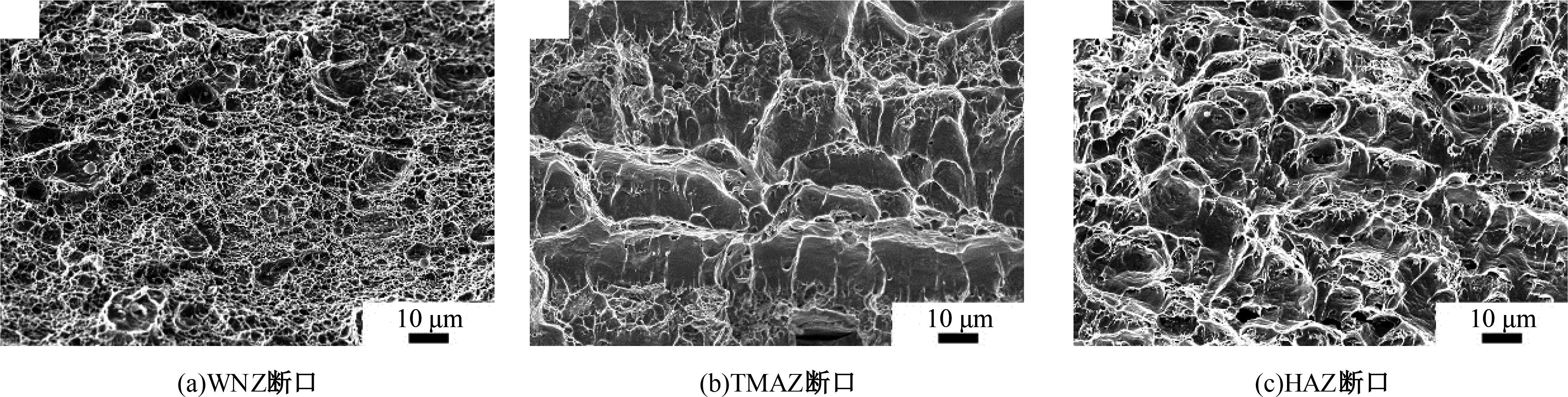
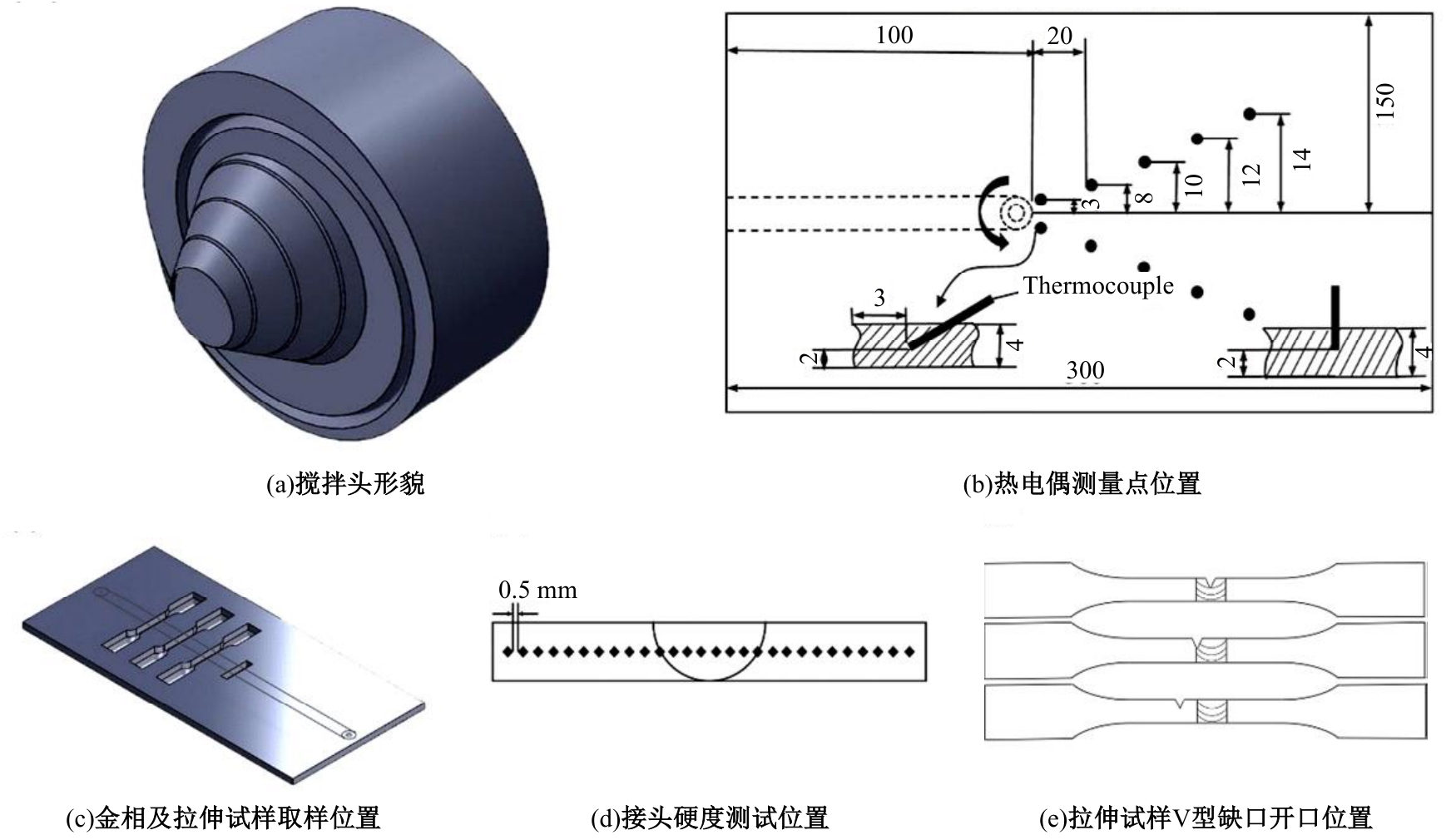
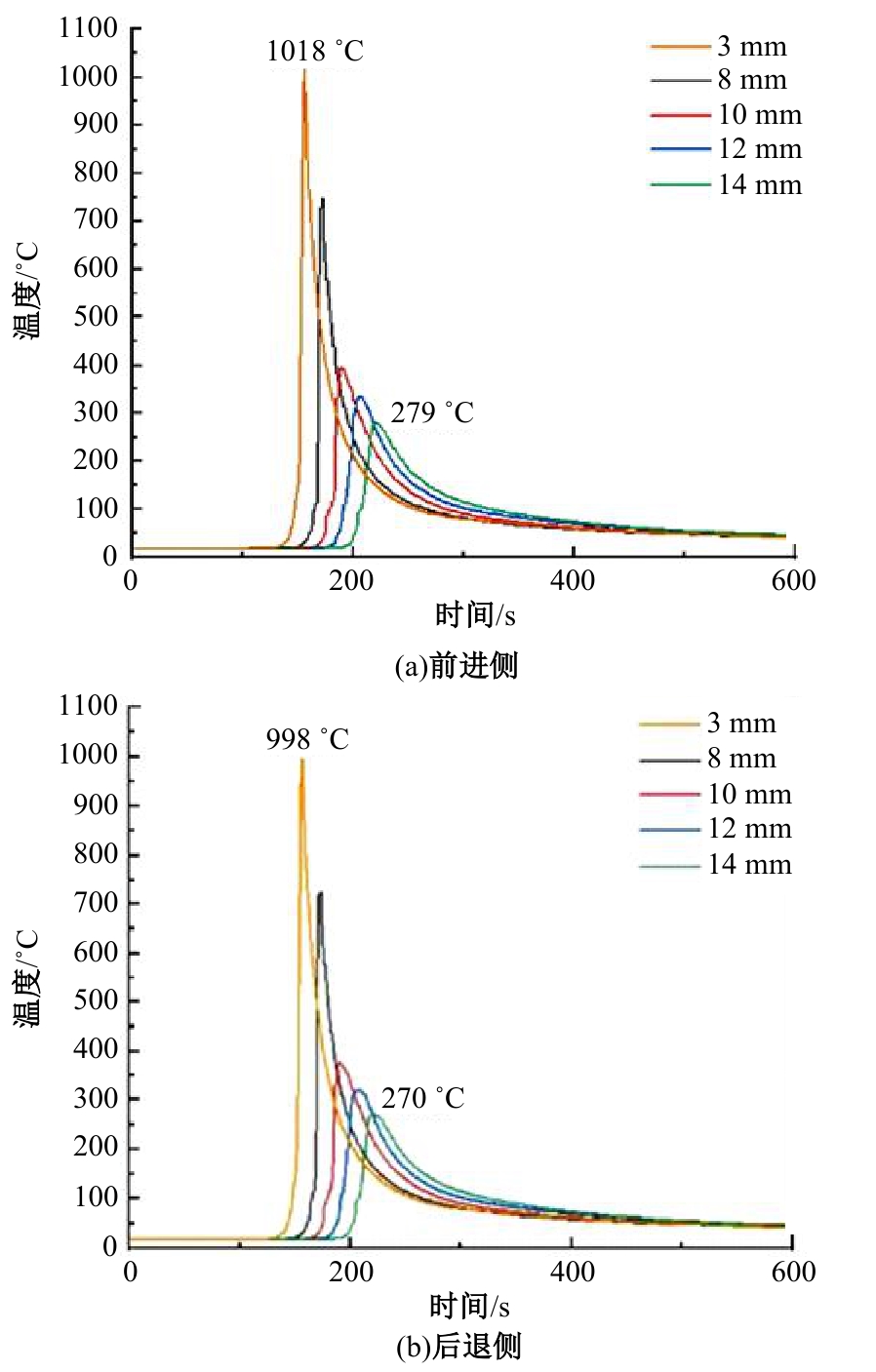
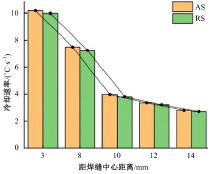
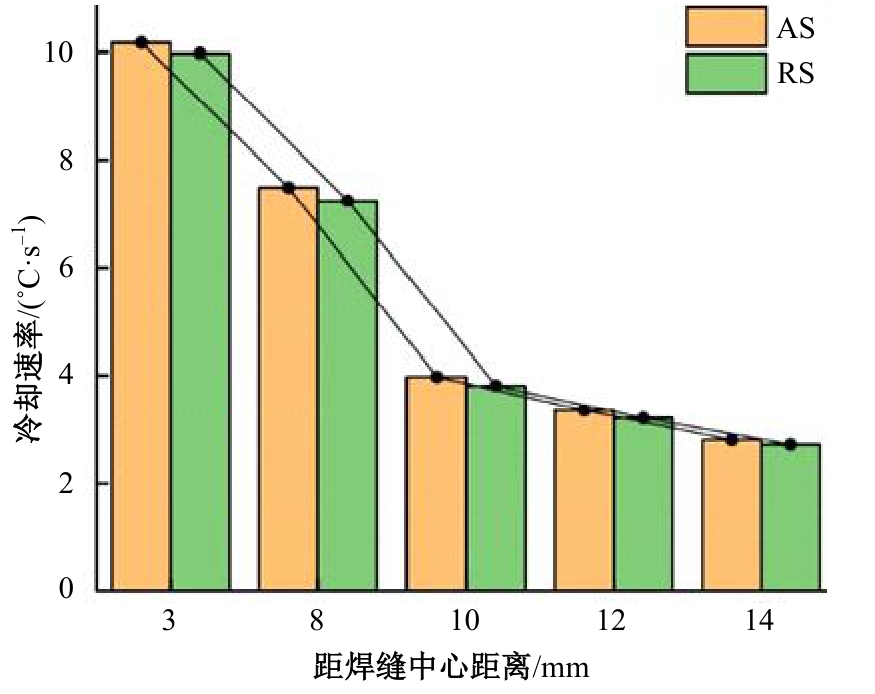
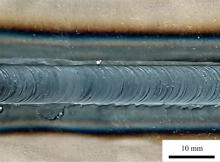
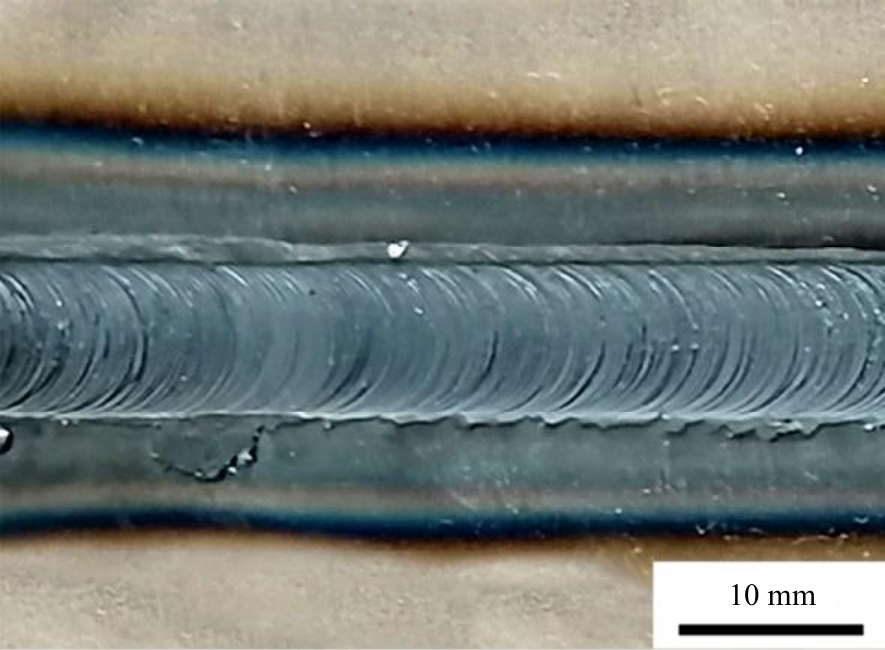
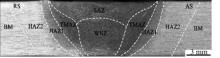
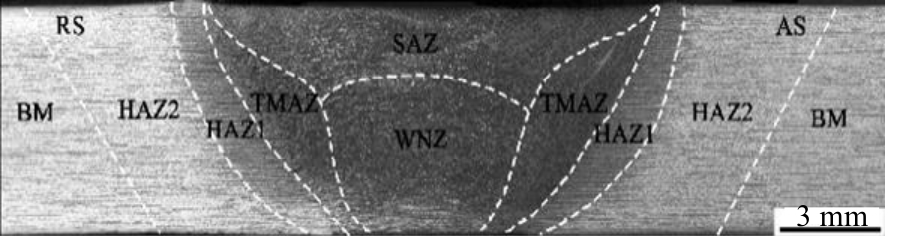
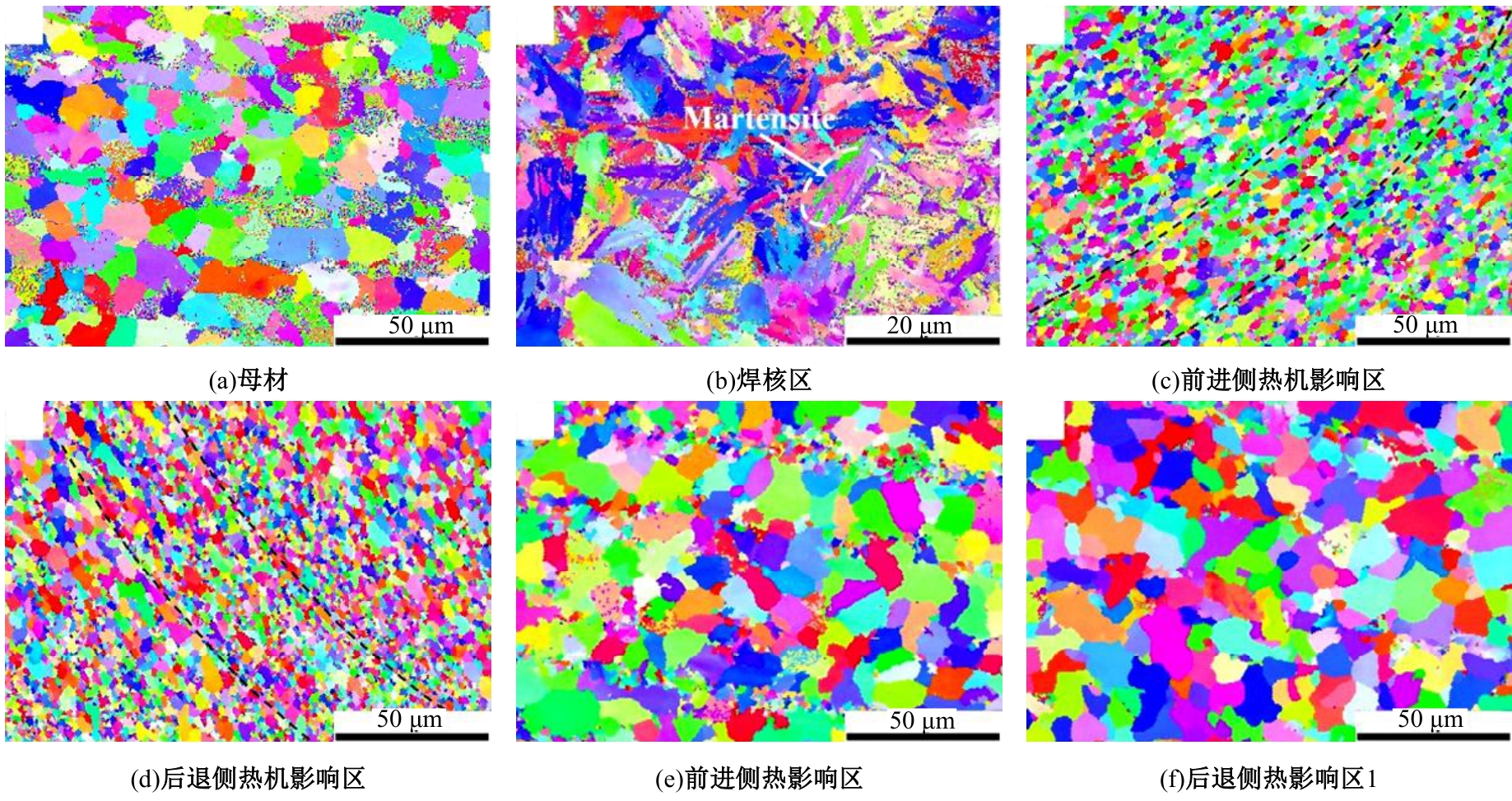
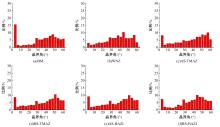
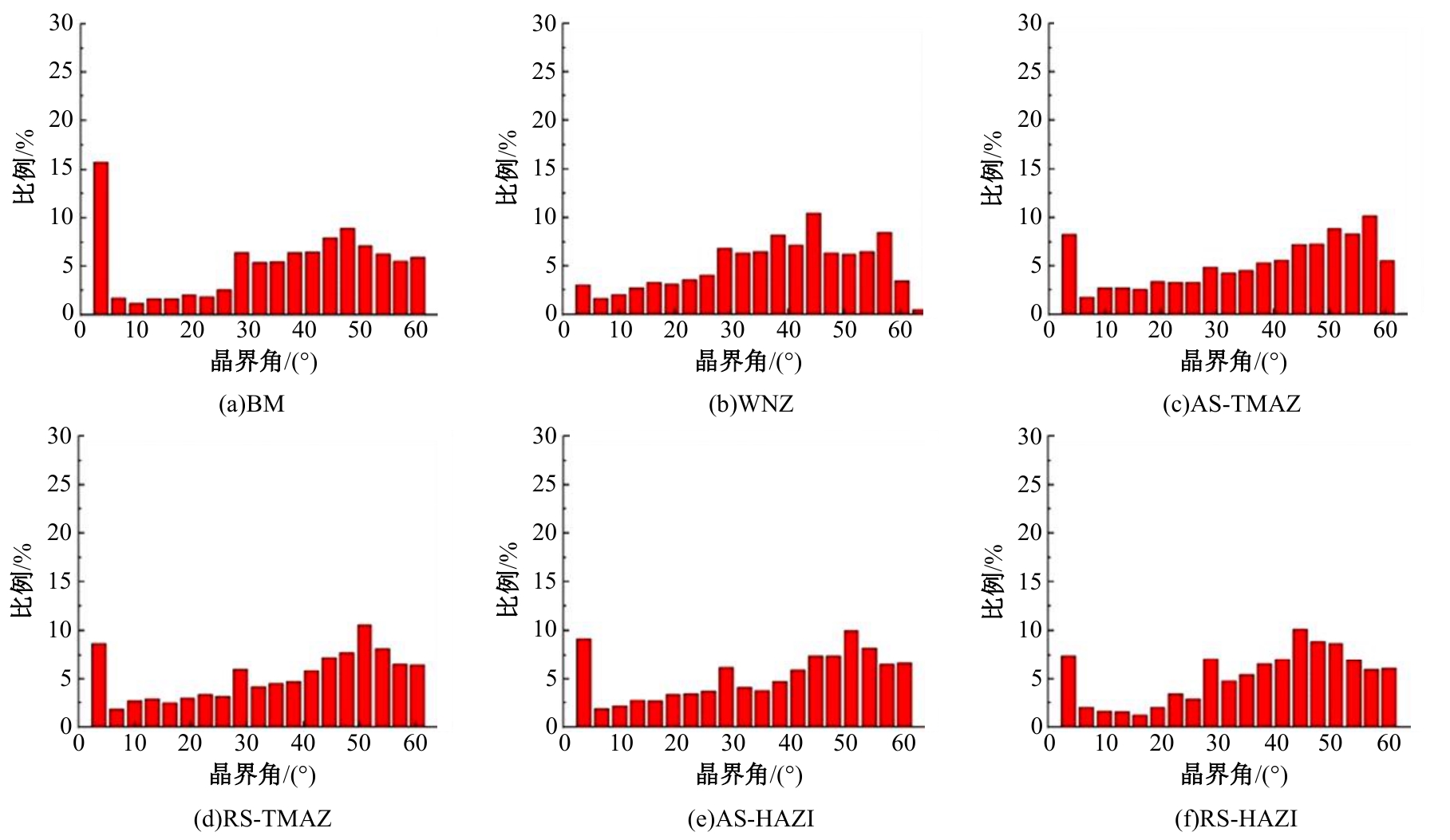
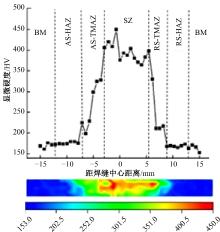
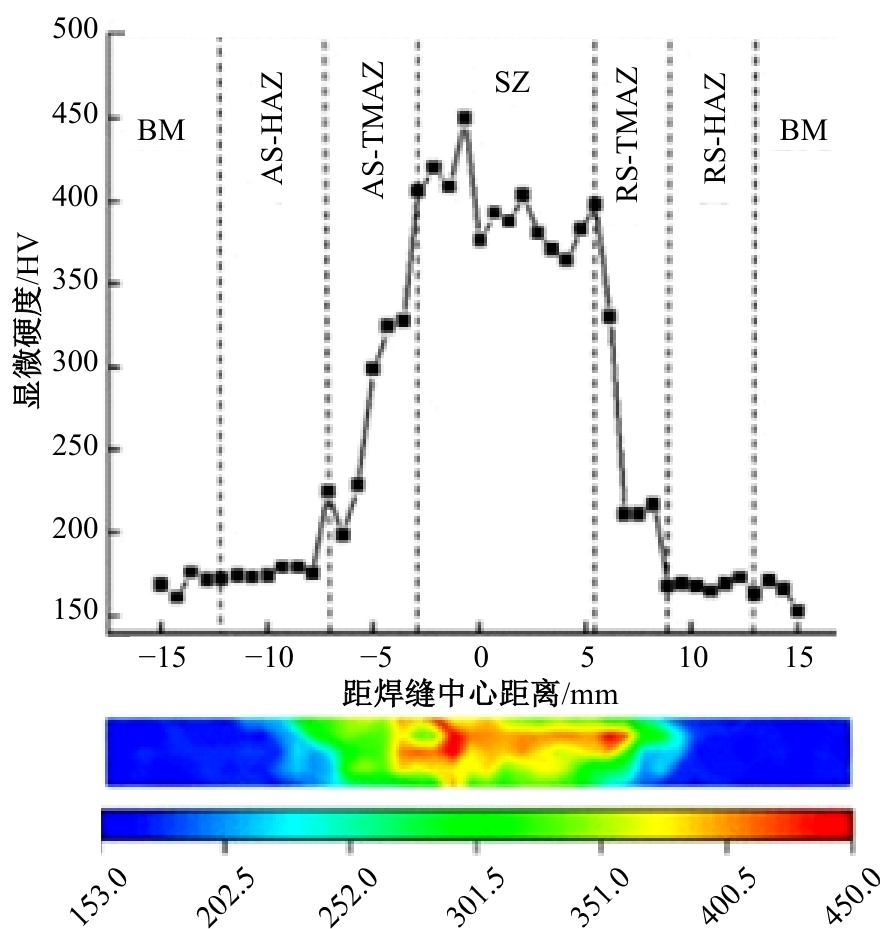
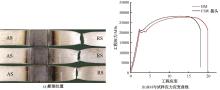
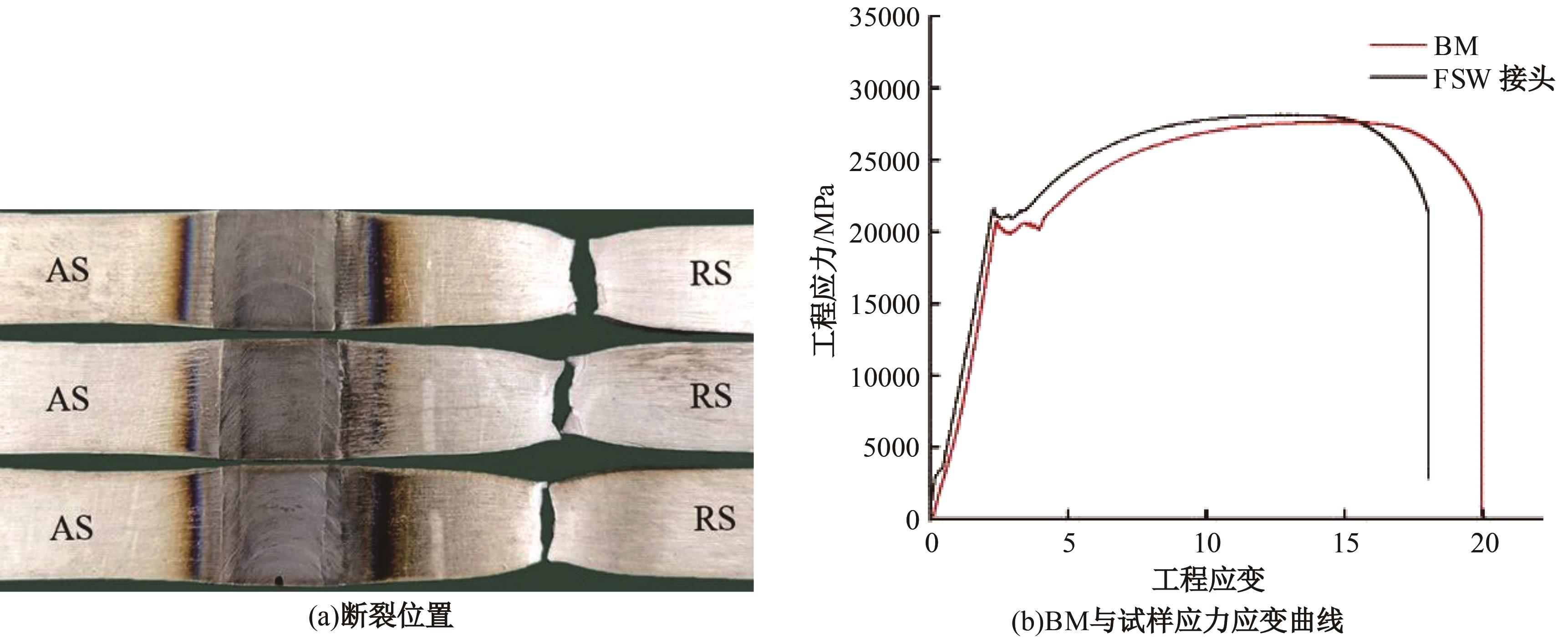
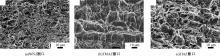
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2530-2538.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231449
Evolution of thermal cycle, microstructures and mechanical properties of SA516Gr.70 steel prepared by friction stir welding
Wen-biao GONG1,2( ),Zi-qi MIAO1,2,Heng CUI3,Xiu-ying WANG4,Wei LIU1,2(
),Zi-qi MIAO1,2,Heng CUI3,Xiu-ying WANG4,Wei LIU1,2( )
)
- 1.Key Laboratory of Advanced Structural Materials,Ministry of Education,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012,China
2.School of Materials Science and Engineering,Changchun University of Technology,Changchun 130012,China
3.Changchun Railway Vehicles Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130062,China
4.The Challenge Petrochemical Machinery Corporation of Maoming (CPM),Maoming 525024,China
