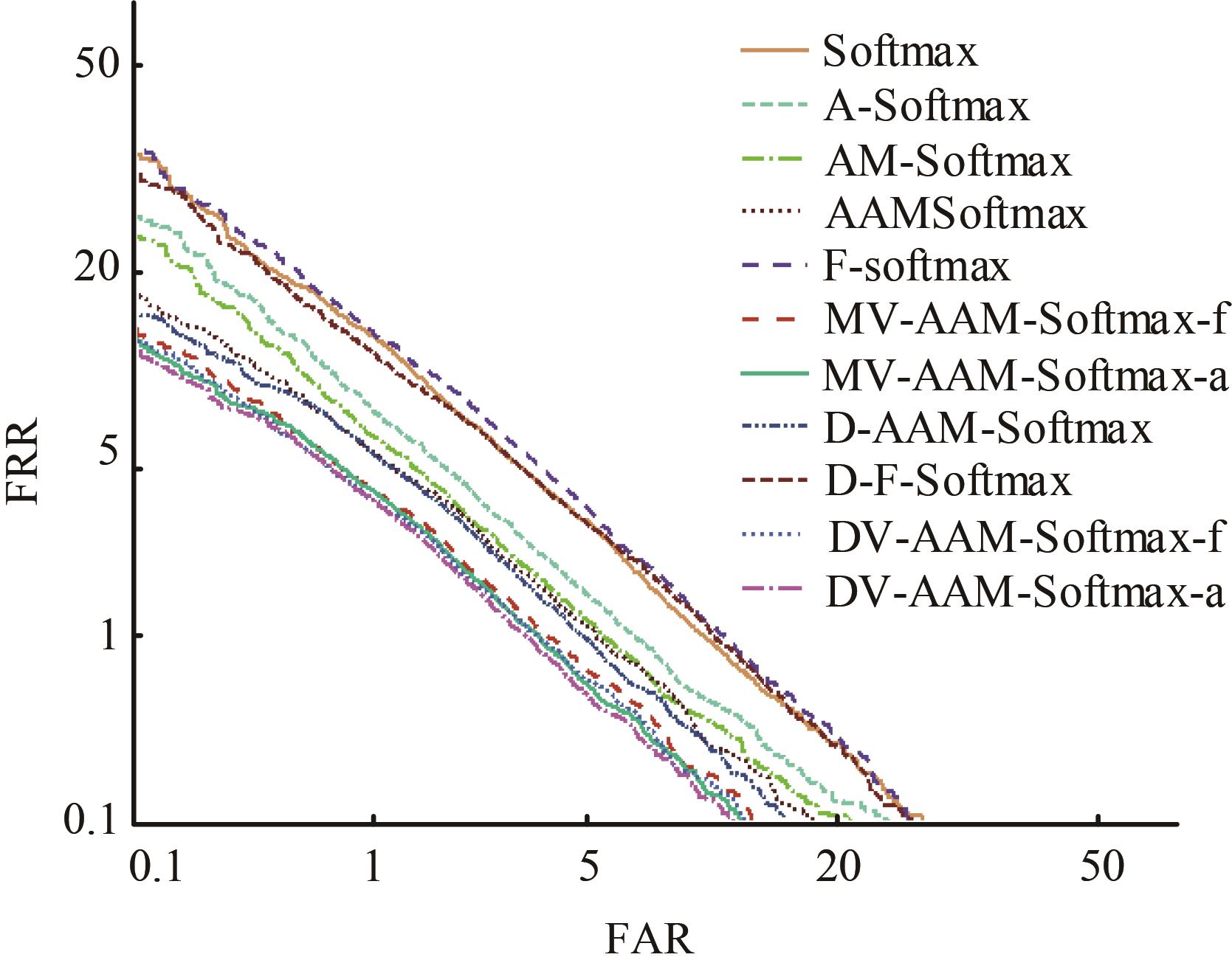
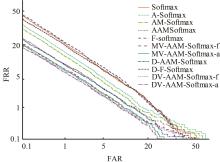
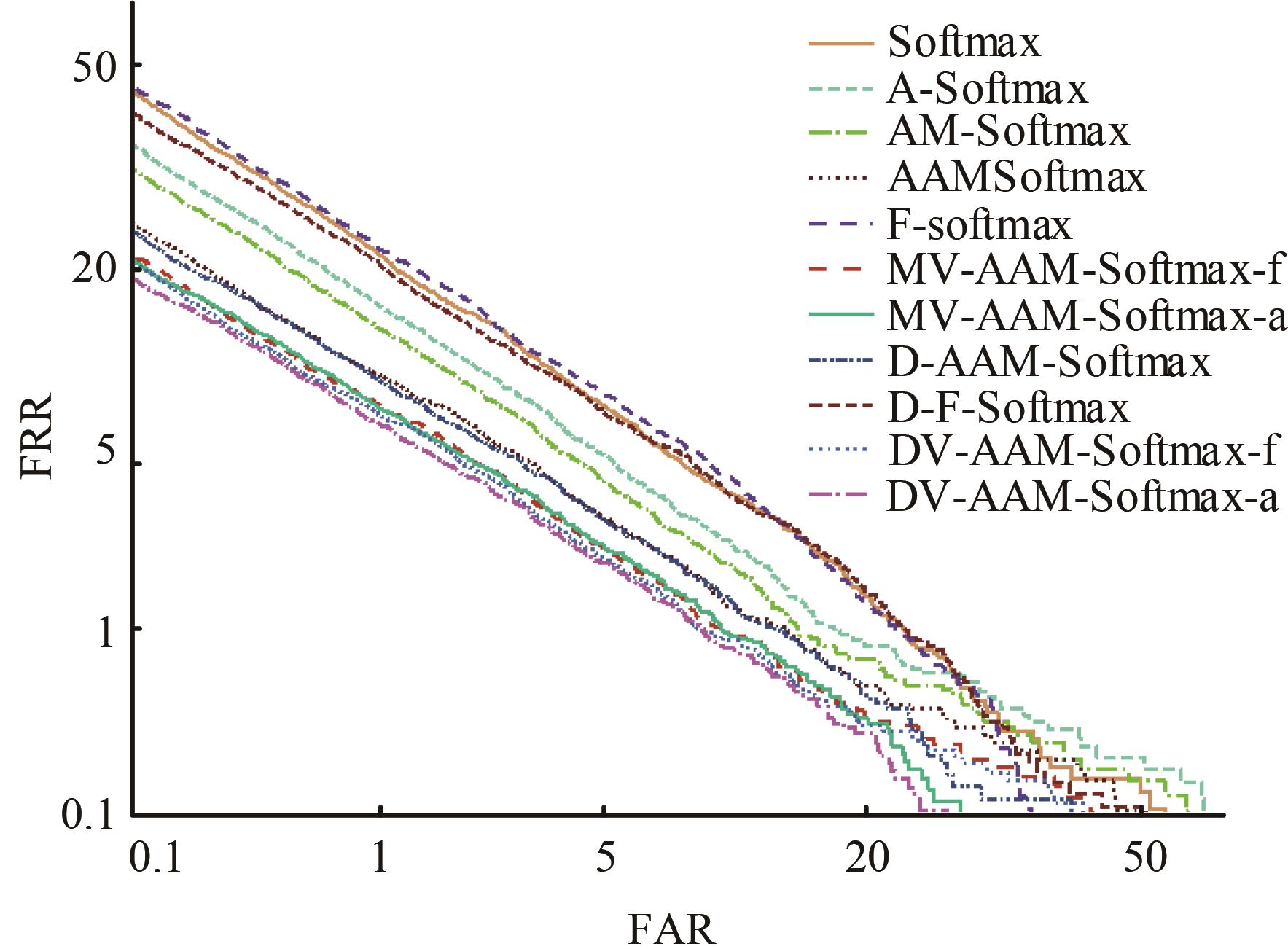
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3318-3326.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221635
Voiceprint recognition method based on novel loss function DV-Softmax
Yi CAO( ),Ping LI,Wei-guan WU,Yu XIA,Qing-yuan GAO
),Ping LI,Wei-guan WU,Yu XIA,Qing-yuan GAO
- School of Mechanical Engineering,Jiangnan University,Wuxi 214122,China
CLC Number:
- TN912.34
| 1 | Ranjan R, Castillo C D, Chellappa R. L2-constrained softmax loss for discriminative face verification[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2017, 3: No.170309507. |
| 2 | Liu W, Wen Y, Yu Z, et al. Sphereface: deep hypersphere embedding for face recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hololulu, USA, 2017: 212-220. |
| 3 | Wang F, Cheng J, Liu W, et al. Additive margin softmax for face verification[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(7): 926-930. |
| 4 | Deng J, Guo J, Xue N, et al. Arcface: additive angular margin loss for deep face recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4690-4699. |
| 5 | Thienpondt J, Desplanques B, Demuynck K. Cross-lingual speaker verification with domain-balanced hard prototype mining and language-dependent score normalization[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2020, 7: No. 200707689. |
| 6 | Li X, Wang W, Wu L J, et al. Generalized focal loss: learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 21002-21012. |
| 7 | Ma C, Sun H, Zhu J, et al. Normalized maximal margin loss for open-set image classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 54276-54285. |
| 8 | Lee J, Wang Y, Cho S. Angular margin-mining softmax loss for face recognition[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 43071-43080. |
