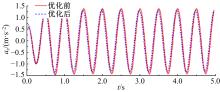
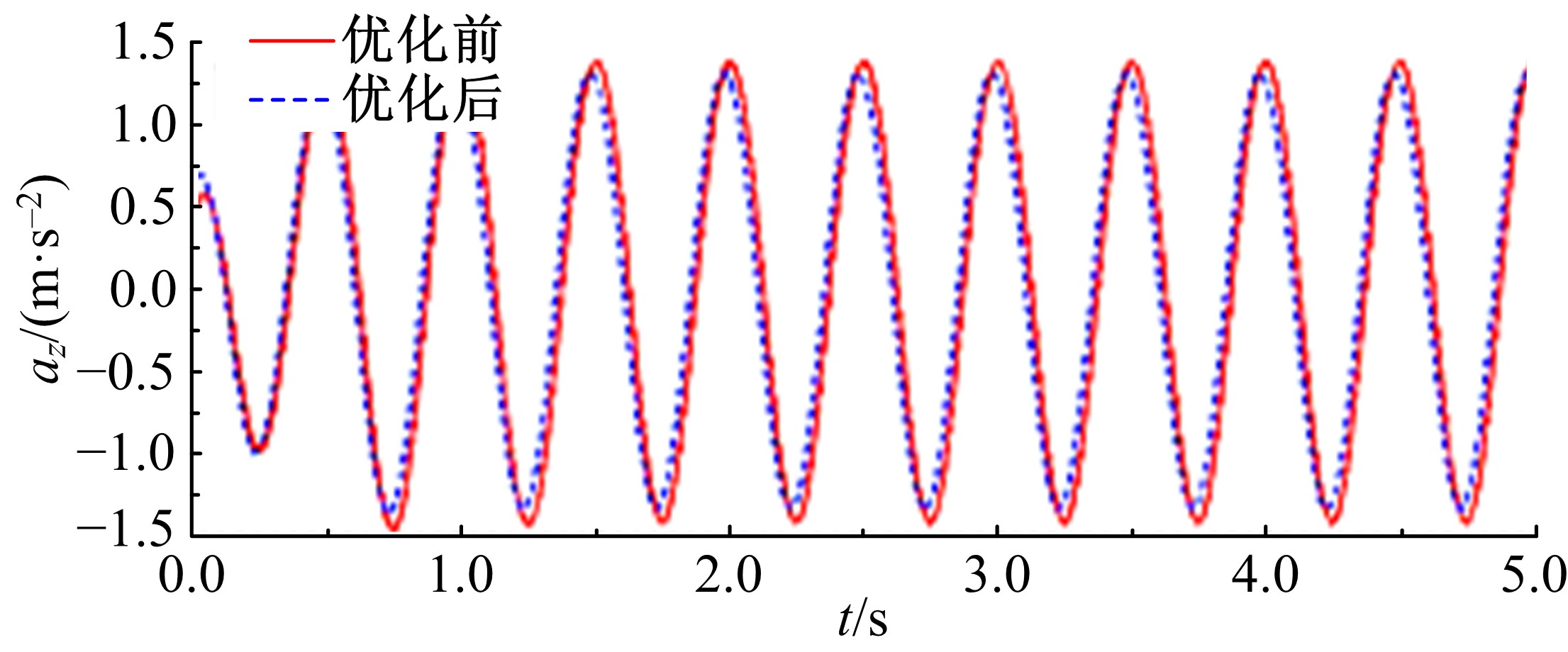
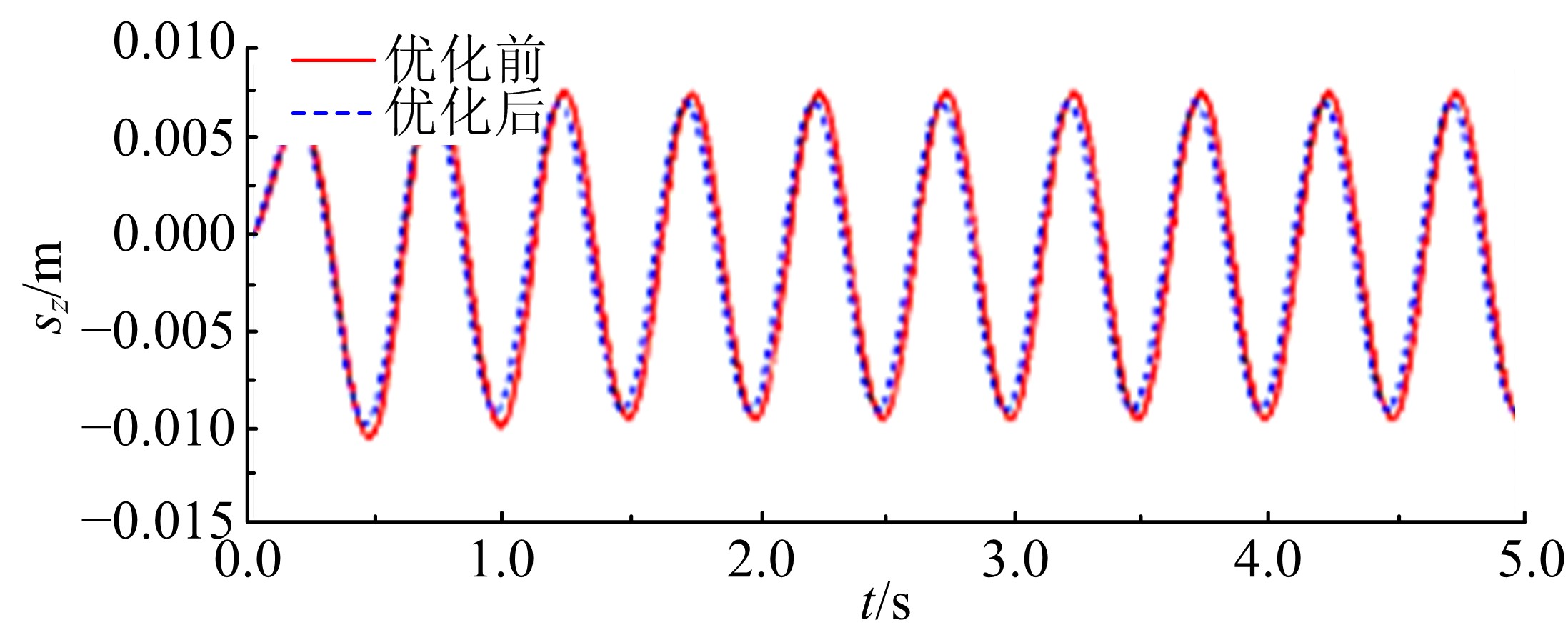
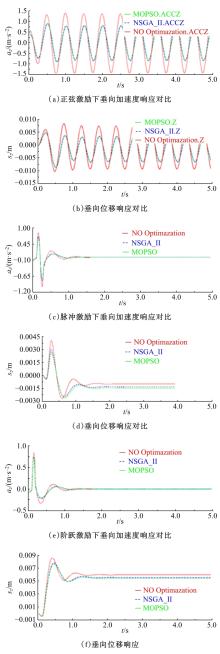
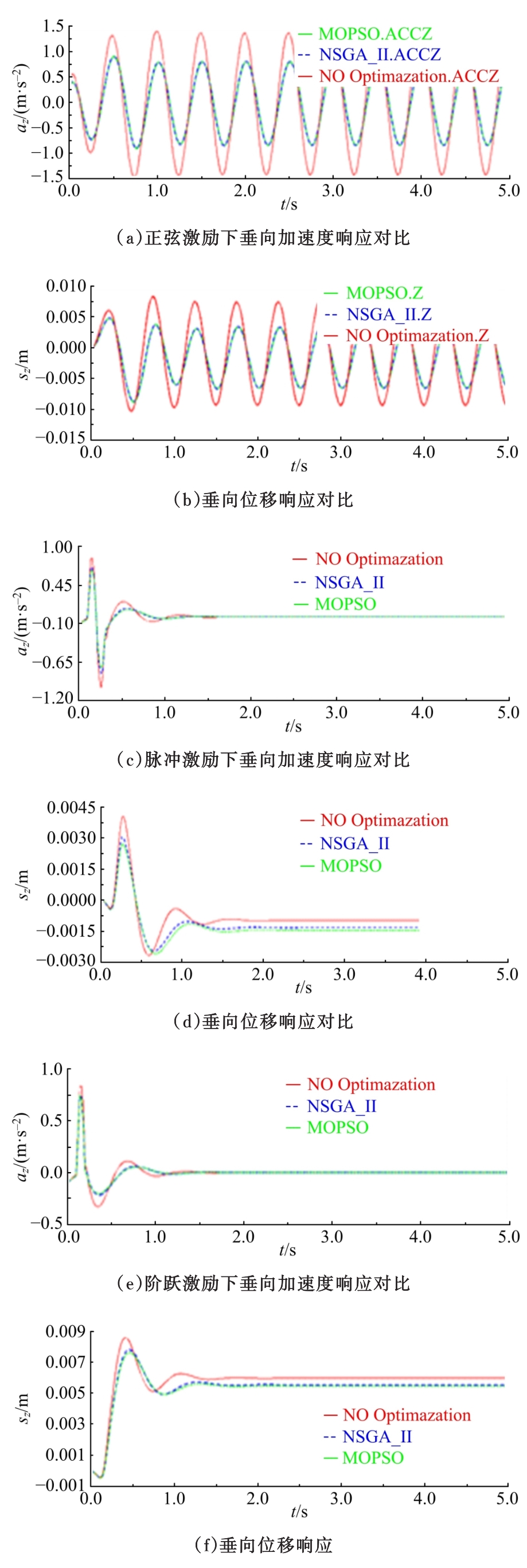
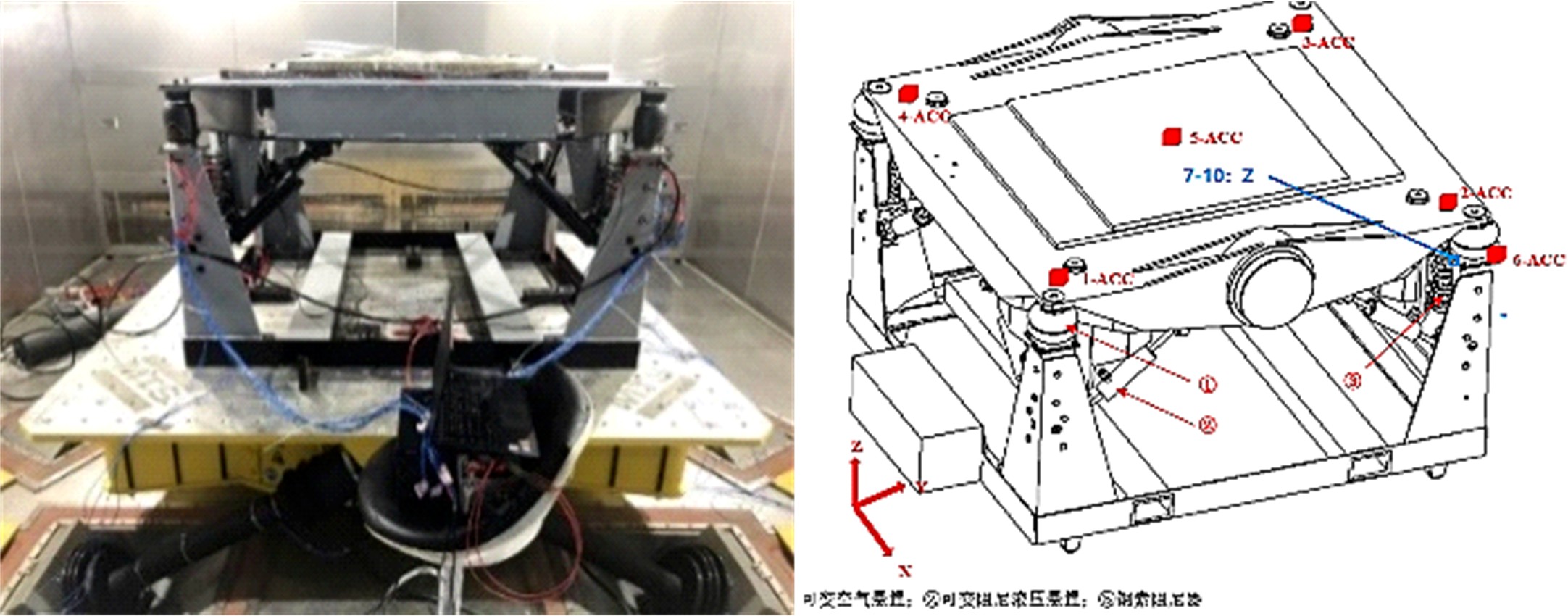
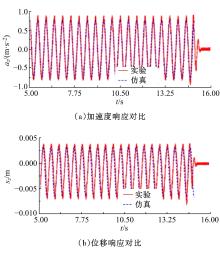
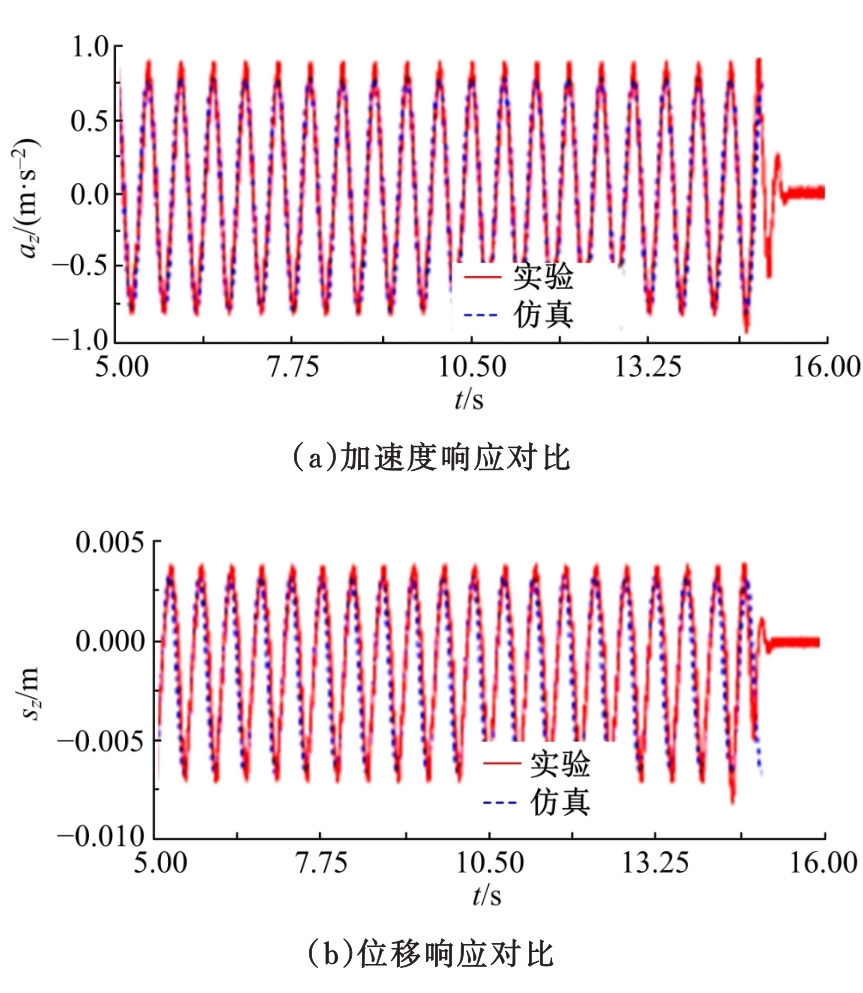
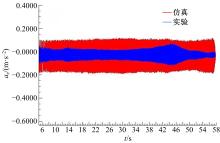
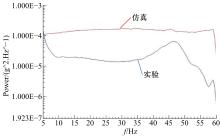
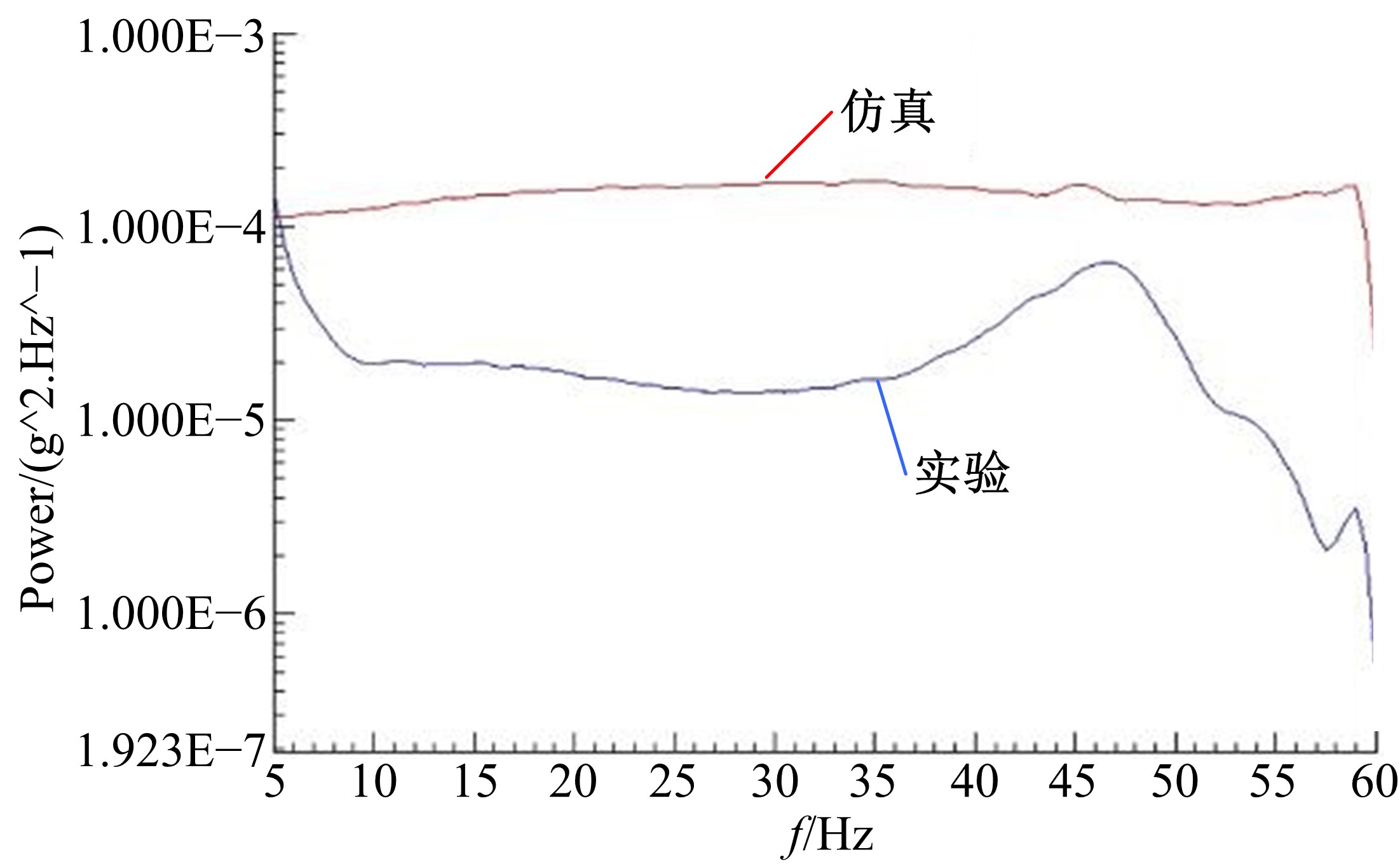
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1608-1616.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190469
Damping optimization of heavy⁃loaded anti⁃vibration platform based on genetic algorithm and particle swarm algorithm
Fang-wu MA( ),Li HAN,Liang WU(
),Li HAN,Liang WU( ),Jin-hang LI,Long-fan YANG
),Jin-hang LI,Long-fan YANG
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U463.99
| 1 | 李耀. 六自由度隔振平台的设计与分析[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学机电学院, 2015. |
