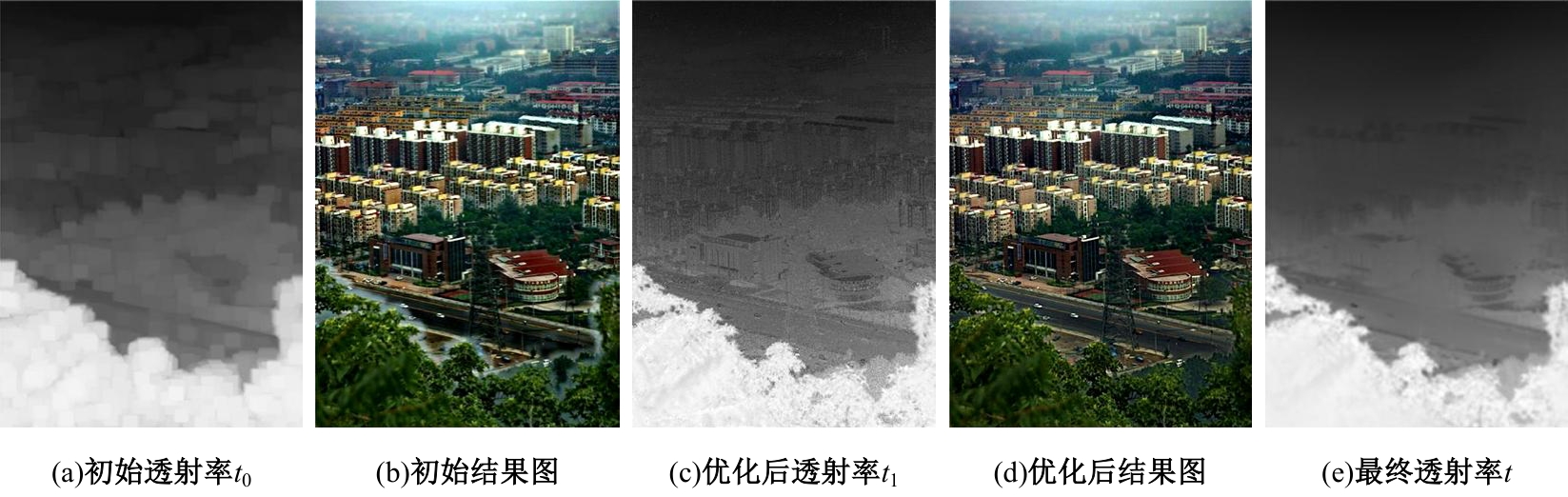
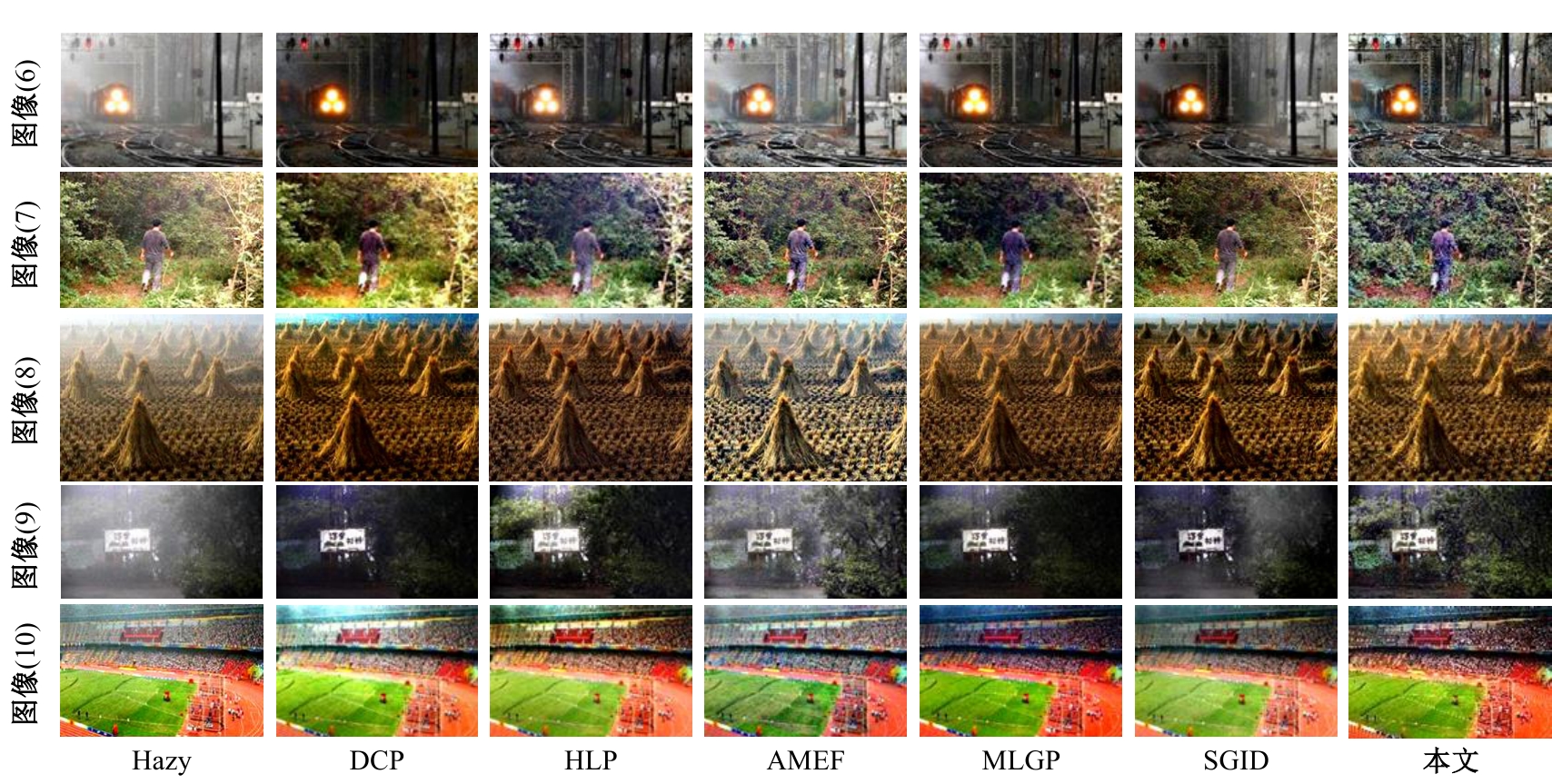
