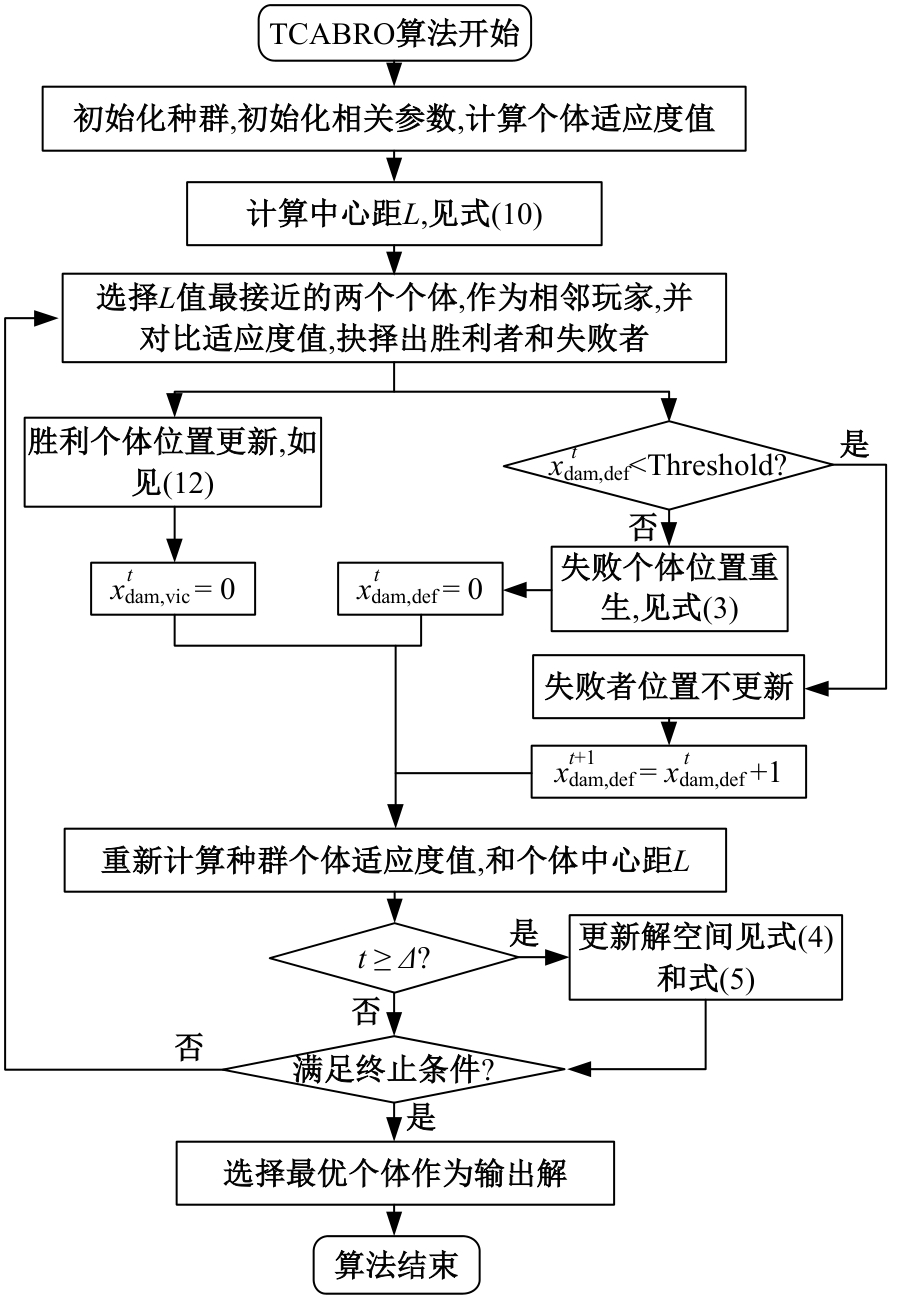
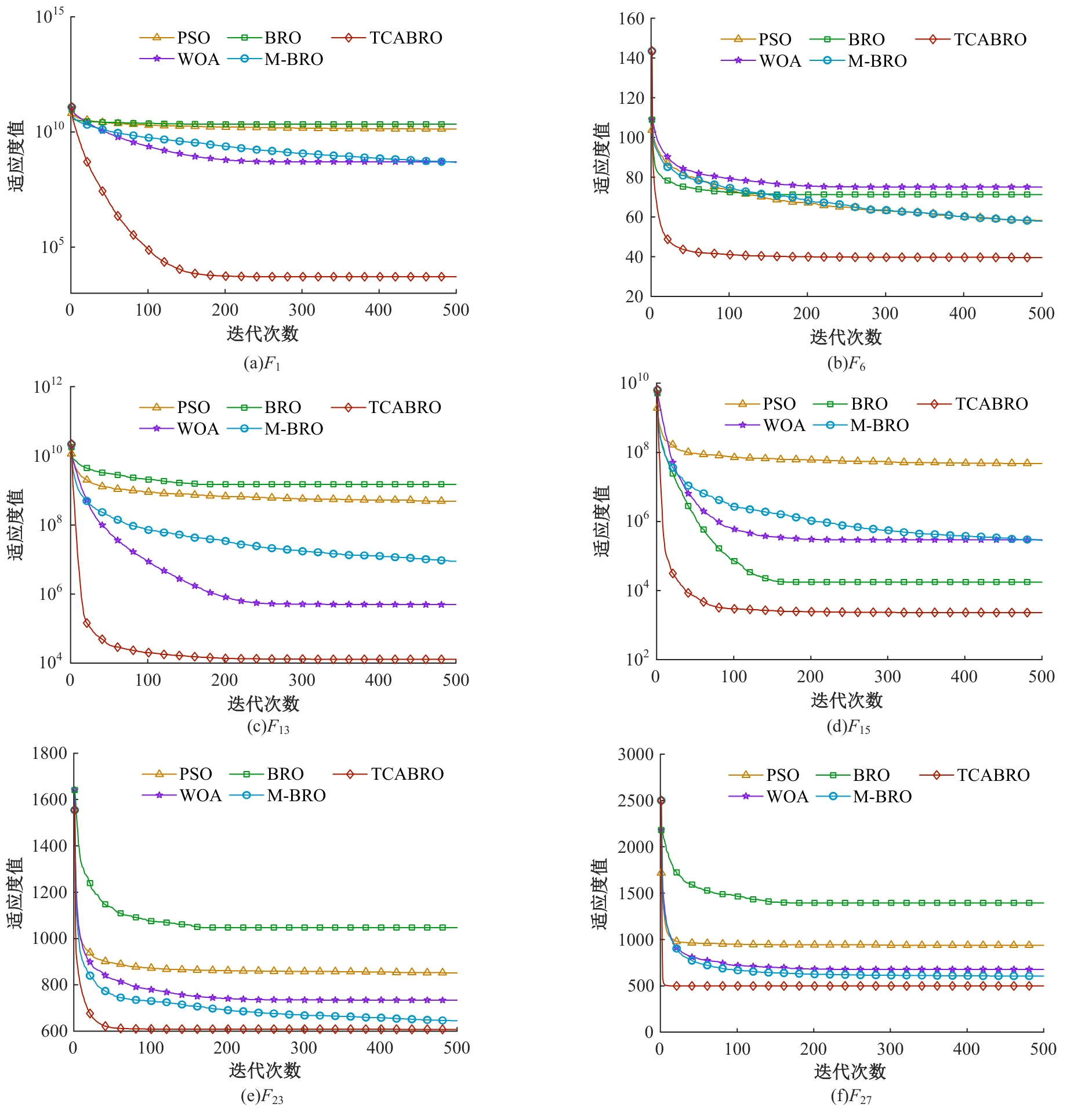
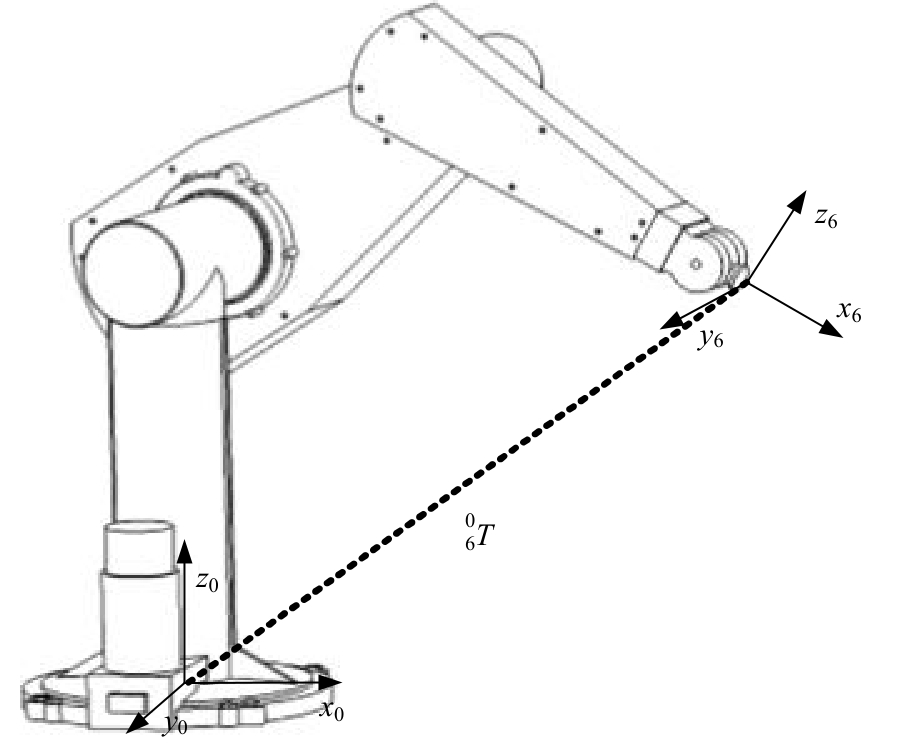
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2703-2710.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231190
Previous Articles Next Articles
Robot inverse kinematics solution based on center selection battle royale optimization algorithm
Yu-fei ZHANG1,2( ),Li-min WANG3(
),Li-min WANG3( ),Jian-ping ZHAO2,Zhi-yao JIA3,Ming-yang LI4
),Jian-ping ZHAO2,Zhi-yao JIA3,Ming-yang LI4
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.School of Information,Guangdong University of Finance and Economics,Guangzhou 510320,China
4.School of Economics and Management,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP301.6
| [1] | Kong Y, Song S, Zhang N, et al. Design and kinematic modeling of in-situ torsionally-steerable flexible surgical robots[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 1864-1871. |
| [2] | Li J, Yu H, Shen N, et al. A novel inverse kinematics method for 6-DOF robots with non-spherical wrist[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2021, 157: 104180. |
| [3] | Starke S, Hendrich N, Zhang J. Memetic evolution for generic full-body inverse kinematics in robotics and animation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(3): 406-420. |
| [4] | Rahkar F T. Battle royale optimization algorithm[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(4): 1139-1157. |
| [5] | Wu H, Zhang X, Song L, et al. A hybrid improved BRO algorithm and its application in inverse kinematics of 7R 6DOF robot[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 14(3): 16878132221085125. |
| [6] | Alamgir F M, Alam M S. A novel deep learning-based bidirectional elman neural network for facial emotion recognition[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(10): 2252016. |
| [7] | Karamnejadi A K, Kakouee A, Mollajafari M, et al. Developed design of battle royale optimizer for the optimum identification of solid oxide fuel cell[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(16): 14169882. |