| Li Yao. Design and analysis of the six-degree-of-freedom vibration-isolation platform[D]. Nanjing: College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015. | |
| 2 | Youn I, Wu L, Youn E, et al. Tomizuka: attitude motion control of the active suspension system with tracking controller[J] Internal Journal of Automotive Technology, 2015, 16(4): 593-601. |
| 3 | 马芳武, 倪利伟, 吴量, 等. 轮腿式全地形移动机器人位姿闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. |
| Ma Fang-wu, Ni Li-wei, Wu Liang, et al. Position and attitude closed loop control of wheel⁃leggedall terrain mobile robot[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1745-1755. | |
| 4 | Wu L, Khan M A, Youn E, et al. Attitude motion control of vehicle including the active passenger seat system[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Design, 2018, 78(1-4): 131-160. |
| 5 | 张抗抗, 徐梁飞, 华剑锋, 等. 基于多目标优化的纯电动车动力系统参数匹配[J]. 汽车工程, 2015, 37(7): 757-765. |
| Zhang Kang-kang, Xu Liang-fei, Hua Jian-feng, et al. A parameter matching method for the powertrain of battery electric vehicle based on multi-objective optimization[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2015, 37(7): 757-765. | |
| 6 | 王庆年, 段本明, 王鹏宇, 等. 插电式混合动力汽车动力传动系参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(1): 1-7. |
| Wang Qing-nian, Duan Ben-ming, Wang Peng-yu, et al. Optimization of powertrain transmission parameters of plug in hybrid electric vehicle[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(1): 1-7. | |
| 7 | 王咏. 高精密设备多自由度平台系统微振动混合控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学深圳研究生院, 2007. |
| Wang Yong. Multi-degree-of-freedom microvibration hybrid control system for high technology facilities[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, Shenzhen Graduate School, 2007. | |
| 8 | 李林, 宣明, 贾宏光, 等. 光电稳定平台隔振系统的设计与优化[J]. 计算机仿真, 2017, 34(3): 77-81. |