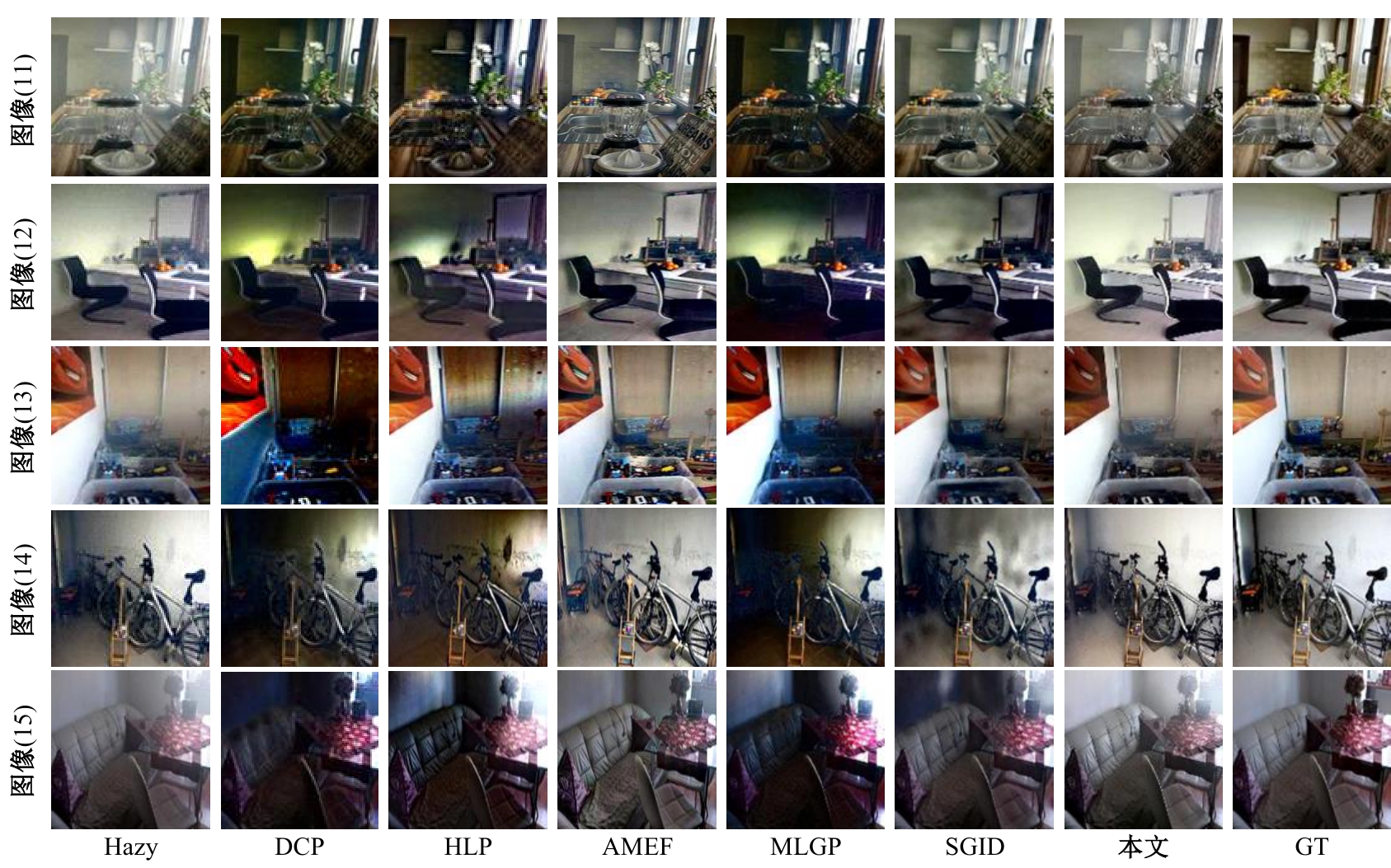
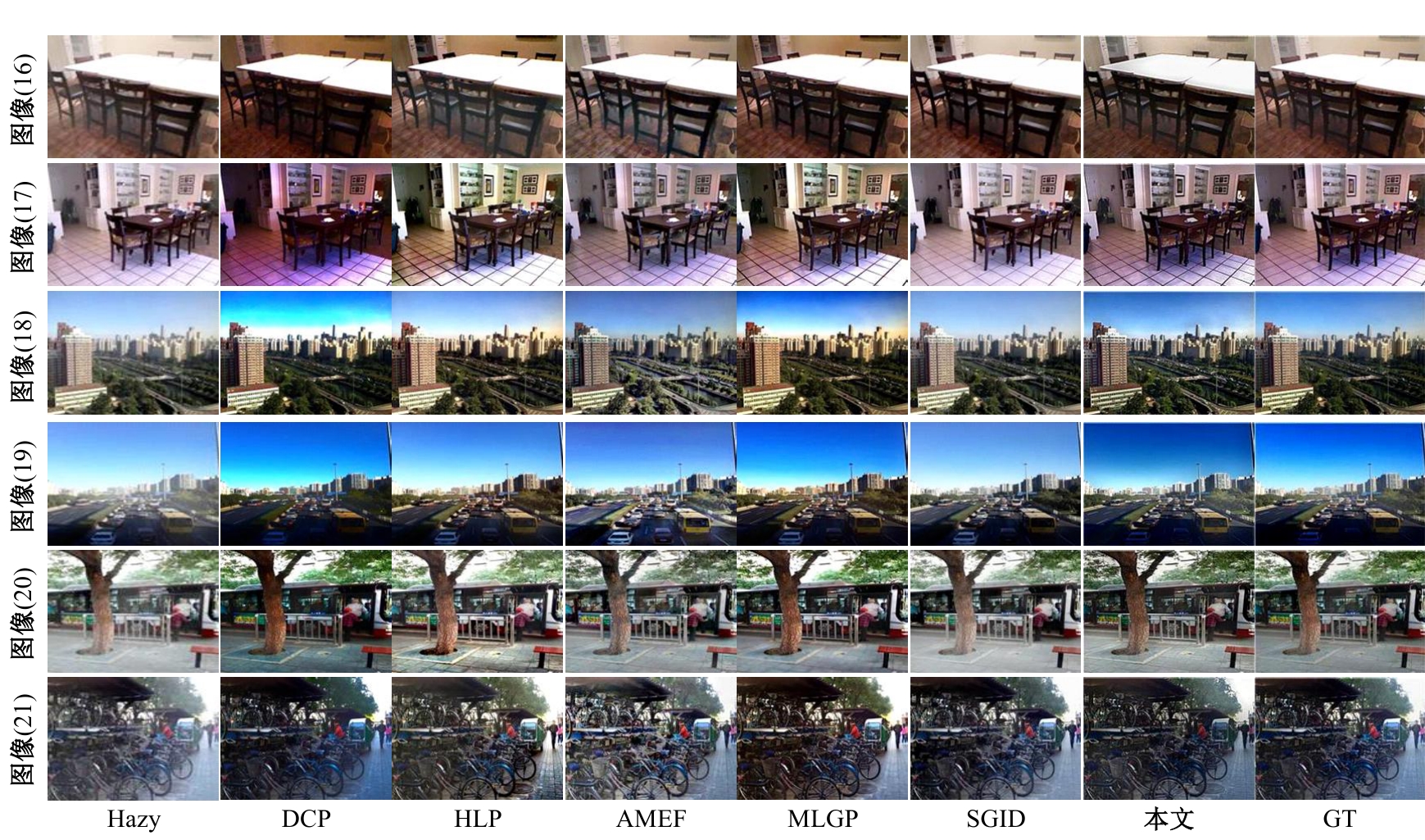