CLC Number:
- TG456.9
| [1] | 张桂源, 郄新哲, 宫文彪,等. 钢铝异种材料搅拌摩擦焊界面组织及性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018, 39(5):159-164. |
| Zhang Gui-yuan, Xin-zhe Qie, Gong Wen-biao, et al. Microstructrue and properties of friction stir welding interface of steel and aluminum dissimilar materials[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2018, 39(5):159-164. | |
| [2] | Imam M, Ueji R, Fujii H. Microstructural control and mechanical properties in friction stir welding of medium carbon low alloy S45C steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 636: 24-34. |
| [3] | 武凯,贾贺鹏,孙宇,等.搅拌摩擦焊技术的研究进展[J].机械制造与自动化,2020,49(6):1-9. |
| Wu Kai, Jia He-peng, Sun Yu, et al. Research progress of friction stir welding[J]. Machine Building and Automation, 2020, 49(6):1-9. | |
| [4] | Karami S, Jafarian H, Eivani A R, et al. Engineering tensile properties by controlling welding parameters and microstructure in a mild steel processed by friction stir welding[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 670: 68-74. |
| [5] | 李国平. 超级双相不锈钢 2707 搅拌摩擦焊焊接接头的组织与性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019, 39(10): 119-125. |
| Li Guo-ping. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded joint of super duplex stainless steel 2707[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2019, 39(10):119-125. | |
