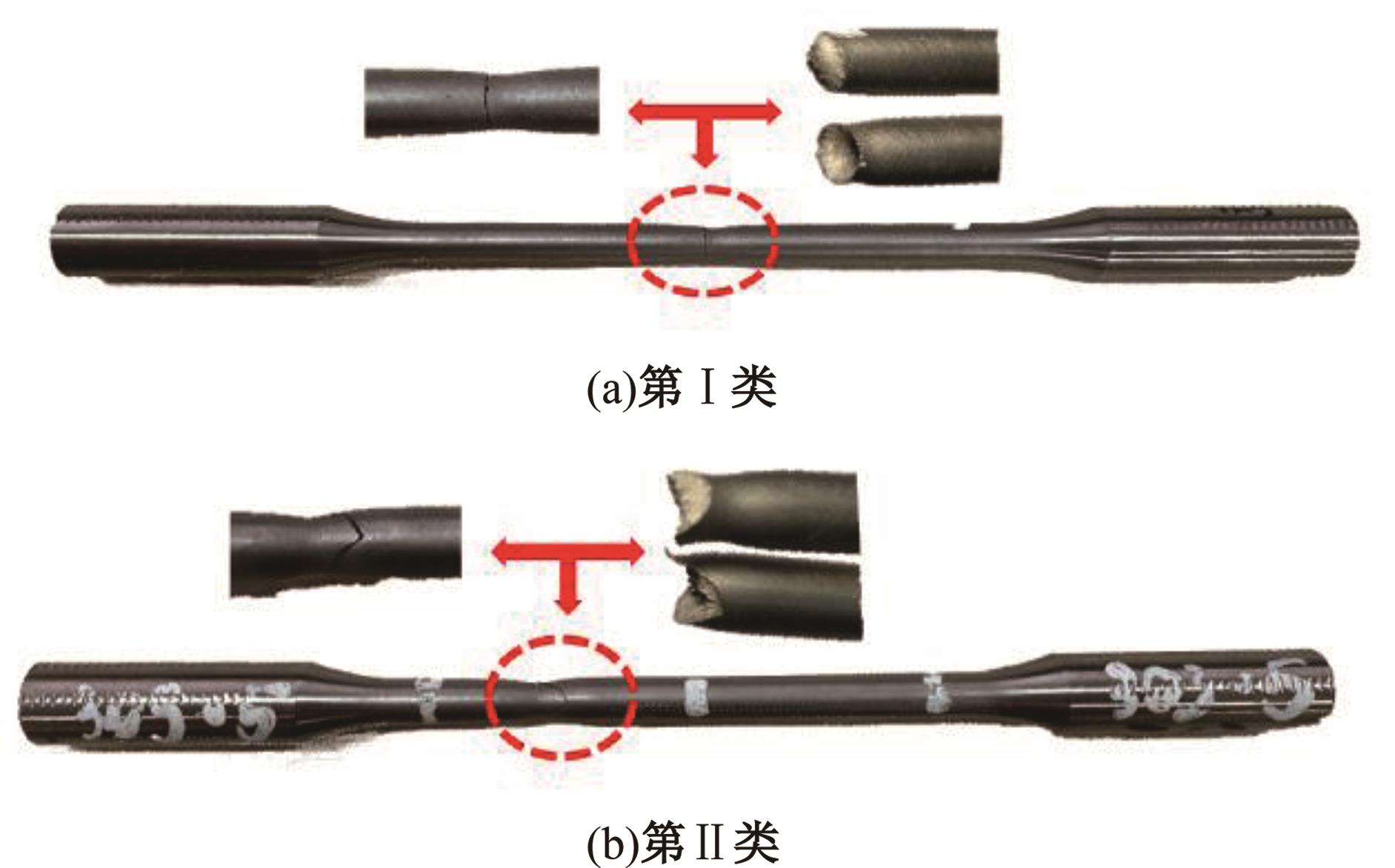
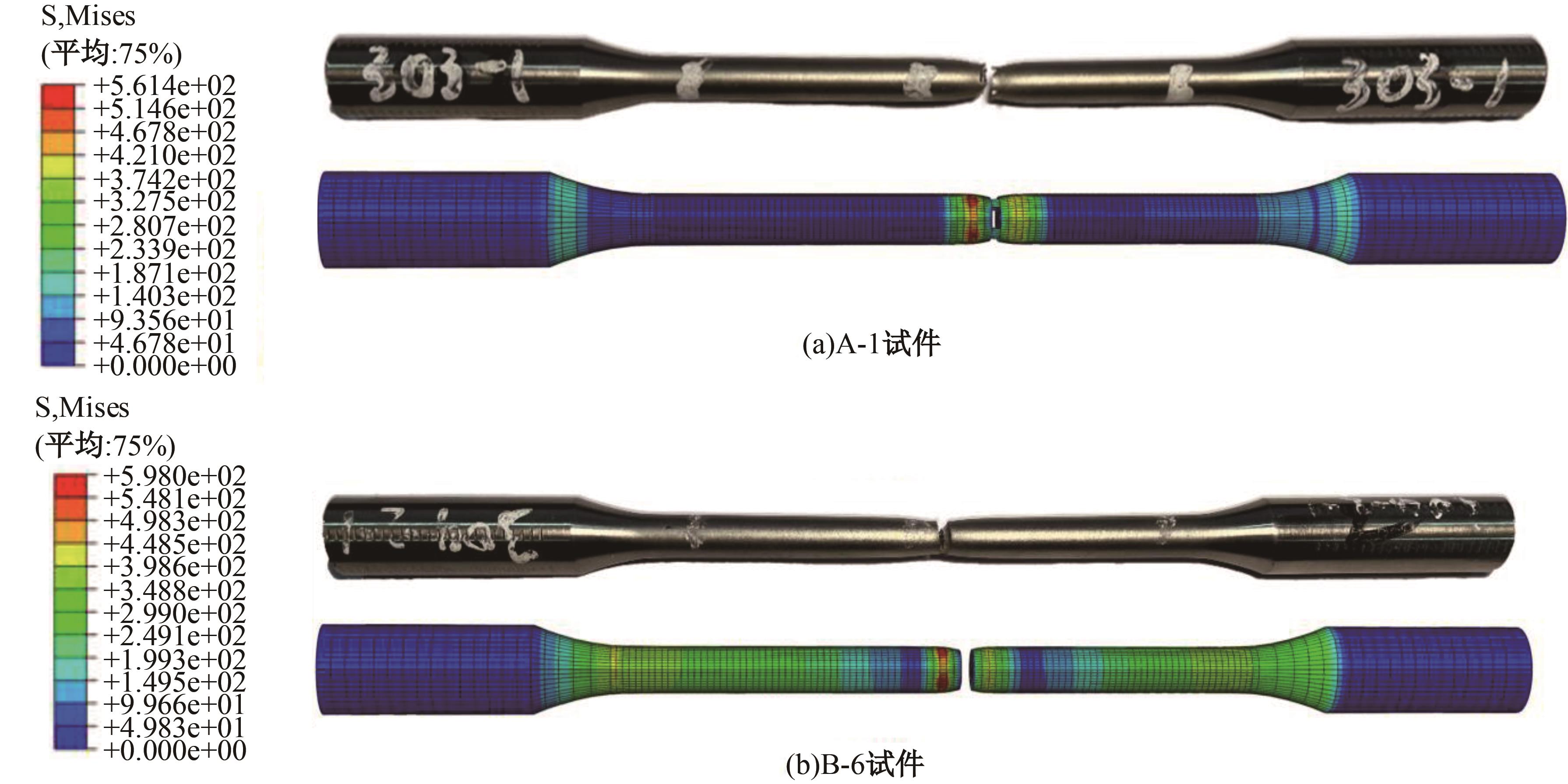
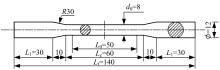
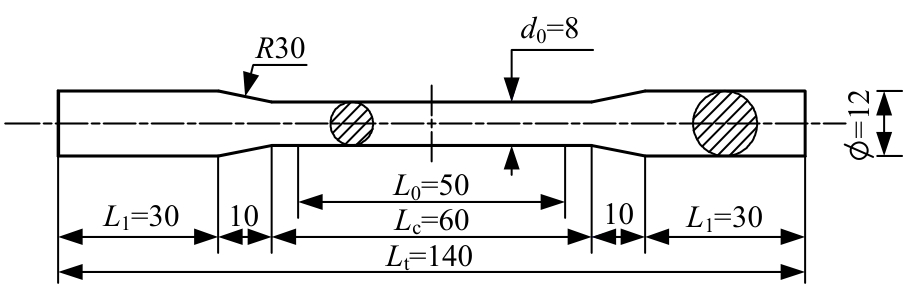
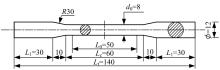
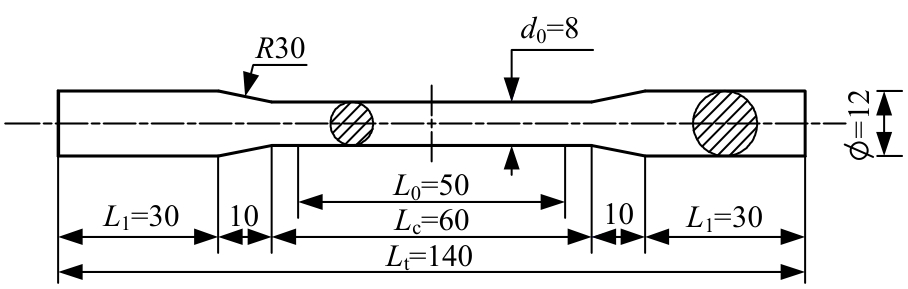
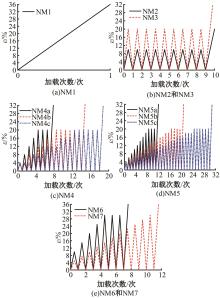
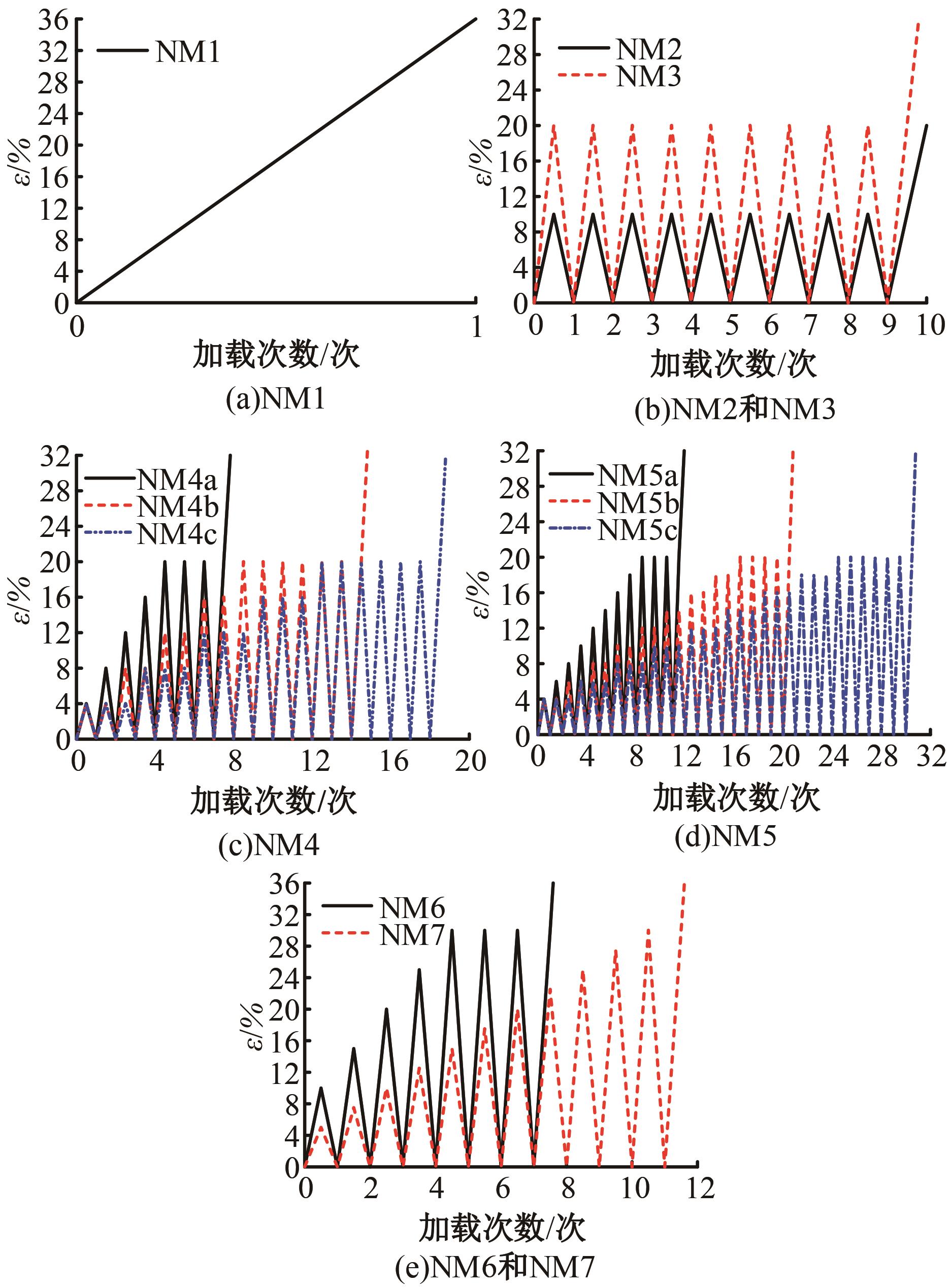
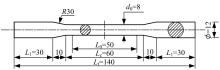
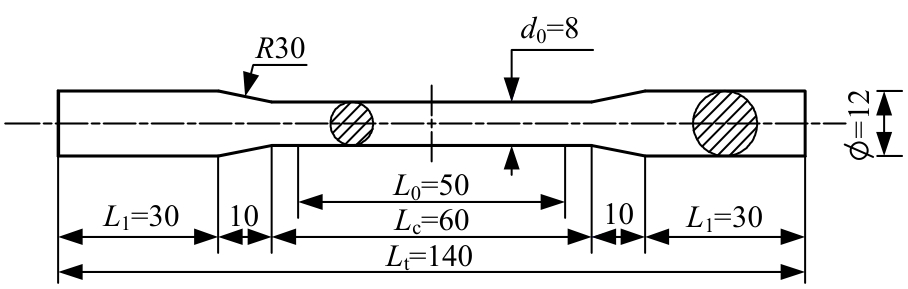
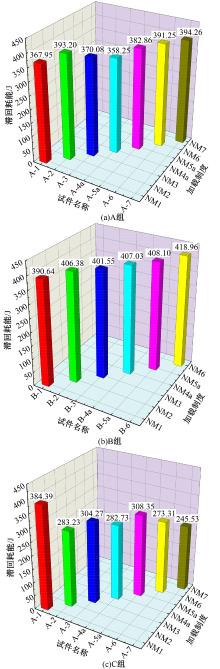
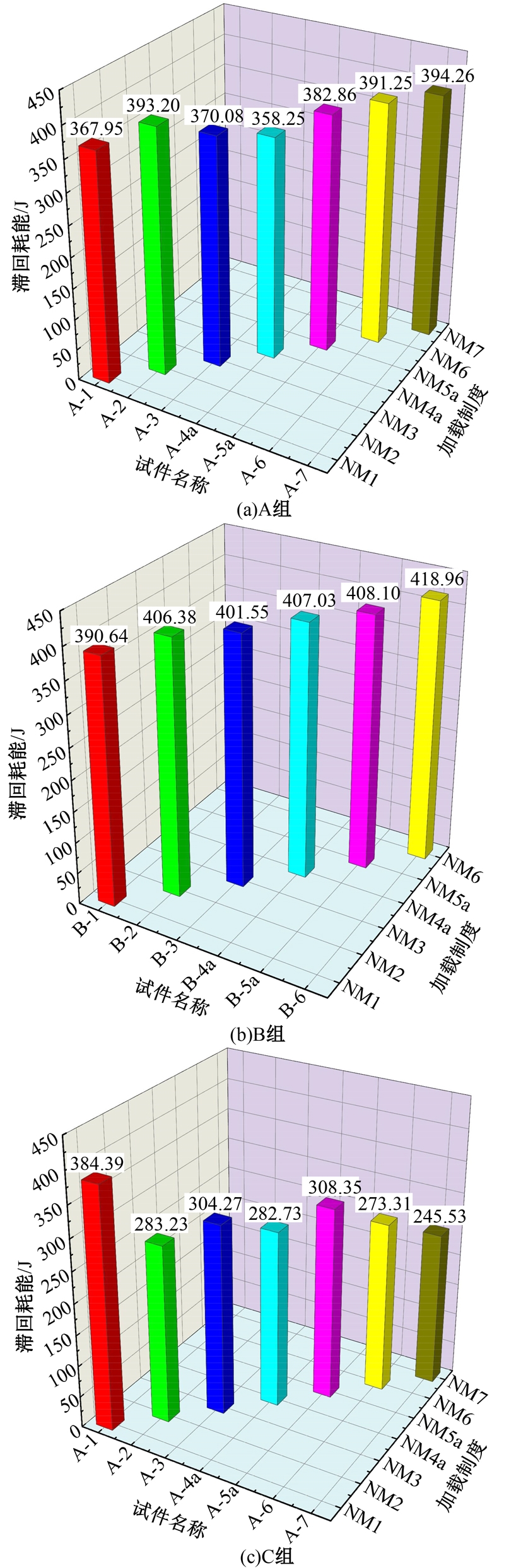
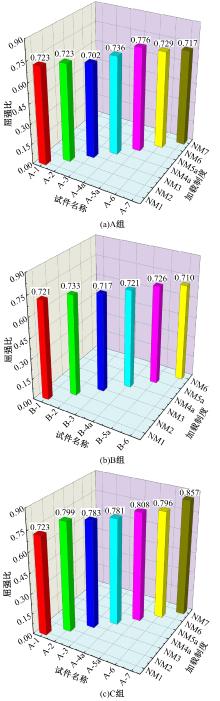
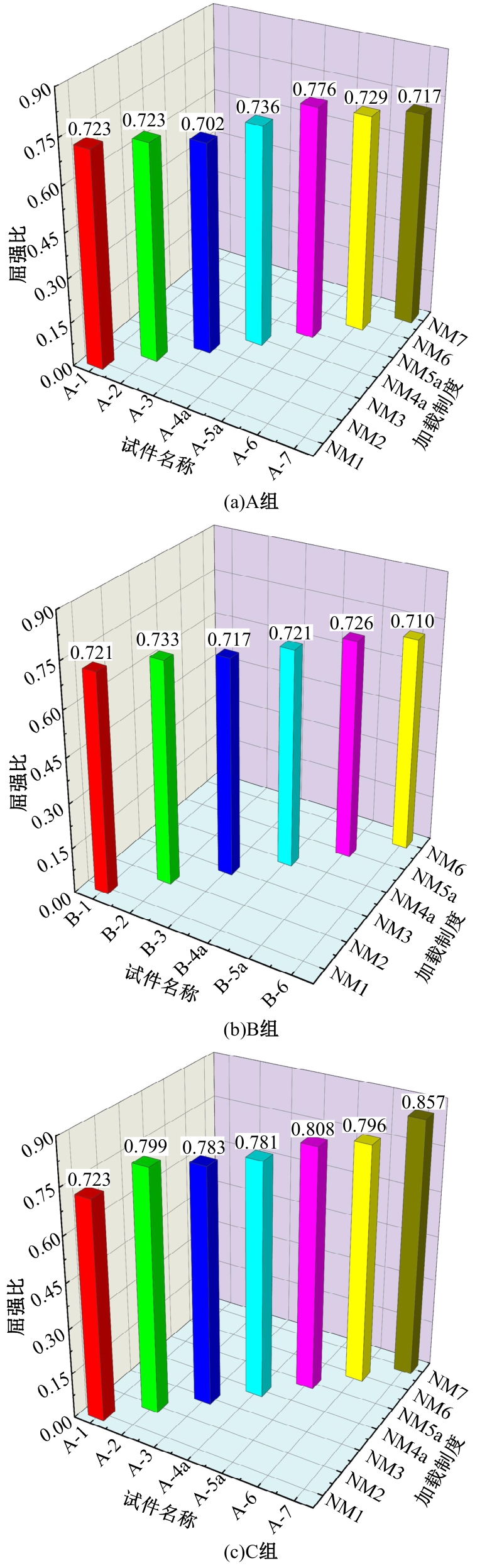
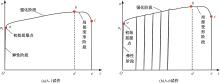
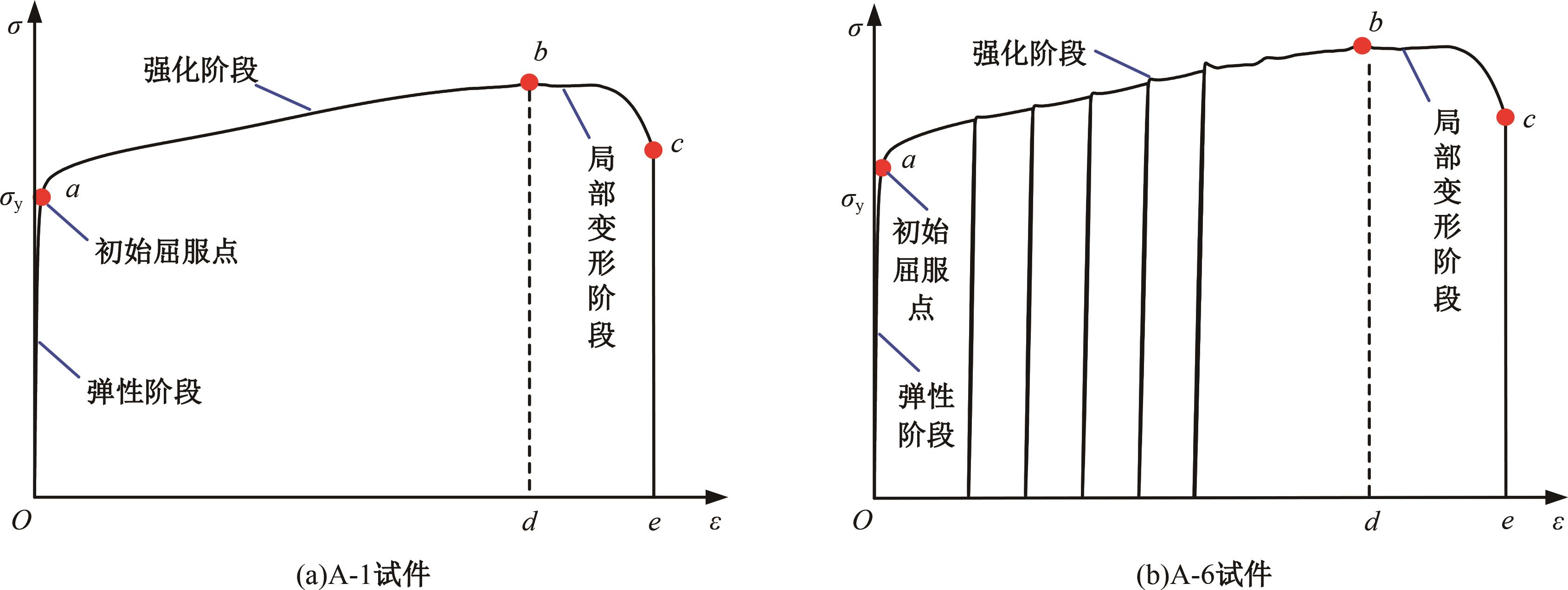
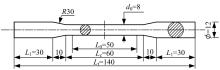
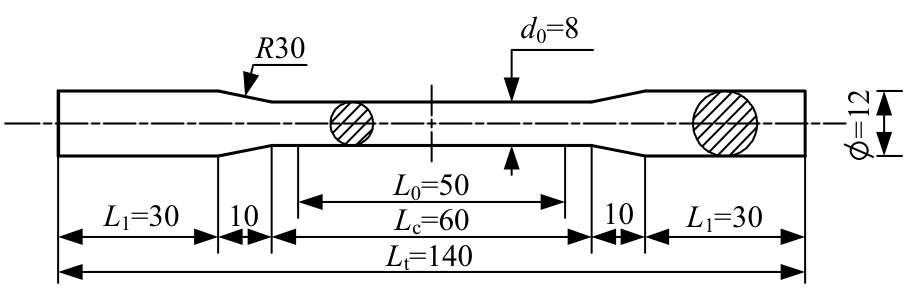
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 912-924.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230569
Previous Articles Next Articles
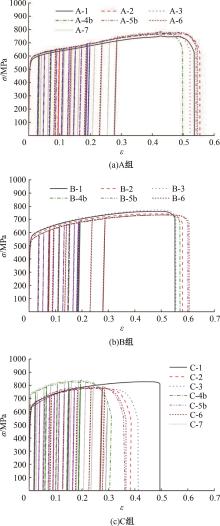
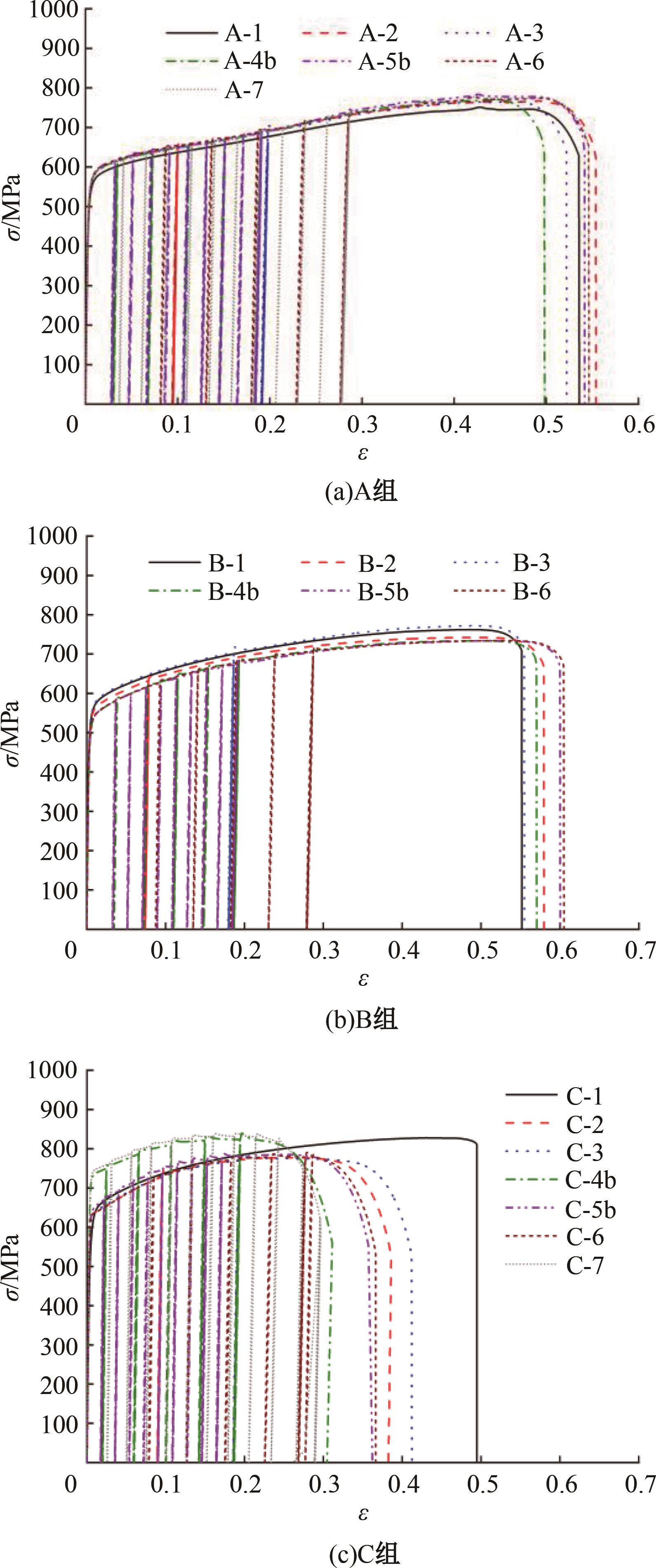
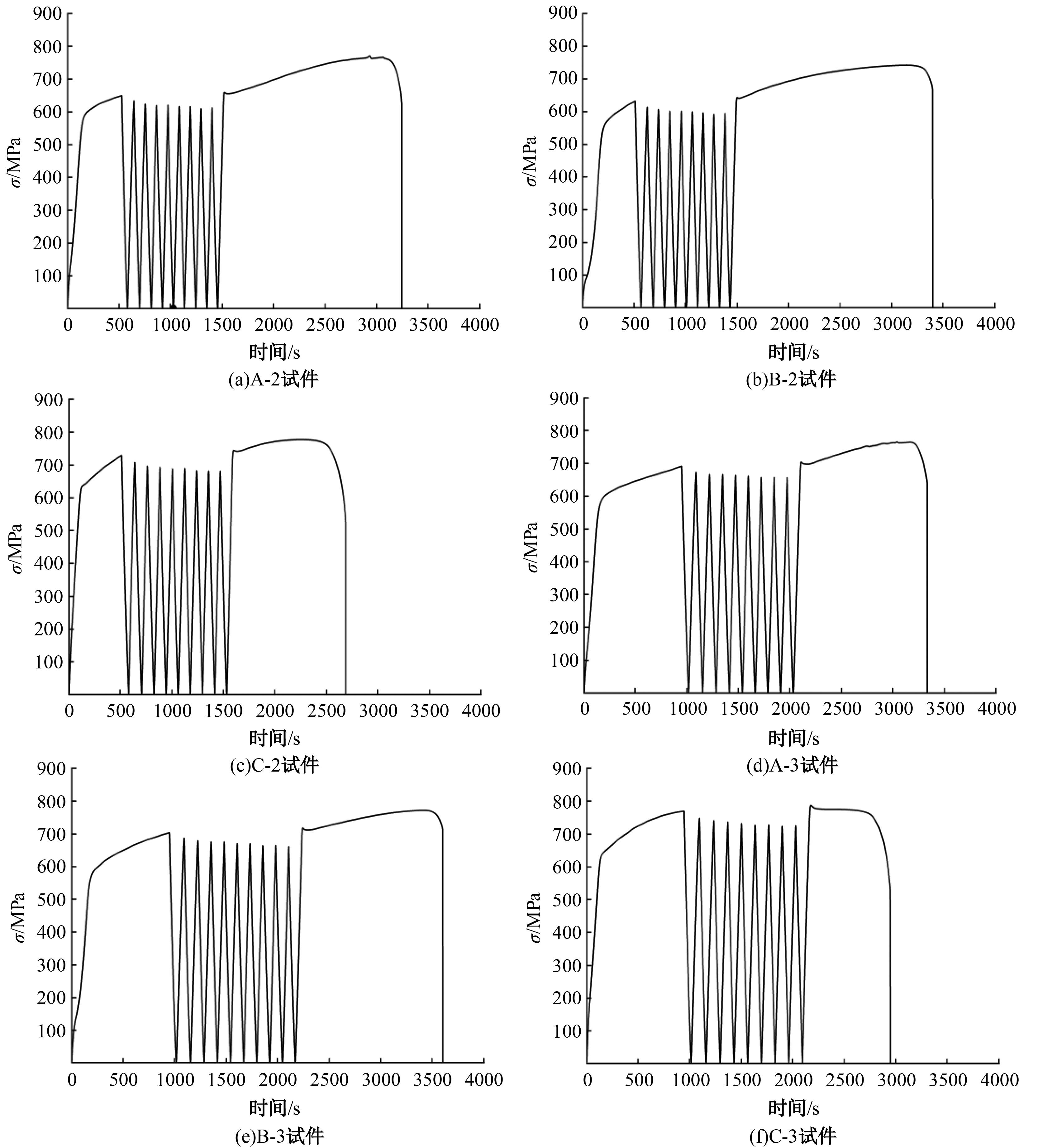
Mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels under monotonic and cyclic loading
Jian-huang YAN1( ),Zhi-yong WANG2,En-hong TANG3,Xue HAN4,Hai-feng LI1(
),Zhi-yong WANG2,En-hong TANG3,Xue HAN4,Hai-feng LI1( ),Zi-qin JIANG5
),Zi-qin JIANG5
