Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 773-780.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180562
Previous Articles Next Articles
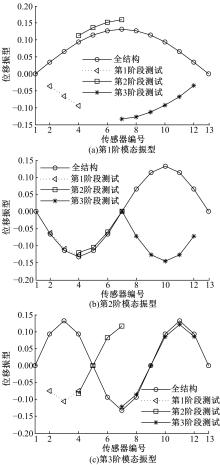
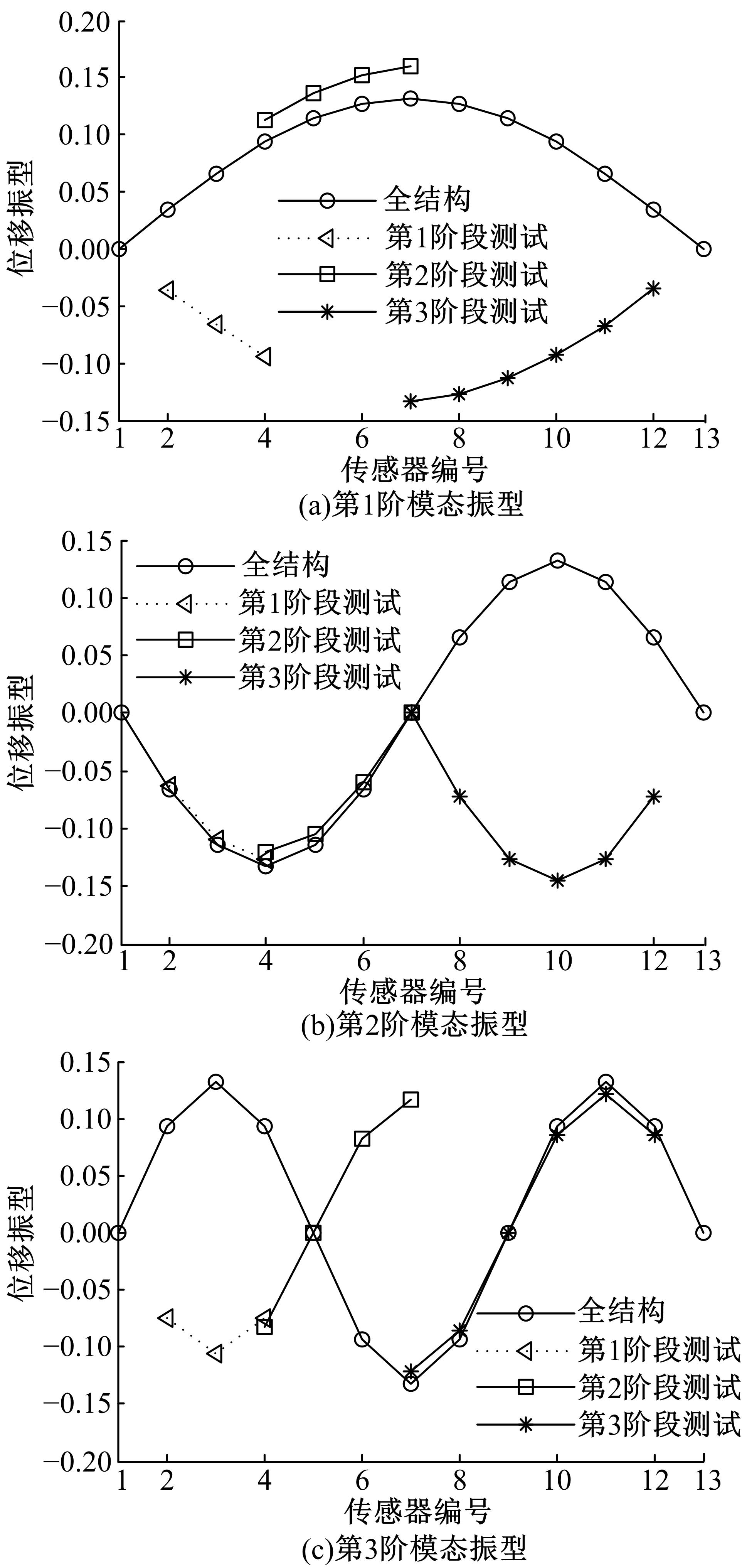
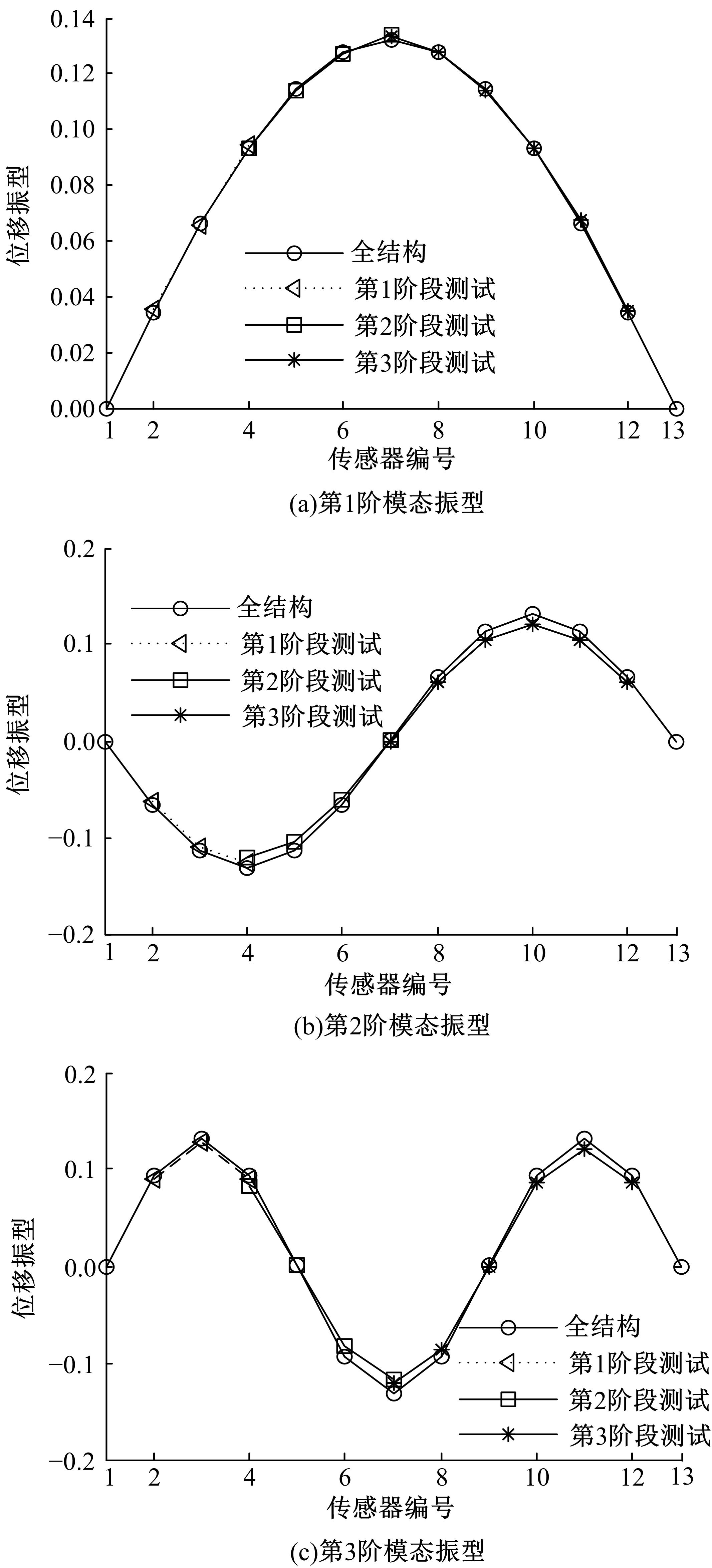
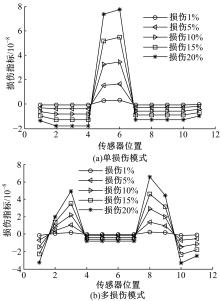
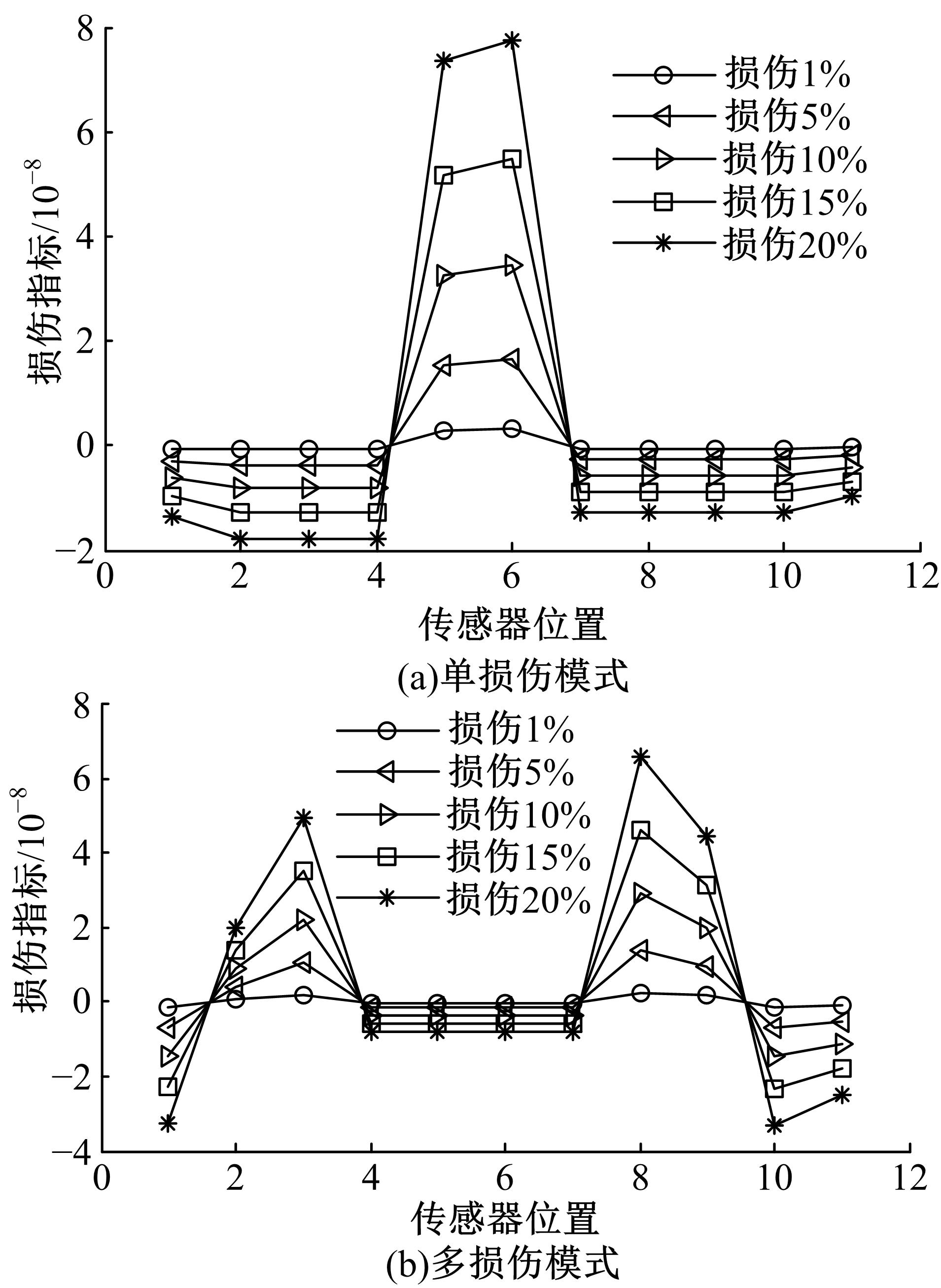
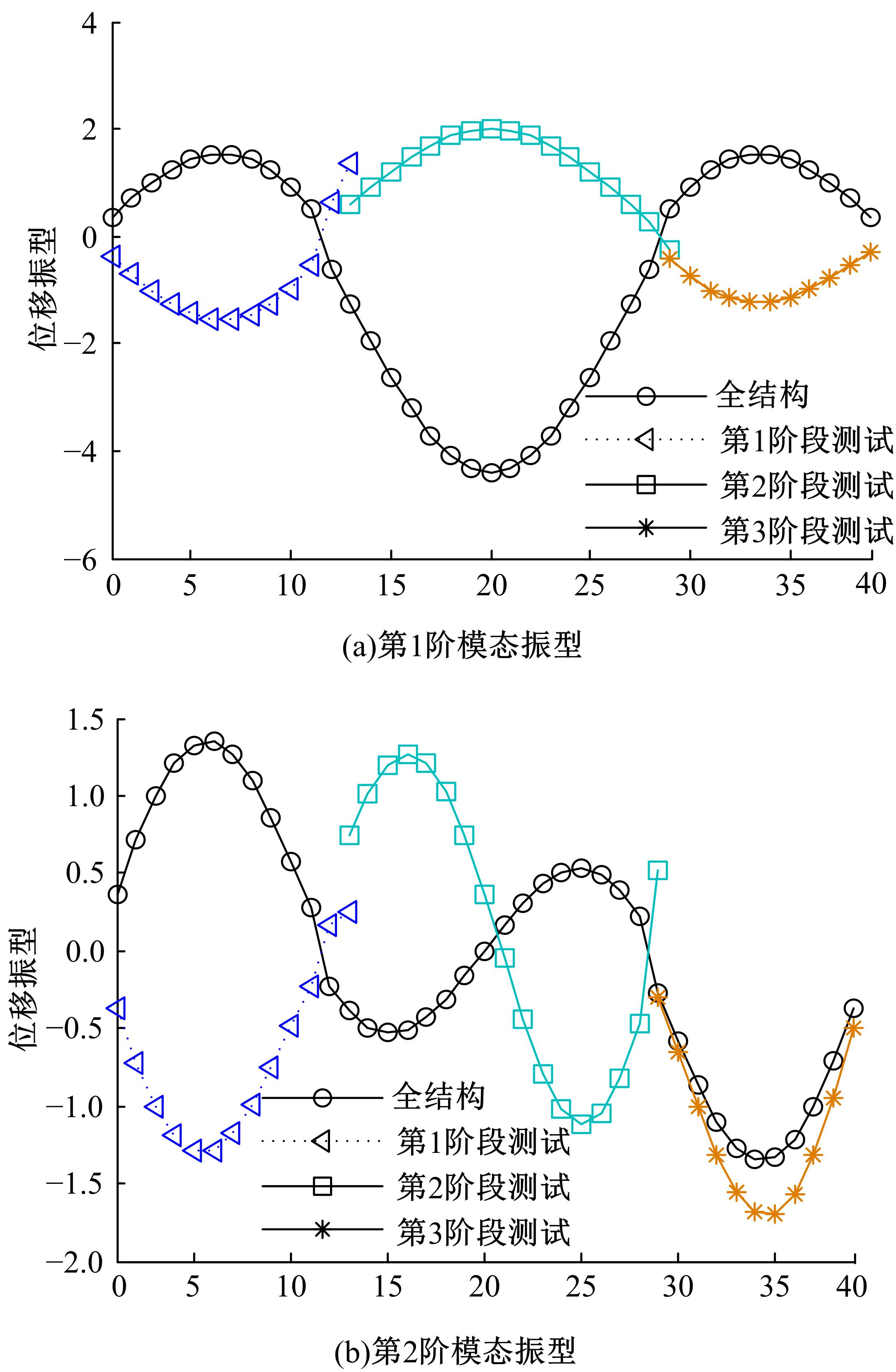
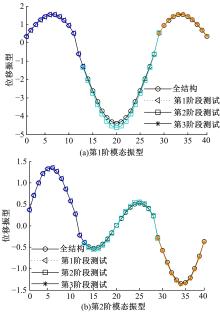
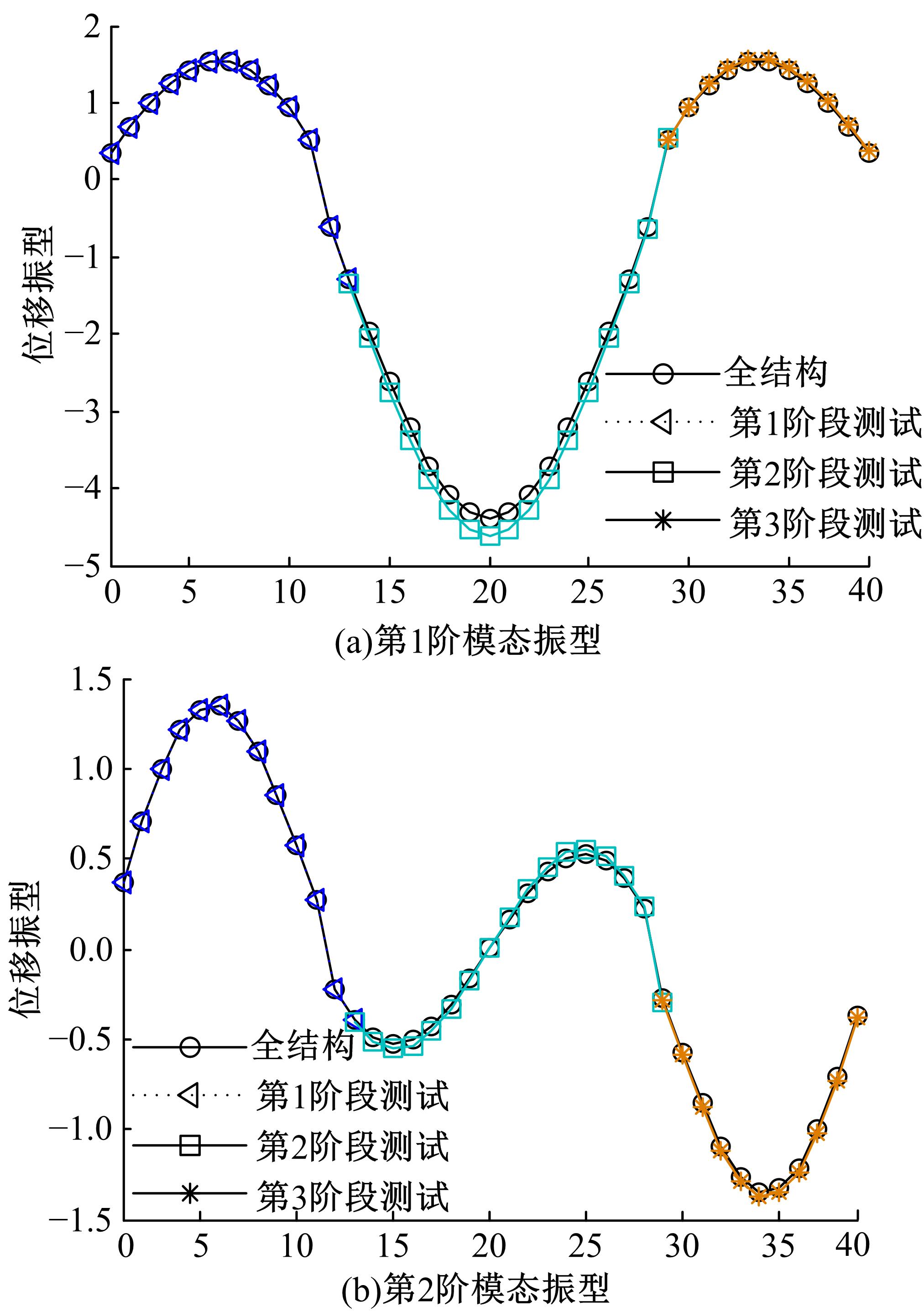
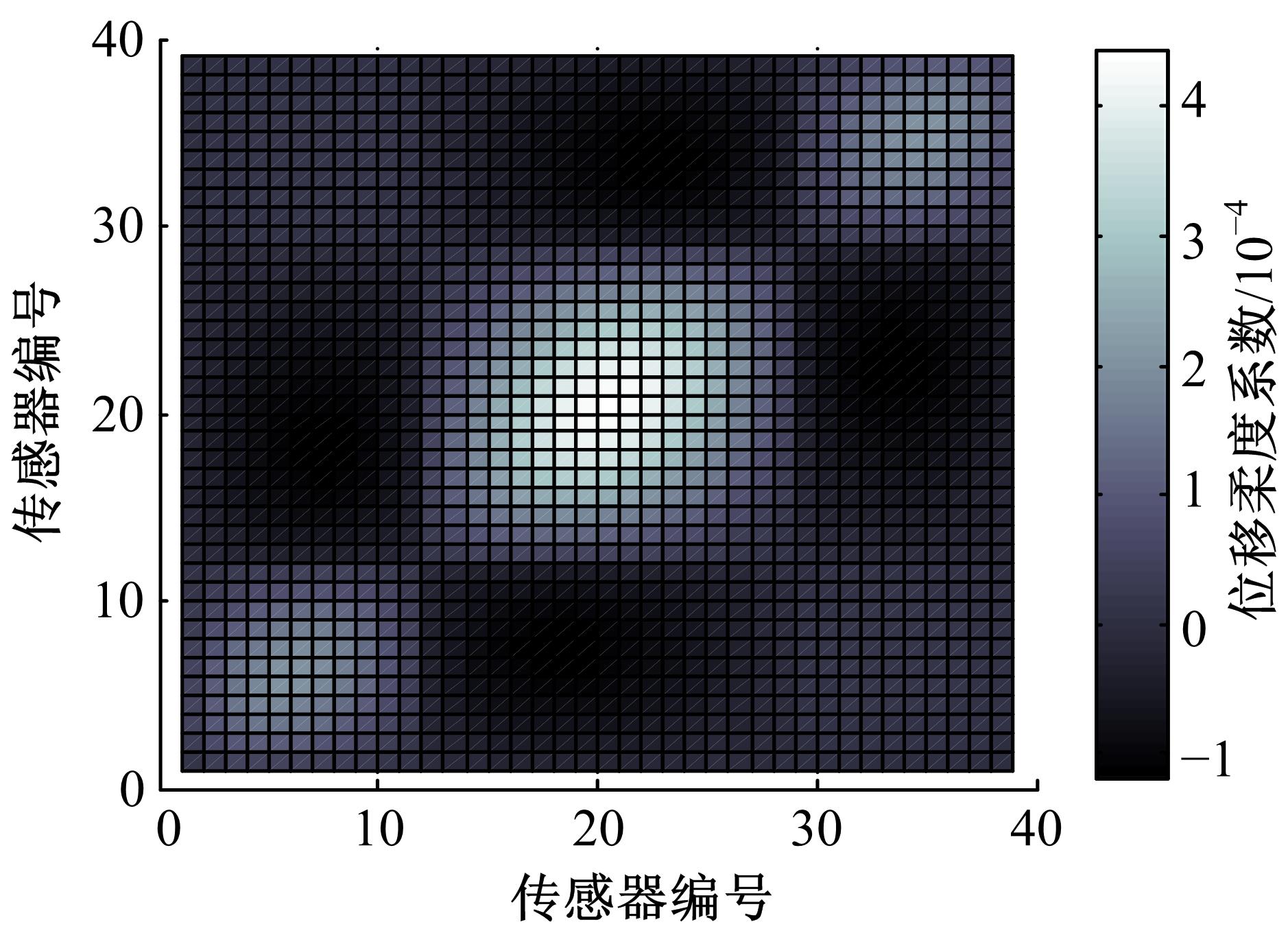
Damage assessment of bridge construction based onmulti⁃stage subregion mobile test
Wan⁃heng LI1,2( ),Lin SHEN1,Shao⁃peng WANG1,Shang⁃chuan ZHAO1(
),Lin SHEN1,Shao⁃peng WANG1,Shang⁃chuan ZHAO1( )
)
- 1. Research Institute of Highway,Ministry of Transport,Beijing 100088, China