| [6] | Kumar L, Yazar K U, Pramanik S. Effect of fusion and friction stir welding techniques on the microstructure, crystallographic texture and mechanical properties of mild steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 754: 400-410. |
| [7] | Ueji R, Fujii H, Cui L, et al. Friction stir welding of ultrafine grained plain low-carbon steel formed by the martensite process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 423(1/2): 324-330. |
| [8] | Fujii H, Cui L, Tsuji N, et al. Friction stir welding of carbon steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 429(1/2): 50-57. |
| [9] | Liu F C, Hovanski Y, Miles M P, et al. A review of friction stir welding of steels: Tool, material flow, microstructure, and properties[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2018, 34(1): 39-57. |
| [10] | Cho H H, Kang S H, Kim S H, et al. Microstructural evolution in friction stir welding of high-strength linepipe steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 34: 258-267. |
| [11] | Wang Y, Tsutsumi S, Kawakubo T, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of weathering mild steel joined by friction stir welding[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 823: 141715. |
| [12] | Xie G M, Duan R H, Xue P, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of X80 pipeline steel joints by friction stir welding under various cooling conditions[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2020, 33(1): 88-102. |
| [13] | Gourgues A F, Flower H M, Lindley T C. Electron backscattering diffraction study of acicular ferrite, bainite, and martensite steel microstructures[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2000, 16(1): 26-40. |
| [14] | Xue P, Ma Z Y, Komizo Y, et al. Achieving ultrafine-grained ferrite structure in friction stir processed weld metal[J]. Materials Letters, 2016, 162: 161-164. |
| [15] | Güleryüz G. Relationship between FSW parameters and hardness of the ferritic steel joints: Modeling and optimization[J]. Vacuum, 2020, 178: 109449. |
| [16] | Sato Y S, Yamanoi H, Kokawa H, et al. Microstructural evolution of ultrahigh carbon steel during friction stir welding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(6): 557-560. |
| [17] | Kelly P M, Nutting J. The martensite transformation in carbon steels[C]∥Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1961, 259: 45-58. |
| [18] | Krauss G, Marder A R. The morphology of martensite in iron alloys[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(9): 2343-2357. |
| [19] | Lienert T J, Stellwag J W L, Grimmett B B, et al. Friction stir welding studies on mild steel[J]. Welding Journal, 2003, 82(1): 1-9. |
| [20] | Boumerzoug Z, Derfouf C, Baudin T. Effect of welding on microstructure and mechanical properties of an industrial low carbon steel[J]. Engineering, 2010, 2(7): 502-506. |
| [21] | Kitahara H, Ueji R, Tsuji N, et al. Crystallographic features of lath martensite in low-carbon steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(5): 1279-1288. |