- 1.College of Civil Engineering,Huaqiao University,Xiamen 361021,China
2.Zhangzhou City Investment Design Consulting Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Zhangzhou 363007,China
3.Fujian Hongchang Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Longyan 364030,China
4.School of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Xiamen Institute of Technology,Xiamen 361021,China
5.College of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
CLC Number:
- TU391
| 1 | 郑宝锋, 舒赣平, 沈晓明. 不锈钢材料常温力学性能试验研究[J]. 钢结构, 2011, 26(5): 1-6, 55. |
| Zheng Bao-feng, Shu Gan-ping, Shen Xiao-ming. Experimental study on material properties of stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Steel Construction (Chinese & English), 2011, 26(5): 1-6, 55. | |
| 2 | 陈乐, 何琨, 梁波, 等. 316不锈钢室温和350 ℃低周疲劳性能研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2017, 38(3): 51-55. |
| Chen Le, He Kun, Liang Bo, et al. Study on low-cycle fatigue property of 316 stainless steel at room temperature and 350 ℃[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2017, 38(3): 51-55. | |
| 3 | 王文权, 王岩新, 王洪潇, 等. SUS301L不锈钢激光焊缝缺陷修复工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2022, 52(1): 79-90. |
| Wang Wen-quan, Wang Yan-xin, Wang Hong-xiao, et al. Defects repair technology of SUS301L stainless steel laser weld[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 79-90. | |
| 4 | 景强, 方翔, 倪静姁, 等. 2304不锈钢钢筋在港珠澳大桥的应用——钢筋耐蚀性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2017, 34(10): 51-56. |
| Jing Qiang, Fang Xiang, Ni Jing-ye, et al. Use of 2304 stainless steel reinforcement in Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau bridge—Corrsion behaviors of 2304 stainless steel reinforcement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2017, 34(10): 51-56. | |
| 5 | Morgenthal G, Sham R, West B. Engineering the tower and main span construction of stonecutters bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2010, 15(2): 144-152. |
| 6 | Nakajima M, Uematsu Y, Kakiuchi T, et al. Effect of quantity of martensitic transformation on fatigue behavior in type 304 stainless steel[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 10(7): 299-304. |
| 7 | Lee W S, Lin R F, Chen R H, et al. Effects of prestrain on high temperature impact properties of 304L stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(4): 754-763. |
| 8 | 刘俭辉, 王生楠, 韦尧兵, 等. 304不锈钢低周疲劳断裂特性的研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2013(17): 84-88. |
