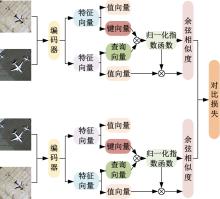
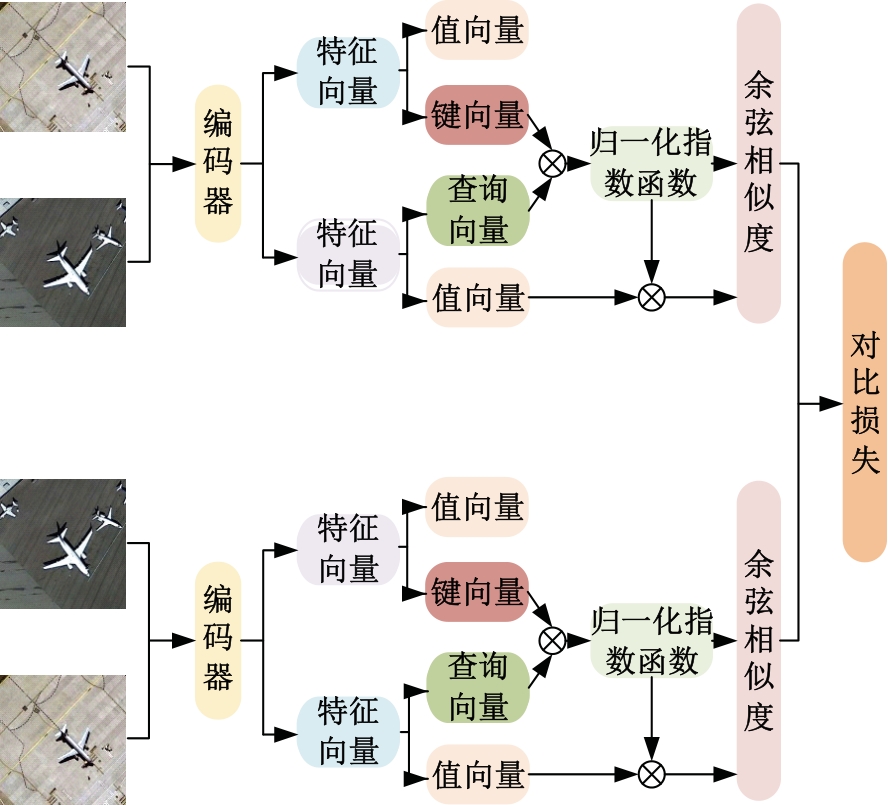
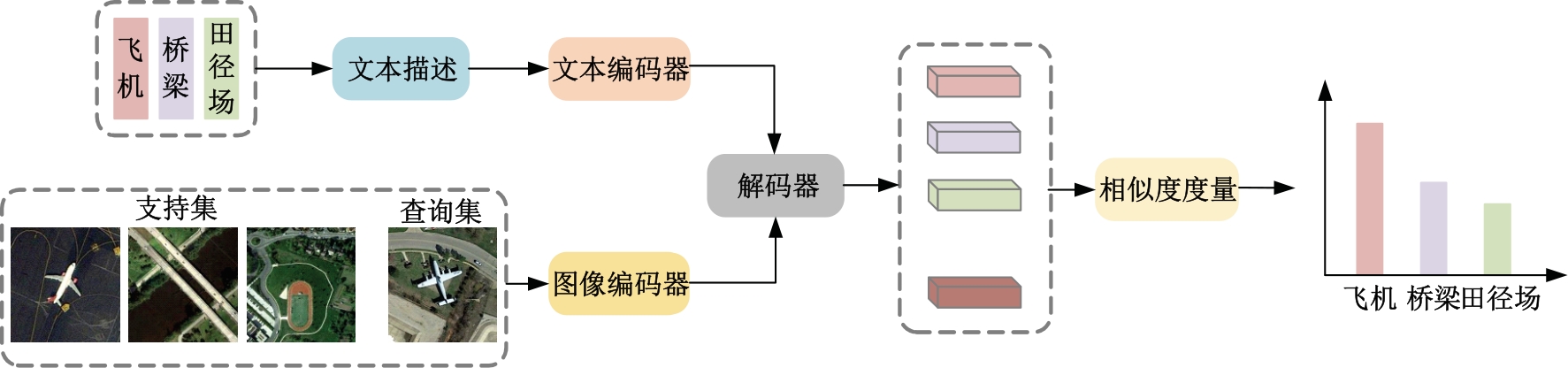
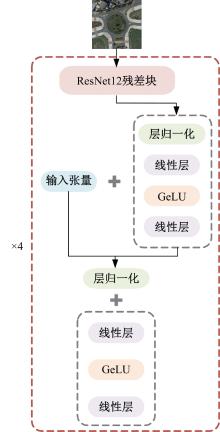
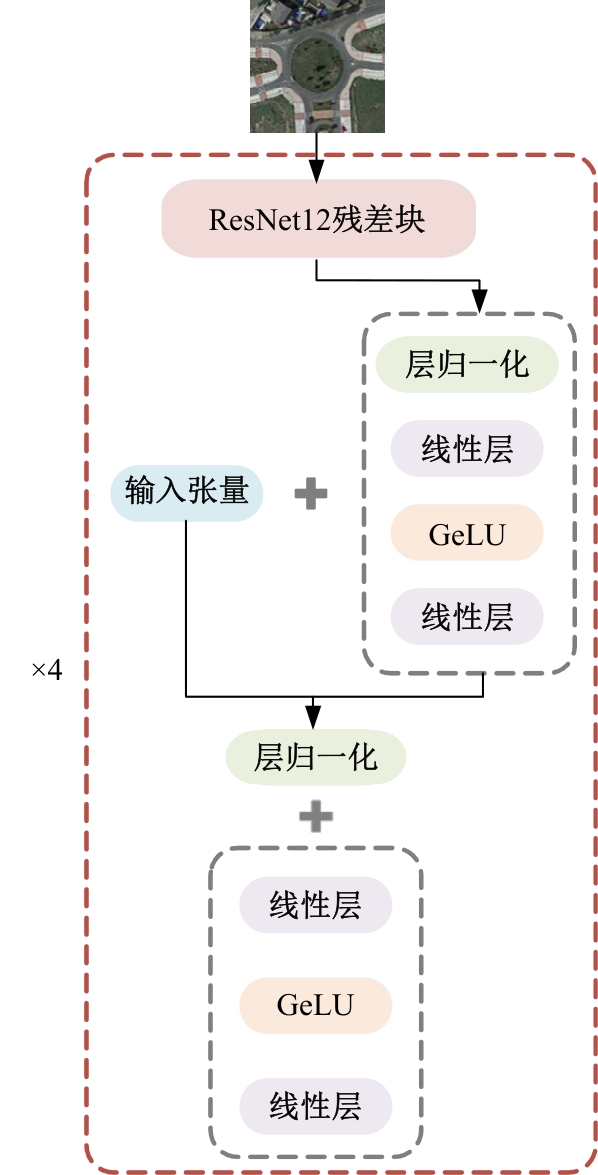
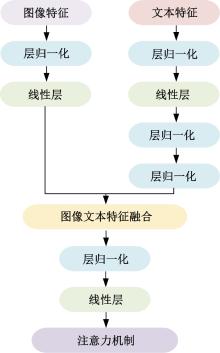
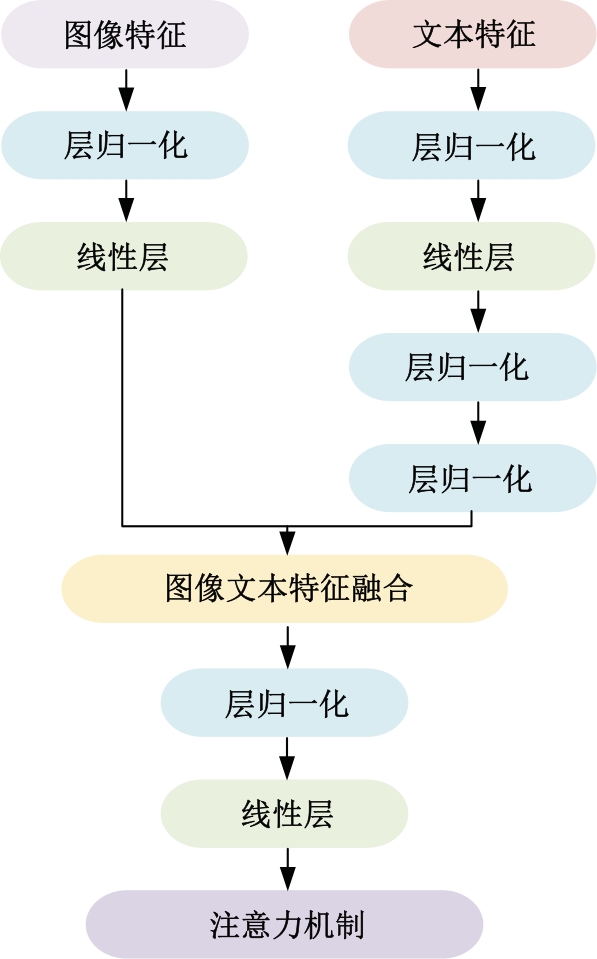
| [1] |
Li L, Han J, Yao X, et al.DLA-MatchNet for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59 (9): 7844-7853.
|
| [2] |
Li X, Shi D, Diao X, et al.SCL-MLNet: boosting few-shot remote sensing scene classification via self-supervised contrastive learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 1-12.
|
| [3] |
崔璐, 张鹏, 车进.基于深度神经网络的遥感图像分类算法综述[J]. 计算机科学,2018, 45 (6): 50-53.
|
|
Cui Lu, Zhang Peng, Che Jin. A review of deep neural network based remote sensing image classification algorithms[J]. Computer Science,2018, 45(6): 50-53.
|
| [4] |
Gong T, Zheng X, Lu X.Meta self-supervised learning for distribution shifted few-shot scene classification[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 1-5.
|
| [5] |
Yuan Z, Tang C, Yang A, et al.Few-shot remote sensing image scene classification based on metric learning and local descriptors[J].Remote Sensing,2023, 15 (3): No.831.
|
| [6] |
