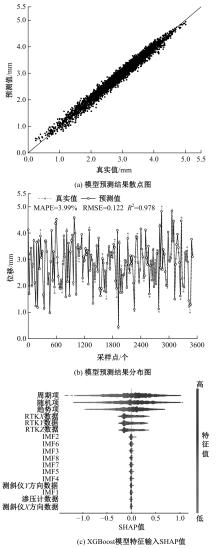
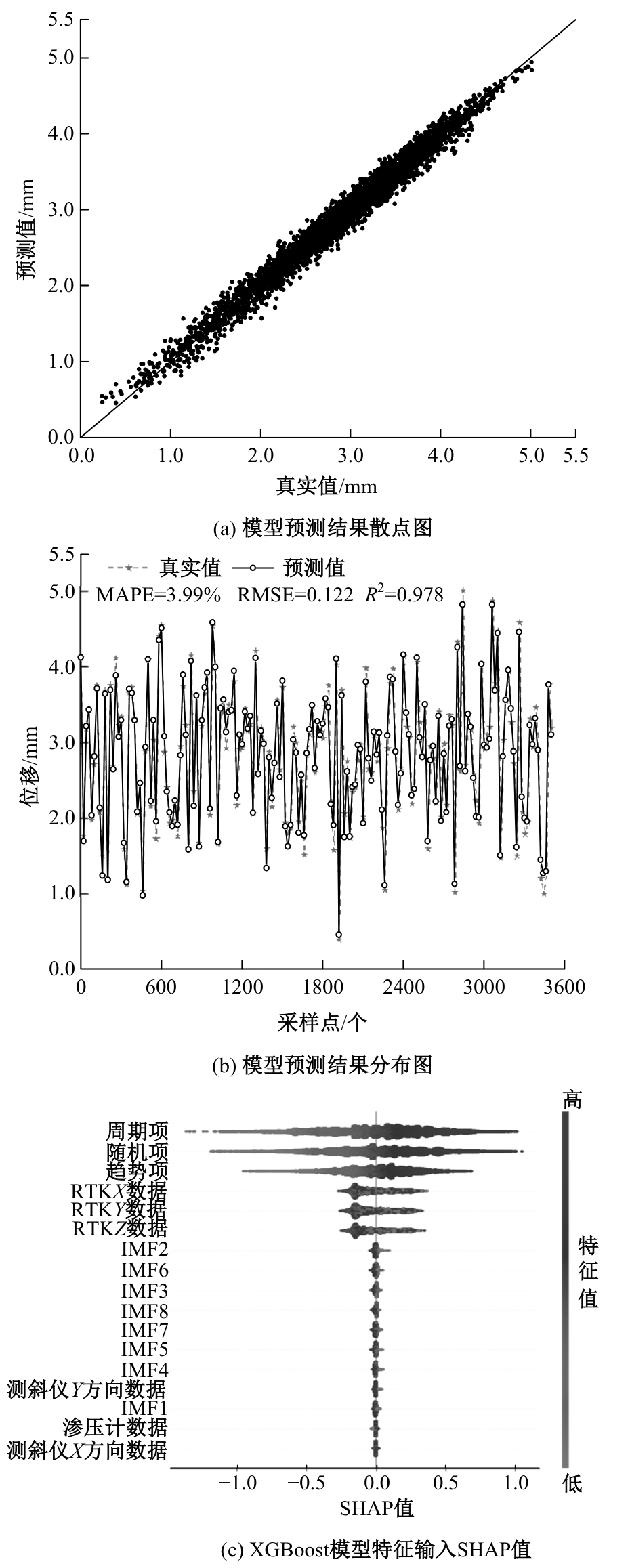
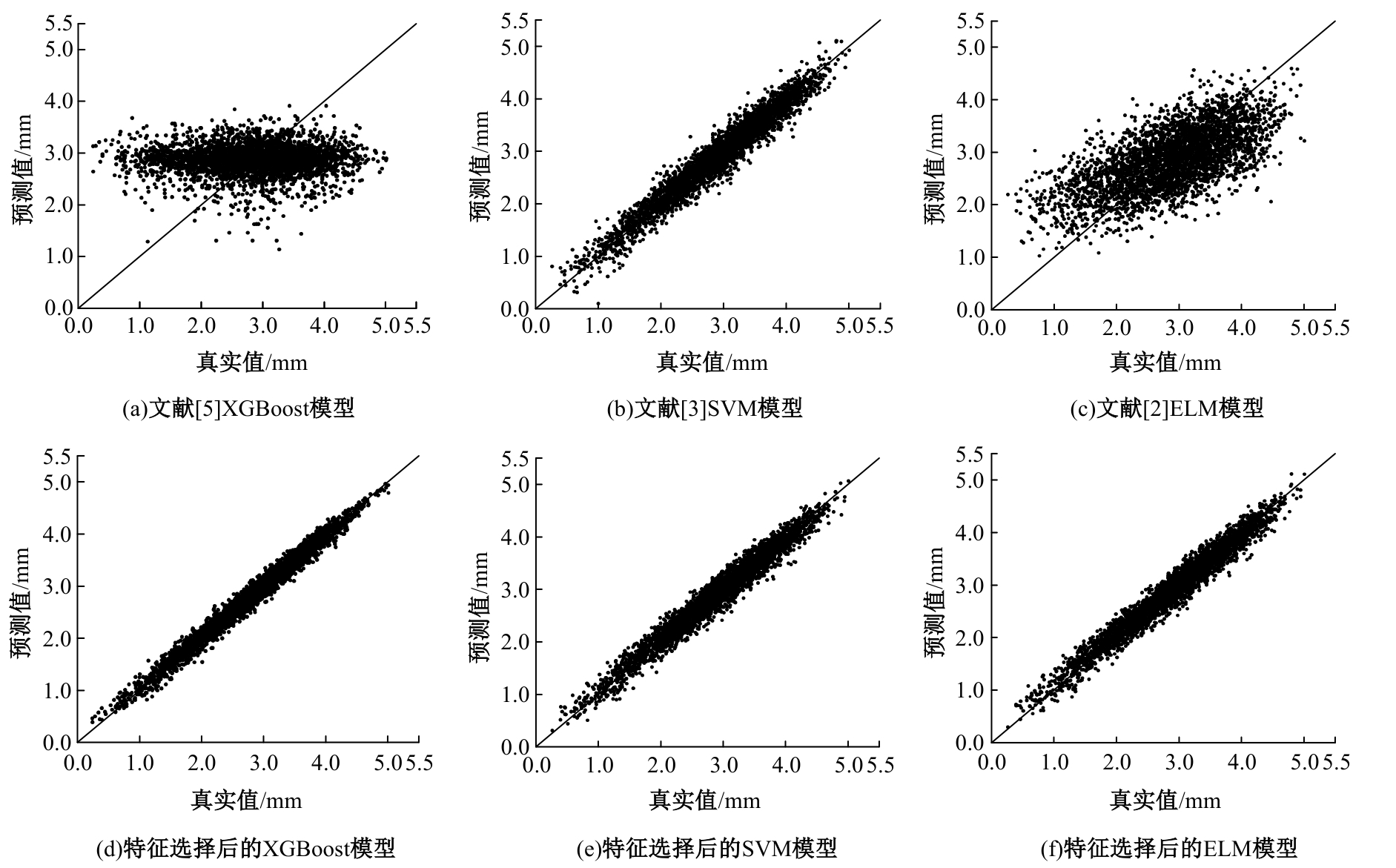
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2320-2332.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231197
Displacement prediction of highway slope based on variational mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting
Zhi-you LONG1,2( ),Zhao-long WAN1,2,Shi DONG1,2(
),Zhao-long WAN1,2,Shi DONG1,2( ),Chao YANG3,Xiao-yang LIU4
),Chao YANG3,Xiao-yang LIU4
- 1.School of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Engineering Research Center of Highway Infrastructure Digitalization,Ministry of Education,Xi'an 710064,China
3.Shaanxi Expressway Engineering Testing Inspection & Testing Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710086,China
4.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- U41
| [1] | 张勤, 白正伟, 黄观文, 等. GNSS滑坡监测预警技术进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(10): 1985-2000. |
| Zhang Qin, Bai Zheng-wei, Huang Guan-wen, et al. Review of GNSS landslide monitoring and early warning[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(10): 1985-2000. | |
| [2] | 李博, 李欣, 芮红, 等. 基于变分模态分解和灰狼优化极限学习机的隧道口边坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(6): 1853-1860. |
| Li Bo, Li Xin, Rui Hong, et al. Displacement prediction of tunnel entrance slope based on variational modal decomposition and grey wolf optimized extreme learning machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1853-1860. | |
| [3] | 李建新, 刘小生, 肖钢, 等. 基于PSR-WSVM模型的边坡位移预测[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(6): 577-580. |
| Li Jian-xin, Liu Xiao-sheng, Xiao Gang, et al. Slope displacement prediction based on PSR-WSVM model[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2020, 40(6): 577-580. | |
| [4] | 张凯, 张科. 基于LightGBM算法的边坡稳定性预测研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 113-120. |
| Zhang Kai, Zhang Ke. Prediction study on slope stability based on LightGBM algorithm[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 113-120. | |
| [5] | 黄智杰, 沈佳, 简文彬, 等. 基于XGBoost模型的降雨诱发阶跃型滑坡位移预测[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2023, 32(2): 217-226. |
| Huang Zhi-jie, Shen Jia, Jian Wen-bin, et al. Displacement prediction of rainfall-induced step-like landslide based on XGBoost model[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2023, 32(2): 217-226. | |
| [6] | Lundberg S M, Lee S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]∥Conference and Workshop on Neural Information Processing Systems. California, Long Beach,USA, 2017: 4765-4774. |