| Liu Jian-hui, Wang Sheng-nan, Wei Yao-bing, et al. Study on low cycle fatigue fracture properties of 304 stainless steel[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 437(17): 84-88. | |
| 9 | 姜公锋, 孙亮, 陈钢. 304不锈钢应变强化疲劳寿命的试验研究[J]. 机械强度, 2014, 36(6): 850-855. |
| Jiang Gong-feng, Sun Liang, Chen Gang. Experimental study of 304 stainless steel fatigue life considering material pre-strain hardening effect[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2014, 36(6): 850-855. | |
| 10 | Zhou F, Li L. Experimental study on hysteretic behavior of structural stainless steels under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 122(7): 94-109. |
| 11 | 钟巍华, 鱼滨涛, 佟振峰, 等. 国产316LN不锈钢的室温低周疲劳行为研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(8): 66-68, 73. |
| Zhong Wei-hua, Yu Bin-tao, Tong Zhen-feng, et al. Research on low cycle fatigue behavior of domestic 316LN stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(8): 66-68, 73. | |
| 12 | Hasunuma S, Ogawa T. Crystal plasticity FEM analysis for variation of surface morphology under low cycle fatigue condition of austenitic stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 127(10): 488-499. |
| 13 | 王元清, 常婷, 石永久. 循环荷载下奥氏体不锈钢的本构关系试验研究[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 42(6): 1175-1179. |