| Li Lin, Xuan Ming, Jia Hong-guang, et al. Design and optimization of vibration isolation system for photoelectric stabilized platform[J]. Computer Simulation, 2017, 34(3): 77-81. | |
| 9 | 谢振盛. 汽車主動式懸吊系統之最佳化控制器設計研究[D]. 台南: 昆山科技大学工程学院, 2007. |
| Xie Zhen-sheng. Study on optimal controllers design for automotive active suspension systems[D]. Tainan: Science and Technology, Kun Shan University of Technology, 2007. | |
| 10 | Wu L, Li J H, Ma F W, et al. Optimal anti-vibration design of vehicle-mounted vibration isolation platform[C]∥ SAE Technical Paper, 2018-01-1400. |
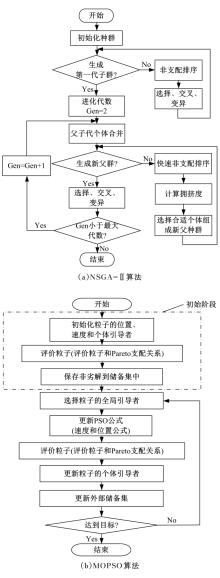
| 11 | Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, et al. A fast elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. |
| 12 | 李杰, 车华军, 哈兰涛. 遗传算法及在汽车悬架参数优化设计中的应用[J]. 汽车技术, 2006(6): 18-21. |
| Li Jie, Che Hua-jun, Lan-tao Ha. The application of genetic algorithm in the optimum design automotive suspension parameter[J]. Automotive Technology, 2006(6): 18-21. | |
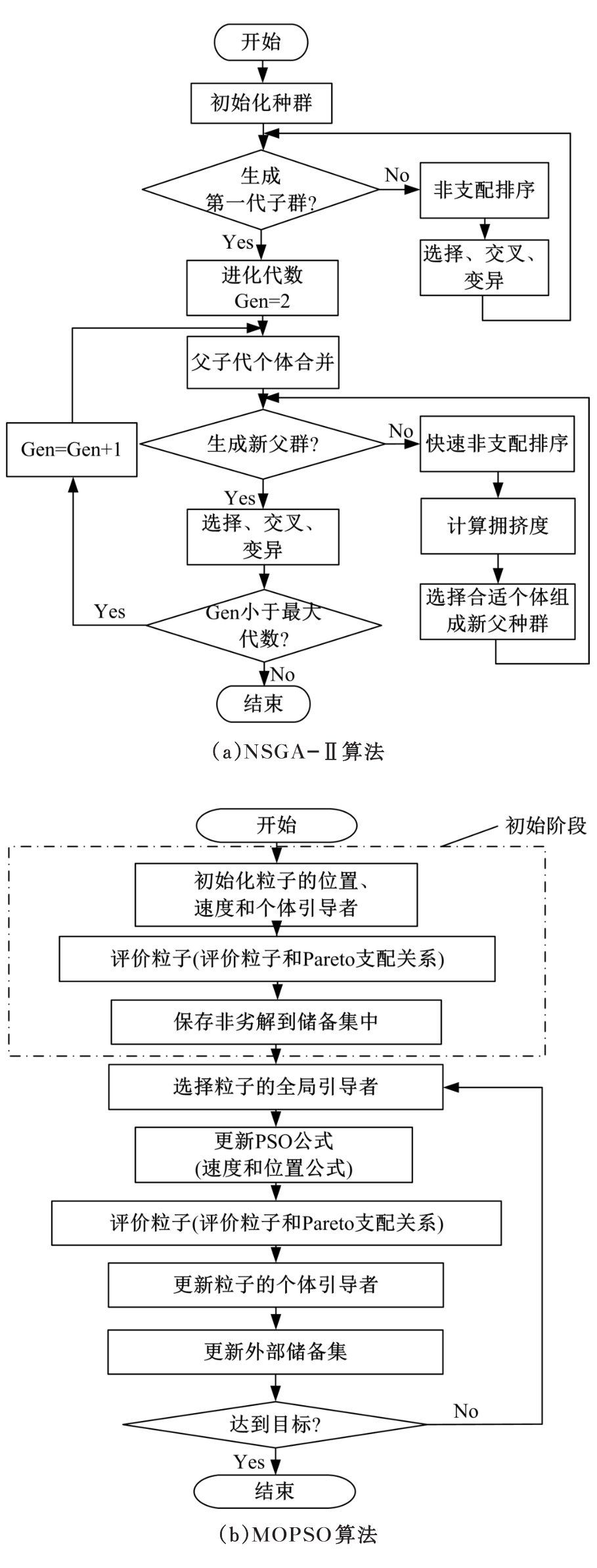