| [8] | Akan T, Agahian S, Dehkharghani R. Battle royale optimizer for solving binary optimization problems[J]. Software Impacts, 2022, 12: 100274. |
| [9] | Akan S, Akan T. Battle royale optimizer with a new movement strategy[J]. Handbook of Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithms, 2022, 9: 265-279. |
| [10] | 国强, 朱国会, 李万臣. 基于混沌麻雀搜索算法的TDOA/FDOA定位[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(2): 593-600. |
| Guo Qiang, Zhu Guo-hui, Li Wan-chen. TDOA/FDOA localization based on chaotic sparrow search algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 593-600. | |
| [11] | Wu G, Mallipeddi R, Suganthan P. Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the CEC 2017 competition on constrained real-parameter optimization[R]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2017. |
| [12] | Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization[C]∥Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth: IEEE, 1995: 1942-1948. |
| [13] | Mirjalili S, Lewis A. The whale optimization algorithm[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2016, 95: 51-67. |
| [14] | Elsherbiny A, Elhosseini M A, Haikal A Y. A new ABC variant for solving inverse kinematics problem in 5 DOF robot arm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 73: 24-38. |
| [15] | Lv X, Zhao M. Application of improved BQGA in robot kinematics inverse solution[J]. Journal of Robotics, 2019, 2019: 1659180. |
| [1] | Wen-hui LI,Chen YANG. Few-shot remote sensing image classification based on contrastive learning text perception [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2393-2401. |
| [2] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Liang LI. Graph similarity measurement algorithm combining global and local fine-grained features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2365-2371. |
| [3] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-peng SUN. Graph node classification algorithm based on similarity random walk aggregation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2069-2075. |