| Wang Yuan-qing, Chang Ting, Shi Yong-jiu. Experimental study on constitutive relationship in austenitic stainless steel under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 42(6): 1175-1179. | |
| 14 | 王萌, 杨维国, 王元清, 等. 奥氏体不锈钢滞回本构模型研究[J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(11): 107-114. |
| Wang Meng, Yang Wei-guo, Wang Yuan-qing, et al. Study on hysteretic constitutive model of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(11): 107-114. | |
| 15 | Obunai K, Kawase K, Fukuta T, et al. Low cycle fatigue life estimation of stainless steel[J]. Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 2018, 3(1): 152-156. |
| 16 | Abarkan I, Shamass R, Achegaf Z, et al. Numerical and analytical studies of low cycle fatigue behavior of 316 LN austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2020, 144(6): No.061507. |
| 17 | 孙治国, 杨葆洋, 张震威, 等. 循环荷载下不锈钢力学性能建模方法[J]. 地震工程学报, 2022, 44(4): 759-767. |
| Sun Zhi-guo, Yang Bao-yang, Zhang Zhen-wei, et al. Modeling method for mechanical behavior of stainless steel under cyclic loading[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(4): 759-767. | |
| 18 | . 金属材料拉伸试验第1部分: 室温试验方法 [S]. |
| 19 | . 钢结构设计标准 [S]. |