| 9 | Boutros F, Damer N, Kirchbuchner F, et al. Elasticface: elastic margin loss for deep face recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1578-1587. |
| 10 | Wang X, Zhang S, Wang S, et al. Mis-classified vector guided softmax loss for face recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020, 34(7): 12241-12248. |
| 11 | Nagrani A, Chung J S, Zisserman A, et al. Voxceleb: a large-scale speaker identification dataset[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2017, 6: No.170608612. |
| 12 | Mclaren M, Ferrer L, Castan D, et al. The speakers in the wild (SITW) speaker recognition database[C]∥ Proceedings of the Interspeech, San Francisco, USA, 2016: 818-822. |
| 13 | Shrivastava A, Gupta A, Girshick R. Training region-based object detectors with online hard example mining[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 761-769. |
| 14 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 15 | Desplanques B, Thienpondt J, Demuynck K, et al. Ecapa-tdnn: emphasized channel attention, propagation and aggregation in tdnn based speaker verification[C]∥Interspeech, Shanghai, China, 2020: 3830-3834. |
| 16 | Shen H, Yang Y, Sun G, et al. Improving fairness in speaker verification via group-adapted fusion network[C]∥ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 2022: 7077-7081. |
| [1] | Meng-xue ZHAO,Xiang-jiu CHE,Huan XU,Quan-le LIU. A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [2] | Yuan-ning LIU,Zi-nan ZANG,Hao ZHANG,Zhen LIU. Deep learning-based method for ribonucleic acid secondary structure prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [3] | Xi ZHANG,Shao-ping KU. Facial super-resolution reconstruction method based on generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 333-338. |
