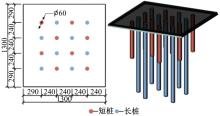
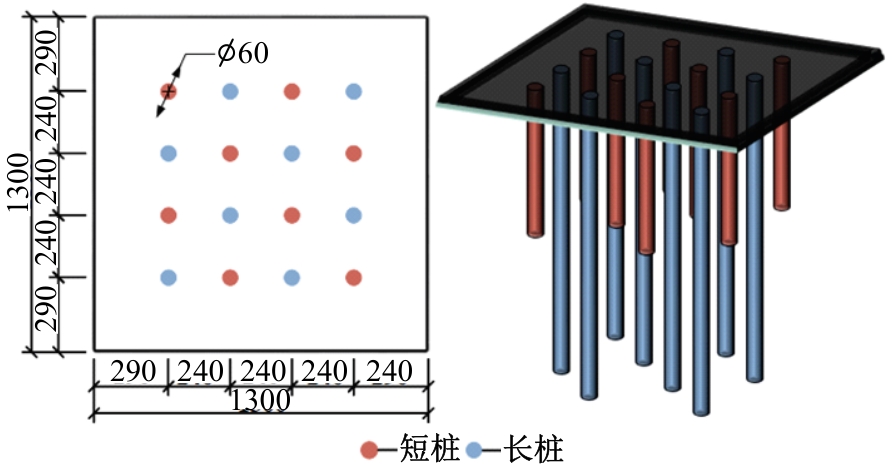
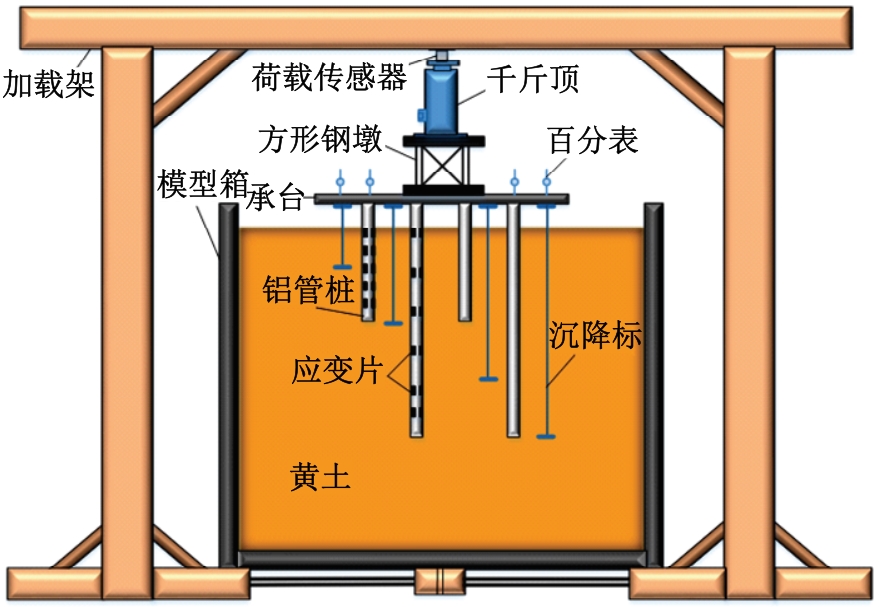
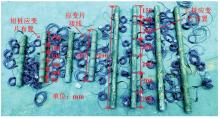
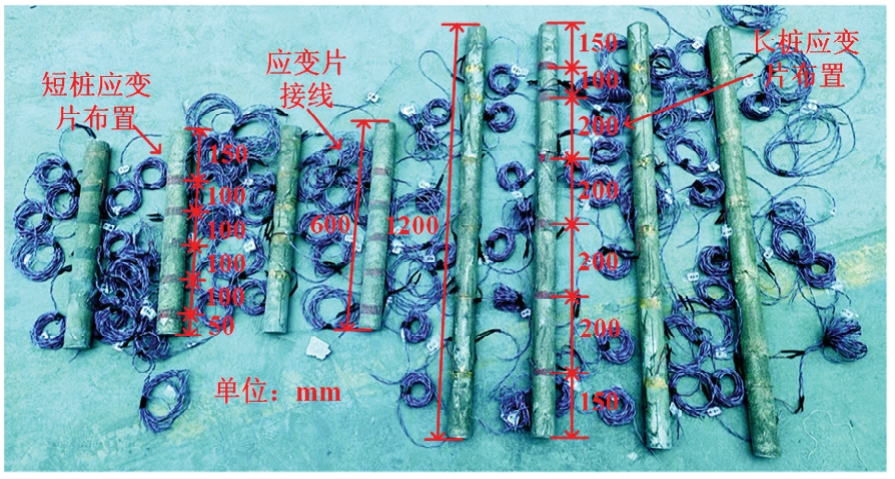
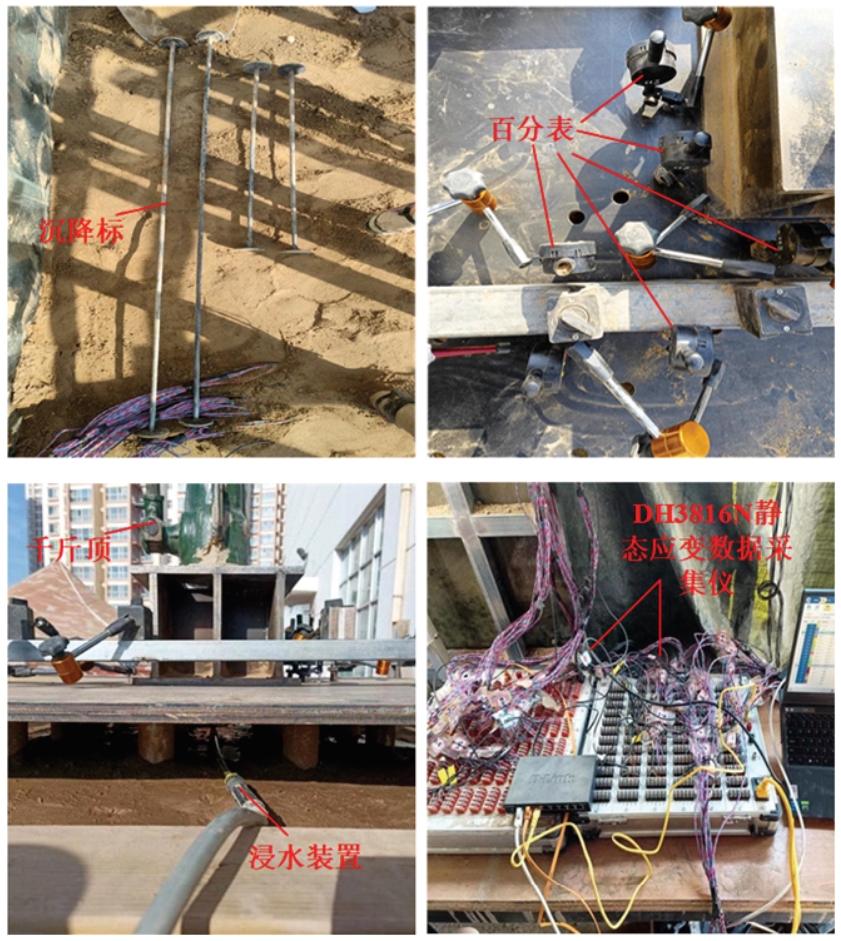
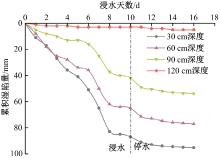
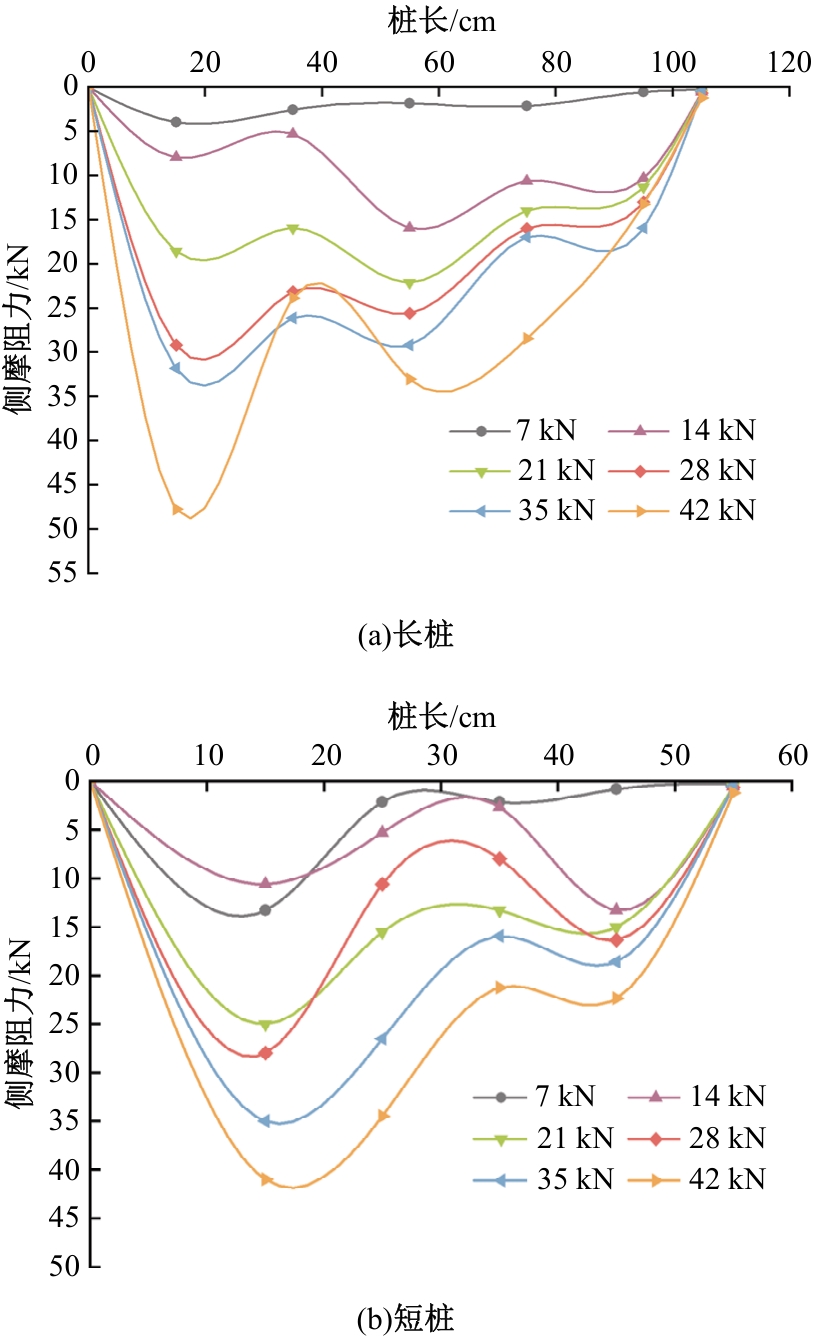
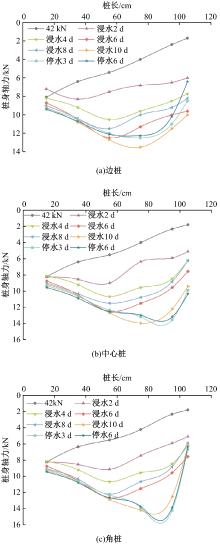
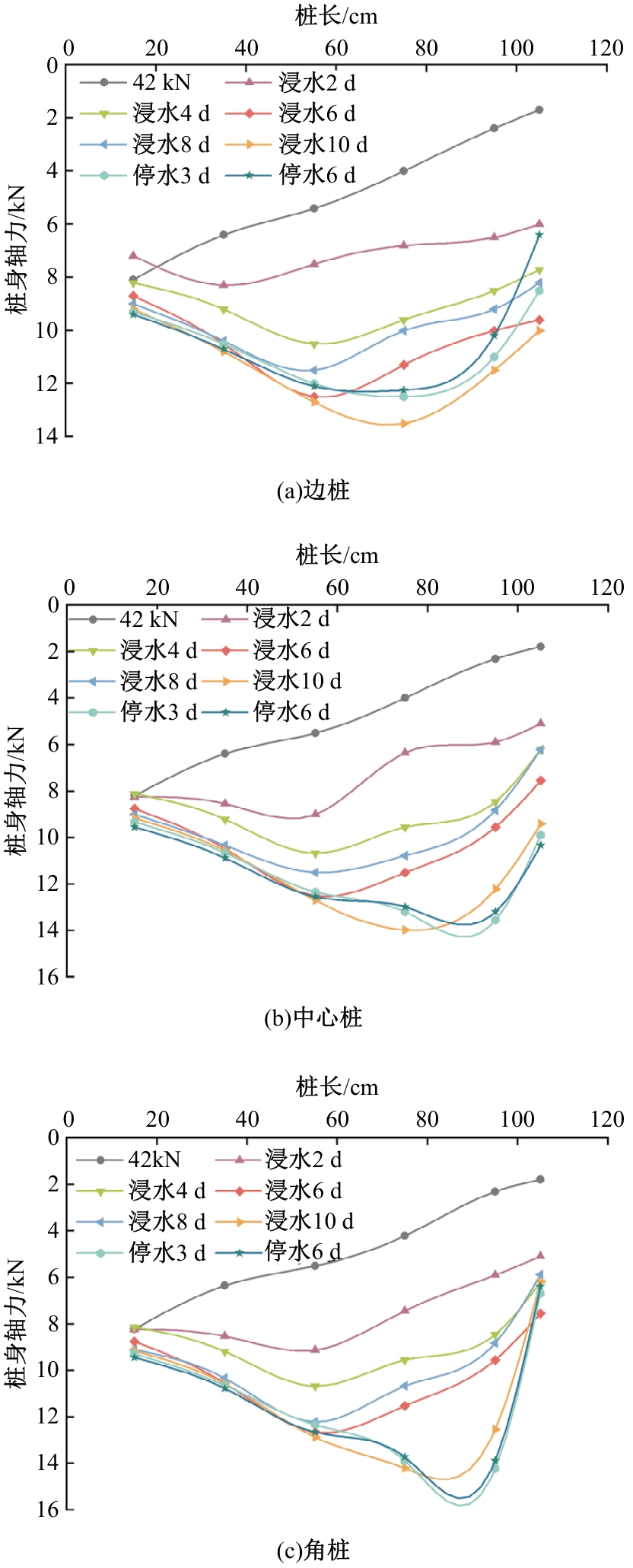
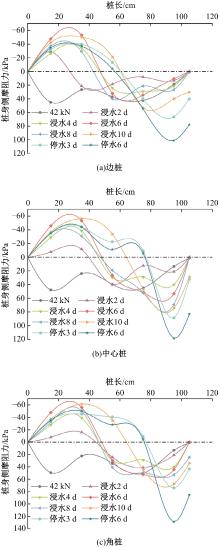
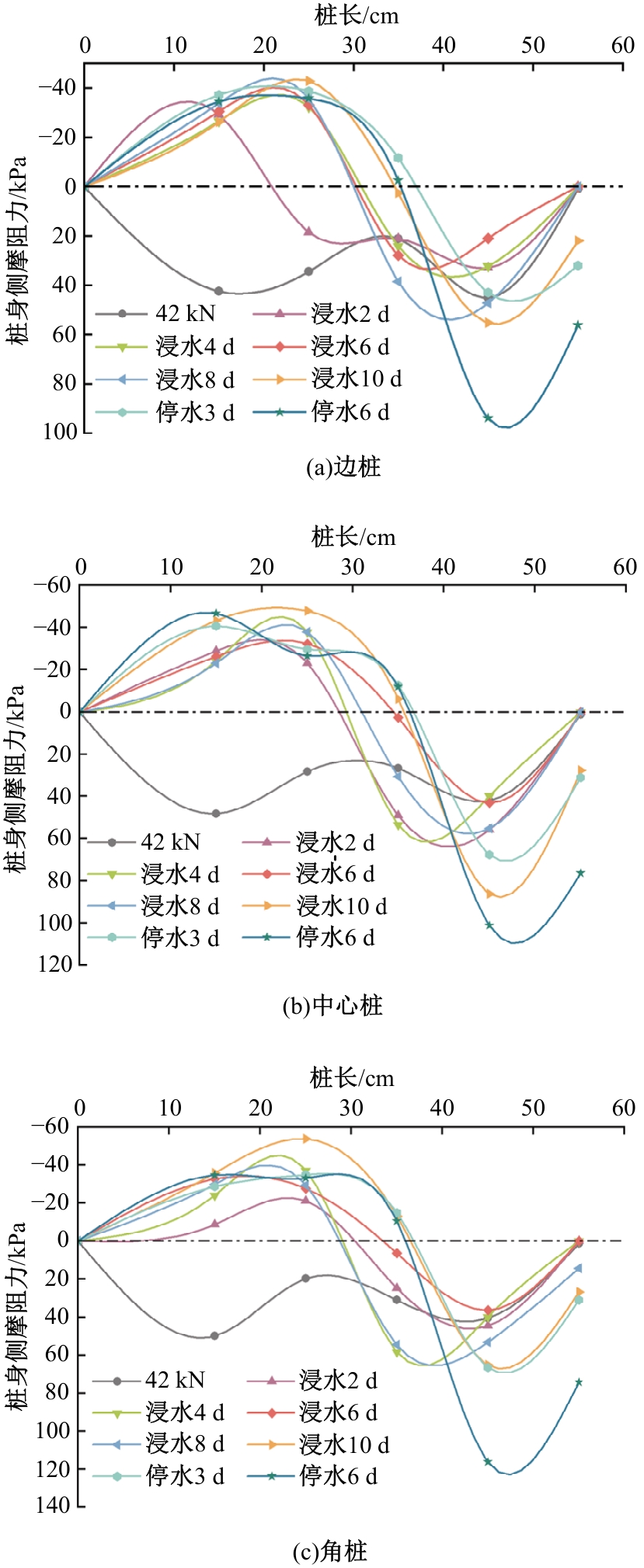
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (12): 3942-3954.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240469
Experimental on bearing characteristics of short and long pile foundation in loess area under submerged condition
Tian-zhong MA1,2,3( ),Jia-jun Yang1,2,3,Zheng-zhen WANG1,2,3(
),Jia-jun Yang1,2,3,Zheng-zhen WANG1,2,3( ),Zhang-jia CHEN1,2,3,Bao-wen GUO1,2,3
),Zhang-jia CHEN1,2,3,Bao-wen GUO1,2,3
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Key Laboratory of Disaster Mitigation in Civil Engineering of Gansu Province,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.Engineering Research Center for Disaster Prevention and Mitigation of Western Civil Engineering,Ministry of Education,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
CLC Number:
- TU473
| [1] | 朱小军, 杨 敏, 杨 桦, 等. 长短桩组合桩基础模型试验及承载性能分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(4): 580-586. |
| Zhu Xiao-jun, Yang Min, Yang Hua, et al. Study on bearing behaviors and model tests of composite pile foundation with long and short piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(4): 580-586. | |
| [2] | 黄茂松, 李波, 程岳. 长短桩组合路堤桩荷载分担规律离心模型试验与数值模拟[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(12): 2543-2550. |