| 20 | Koplik J, Needleman A. Void growth and coalescence in porous plastic solids[J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1988, 24(8): 835-853. |
| 21 | Johnson G R, Cook W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1983, 21: 541-548. |
| 22 | 李云飞, 曾祥国, 盛鹰, 等. 基于实验的钛合金优化动态本构模型与有限元模拟[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(24): 137-142. |
| Li Yun-fei, Zeng Xiang-guo, Sheng Ying, et al. An optimal dynamic constitutive modeling of titanium alloy and FE simulation[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(24): 137-142. |
| [1] | Wei-song YANG,An ZHANG,Wei-xiao XU,Hai-sheng LI,Ke DU. Seismic performance of stiffness enhanced metal coupling beam damper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2469-2483. |
| [2] | Qi-wu YAN,Zhong-liang ZOU. Hybrid algorithm for seismic energy-dissipated structures based on optimal placement of dampers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2267-2274. |
| [3] | Yi-fan LIU,Zhi-wei MIAO,Chen SHEN,Xiang-dong GENG. Evaluation of mechanical properties of non-uniform corroded rebars based on Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1007-1015. |
| [4] | Jia-cheng FENG,Wen-biao GONG,Chuan JU,Yu-peng LI,Yu-meng SUN,Rui ZHU. Thermal cycle and microstructures characteristic of bobbin tool friction stir welded 2024 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3184-3191. |