| [7] | 周超, 殷坤龙, 黄发明. 混沌序列WA-ELM耦合模型在滑坡位移预测中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(9): 2674-2680. |
| Zhou Chao, Yin Kun-long, Huang Fa-ming. Application of the chaotic sequence WA-ELM coupling model in landslide displacement prediction[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(9): 2674-2680. | |
| [8] | 任超, 梁月吉, 庞光锋, 等. 经验模态分解和遗传小波神经网络法用于边坡变形预测[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2014, 31(6): 551-555. |
| Ren Chao, Liang Yue-ji, Pang Guang-feng, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and genetic algorithm wavelet neural network for slope deformation prediction research[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2014, 31(6): 551-555. | |
| [9] | 谢博, 施富强, 廖学燕, 等. 边坡位移的EEMD-PSO-ELM模型预测方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(3):157-162. |
| Xie Bo, Shi Fu-qiang, Liao Xue-yan, et al. Slope displacement prediction method based on EEMD-PSO-ELM model[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(3): 157-162. | |
| [10] | 周福成, 唐贵基, 何玉灵. 基于改进VMD的风电齿轮箱不平衡故障特征提取[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(5): 170-176. |
| Zhou Fu-cheng, Tang Gui-ji, He Yu-ling. Unbalanced fault feature extraction for wind power gearbox based on improved VMD[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(5): 170-176. | |
| [11] | 蔡艳平, 范宇, 陈万, 等. 改进时频分析和特征融合在内燃机故障诊断中的应用[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(16): 1901-1911. |
| Cai Yan-ping, Fan Yu, Chen Wan, et al. Applications of improved time-frequency analysis and feature fusion in fault diagnosis of IC engines[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(16): 1901-1911. | |
| [12] | 唐贵基, 王晓龙. 参数优化变分模态分解方法在滚动轴承早期故障诊断中的应用[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(5): 73-81. |
| Tang Gui-ji, Wang Xiao-long. Parameter optimized variational mode decomposition method with application to incipient fault diagnosis of rolling bearing[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(5): 73-81. | |
| [13] | Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531-544. |
| [14] | 黄钦, 谭翠, 杨波. 基于XGBoost算法的亚热带地区生态旅游适宜性评价方法研究[J]. 地球信息科学报, 2024, 26(2): 303-317. |
| Huang Qin, Tan Cui, Yang Bo. Research on the evaluation method of ecotourism suitability in subtropical regions based on XGBoost algorithm[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 2024, 26(2): 303-317. | |
| [15] | 闫孟婷, 毛玉鑫, 张天遥, 等. 基于SHAP-XGBoost混合模型的梯级水电站流量动态滞时研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2023, 51(11): 159-167. |