| Huang Mao-song, Li Bo, Cheng Yue. Centrifugal model test and numerical simulation of pile load sharing law for embankment piles with long and short pile combinations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(12): 2543-2550. | |
| [3] | 娄炎, 何宁, 娄斌. 长短桩复合地基中的土拱效应及分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(1): 77-80. |
| Lou Yan, He Ning, Lou Bin. Soil arch effect and analysis in long and short pile composite foundation [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(1): 77-80. | |
| [4] | 郭院成, 张四化, 李明宇. 长短桩复合地基试验研究及数值模拟分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2010, 32(): 232-235. |
| Guo Yuan-cheng, Zhang Si-hua, Li Ming-yu. Test research and numerical simulation analysis of long-short piles composite foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 32(Sup.2): 232-235. | |
| [5] | 高登辉, 赵宽耀, 金松丽, 等. 大厚度自重湿陷性黄土场地桩基负摩阻力计算方法研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(): 231-235. |
| Gao Deng-hui, Zhao Kuan-Yao, Jin Song-li, et al. Calculation method of negative friction resistance of pile foundation in heavy weight collapsible loess site[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(Sup.1): 231-235. | |
| [6] | Ye S H, Zhao Z F, Zhu Y P. Study on negative friction of pile foundation in single homogeneous soil layer in collapsible loess area of Northwest China[J], Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14(12): 1-13 |
| [7] | 马天忠, 孙晨东, 高玉广, 等. 浸水状态下湿陷性黄土场地螺旋灌注桩负摩阻力与土体湿陷规律试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(8): 151-161. |
| Ma Tian-zhong, Sun Chen-dong, Gao Yu-guang, et al. Experiment on negative friction resistance of spiral cast-in-place pile and soil collapse rule in collapsible loess site under flood condition[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transportation, 2022, 35(8): 151-161. | |