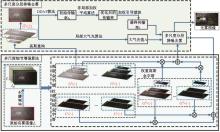
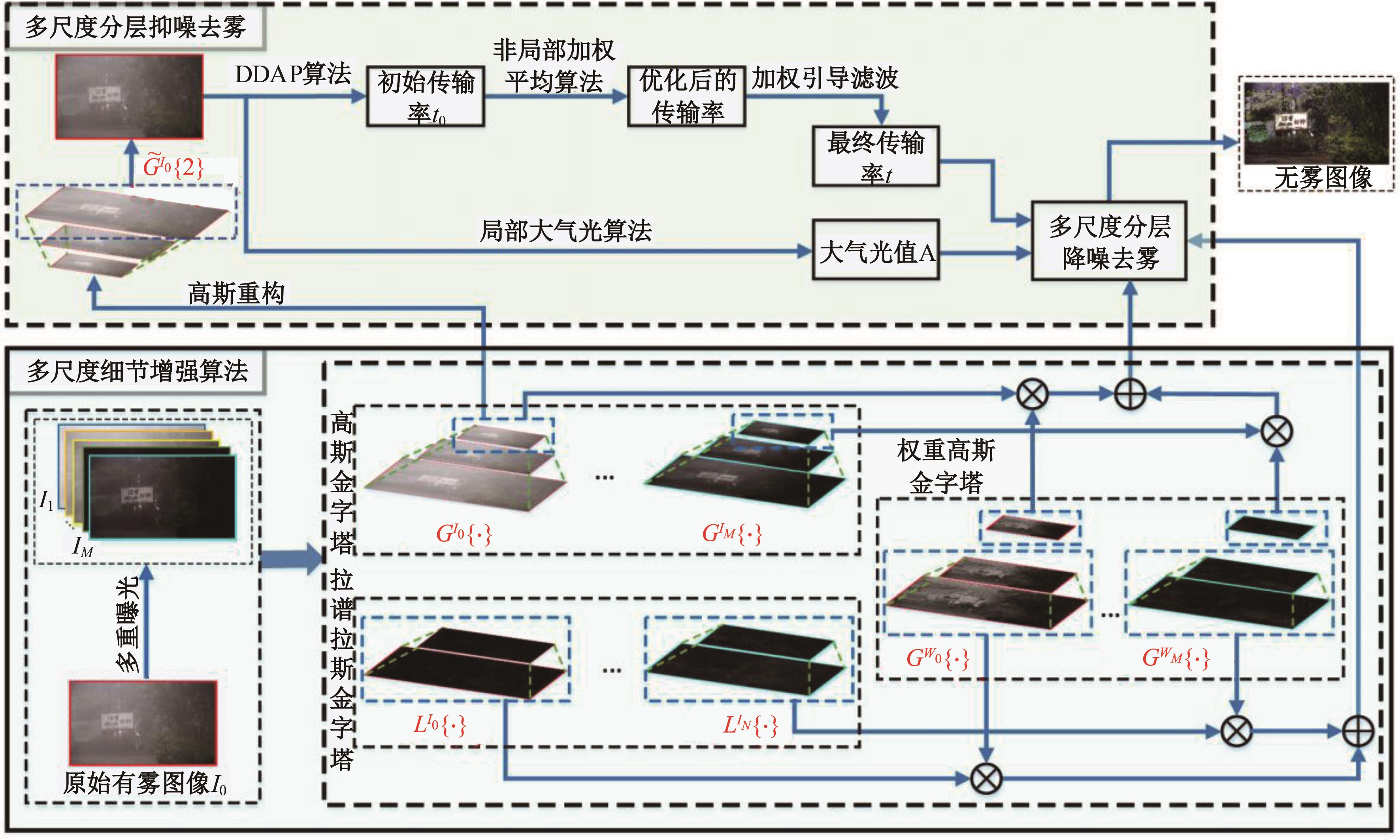
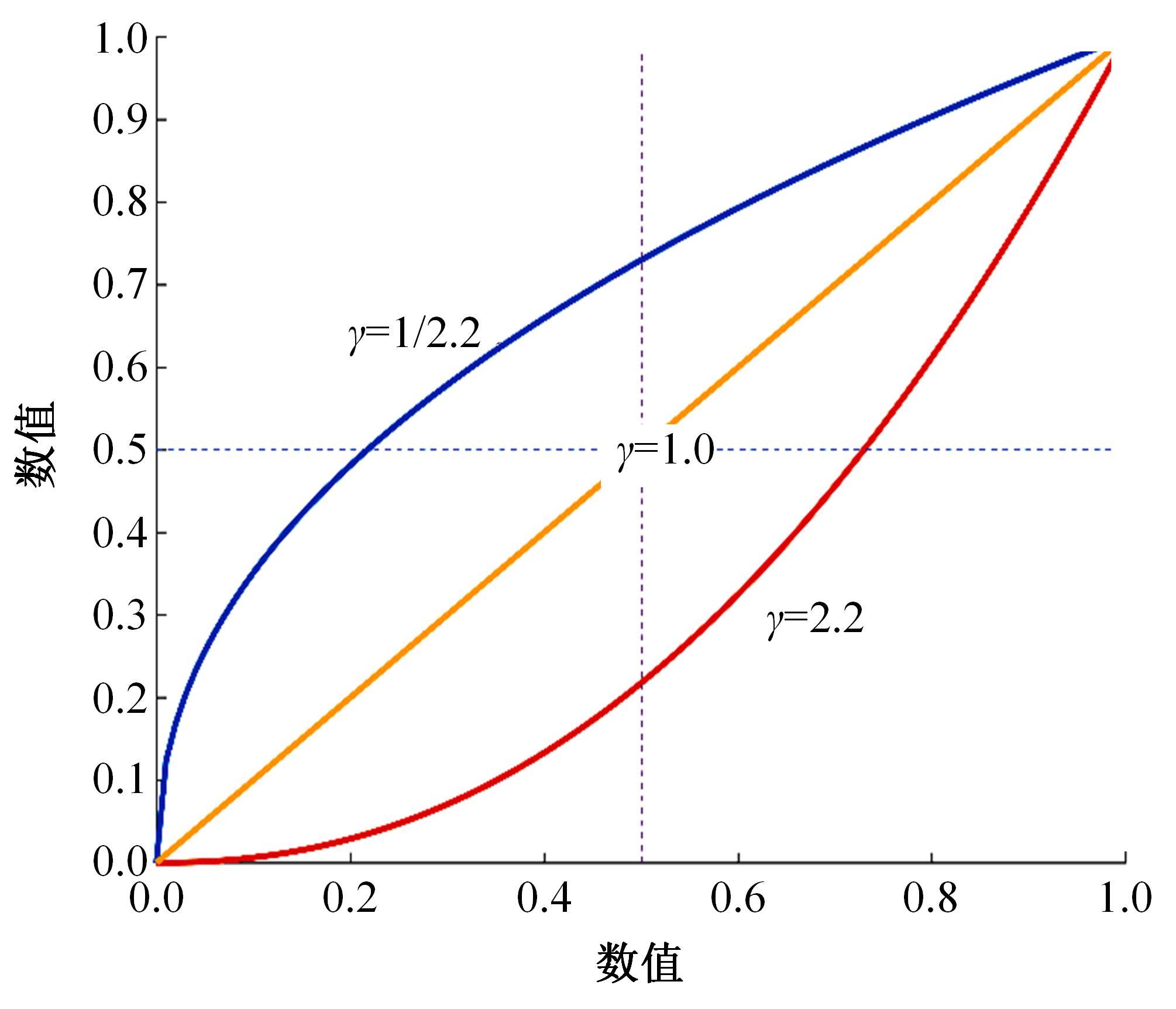
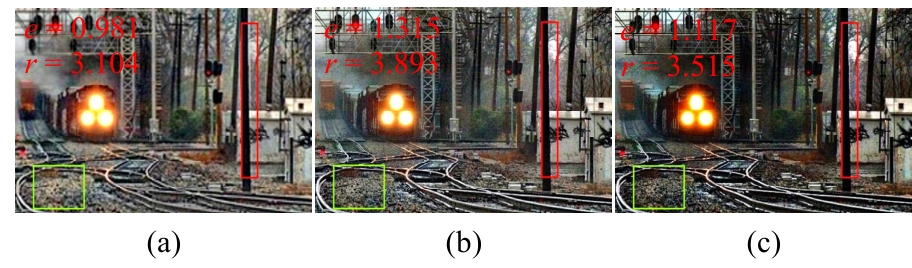
| [1] |
Thejas K, Chandra S. Autonomous bot using machine learning and computer vision[J].SN Computer Science, 2021, 2(4): 251.