| [22] | Tiwari A, Sing P, Biswas P, et al. Friction stir welding of low-carbon steel[C]∥Advances in Materials, Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Kolkata, India, 2019: 209-226. |
| [23] | Zhang Y N, Cao X, Larose S, et al. Review of tools for friction stir welding and processing[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2012, 51(3): 250-261. |
| [24] | Tiwari A, Singh P, Biswas P, et al. Friction stir welding of low-carbon steel[C]∥Advances in Materials, Mechanical and Industrial Engineering: Selected Contributions from the First International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, Kolkata, India, 2019: 209-226. |
| [25] | Lakshminarayanan A K, Balasubramanian V, Salahuddin M. Microstructure, tensile and impact toughness properties of friction stir welded mild steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2010, 17(10): 68-74. |
| [26] | Yang H S, Bhadeshia H. Austenite grain size and the martensite-start temperature[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 60(7): 493-495. |
| [27] | Santos T F A, Idagawa H S, Ramirez A J. Thermal history in UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel friction stir welds[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2014, 19(2): 150-156. |
| [28] | Cho H H, Han H N, Hong S T, et al. Microstructural analysis of friction stir welded ferritic stainless steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(6): 2889-2894. |
| [29] | Wang H, Wang K, Wang W, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of low-carbon Q235 steel welded using friction stir welding[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2020, 33(11): 1556-1570. |
| [30] | Sato Y S, Yamanoi H, Kokawa H, et al. Microstructural evolution of ultrahigh carbon steel during friction stir welding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(6): 557-560. |
| [31] | 李志兴. 搅拌摩擦焊接超级奥氏体不锈钢654SMO厚板的组织与性能研究[D].沈阳:东北大学材料科学与工程学院,2020. |
| Li Zhi-xing. Study on microstructure and properties of super austenitic stainless steel 654SMO thick plate for friction stir welding[D]. Shenyang: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Northeastern University, 2020. | |
| [32] | Krauss G. Martensite in steel: strength and structure[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1999, 273: 40-57. |
| [33] | Qiao K, Wang K, Wang J, et al. Microstructural evolution and deformation behavior of friction stir welded twin-induced plasticity steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 169: 68-81. |
| [1] | Jun-rong LI,Yong HU,Jia-jian MENG,Zhi-yuan ZHU,Jian-hai ZHANG,Hong-wei ZHAO. Laser ultrasonic detection of mechanical parameters of nickel-based alloy under variable temperature environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2172-2179. |
| [2] | Jin-lan AN,Lan-bin WANG,Song ZHOU,Yan-qing HUANG. Microstructure of titanium alloy heat affected zone repaired by laser deposition and properties of subsequent heat treatment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1931-1939. |