| [8] | 郑一峰, 毛健, 梁世忠, 等. 高填土场地考虑土体固结的桩基负摩阻力[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(4): 1075-1081. |
| Zheng Yi-feng, Mao Jian, Liang Shi-zhong, et al. Negative frictional resistance of pile foundation considering soil consolidation in high fill sites[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(4): 1075-1081. | |
| [9] | 张延杰, 王旭, 梁庆国, 等. 浸水条件下湿陷性黄土地基群桩基础承载特性模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(): 219-223. |
| Zhang Yan-Jie, Wang Xu, Liang Qing-Guo, et al. Model test of bearing capacity of pile group foundation on collapsible loess foundation under water immersion condition[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(Sup.1): 219-223. | |
| [10] | 曹明, 陈龙珠, 陈胜立, 等. 长短桩桩筏基础相互作用系数解法及分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2007, 3(2): 382-388. |
| Cao Ming, Chen Long-zhu, Chen Sheng-li, et al. An interaction factor approach and analysis for long-short-pile piled raft foundations[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2007, 3(2): 382-388. | |
| [11] | 林本海, 方辉. 长短桩高强复合地基在高层建筑中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(): 302-307. |
| Lin Ben-hai, Fang Hui. Application of long and short piles high strength composite foundation to high-rise building[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(Sup.2): 302-307. | |
| [12] | 佟建兴, 孙训海, 杨新辉, 等. 长短刚性桩复合地基桩、土承载性状与厚径比相关关系试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(5): 955-960. |
| Tong Jian-Xing, Sun Xun-Hai, Yang Xin-Hui, et al. Experimental study on the correlation between pile and soil bearing properties and thickness-to-diameter ratio of short and long rigid pile composite foundations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(5): 955-960. | |