Snell J, Swersky K, Zemel R.Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30:No. 05175.
|
| [7] |
Sung F, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1199-1208.
|
| [8] |
Ye H J, Hu H, Zhan D C, et al. Few-shot learning via embedding adaptation with set-to-set functions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle,USA, 2020: 8808-8817.
|
| [9] |
Cheng G, Cai L, Lang C, et al.SPNet: Siamese-prototype network for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2021, 60: 1-11.
|
| [10] |
Cheng K, Yang C, Fan Z, et al. TeAw: Text-aware few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1-5.
|
| [11] |
Khosla P, Teterwak P, Wang C, et al.Supervised contrastive learning[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 18661-18673.
|
| [12] |
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al.Attention is all you need[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: No. 03762.
|
| [13] |
Radford A, Kim J W, Hallacy C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Jeju Island, Repubic of Korea, 2021: 8748-8763.
|
| [14] |
Li Y, Zhu Z, Yu J-G, et al.Learning deep cross-modal embedding networks for zero-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(12): 10590-10603.
|
| [15] |
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778.
|
| [16] |
Tolstikhin I O, Houlsby N, Kolesnikov A, et al.Mlp-mixer: an all-mlp architecture for vision[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2021, 34: 24261-24272.
|
| [17] |
Cheng G, Han J, Lu X.Remote sensing image scene classification: benchmark and state of the art[J].Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105 (10): 1865-1883.
|
| [18] |
Xia G S, Hu J, Hu F, et al.AID: a benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965-3981.
|
| [19] |
Yang Y, Newsam S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification[C]∥Proceedings of the 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA,2010: 270-279.
|
| [20] |
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141.
|
| [21] |
Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Online, 2020: 11534-11542.
|
| [22] |
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, et al. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Glasgow, England, 2018: 3-19.
|
| [23] |
Fu R, Hu Q, Dong X, et al.Axiom-based grad-cam: Towards accurate visualization and explanation of cnns[J/OL].[2023-10-11].,2020
|