2. Zhonglu Traffic Inspection and Certification Co. , Ltd. ,Beijing 100088,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| 1 | RaghavendracharM, AktanA E. Flexibility by multireference impact testing for bridge diagnostics[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1992, 118(8): 2186⁃2203. |
| 2 | DewolfJ T, ZhaoJ. Sensitivity study for vibrational parameters used in damage detection[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1999, 125(4): 410⁃416. |
| 3 | 周云, 蒋运忠, 易伟建, 等. 基于模态柔度理论的结构损伤诊断试验研究[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 42(5): 36⁃45. |
| ZhouYun, JiangYun⁃zhong, YiWei⁃jian, et al. Experim⁃ental research on structural damage detection base on modal flexibility theory[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2015, 42(5): 36⁃45. | |
| 4 | 林贤坤, 张令弥, 郭勤涛, 等. 基于模态挠度法的预应力连续箱梁桥状态评估[J]. 土木工程学报, 2010, 43(10): 83⁃90. |
| LinXian⁃kun, ZhangLing⁃mi, GuoQin⁃tao, et al. Application of modal deflection method for condition assessment of prestressed concrete continuous box-girder bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2010, 43(10): 83⁃90. | |
| 5 | 林贤坤, 覃柏英, 张令弥, 等. 基于不中断交通运行模态分析的模态挠度法在桥梁状态评估中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(14): 52⁃57. |
| LinXian⁃kun, QinBo⁃ying, ZhangLing⁃mi, et al. Application of modal deflection method in condition assessment of a bridge on operation modal analysis without interrupting traffic[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(14): 52⁃57. | |
| 6 | 邱飞力, 张立民, 张卫华. 基于模态柔度矩阵的结构损伤识别[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2015, 35(4): 101⁃106. |
| QiuFei⁃li, ZhangLi⁃ming, ZhangWei⁃hua. Structure damage detection based on modal flexibility[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2015, 35(4): 101⁃106. | |
| 7 | 曹晖, MichaelI F. 基于模态柔度曲率的损伤检测方法[J]. 工程力学, 2006, 23(4): 33⁃38. |
| CaoHui, MichaelI F. Nondestructive damage evaluation indicator based on modal flexibility curvature[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(4): 33⁃38. | |
