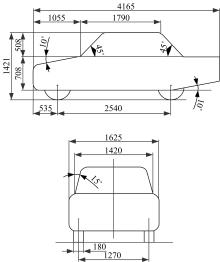
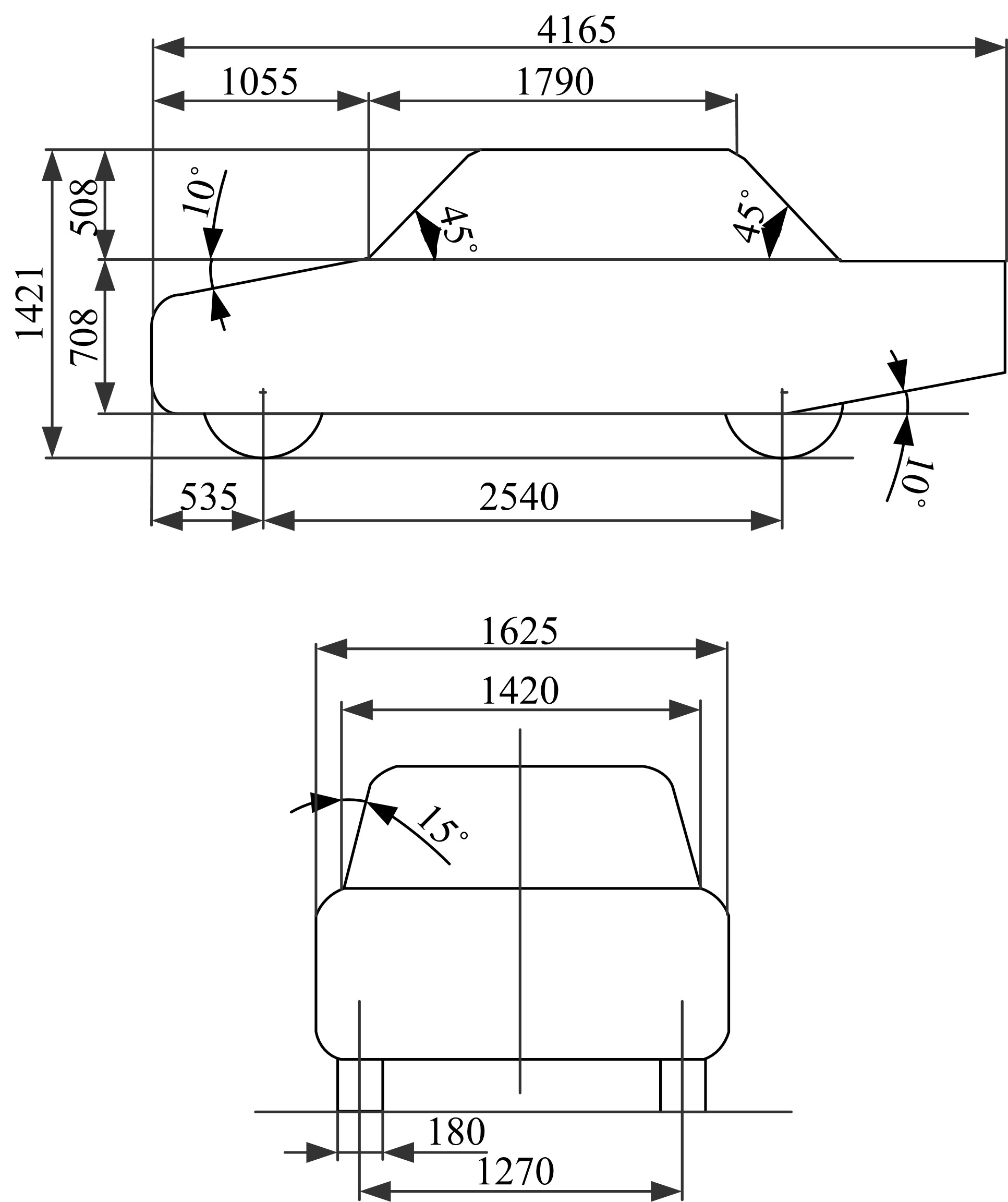
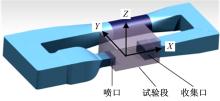
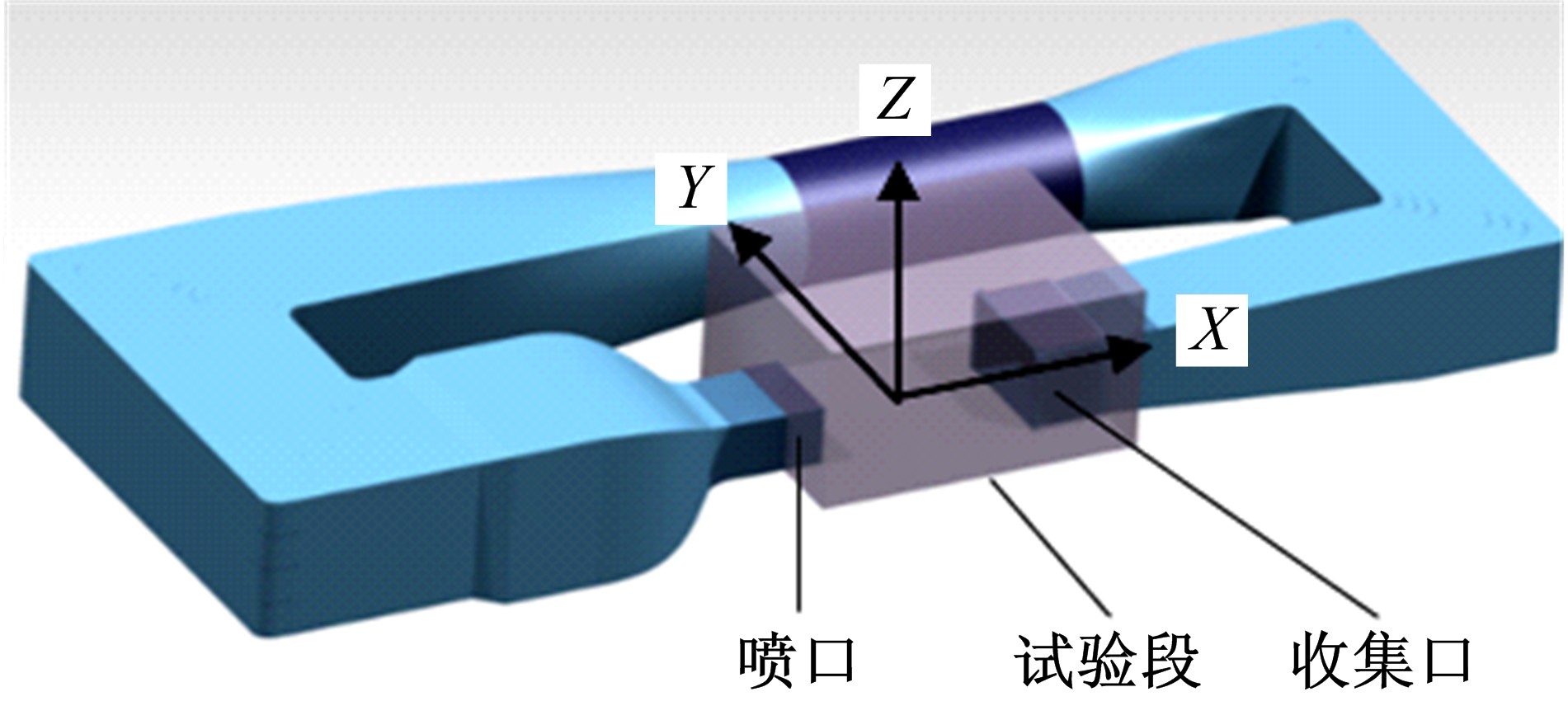
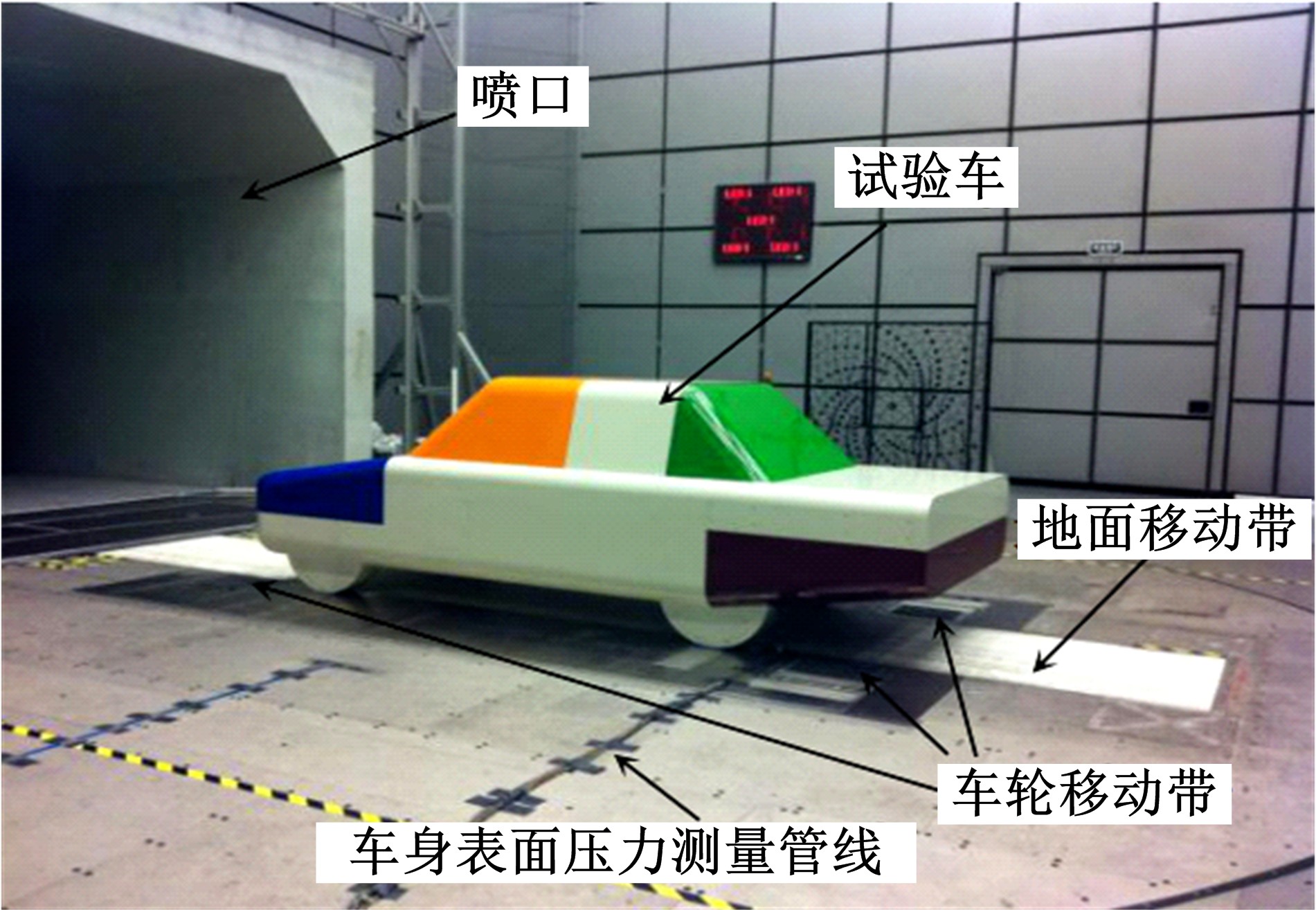
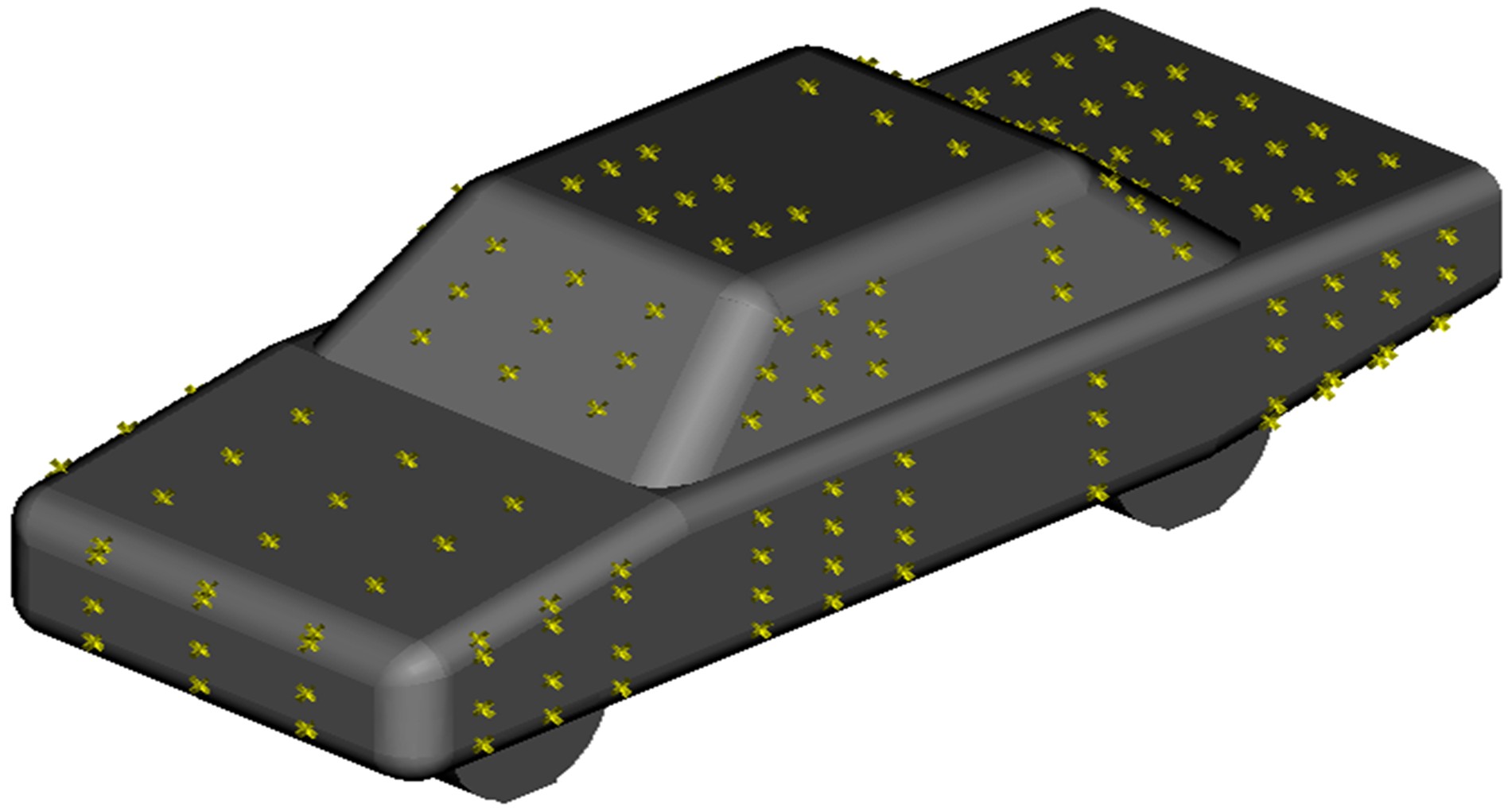
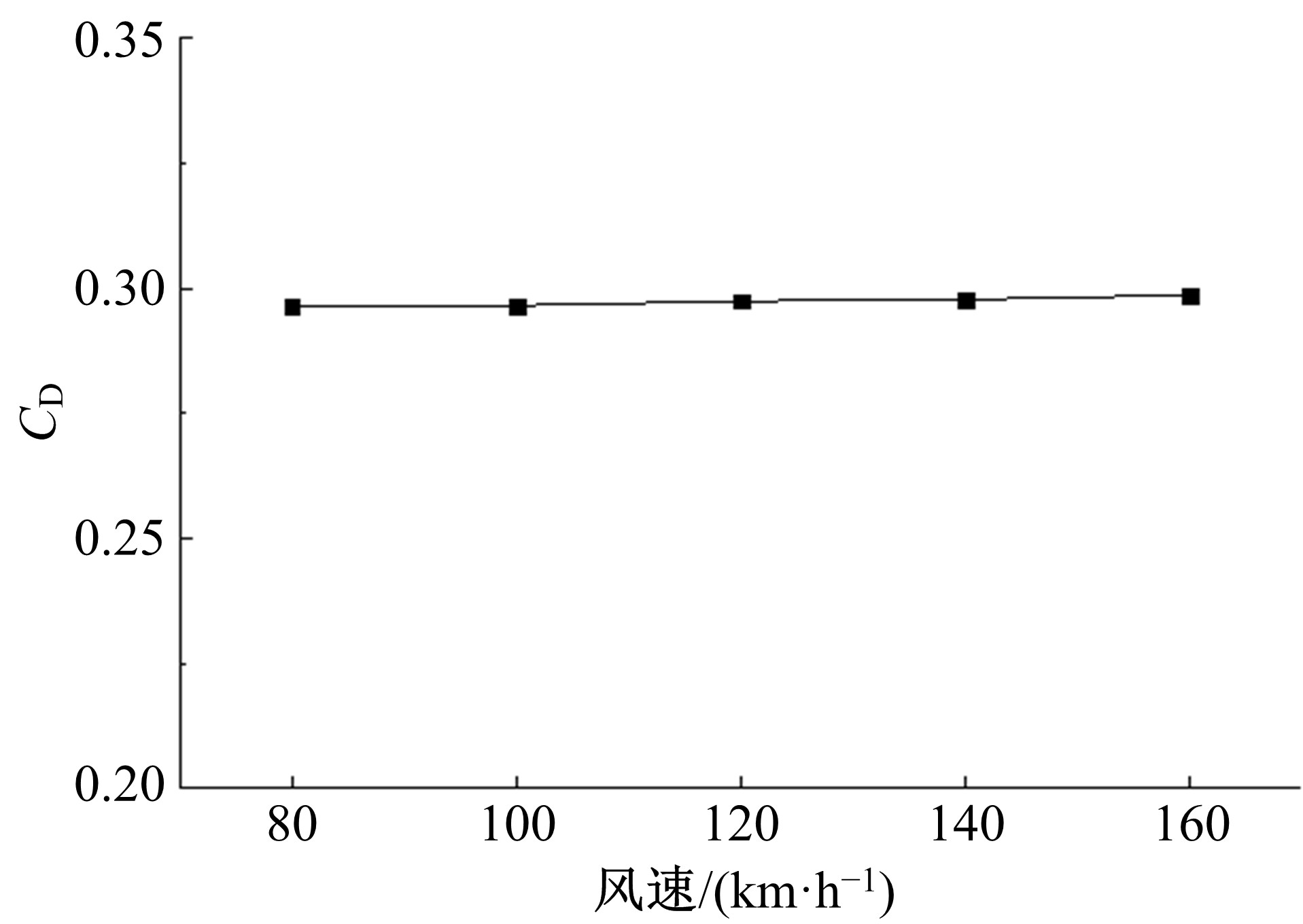
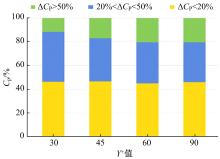
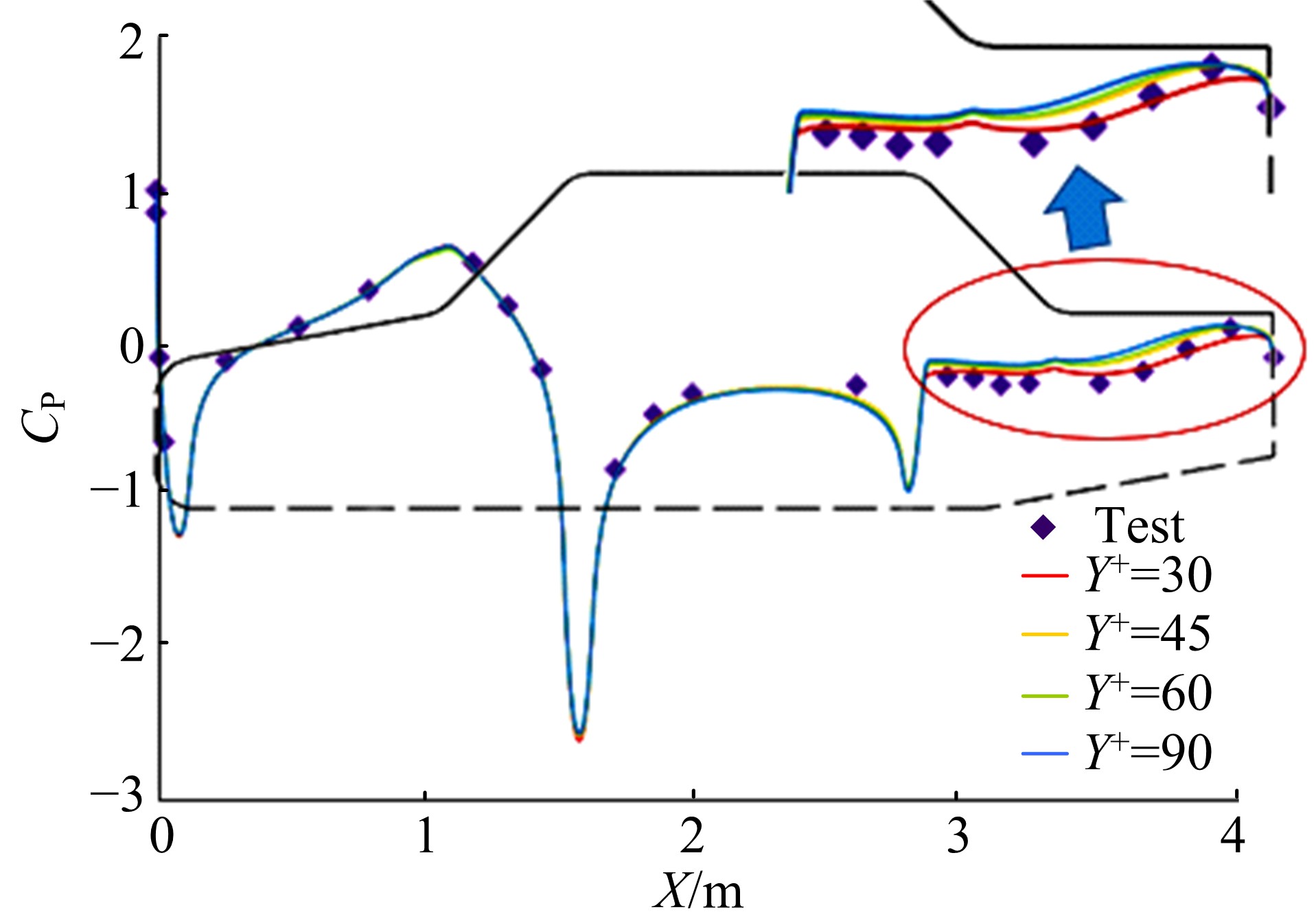
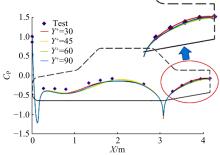
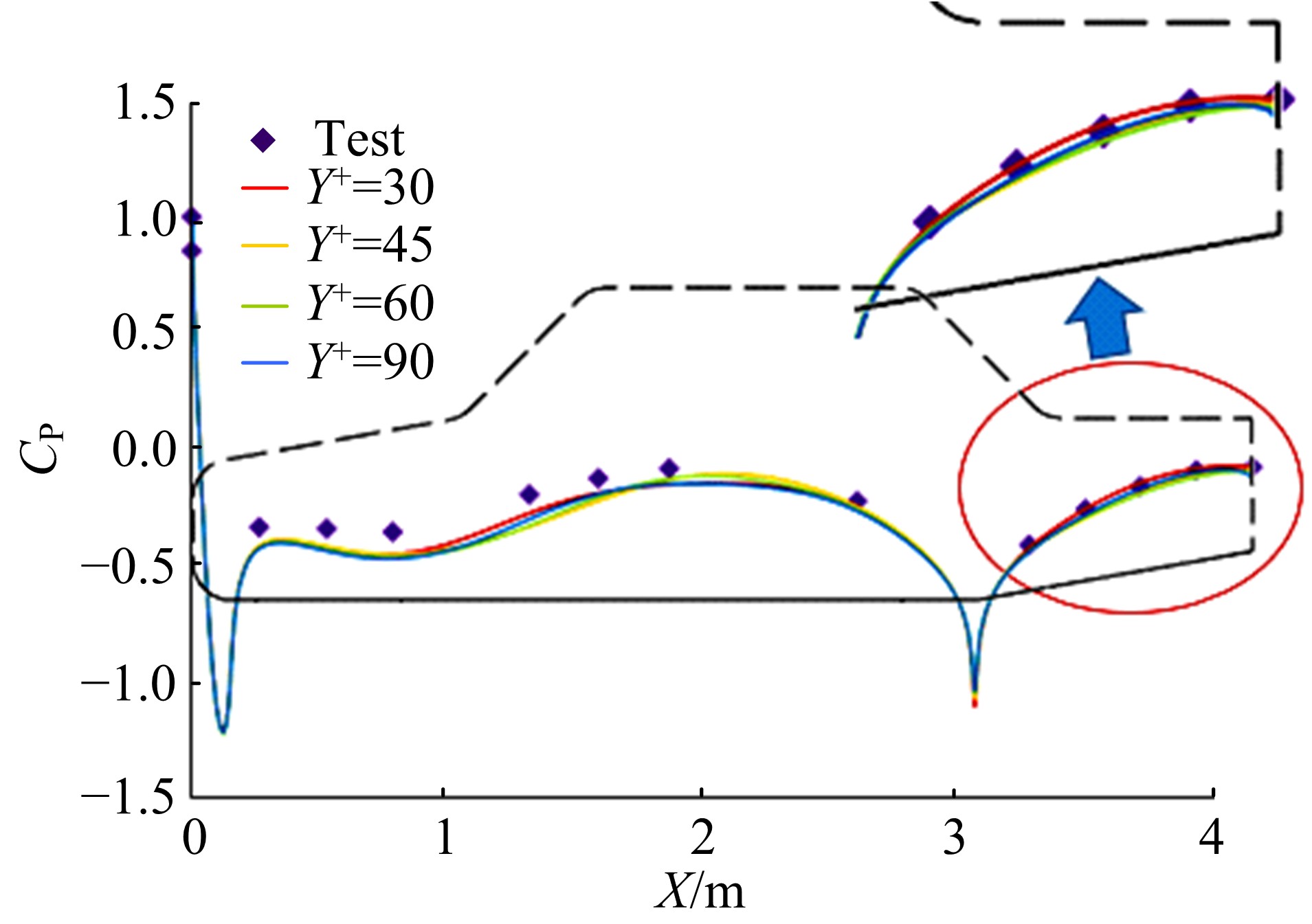
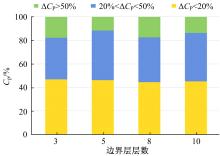
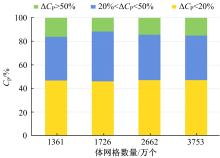
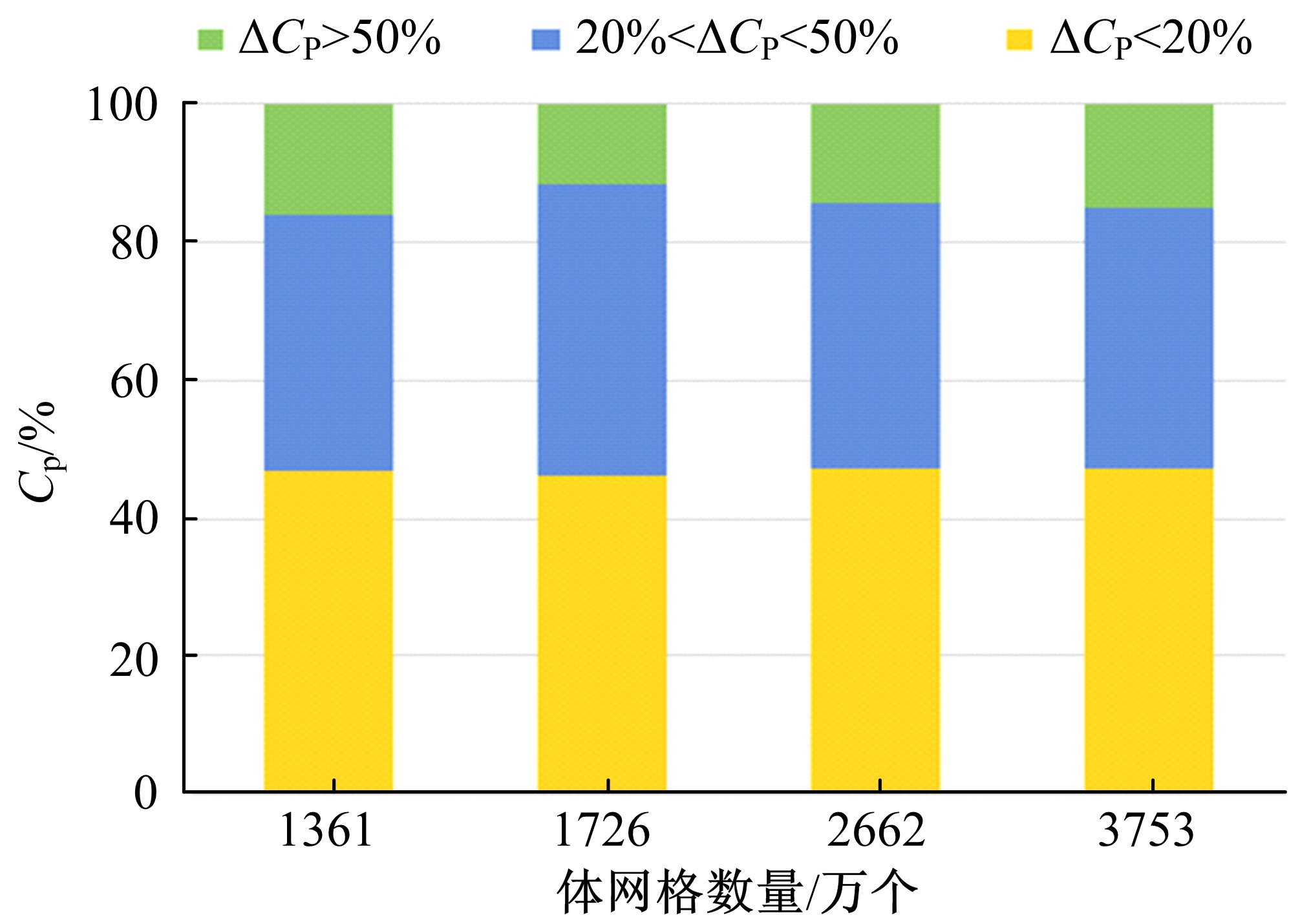
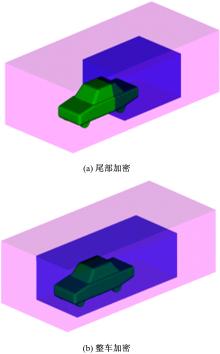
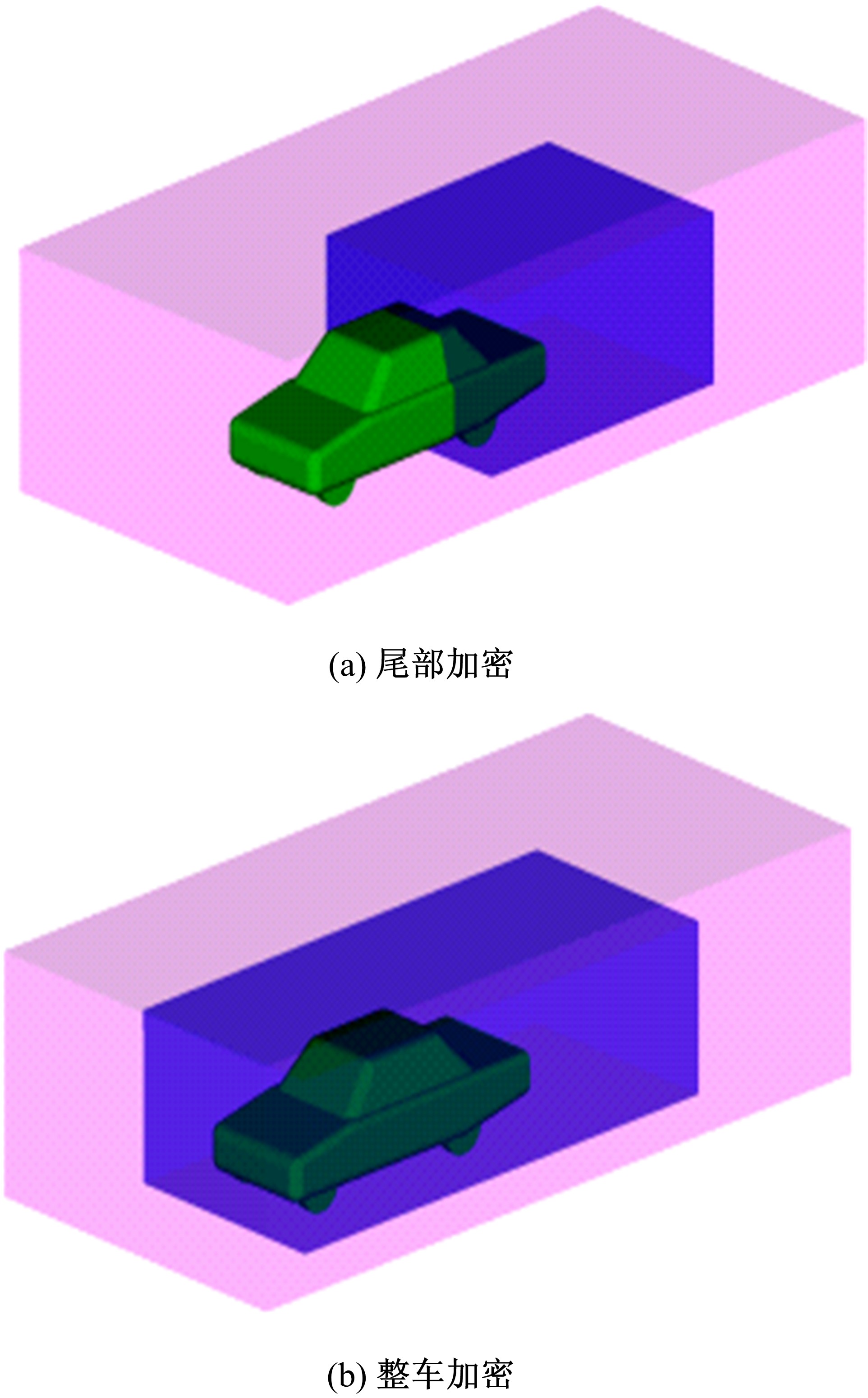
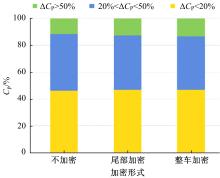
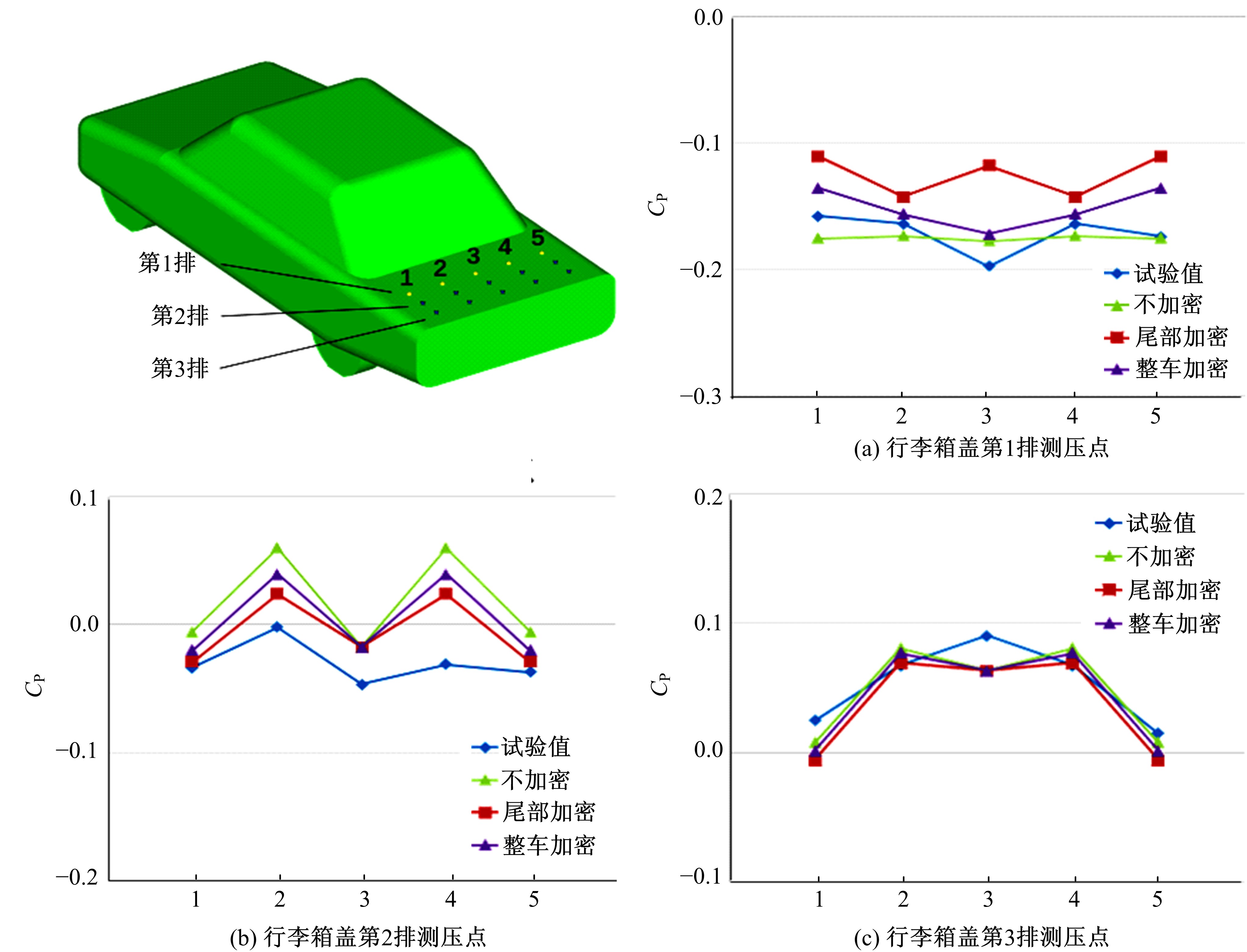
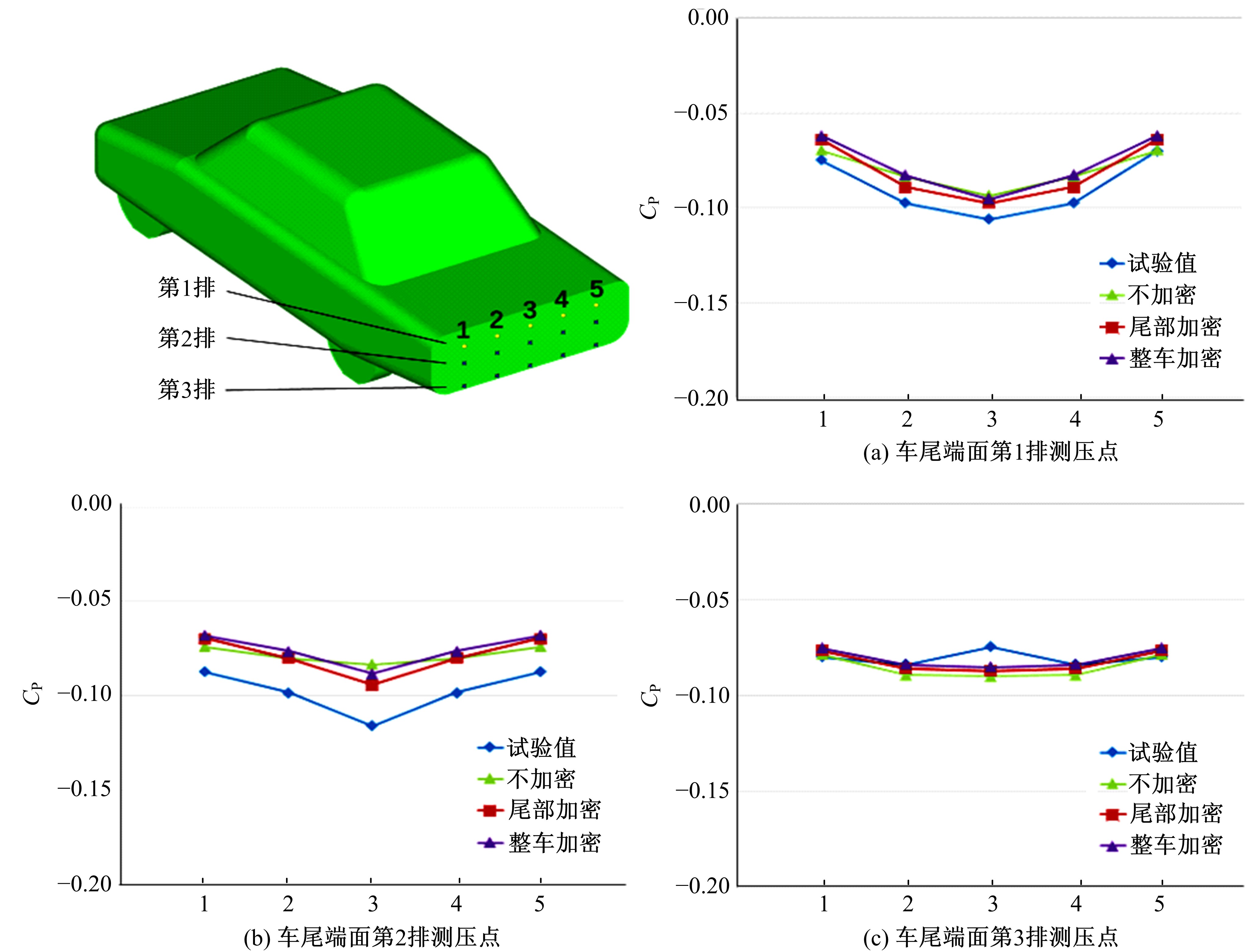
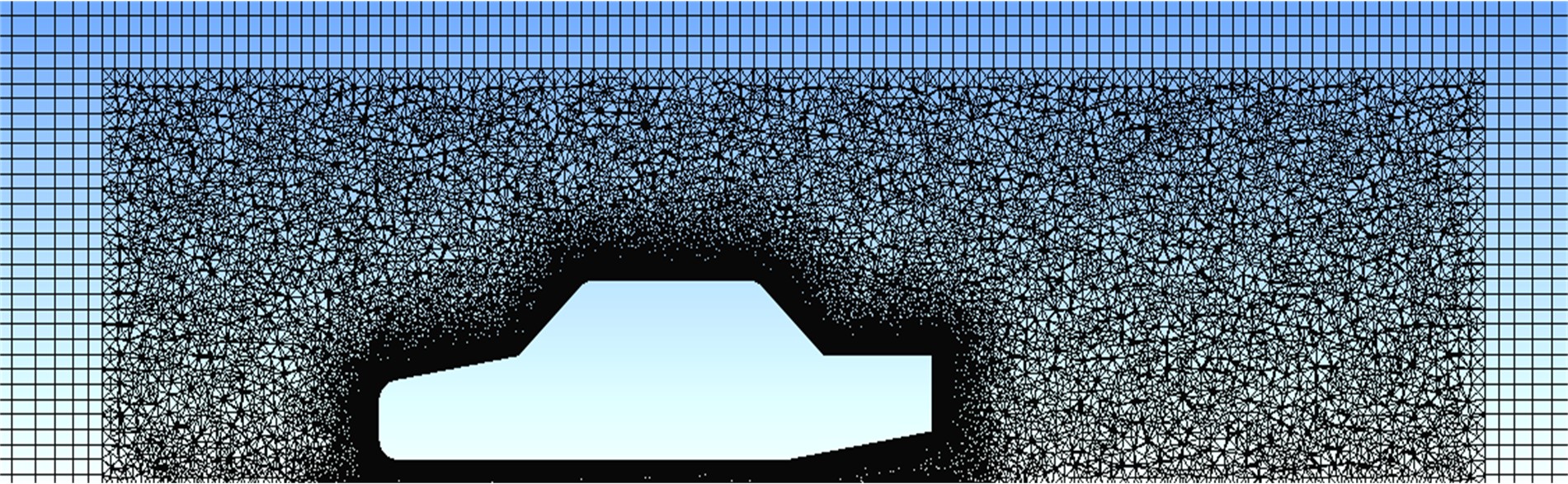
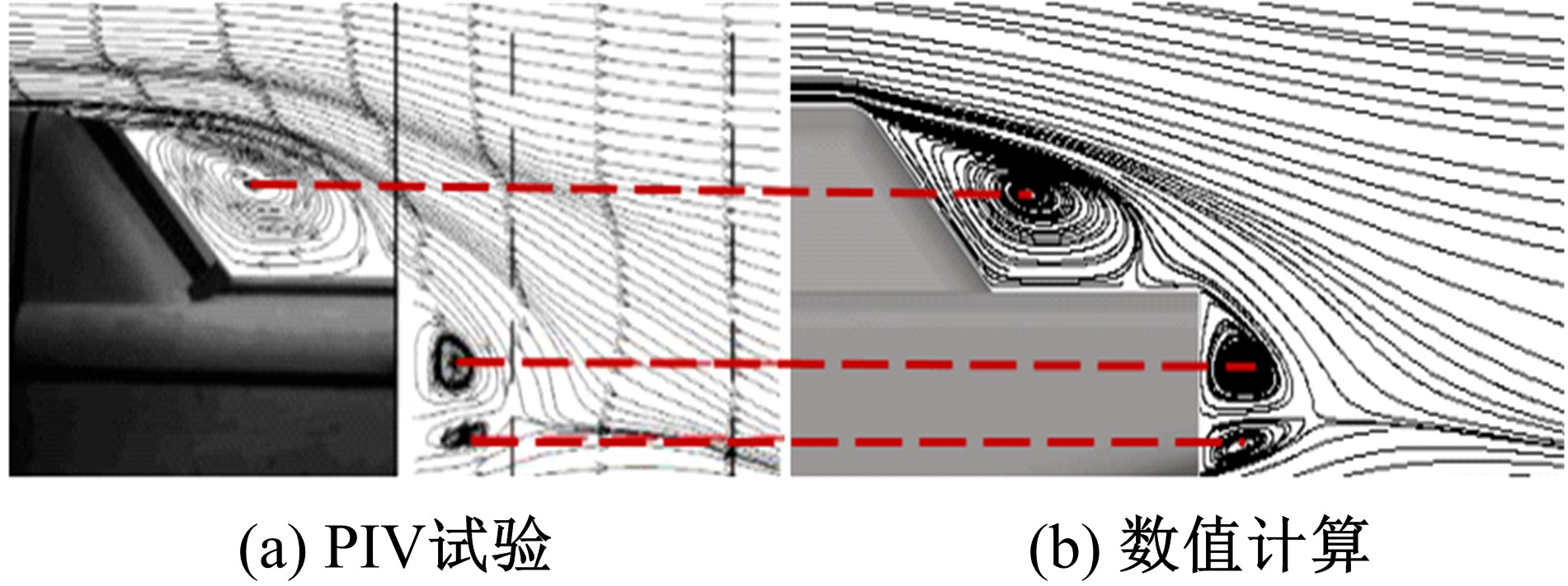
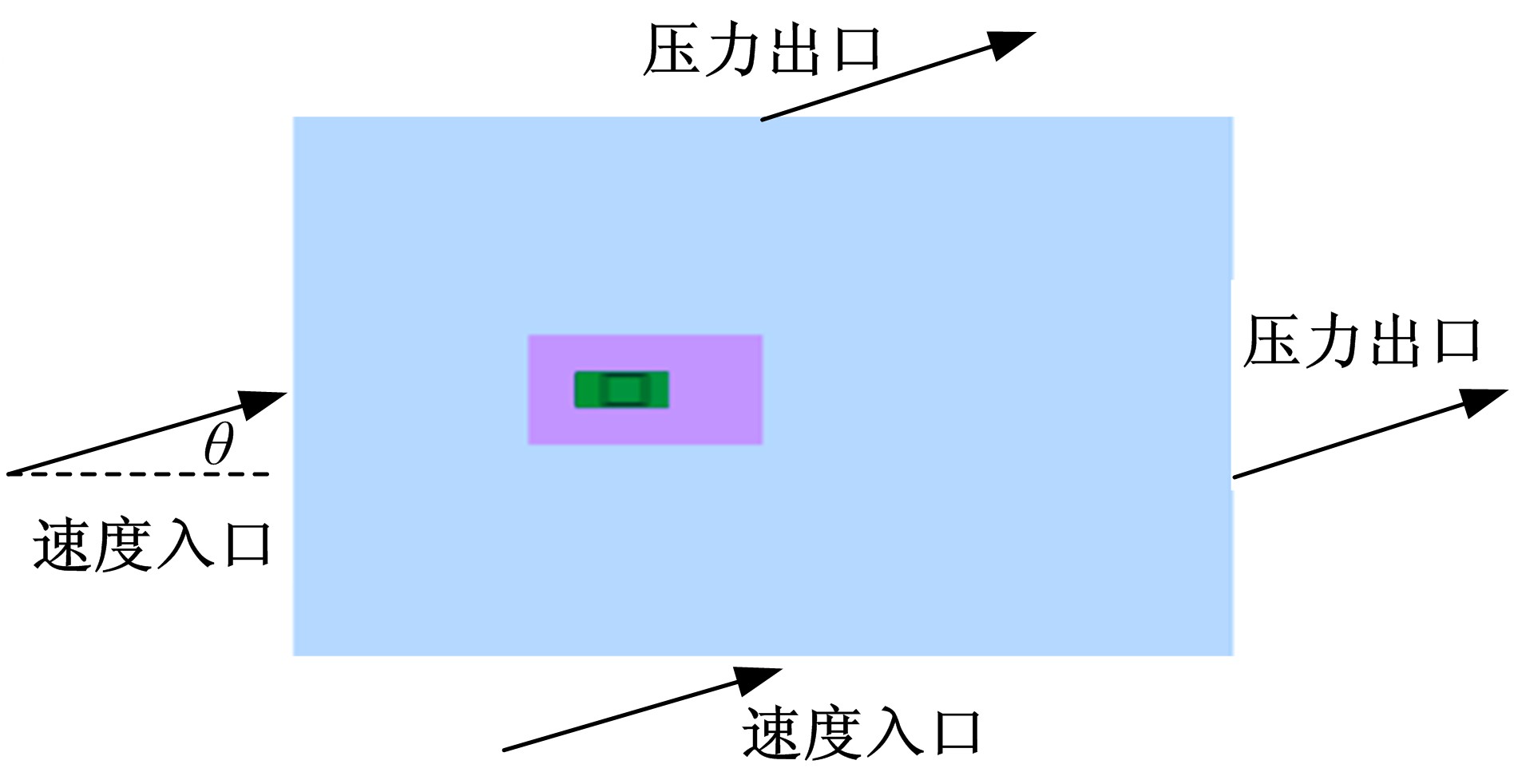
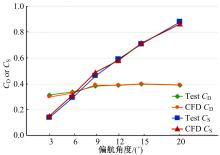
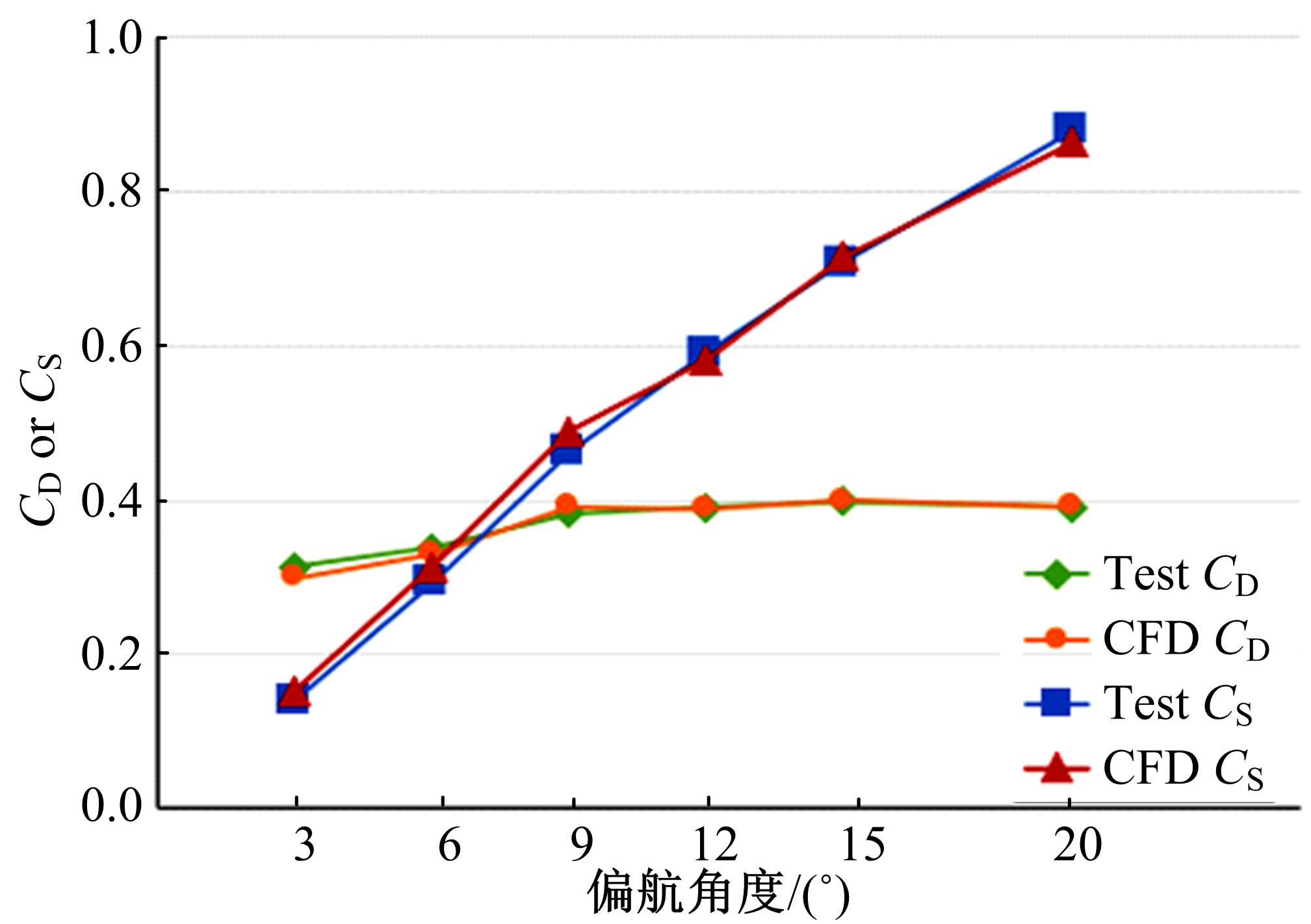
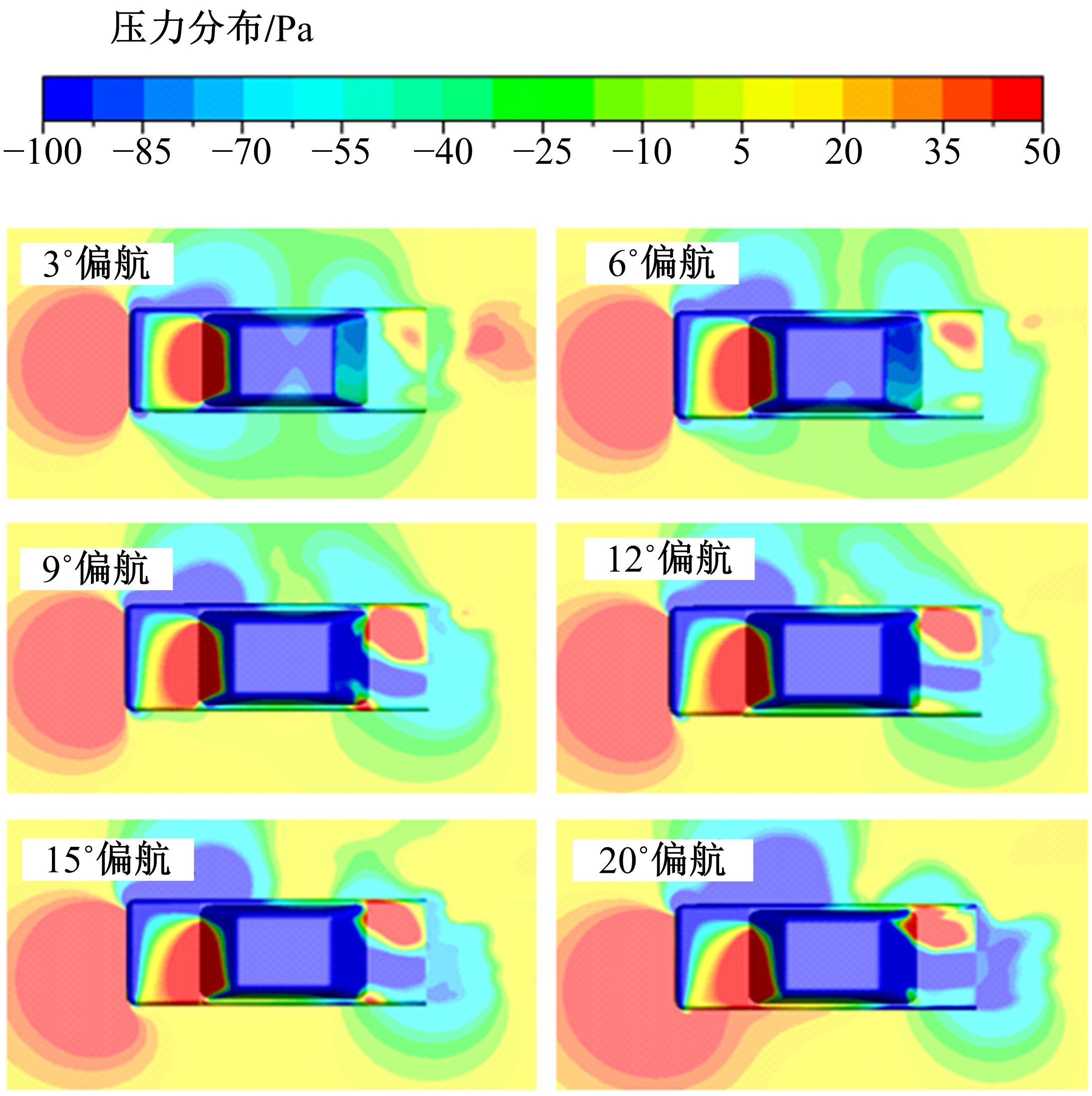
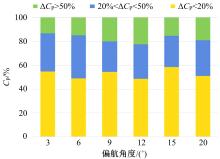