| [3] | Jian-huang YAN,Zhi-yong WANG,En-hong TANG,Xue HAN,Hai-feng LI,Zi-qin JIANG. Mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels under monotonic and cyclic loading [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 912-924. |
| [4] | Lei WANG,Dong-xia LI,Song ZHOU,Li HUI,Zhen-xin SHEN. Fatigue crack propagation behavior and life prediction of 2024-O aluminum alloy FSW joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1563-1569. |
| [5] | Yi LI,Tian-bao LIU,Shao-qiang WANG,Ji-cai LIANG. Effect of soft carbon black on properties of natural rubber-based magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1548-1554. |
| [6] | Yi-fan LIU,Zhi-wei MIAO,Chen SHEN,Xiang-dong GENG. Evaluation of mechanical properties of non-uniform corroded rebars based on Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1007-1015. |
| [7] | Jia-cheng FENG,Wen-biao GONG,Chuan JU,Yu-peng LI,Yu-meng SUN,Rui ZHU. Thermal cycle and microstructures characteristic of bobbin tool friction stir welded 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3184-3191. |
| [8] | Xiao-hong LU,Jin-hui QIAO,Yu ZHOU,Chong MA,Guo-chuan SUI,Zhuo SUN. Research progress of temperature field in friction stir welding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 1-17. |