| [4] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhe GUO,Yu-si FAN. Feature representation algorithm for imbalanced classification of multi⁃omics cancer data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 2089-2096. |
| [5] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [6] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Yu-ning WU,Quan-le LIU. A weighted isomorphic graph classification algorithm based on causal feature learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [7] | Li-ming LIANG,Long-song ZHOU,Jiang YIN,Xiao-qi SHENG. Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [8] | Dondrub LHAKPA,Duoji ZHAXI,Jie ZHU. Tibetan text normalization method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3577-3588. |
| [9] | Yu-xin YE,Luo-jia XIA,Ming-hui SUN. Gesture input method based on transparent keyboard in augmented reality environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3274-3282. |
| [10] | Na CHE,Yi-ming ZHU,Jian ZHAO,Lei SUN,Li-juan SHI,Xian-wei ZENG. Connectionism based audio-visual speech recognition method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2984-2993. |
| [11] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN. Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [12] | Shan XUE,Ya-liang ZHANG,Qiong-ying LYU,Guo-hua CAO. Anti⁃unmanned aerial vehicle system object detection algorithm under complex background [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [13] | Zheng ZHANG,Qi-dan ZHU,Xiao-long LYU,Xing FAN. Optimized method for solving inverse kinematics of redundant manipulator [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3379-3387. |
| [14] | Zhen WANG,Xiao-han YANG,Nan-nan WU,Guo-kun LI,Chuang FENG. Ordinal cross entropy Hashing based on generative adversarial network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3536-3546. |
| [15] | Feng-feng ZHOU,Zhen-wei YAN. A model for identifying neuropeptides by feature selection based on hybrid features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
|