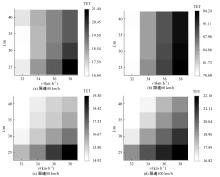
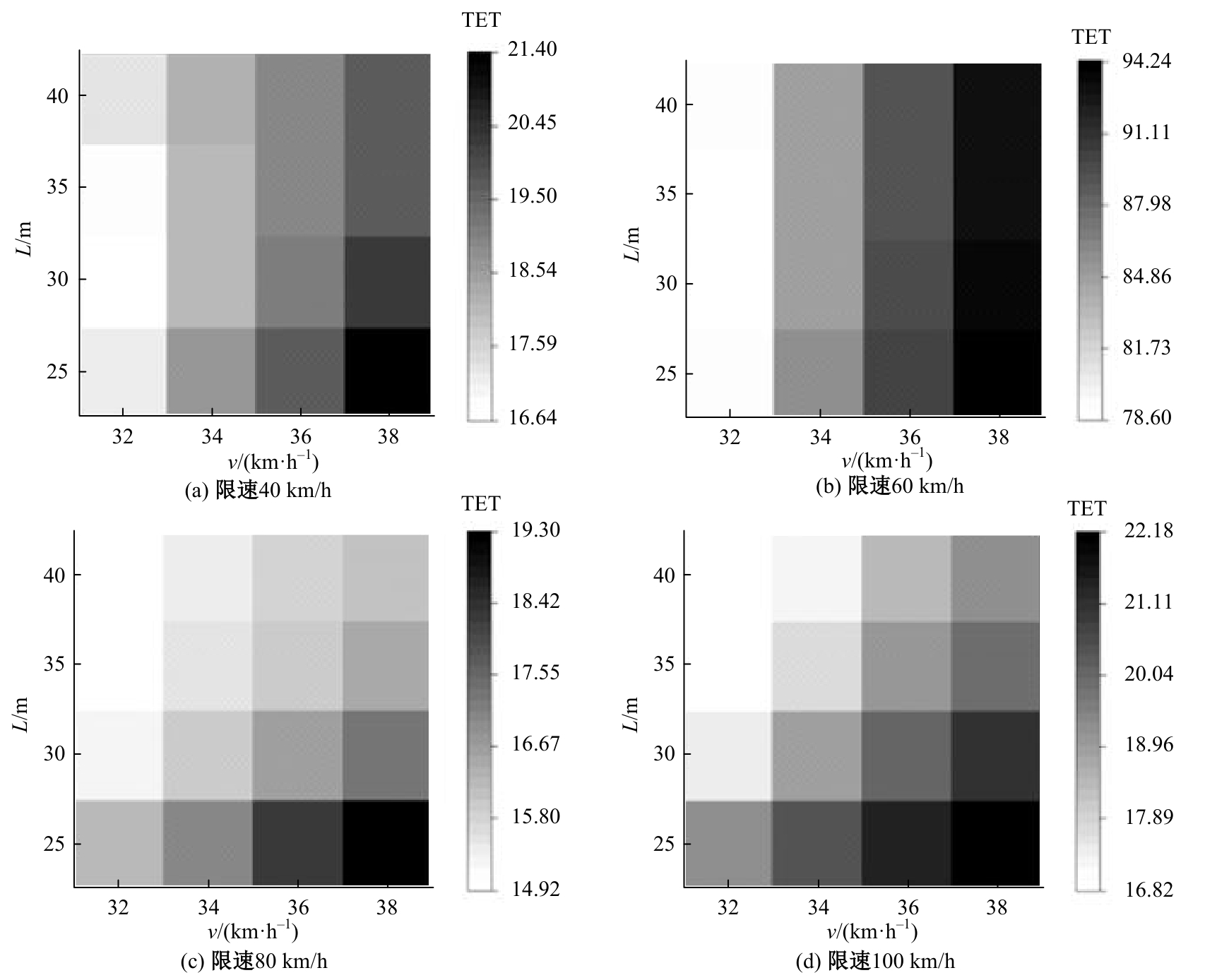
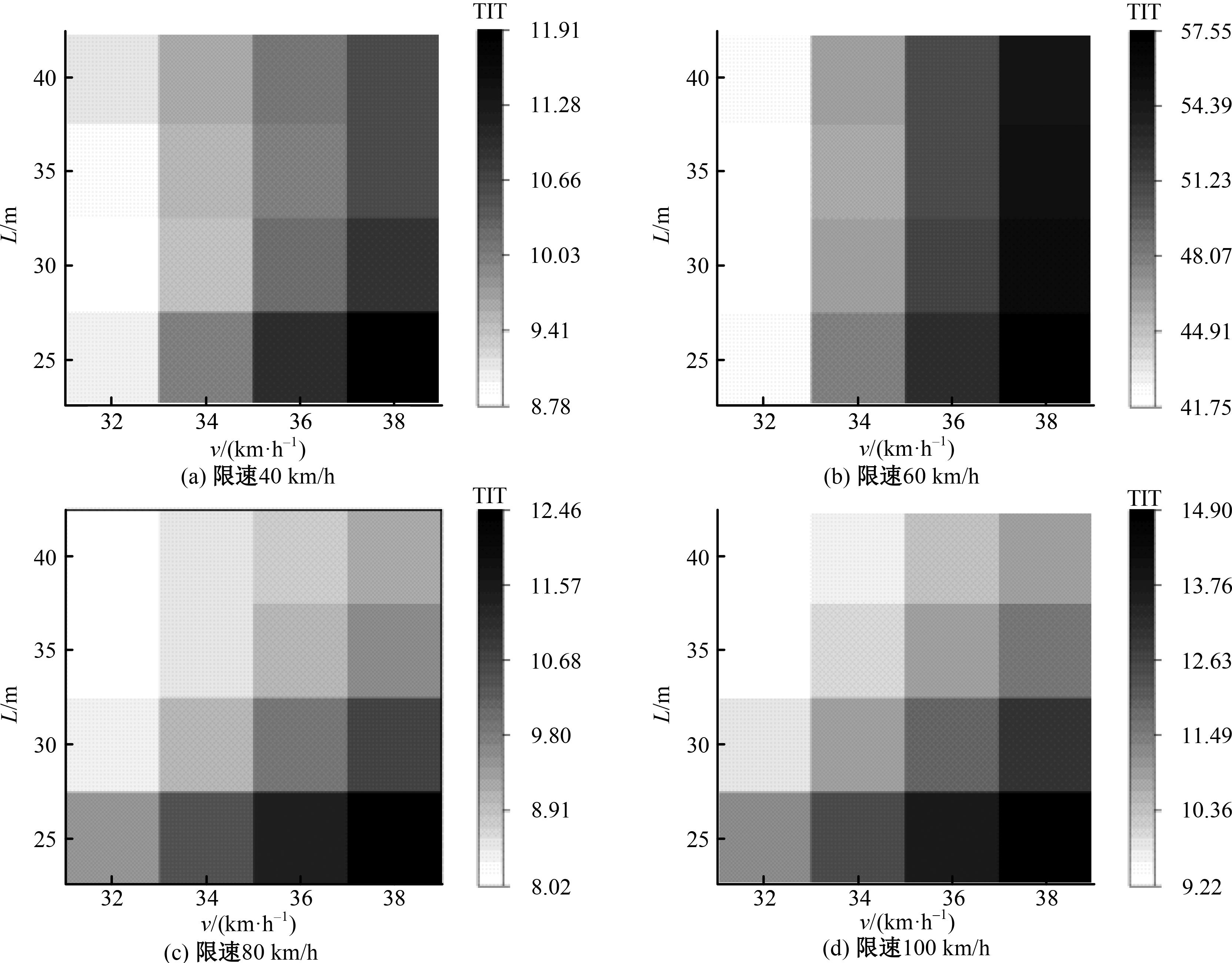
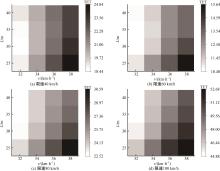
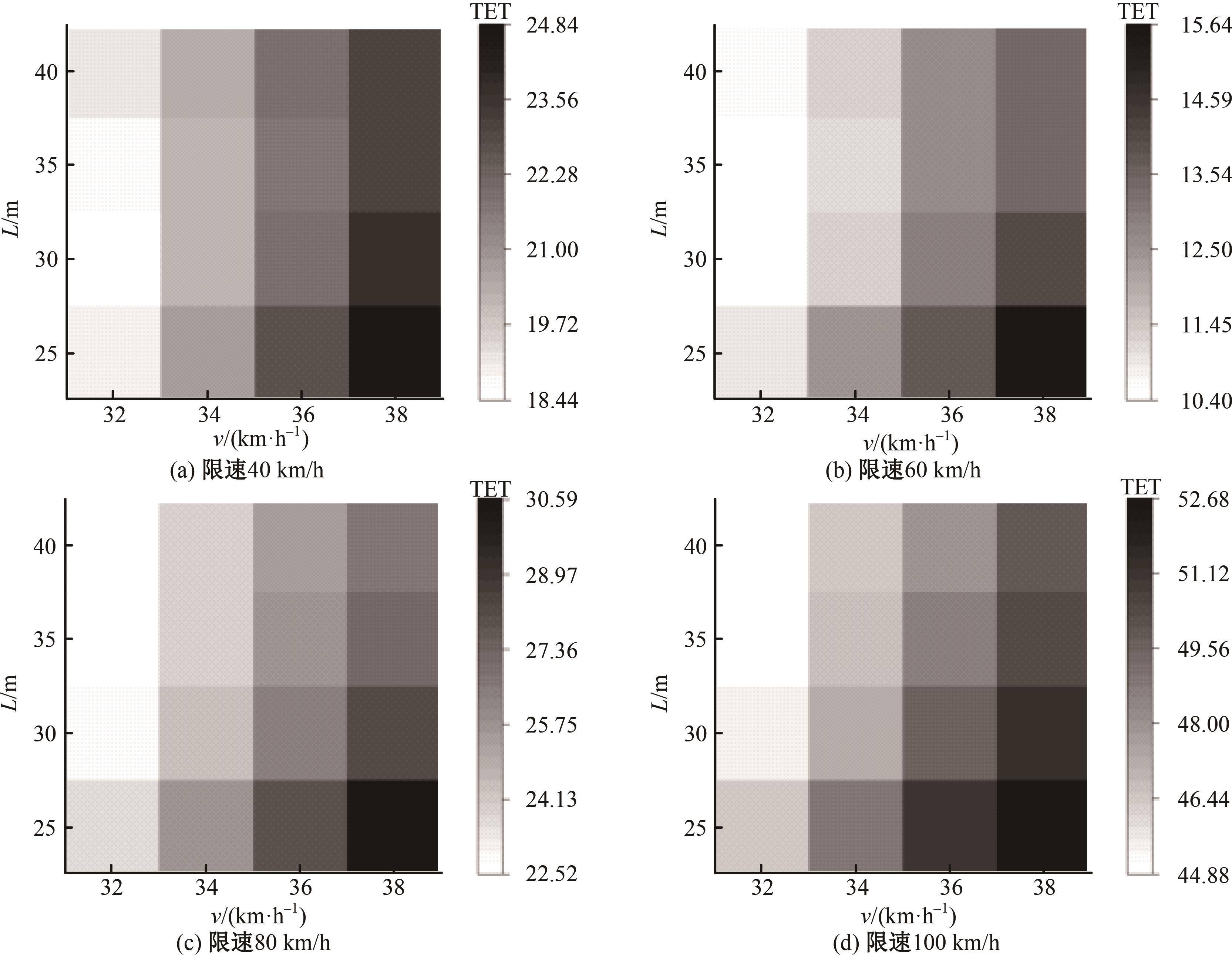
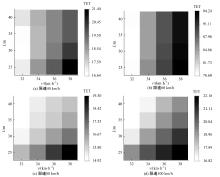
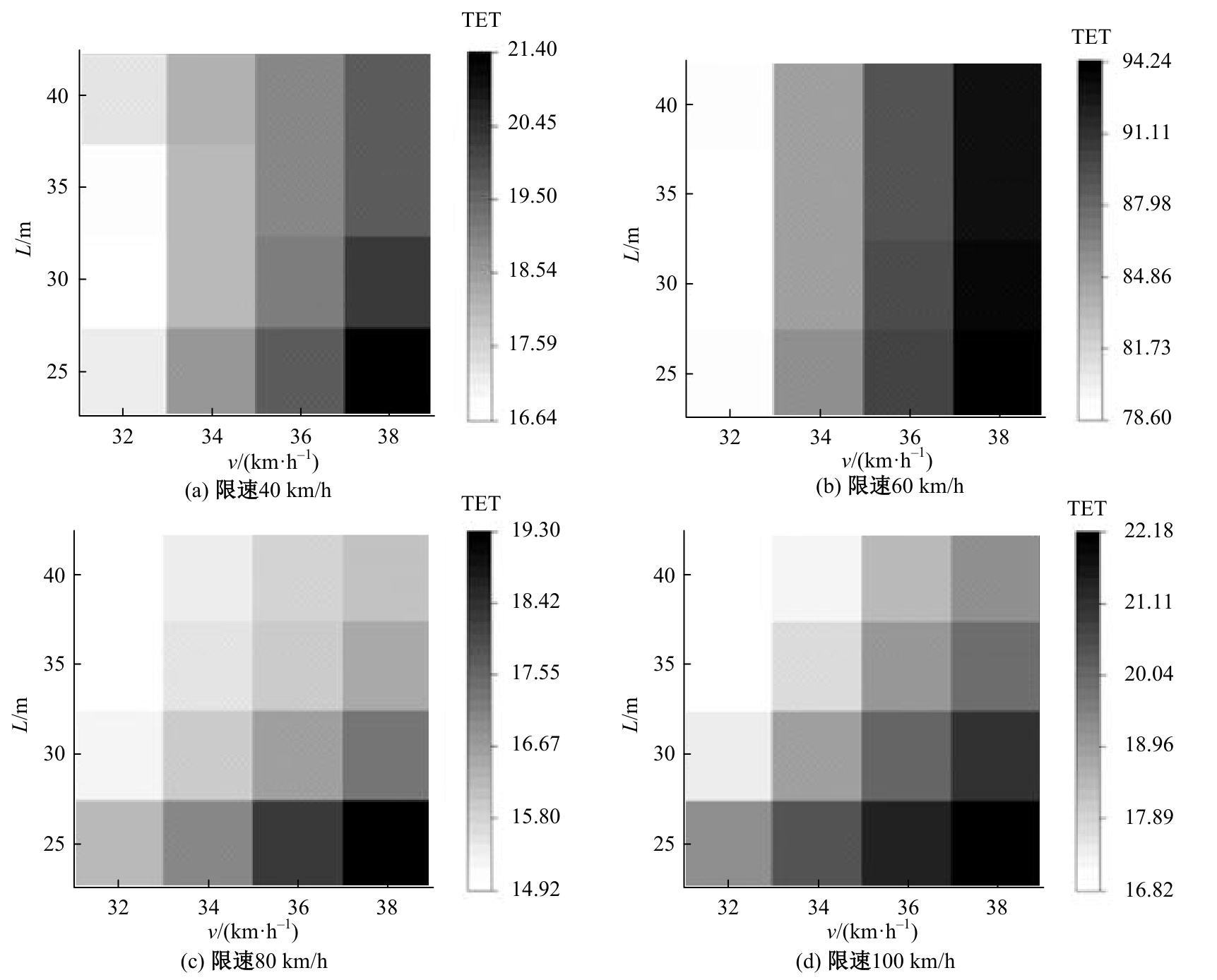
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1241-1249.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230634
Previous Articles Next Articles
Car-following safety analysis and control strategy for foggy freeway
Yan-yan QIN1( ),Teng-fei XIAO1,Qin-zhong LUO1,Bao-jie WANG2(
),Teng-fei XIAO1,Qin-zhong LUO1,Bao-jie WANG2( )
)
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Management,Control and Cycle Repair Technology for Traffic Network Facilities in Ecological Security Barrier Area(Chang'an University),Xi'an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | Shangguan Q Q, Fu T, Liu S. Investigating rear-end collision avoidance behavior under varied foggy weather conditions: a study using advanced driving simulator and survival analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2020, 139:No. 105499. |
| 2 | 吴兵, 翟犇, 卢建涛, 等. 基于安全风险的恶劣天气下高速公路建议车速确定方法[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 48(11): 1570-1578. |
| Wu Bing, Zhai Ben, Lu Jian-tao, et al. Determination of freeway recommended speed based on safety risk under adverse weather conditions[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2020, 48(11): 1570-1578. | |
| 3 | Das A, Ghasemzadeh A, Ahmed M M. Analyzing the effect of fog weather conditions on driver lane-keeping performance using the SHRP2 naturalistic driving study data[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2019, 68: 71-80. |