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 1043-1053.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180226
Aerodynamic calculation of MIRA model correlated with wind tunnel test
Hua ZHOU1,2( ),Zhi⁃gang YANG1,2,3(
),Zhi⁃gang YANG1,2,3( ),Hui ZHU1,2
),Hui ZHU1,2
- 1. Shanghai Automotive Wind Tunnel Center, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
2. Shanghai Key Lab of Vehicle Aerodynamics and Vehicle Thermal Management Systems, Shanghai 201804, China
3. Beijing Research Center, Commercial Aircraft Corporation of China, Beijing 102200, China
CLC Number:
- U467.1
| 1 | Hucho W H . Aerodynamics of Road Vehicles[M]. Warrendale: Society of Automotive Engineers, 1998. |
| 2 | 姜乐华, 谷正气 . CFD在汽车空气动力学研究中的应用[J]. 湖南大学学报, 1997, 24(4): 52⁃56. |
| Jiang Le⁃hua , Gu Zheng⁃qi . The application of CFD methods to automobile aerodynamics[J]. Journal of Hunan University, 1997, 24(4): 52⁃56. | |
| 3 | 傅立敏, 王靖宇 . 汽车三维分离流动特性的数值研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2000, 22(6): 361⁃364, 376. |
| Fu Li⁃min , Wang Jing⁃yu . Numerical study of separated flow around after⁃body of road vehicle[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2000, 22(6): 361⁃364, 376. | |