| [13] | 葛忻声, 鹿宏伟, 李斌, 等. 长短桩复合地基荷载分担比 的试验研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2012, 43(3): 362-367. |
| Ge Xin-sheng, Lu Hong-wei, Li Bin, et al. Model test study on load sharing ratio of composite foundation with long-short piles[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2012, 43(3): 362-367. | |
| [14] | 杨桦, 杨敏, 王伟. 长短桩组合桩基础地基中的应力场和位移分析[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 34(5): 593-597. |
| Yang Hua, Yang Min, Wang Wei. Stress and displacement in subsoil of long short pile foundation[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 34(5): 593-597. | |
| [15] | 于光明, 龚维明, 戴国亮, 等.考虑固结流变的软土地基单桩下拉荷载计算[J], 东南大学学报: 自然科学版,2020, 50(4): 606-615. |
| Yu Guang-ming, Gong Wei-ming, Dai Guo-liang, et al. Calculation of pull down load of single pile on soft soil foundation considering consolidation rheology[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(4): 606-615. | |
| [16] | Yan W B, Gao X L. Computer simulation and model test study on influence of water immersion degree on wind power generation pile stress[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2033(1): 1-12 |
| [17] | 叶观宝, 郑文强, 张振. 大面积填土场地中摩擦型桩负摩阻力分布特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(): 440-448. |
| Ye Guan-bao, Zheng Wen-qiang, Zhang Zhen. Research on the negative friction resistance distribution characteristics of friction pile in large area filling site[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(Sup.1): 440-448. | |
| [18] | 陈天镭, 谢飒, 吴健. 自重湿陷性黄土地基中双向螺旋挤土灌注桩负摩阻力的浸水试验研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2020, 50(6): 11-15. |