| 4 | Hammit B E, Ghasemzadeh A, James R M, et al. Evaluation of weather-related freeway car-following behavior using the SHRP2 naturalistic driving study database[J]. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 2018, 59: 244-259. |
| 5 | Rosey F, Aillerie I, Espie S, et al. Driver behaviour in fog is not only a question of degraded visibility—a simulator study[J]. Safety Science, 2017, 95: 50-61. |
| 6 | Huang Y, Yan X D, Li X M, et al. Improving car-following model to capture unobserved driver heterogeneity and following distance features in fog condition[J]. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science, 2022, 10: 1-24. |
| 7 | 高坤, 涂辉招, 时恒, 等. 雾霾天气低能见度对不同跟驰状态驾驶行为的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1716-1727. |
| Gao Kun, Tu Hui-zhao, Shi Heng, et al. Effect of low visibility in haze weather condition on longitudinal driving behavior in different car-following stages[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1716-1727. | |
| 8 | Das A, Ahmed M M. Adjustment of key lane change parameters to develop microsimulation models for representative assessment of safety and operational impacts of adverse weather using SHRP2 naturalistic driving data[J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2022, 81: 9-20. |
| 9 | Zhai B, Lu J T, Wang Y L, et al. Real-time prediction of crash risk on freeways under fog conditions[J]. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 287-298. |