| 4 | 严鹏, 吴光强, 傅立敏, 等 . 轿车外流场数值模拟[J]. 同济大学学报, 2003, 31(9): 1082⁃1086. |
| Yan Peng , Wu Guang⁃qiang , Fu Li⁃min , et al . Numerical simulation of flow field around car[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2003, 31(9): 1082⁃1086. | |
| 5 | 吴军, 钟志华, 谷正气 . 汽车外流场数值仿真的进一步研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2003, 39(9): 110⁃113. |
| Wu Jun , Zhong Zhi⁃hua , Gu Zheng⁃qi . Further study on numerical simulation of flow around automobiles[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2003, 39(9): 110⁃113. | |
| 6 | Shih T H , Liou W W , Shabbir A , et al . A new k⁃ε eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows: model development and validation[J]. Computers and Fluids, 1995, 24(3): 227⁃238. |
| 7 | 张英朝, 薛学栋, 丁伟,等 . 某两厢车气动外形减阻自动优化设计[J]. 同济大学学报, 2016, 44(11): 1771⁃1776. |
| Zhang Ying⁃chao , Xue Xue⁃dong , Ding Wei , et al . Automobile shape optimization of hatchback to reduce aerodynamic drag[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2016, 44(11): 1771⁃1776. | |
| 8 | 朱晖, 杨志刚 . 两方程模型计算轿车气动性能的适用性研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(11): 1283⁃1287, 1337. |
| Zhu Hui , Yang Zhi⁃gang . A study on the applicability of two⁃equation models to the calculation of aerodynamic performance of Sedan[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(11): 1283⁃1287, 1337. | |
| 9 | Ashton N , Revell A . Comparison of rans and des methods for the drivaer automotive body[C]∥SAE Paper, 2015⁃01⁃1538. |
| 10 | Palaskar P M , Kumar V , Vaidya R . Methodology development to accurately predict aerodynamic drag and lift for passenger vehicles using CFD[C]∥SAE Paper, 2016⁃01⁃1600. |
| 11 | Ahmad N E , Abo⁃Serie E , Gaylard A . Mesh optimization for ground vehicle aerodynamics[J]. CFD Letters, 2010, 2(1): 54⁃65. |
| 12 | Gaylard A P , Baxendale A J , Howell J P . The use of CFD to predict the aerodynamic characteristics of simple automotive shapes[C]∥SAE Paper, 980036. |
| 13 | Zhang Ying⁃chao , Ding Wei , Zhang Yu . Aerodynamic shape optimization based on the MIRA reference car model[C]∥SAE Paper, 2014⁃01⁃0603. |