| Chen Tian-Lei, Xie Sa, Wu Jian. Immersion of negative friction resistance of bidirectional spiral squeeze pile in self-weight collapsible loess foundation experimental research[J]. Industrial Architecture, 2020, 50(6): 11-15. | |
| [19] | Zhao Zhunag-fu, Ye Shuai-hua, Zhu Yan-peng, et al. Scale model test study on negative skin friction of piles considering the collapsibility of loess[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2022, 17(2): 601-611. |
| [20] | Di S J, Lyu J J, Gao X J, Research on optimize design of pile foundations in collapsible loess areas[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 643(1): 1-6. |
| [21] | 范孟华, 闫保衡, 朱润朝, 等. 堆载作用下单桩中性点位置与负摩阻力特性研究[J]. 河南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 52(3): 329-336. |
| Fan Meng-hua, Yan Bao-heng, Zhu Run-chao, et al. Study on neutral point position and negative friction resistance of single pile under overload[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 52(3): 329-336. | |
| [22] | Chiou J S, Wei W T. Numerical investigation of pile-head load effects on the negative skin friction development of a single pile in consolidating ground[J]. Acta Geotechnica: An International Journal for Geoengineering, 2021, 16(6): 1867-1878. |
| [23] | Liu Y H, Yang P, Xue S, et al. Influence of dredger fill self-consolidation on development of negative skin friction of piles[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2020, 13(15): 1-8. |
| [24] | . 建筑基桩检测技术规范 [S]. |
| [25] | . 湿陷性黄土地区建筑规范 [S]. |
| [26] | 钱鸿缙, 王继堂, 罗玉生, 等. 湿陷性黄土地基[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1985. |
| [27] | .建筑桩基技术规范 [S]. |