| 8 | 刘寒冰, 焦峪波, 程永春, 等. 基于模态曲率理论及神经网络的简支梁桥损伤识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(4): 963⁃967. |
| LiuHan⁃bing, JiaoYu⁃bo, ChengYong⁃chun, et al. Damage identification for simply supported beam bridge based on modal curvature theory and neuralnetwor[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(4): 963⁃967. | |
| 9 | 赵云鹏, 于天来, 焦峪波, 等. 异形桥梁损伤识别方法及参数影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2016, 46(6): 1858⁃1866. |
| ZhaoYun⁃peng, YuTian⁃lai, JiaoYu⁃bo, et al. Damage identification method and factor evalution for irregular⁃shaped bridge[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1858⁃1866. | |
| 10 | 徐士代. 环境激励下工程结构模态参数识别[D]. 南京:东南大学仪器科学与工程学院, 2006. |
| XuShi⁃dai. Applied investigation of the modal identification for engineering structures undergoing ambient excitation[D]. Nanjing: College of Instrumental Science and Engineering, Southeast University, 2006. | |
| 11 | PeetersB, MaeckJ, De RoeckG. Vibration based damage detection in civil engineering: excitation sources and temperature effects[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2001, 10(3): 518⁃527. |
| 12 | Lopez⁃AenlleM, BrinckerR, PelayoF, et al. On exact and approximated formulations for scaling mode shapes in operational modal analysis by mass and stiffness change[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2012, 331(3): 622⁃637. |
| [1] | HUI Ying-xin,MAO Ming-jie,LIU Hai-feng,ZHANG Shang-rong. Influence of structural seismic response of bridges crossing active fault [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1725-1734. |
| [2] | ZHENG Yi-feng, ZHAO Qun, BAO Wei, LI Zhuang, YU Xiao-fei. Wind resistance performance of long-span continuous rigid-frame bridge in cantilever construction stage [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 466-472. |