| 13 | 张勇, 巩敦卫. 先进多目标粒子群优化理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. |
| 14 | 周红妮, 冯樱, 赵慧勇, 等. 基于ISIGHT 集成技术的某重卡双轴转向机构多目标优化[J]. 汽车研究与开发, 2015, 6(4): 26-30. |
| Zhou Hong-ni, Feng Ying, Zhao Hui-yong, et al. Multi-objective optimization on dual-axle steering mechanism of a heavy vehicle based on integration technology of ISIGHT[J]. Automobile Research and Development, 2015, 6(4): 26-30. |
| [1] | Xue-shen CHEN,Tao CHEN,Tao WU,Xu MA,Ling-chao ZENG,Lin-tao CHEN. Design and experiment on harvester for winter planting potato of straw coverage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 749-757. |
| [2] | Yin-ping LI,Tian-xu JIN,Li LIU. Design and dynamic characteristic simulation of pantograph⁃catenary continuous energy system for pure electric LHD [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 454-463. |
| [3] | Fang-wu MA,Hong-yu LIANG,Ying ZHAO,Meng YANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi⁃objective crashworthiness optimization design of concave triangles cell structure with negative Poisson′s ratio [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [4] | Zhong-yi CAI,Fan-xiang MENG,Qing-min CHEN,Xuan ZHAO. Preform optimization for near-net-shape forming process of complex knuckle forging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 84-90. |
| [5] | Fu-chun JIA,Xian-jie MENG,Yu-long LEI. Optimal design of two degrees of freedom dynamic vibration absorber based on multi-objective genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1969-1976. |
| [6] | QIU Xiao-ming, WANG Yin-xue, YAO Han-wei, FANG Xue-qing, XING Fei. Multi-objective optimization of resistance spot welding parameters for DP1180/DP590 using grey relational analysis based Taguchi [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1147-1152. |