| [4] | Hui-zhi XU,Shi-sen JIANG,Xiu-qing WANG,Shuang CHEN. Vehicle target detection and ranging in vehicle image based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [5] | Lu Li,Jun-qi Song,Ming Zhu,He-qun Tan,Yu-fan Zhou,Chao-qi Sun,Cheng-yu Zhou. Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [6] | Lei ZHANG,Jing JIAO,Bo-xin LI,Yan-jie ZHOU. Large capacity semi structured data extraction algorithm combining machine learning and deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [7] | Bai-you QIAO,Tong WU,Lu YANG,You-wen JIANG. A text sentiment analysis method based on BiGRU and capsule network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [8] | Xin-gang GUO,Ying-chen HE,Chao CHENG. Noise-resistant multistep image super resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [9] | Li-ping ZHANG,Bin-yu LIU,Song LI,Zhong-xiao HAO. Trajectory k nearest neighbor query method based on sparse multi-head attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [10] | Ming-hui SUN,Hao XUE,Yu-bo JIN,Wei-dong QU,Gui-he QIN. Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [11] | Yu-kai LU,Shuai-ke YUAN,Shu-sheng XIONG,Shao-peng ZHU,Ning ZHANG. High precision detection system for automotive paint defects [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [12] | Xiong-fei LI,Zi-xuan SONG,Rui ZHU,Xiao-li ZHANG. Remote sensing change detection model based on multi⁃scale fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [13] | Guo-jun YANG,Ya-hui QI,Xiu-ming SHI. Review of bridge crack detection based on digital image technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [14] | Bin ZHAO,Cheng-dong WU,Xue-jiao ZHANG,Ruo-huai SUN,Yang JIANG. Target grasping network technology of robot manipulator based on attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3423-3432. |
| [15] | Yong WANG,Yu-xiao BIAN,Xin-chao LI,Chun-ming XU,Gang PENG,Ji-kui WANG. Image dehazing algorithm based on multiscale encoding decoding neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3626-3636. |
|
||