| [3] | WEI Zhi-gang, LIU Han-bing, SHI Cheng-lin, GONG Ya-feng. Calculation of transverse distribution coefficient of simply supported beam bridge with effect of bridge deck pavement [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 105-112. |
| [4] | GONG Ya-feng, HE Yu-long, TAN Guo-jin, SHEN Yang-fan. Anti-overturning stability analysis for three-span continuous curved girder bridge with single column pier [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 133-140. |
| [5] | WEI Zhi-gang, SHI Cheng-lin, LIU Han-bing, ZHANG Yun-long. Dynamic characteristics of steel-concrete composite simply supported beam under vehicles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1744-1752. |
| [6] | ZHANG Yun-long, LIU Zhan-ying, WU Chun-li, WANG Jing. Static and dynamic responses of steel-concrete composite beams [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 789-795. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yun-peng, YU Tian-lai, JIAO Yu-bo, GONG Ya-feng, SONG Gang. Damage identification method and factor evaluation for irregular-shaped bridge [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1858-1866. |
| [8] | CAO Shan-shan, LEI Jun-qing. Fatigue life prediction of steel structure considering interval uncertainty [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 804-810. |
| [9] | TAN Guo-jin, LIU Zi-yu, WEI Hai-bin, WANG Long-lin. Calculation of natural frequency of simply supported beam bridge reinforced with eccentric prestressed tendons [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 798-803. |
| [10] | LIU Han-bing, SHI Cheng-lin, TAN Guo-jin. Finite element solution of composite beam with effect of shear slip [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 792-797. |
| [11] | XIAO Yun, LEI Jun-qing, ZHANG Kun, LI Zhong-san. Fatigue stiffness degradation of prestressed concrete beam under multilevel amplitude cycle loading [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(03): 665-670. |
| [12] | JIAO Chang-ke, LI Ai-qun, WU Xiao-ping. Double-deck long-span cable-stayed bridge seismic response to multi-support excitation [J]. , 2012, 42(04): 910-917. |
| [13] | XIN Da-bo, WANG Liang, DUAN Zhong-dong, OU Jin-ping, LI Hui, LI Zhong-hua. Static characteristics of bridge deck sections of long-span bridges under simultaneous actions of wind and rain [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 174-179. |
| [14] | TAN Guo-jin, WANG Long-lin, CHENG Yong-chun. Prediction method for cable tension state of cable-stayed bridges based on grey system theory in cold areas [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 170-173. |
| [15] | GONG Ya-feng, CHENG Yong-chun, JIAO Yu-bo. Damage identification of urban overpasses based on static strain data and neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 164-169. |
|