| [5] | Wei-hua WANG,Yong-bin ZHU,Shen-jun QI,Jing-si HUO,Xiu-quan GUO,Zhen-an ZHONG. Mechanical behavior on friction energy dissipation reduced beam section connection of steel beams [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1400-1410. |
| [6] | Fen YE,Shi-yuan HU. Mechanical properties of ultra⁃thin overlay considering load transfer capacity of old cement pavement joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [7] | Hai-bin WEI,Xiang-yan WANG,Fu-yu WANG,Yong ZHANG. Mechanical properties and micro analysis of AC-25 asphalt mixture based on vibration forming [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1269-1276. |
| [8] | Yong-chun CHENG,He LI,Li-ding LI,Hai-tao WANG,Yun-shuo BAI,Chao CHAI. Analysis of mechanical properties of asphalt mixture affected by aggregate based on grey relational degree [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [9] | Han-bing LIU,Xin GAO,Ya-feng GONG,Shi-qi LIU,Wen-jun LI. Influence of surface treatment on basalt fiber reactive powder concrete mechanical properties and fracture characteristics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 936-945. |
| [10] | Guang-tai ZHANG,Lu-yang ZHANG,Guo-hua XING,Yin-long CAO,Bao YI. Seismic performance of steel⁃polypropylene hybrid fiber reinforced concrete shear wall [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 946-955. |
| [11] | Hong-liang XIANG,Sheng-tao CHEN,Li-ping DENG,Wei ZHANG,Tu-sheng ZHAN. Microstructure and properties of microalloying 2205 duplex stainless steel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1645-1652. |
| [12] | Jin-guo WANG,Zhi-qiang WANG,Shuai REN,Rui-fang YAN,Kai HUANG,Jin GUO. Effect of Ti addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of ductile iron [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1653-1662. |
| [13] | Ming LI,Hao-ran WANG,Wei-jian ZHAO. Experimental of loading-bearing capacity of one-way laminated slab with shear keys [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 654-667. |
| [14] | Ming LI,Hao-ran WANG,Wei-jian ZHAO. Mechanical properties of laminated slab with shear keys [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1509-1520. |
| [15] | Xin TONG,Ya-jiao ZHANG,Yu-shan HUANG,Zheng-zheng HU,Qing WANG,Zhi-hui ZHANG. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 304L stainless steel processed by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1615-1621. |
|
||