| [9] | Lei WANG,Bing-han HUANG,Jia-hui CONG,Li HUI,Song ZHOU,Yong-zhen XU. Effect of ultrasonic impact on fatigue performance of friction stir weld [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2542-2548. |
| [10] | Fen YE,Shi-yuan HU. Mechanical properties of ultra⁃thin overlay considering load transfer capacity of old cement pavement joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [11] | Hai-bin WEI,Xiang-yan WANG,Fu-yu WANG,Yong ZHANG. Mechanical properties and micro analysis of AC-25 asphalt mixture based on vibration forming [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1269-1276. |
| [12] | Yi-sa FAN,Jing-xin NA,Lin-jian SHANGGUAN. Method for checking bonding strength of high⁃speed EMU side window based on residual strength [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 840-846. |
| [13] | Yong-chun CHENG,He LI,Li-ding LI,Hai-tao WANG,Yun-shuo BAI,Chao CHAI. Analysis of mechanical properties of asphalt mixture affected by aggregate based on grey relational degree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [14] | Han-bing LIU,Xin GAO,Ya-feng GONG,Shi-qi LIU,Wen-jun LI. Influence of surface treatment on basalt fiber reactive powder concrete mechanical properties and fracture characteristics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 936-945. |
| [15] | Hong-liang XIANG,Sheng-tao CHEN,Li-ping DENG,Wei ZHANG,Tu-sheng ZHAN. Microstructure and properties of microalloying 2205 duplex stainless steel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1645-1652. |
|
||