| 10 | Wu Y N, Abdel A M, Cai Q, et al. Developing an algorithm to assess the rear-end collision risk under fog conditions using real-time data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 87: 11-25. |
| 11 | 黄岩, 闫学东, 李晓梦, 等. 基于多用户驾驶模拟平台的雾天高速公路跟驰模型参数标定及验证[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(8): 320-330. |
| Huang Yan, Yan Xue-dong, Li Xiao-meng, et al. Parameters calibration and validation for car-following models in freeway under foggy conditions based on multi-user driving simulator system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(8): 320-330. | |
| 12 | Minderhoud M M, Bovy P H L. Extended time-to-collision measures for road traffic safety assessment[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2001, 33(1): 89-97. |
| 13 | Hassanin O, Wang X S, Wu X B, et al. Efficiency performance and safety evaluation of the responsibility-sensitive safety in freeway car-following scenarios using automated longitudinal controls[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2022, 177:No. 106799. |
| 14 | Han Y, Yu H, Li Z B, et al. An optimal control-based vehicle speed guidance strategy to improve traffic safety and efficiency against freeway jam waves[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 163: No.106429. |
| 15 | 秦严严,刘小辉,唐热情. 交通流分析理论[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2023. |
| 16 | 罗瑞发, 郝慧君, 徐桃让, 等. 考虑智能网联车队强度的混合交通流基本图模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(2): 405-412. |
| Luo Rui-fa, Hao Hui-jun, Xu Tao-rang, et al. Fundamental diagram model of mixed traffic flow of connected and automated vehicles considering vehicles degradations and platooning intensity[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 405-412. | |