| 14 | Le G G M , Garry K P . On the use of reference models in automotive aerodynamics[C]∥SAE Paper, 2004⁃01⁃1308. |
| 15 | Lawson A A , Dominy R G , Sims⁃Williams D B , et al . A comparison between on⁃road and wind tunnel surface pressure measurements on a mid⁃sized hatchback[C]∥SAE Paper, 2007⁃01⁃0898. |
| 16 | Gu Zheng⁃qi , Song Xin , Jian Ye⁃jie , et al . Optimization of the realizable k⁃ε turbulence model especially for the simulation of road vehicle[C]∥SAE Paper, 2012⁃01⁃0778. |
| 17 | Wang Y , Xin Y , Gu Z , et al . Numerical and experimental investigations on the aerodynamic characteristic of three typical passenger vehicles[J]. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 7(4): 659⁃671. |
| 18 | 龚旭, 谷正气, 李振磊, 等 . 侧风状态下轿车气动特性数值模拟方法的研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2010, 32(1): 13⁃16. |
| Gong Xu , Gu Zheng⁃qi , Li Zhen⁃lei , et al . A study on the numerical simulation of car aerodynamic characteristics under crosswind conditions[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2010, 32(1): 13⁃16. |
| [1] | Jing LI,Qiu⁃jun SHI,Peng LIU,Ya⁃wei HU. Neural network sliding mode control of commercial vehicle ABS based on longitudinal vehicle speed estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1017-1025. |
| [2] | Shun YANG,Yuan⁃de JIANG,Jian WU,Hai⁃zhen LIU. Autonomous driving policy learning based on deep reinforcement learning and multi⁃type sensor data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [3] | Xin CHEN,Ming LI,Xin⁃jian RUAN,Ning WANG,Jia⁃ning WANG. Investigation of vortical structures in wake of Ahmed body by delayed detached⁃eddy simulation turbulence model using immersed boundary method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1034-1042. |
| [4] | CHANG Cheng,SONG Chuan-xue,ZHANG Ya-ge,SHAO Yu-long,ZHOU Fang. Minimizing inverter capacity of doubly-fed machine driving electric vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1629-1635. |
| [5] | XI Li-he,ZHANG Xin,SUN Chuan-yang,WANG Ze-xing,JIANG Tao. Adaptive energy management strategy for extended range electric vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1636-1644. |