| [7] | WANG Deng-feng, ZHANG Shuai, WANG Yong, CHEN Hui. Optimization design of assembled wheel based on performance of fatigue and 13° impact [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 44-56. |
| [8] | YU Fan-hua, LIU Ren-yun, ZHANG Yi-min, ZHANG Xiao-li, SUN Qiu-cheng. Swarm intelligence algorithm of dynamic reliability-based robust optimization design of mechanic components [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1903-1908. |
| [9] | ZHOU Fang, SONG Chuan-xue, LIANG Tian-wei, XIAO Feng. Parameter matching of on-board hybrid energy storage system using NSGA-II algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1336-1343. |
| [10] | LIU Ying, ZHANG Kai, YU Xiang-jun. Multi-objective optimization of hydrostatic bearing of hollow shaft based on surrogate model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1130-1137. |
| [11] | HU Kan, YU Ye, YING Liang, HU Ping, HOU Wen-bin. Optimization design of hot-stamping beam structure considering rollover crash safety of school bus [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 884-890. |
| [12] | YU Fan-hua, LIU Ren-yun, ZHANG Yi-min, SUN Qiu-cheng, ZHANG Xiao-li. Intelligent algorithm for optimized dynamic reliability design of mechanic structure [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1269-1275. |
| [13] | ZHANG Dong-hao, XIANG Chang-le, HAN Li-jin, ZHENG Hai-liang. Multi-objective optimization hierarchic control method for power-split hybrid electric vehicles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 373-382. |
| [14] | ZHOU Jie, LUO Yan, WANG Xun, WANG Hui, LI Yang, TAO Ya-ping. Multi-objective optimization of stamping forming process of head based on response surface model [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 205-212. |
| [15] | ZHU Bing, JIA Xiao-feng, WANG Yu, WU Jian, ZHAO Jian, DENG Wei-wen. Rapid prototype test for integrated vehicle dynamic control using two dSPACE simulators [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 8-14. |
|
||