| 17 | 秦严严, 杨晓庆, 王昊. 智能网联混合交通流CO2排放影响及改善方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| Qin Yan-yan, Yang Xiao-qing, Wang Hao. Impacts of CO2 emissions and improving method for connected and automated mixed traffic flow[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 150-158. |
| [1] | Zhen-jiang LI,Li WAN,Shi-rui ZHOU,Chu-qing TAO,Wei WEI. Dynamic estimation of operational risk of tunnel traffic flow based on spatial-temporal Transformer network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1336-1345. |
| [2] | Yi-yong PAN,Xiang-yu XU. Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [3] | Lei SHANG,Ping YANG,Xiang-guo YANG,Jian-xin PAN,Jun YANG,Meng-ru ZHANG. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on APSO-BP-PID control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2401-2413. |
| [4] | Xi-zhen ZHOU,He GONG,Dun-dun LI,Yan-jie JI,Jie YAN. Nonlinear model for impact of built environment on curb parking spaces occupancy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [5] | Ya-qin QIN,Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE. Vehicle cooperative obstacle avoidance strategy driven by CLAM model and trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [6] | Yun PU,Yin XU,Hai-xu LIU,Yi-fan TAN. An improved car⁃following model for connected and automated vehicles considering impact of multiple vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1285-1292. |
| [7] | Xue-jing DU,Ning WANG,Jie ZHANG,Yu-long PEI. Control strategy of lateral stability of semi-trailer train in dangerous section of cold area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 996-1006. |