| [6] | HE Ren,YANG Liu,HU Dong-hai. Design and analysis of refrigeration system supplied by solar auxiliary power of refrigerator car [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1645-1652. |
| [7] | NA Jing-xin,MU Wen-long,FAN Yi-sa,TAN Wei,YANG Jia-zhou. Effect of hygrothermal aging on steel-aluminum adhesive joints for automotive applications [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1653-1660. |
| [8] | LIU Yu-mei,LIU Li,CAO Xiao-ning,XIONG Ming-ye,ZHUANG Jiao-jiao. Construction on collision avoidance model of bogie dynamic simulation test bench [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1661-1668. |
| [9] | GUO Hao-tian,XU Tao,LIANG Xiao,YU Zheng-lei,LIU Huan,MA Long. Optimization on thermal surface with rib turbulator inspired by turbulence of alopias' gill in simplified gas turbine transition piece [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1793-1798. |
| [10] | SONG Da-feng, WU Xi-tao, ZENG Xiao-hua, YANG Nan-nan, LI Wen-yuan. Life cycle cost analysis of mild hybrid heavy truck based on theoretical fuel consumption model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1313-1323. |
| [11] | ZHU Jian-feng, ZHANG Jun-yuan, CHEN Xiao-kai, HONG Guang-hui, SONG Zheng-chao, CAO Jie. Design modification for automotive body structure based on seat pull safety performance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1324-1330. |
| [12] | JIN Li-sheng, XIE Xian-yi, GAO Lin-lin, GUO Bai-cang. Distributed electric vehicle stability control based on quadratic programming [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1349-1359. |
| [13] | GONG Ya-feng, WANG Bo, WEI Hai-bin, HE Zi-heng, HE Yu-long, SHEN Yang-fan. Surface subsidence law of double-line shield tunnel based on Peck formula [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1411-1417. |
| [14] | WANG De-jun, WEI Wei-li, BAO Ya-xin. Actuator fault diagnosis of ESC system considering crosswind interference [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1548-1555. |
| [15] | ZHAO Wei-qiang, GAO Ke, WANG Wen-bin. Prevention of instability control of commercial vehicle based on electric-hydraulic coupling steering system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1305-1312. |
|
||