| [1] | Zheng-lei YU,Chao-lei ZHANG,Li-xin CHEN,Ping HU,Tao XU,Bin-kai GUO. Bionic structure design and acoustic and mechanical properties of expressway sound barrier panels [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(9): 3079-3088. |
| [2] | Huan LI,Qian-xi LIU,Chang-xin ZHANG,Jian ZHANG. Dynamic friction action and ultrasonic softening during high-power ultrasonic welding process of pure copper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2548-2554. |
| [3] | Ping YUAN,Ya-fu CAI,Li-zhao DAI,Bi-qin DONG,Lei WANG. Topology search method for structural 3D load paths based on distortion control of corrosion-damaged elements [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2212-2222. |
| [4] | Qiong FENG,Xiao-yang XIE,Peng-hui WANG,Hong-xia QIAO,Yun-xia MA. Prediction of reinforced concrete durability based on whale optimization algorithm-back propagation neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(7): 2276-2285. |
| [5] | Zi-ming HE,Ai-qin SHEN,Lu-sheng WANG,Yin-chuan GUO,Jiang-fei HE. Review on strengthening technology of recycled concrete aggregate and its effect on performance of recycled aggregate concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 790-810. |
| [6] | Jie YUAN,Jun-bo WANG,Xin CHEN,Xin HUANG,Ao-xiang ZHANG,An-qi CUI. Research progress on application of artificial intelligence in ultra⁃high performance concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 771-789. |
| [7] | Fu-cheng WANG,Xin-rong ZHAO,Jia-bing TIAN,Guo-liang XIE,Li-ming ZHOU. Influence of rice straw ash on compressive properties and microstructure of concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2620-2630. |