| [8] | Hui SONG,Da-yi QU,Shao-jie WANG,Tao WANG,Zi-yi YANG. Connected mixed traffic flow car-following model and stability analysis considering multiple vehicles response [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3220-3230. |
| [9] | You ZHOU,Wei HONG,Fang-xi XIE,Yu LIU,Xun GONG,Xiao-ping LI. Influence of valve control strategy to improve un⁃throttle engine performance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 55-65. |
| [10] | Hong-tao LI,Lin-hong WANG,Jun-da LI. Influence of lighting and speed limit on visual search ability at highway intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [11] | Bing HUI,Wei LIU,Yu-kun ZHOU,Shu-qi LI. Simulation on driving safety of bridge /tunnel connecting section of expressway under strong crosswind [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2312-2320. |
| [12] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [13] | Zhen-liang LIU,Cun-bao ZHAO,Yun-peng WU,Mi-na MA,Long-shuang MA. Life⁃cycle seismic resilience assessment of highway bridge networks using data⁃driven method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [14] | Hong-fei JIA,Ying-jun XU,Li-li YANG,Nan WANG. League member selection and benefit distribution of commercial vehicles multi⁃modal transportation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [15] | Chao SUN,Hao-wei YIN,Wen-yun TANG,Zhao-ming CHU. Sensor deployment strategy and expansion inference of mobile phone data for traffic demand estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
|