|
| [2] |
Hassan N, Ullah S, Bhatti N, et al. A cascaded approach for image defogging based on physical and enhancement models[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2020, 14(5): 867-875.
|
| [3] |
Haller I, Nedevschi S. Design of interpolation functions for subpixel-accuracy stereo-vision systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(2): 889-898.
|
| [4] |
Soni B, Mathur P. An improved image dehazing technique using CLAHE and guided filter[C]//2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2020:902-907.
|
| [5] |
Sarkar M, Sarkar P R, Mondal U, et al. Empirical wavelet transform‐based fog removal via dark channel prior[J]. IET Image Processing, 2020, 14(6): 1170-1179.
|
| [6] |
Sankar M R, Krishna P R, Yamini A,et al. Optimization of single image dehazing based on stationary wavelet transform[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Cyber Physical Systems, Hainan, China, 2023: 414-421.
|
| [7] |
Su C, Li Z, Wei Z L, et al. Clarity method of low-illumination and dusty coal mine images based on improved Amef[J]. Informatica, 2023, 47: 101-114.
|
| [8] |
张驰, 谭南林, 李响, 等. 基于改进型Retinex算法的雾天图像增强技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2019, 45(2): 309-316.
|
|
Zhang Chi, Tan Nan-lin, Li Xiang, et al. Foggy image enhancement technology based on improved Retinex algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2019, 45(2): 309-316.
|
| [9] |
Wang J B, Lu K, Xue J, et al. Single image dehazing based on the physical model and MSRCR algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 28(9): 2190-2199.
|
| [10] |
Cai B L, Xu X M, Jia K, et al.DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198.
|
| [11] |
Frants V, Agaian S, Panetta K. QCNN-H: Single-image dehazing using quaternion neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(9): 5448-5458.
|
| [12] |
李硕士, 刘洪瑞, 甘永东, 等. 基于残差密集块与注意力机制的图像去雾网络[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 48(6): 112-118.
|
|
Li Shuo-shi, Liu Hong-rui, Gan Yong-dong, et al. Image dehazing network based on residual dense block and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2021, 48(6): 112-118.
|
| [13] |
Lyu Z, Chen Y, Hou Y M. MCPNet: Multi-space color correction and features prior fusion for single-image dehazing in non-homogeneous haze scenarios[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 150: No.110290.
|
| [14] |
Yi W C, Dong L Q, Liu M, et al. Priors-assisted dehazing network with attention supervision and detail preservation[J]. Neural Networks, 2024, 173: No.106165.
|
| [15] |
Wang S B, Mei X S, Kang P S, et al. DFC-dehaze: an improved cycle-consistent generative adversarial network for unpaired image dehazing[J]. The Visual Computer, 2024, 40(4): 2807-2818.
|
| [16] |
肖进胜, 申梦瑶, 雷俊锋, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的雾霾场景图像转换算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(1): 165-176.
|
|
Xiao Jin-sheng, Shen Meng-yao, Lei Jun-feng, et al. Haze scene image conversion algorithm based on generative adversarial network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(1): 165-176.
|
| [17] |
Wang P Y, Zhu H Q, Huang H, et al. TMS-GAN:a twofold multi-scale generative adversarial network for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(5): 2760-2772.