| Yan Meng-ting, Mao Yu-xin, Zhang Tian-yao, et al. Dynamic hysteresis of cascade hydropower station discharge based on SHAP-XGBoost hybrid model[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2023, 51(11): 159-167. | |
| [16] | 杨川, 林日成, 季建勇, 等. 基于图深度学习与北斗监测的边坡位移预测研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2024, 32(2): 612-622. |
| Yang Chuan, Lin Ri-cheng, Ji Jian-yong, et al. Slope displacement prediction research based on the graph deep learning and beidou monitoring[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2024, 32(2): 612-622. | |
| [17] | 张俊, 张建群, 钟敏, 等. 基于PSO-VMD-MCKD方法的风机轴承微弱故障诊断[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2020, 40(2): 287-296, 418. |
| Zhang Jun, Zhang Jian-qun, Zhong Min, et al. PSO-VMD-MCKD based fault diagnosis for incipient damagein wind turbine rolling bearing[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2020, 40(2): 287-296, 418. | |
| [18] | 赵博超, 马嘉骏, 崔磊, 等. 基于改进VMD-XGBoost-BILSTM组合模型的光伏发电异常检测方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2024, 50(3): 306-316. |
| Zhao Bo-chao, Ma Jia-jun, Cui Lei, et al. Photovoltaic anomaly detection based on improved VMD-XGBoost-BILSTM hybrid model[J]. Computer Engineering, 2024, 50(3): 306-316. | |
| [19] | 徐开心, 戴宁, 汝欣, 等. 基于概率分布和XGBoost决策算法的织机异常数据处理方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2025, 31(6): 2021-2130. |
| Xu Kai-xin, Dai Ning, Ru Xin, et al. Loom abnormal data processing method based on probability distribution and XGBoost decision algorithm[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 31(6): 2021-2130. | |
| [20] | 吴飞, 王鹏程, 杨康. 基于PCA-SSA-XGBoost的车辆驾驶性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2025, 55(1): 355-365. |
| Wu Fei, Wang Peng-cheng, Yang Kang. Drivability evaluation model based on PCA-SSA-XGBoost[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 355-365. |
| [1] | Yao-gang TIAN,Jing JIANG,Cheng ZHAO,Xiao-min YANG,Jun ZHANG,Kan JIA. Temperature resistance mechanism of high-early-strength cement mortar modified with waterborne epoxy resin [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2203-2211. |
| [2] | Kang YAO,Qiao DONG,Xue-qin CHEN,Bin SHI,Shi-ao YAN,Xiang WANG. Mixed⁃mode mesoscale fracture behavior of concrete based on a phase field regularized cohesive zone model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2286-2297. |