| [8] | Ce LIANG,Min LI,Yi LI,Ji-cai LIANG,Qi-gang HAN. Numerical simulation on friction characteristics of rubber bushing with bionic flexible surfaces [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2181-2186. |
| [9] | Qiong FENG,Hao-zheng TIAN,Hong-xia QIAO,Teng-fei NIAN,Wen-wen HAN. Corrosion deterioration and equivalent relationship between natural exposure and salt spray accelerated environment of reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 494-505. |
| [10] | Xiao HAN,Xian-zhang LING,Shuang TIAN,Sheng-yi CONG. Analysis and control of mud spillover in high⁃speed railway ballast⁃track subgrade caused by grouting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 506-515. |
| [11] | Li-zhao DAI,Chong WANG,Ping YUAN,Lei WANG. Prediction model for shear capacity of corroded RC beams based on interpretable machine learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3231-3243. |
| [12] | Qing-feng YAN,Ji-gang ZHANG,Tao WANG,De-gang CHEN,You-sheng YU,Ying-chun YANG. Seismic performance of connection joints between prefabricated prefinished volumetric construction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 505-514. |
| [13] | Ce LIANG,Fu-lei HUANG,Ji-cai LIANG,Yi LI. Numerical simulation on deformation of protective beam with “日”-shaped section during rotary draw bending [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3397-3403. |
| [14] | Wei-hong CHEN,Yan CHEN,Qiu-rong HONG,Shuang-shuang CUI,Xue-yuan YAN. Seismic performance of earthquake⁃damaged precast concrete frame structures strengthened with BRBs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1817-1825. |
| [15] | Zhao-yi HE,Jin-feng LI,Wen ZHOU,Zhi-tao GUAN. Dynamic modulus of porous asphalt concrete and its prediction model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1375-1385. |
|
||