|
| [18] |
Zhang J, Dong Q Q, Song W J. GGADN: guided generative adversarial dehazing network[J]. Soft Computing, 2021, 27(3): 1731-1741.
|
| [19] |
Wang Y Z, Yan X F, Wang F, et al. UCL-dehaze:toward real-world image dehazing via unsupervised contrastive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 1361-1374.
|
| [20] |
Meng G F, Wang Y, Duan J Y, et al.Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization[C]∥2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 617-624.
|
| [21] |
王柯俨, 胡妍, 王怀, 等. 结合天空分割和超像素级暗通道的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384.
|
|
Wang Ke-yan, Hu Yan, Wang Huai, et al. Sky segmentation and super dark channel at pixel level image to fog algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition, 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384.
|
| [22] |
Kim S E, Park T H, Eom I K. Fast single image dehazing using saturation based transmission map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2019, 29: 1985-1998.
|
| [23] |
Liu Y, Shang J X, Pan L, et al. A unified variational model for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Access,2019, 7: 15722-15736.
|
| [24] |
高原原, 胡海苗. 基于多子块协同单尺度Retinex的浓雾图像增强[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(5): 944-951.
|
|
Gao Yuan-yuan, Hu Hai-miao. Foggy image enhancement based on multi-block coordinated single-scale Retinex[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2019, 45(5): 944-951.
|
| [25] |
Galdran A. Image dehazing by artificial multiple-exposure image fusion[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 149: 135-147.
|
| [26] |
Qu L H, Liu S L, Wang M N, et al. Rethinking multi-exposure image fusion with extreme and diverse exposure levels: A robust framework based on Fourier transform and contrastive learning[J]. Information Fusion, 2023, 92: 389-403.
|
| [27] |
Xu K, Wang Q, Xiao H Q, et al.Multi-exposure image fusion algorithm based on Improved weight function[J]. Frontiers in Neurorobotics, 2022, 16: No.846580.
|
| [28] |
Yang G, Li J, Gao X B. A dual domain multi-exposure image fusion network based on spatial-frequency integration[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 598: No.128146.
|
| [29] |
Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522- 3533.
|
| [30] |
Mertens T, Kautz J, Van R F. Exposure fusion[C]∥15th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications (PG'07), Tokyo, Japan, 2007: 382-390.
|
| [31] |
Hautière N, Tarel J P, Aubert D, et al. Blina contrast enhancement assessment by gradient ratioing at visible edges[J]. Image Analysis and Stereology, 2008, 27(2): 87.
|
| [32] |
Nayar S K, Narasimhan S G.Vision in bad weather [C]∥Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Corinth, Greece, 1999: 820-827.
|
| [33] |
Cantor A. Optics of the atmosphere—scattering by molecules and particles[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 1978, 14(9): 698-699.
|
| [34] |
He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[C]∥2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 1956-1963.
|
| [35] |
Li Z G, Shu H Y, Zheng C B. Multi-scale single image dehazing using Laplacian and Gaussian Pyramids[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 9270-9279.
|
| [36] |
Berman D, Treibitz T, Avidan S. Non-local Image dehazing[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1674-1682.
|
| [37] |
Li Z G, Zheng J H, Zhu Z J, et al. Weighted guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 120-129.
|
| [38] |
Li Z G, Zheng J H. Single image de-hazing using globally guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 442-450.
|
| [39] |
杨燕, 王志伟. 基于补偿透射率和自适应雾浓度系数的图像复原算法[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(1):66-75.
|
|
Yang Yan, Wang Zhi-wei. Image restoration algorithm based on compensated transmittance and adaptive haze concentration coefficient[J]. Journal of Communications, 2020, 41(1): 66-75.
|
| [40] |
Bai H R, Pan J S, Xiang X G, et al. Self-guided image dehazing using progressive feature fusion[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 1217-1229.
|
| [41] |
Ancuti C, Ancuti C O, Timofte R, et al. I-HAZE: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free indoor images[C]∥Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems:19th International Conference, ACIVS 2018, Poitiers, France, 2018: 620-631.
|
| [42] |
Li B, Ren W, Fu D, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(1): 492-505.
|
| [43] |
Huynh-Thu Q, Ghanbari M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment[J]. Electronics Letters, 2008, 44(13): 800.
|
| [44] |
Wang Z, Bovik A C, Sheikh H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612.
|