| [3] | Wan-feng WEI,Hong-gang ZHANG,Yang-peng ZHANG,Fan YANG,Bo-ming TANG,Ling-yun KONG. Research progress on modification mechanism, preparation and performance of waste rubber powder modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1834-1853. |
| [4] | Zhen YANG,Rui-ping ZHENG,Zhe GONG. Highway infrastructure performance and traffic state prediction on road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1973-1983. |
| [5] | An-shun ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Feng GAO. Shear properties and stress-strain relationships characterization of Changsha compacted clay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1604-1616. |
| [6] | Yan-fei LI,Jia-ning WU. Human pose local feature recognition algorithm based on improved RBF neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1749-1755. |
| [7] | Qing-liang JIN,Xin-sen ZHOU,Yi CHEN,Cheng-wen WU. Predictive model for identifying innovative university talents based on the swarm intelligence evolution enhanced kernel extreme learning machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1763-1771. |
| [8] | Yi GUO,Shu-wei WEI,Tao JIANG. Urban passenger transport planning algorithm based on location potential energy and multi source data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1328-1335. |
| [9] | Li-ming WANG,Zi-kun SONG,Hui ZHOU,Wen WEI,Hao YUAN. Rheological response and response mechanism of petroleum asphalt treated with ultrasound [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1346-1355. |
| [10] | Jun-peng XU,Chuan-feng ZHENG,Yan-tao DU,Yu-hang WANG,Zheng LU,Wen-jun FAN. Damage effects of water⁃heat⁃force coupling in permeable asphalt mixture in cold region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 877-887. |
| [11] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [12] | Hua-zhen FANG,Li LIU,Qing GU,Xiao-feng XIAO,Yu MENG. Driving intention recognition based on trajectory prediction and extreme gradient boosting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 623-630. |
| [13] | Teng-fei NIAN,Zhao HAN,Zhi-qiang WEI,Guo-wei WANG,Jin-guo GE,Ping LI. Mesoscopic numerical modeling method of asphalt mix considering aggregate morphology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 639-652. |
| [14] | Yan-hai YANG,Bai-chuan LI,Ye YANG,Chong-hua WANG,Liang YUE. Aggregate ellipsoidal surface base reconstruction with virtual splitting tests [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 653-663. |
| [15] | Fei WU,Peng-cheng WANG,Kang YANG. Drivability evaluation model based on PCA-SSA-XGBoost [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 105-115. |
|
||