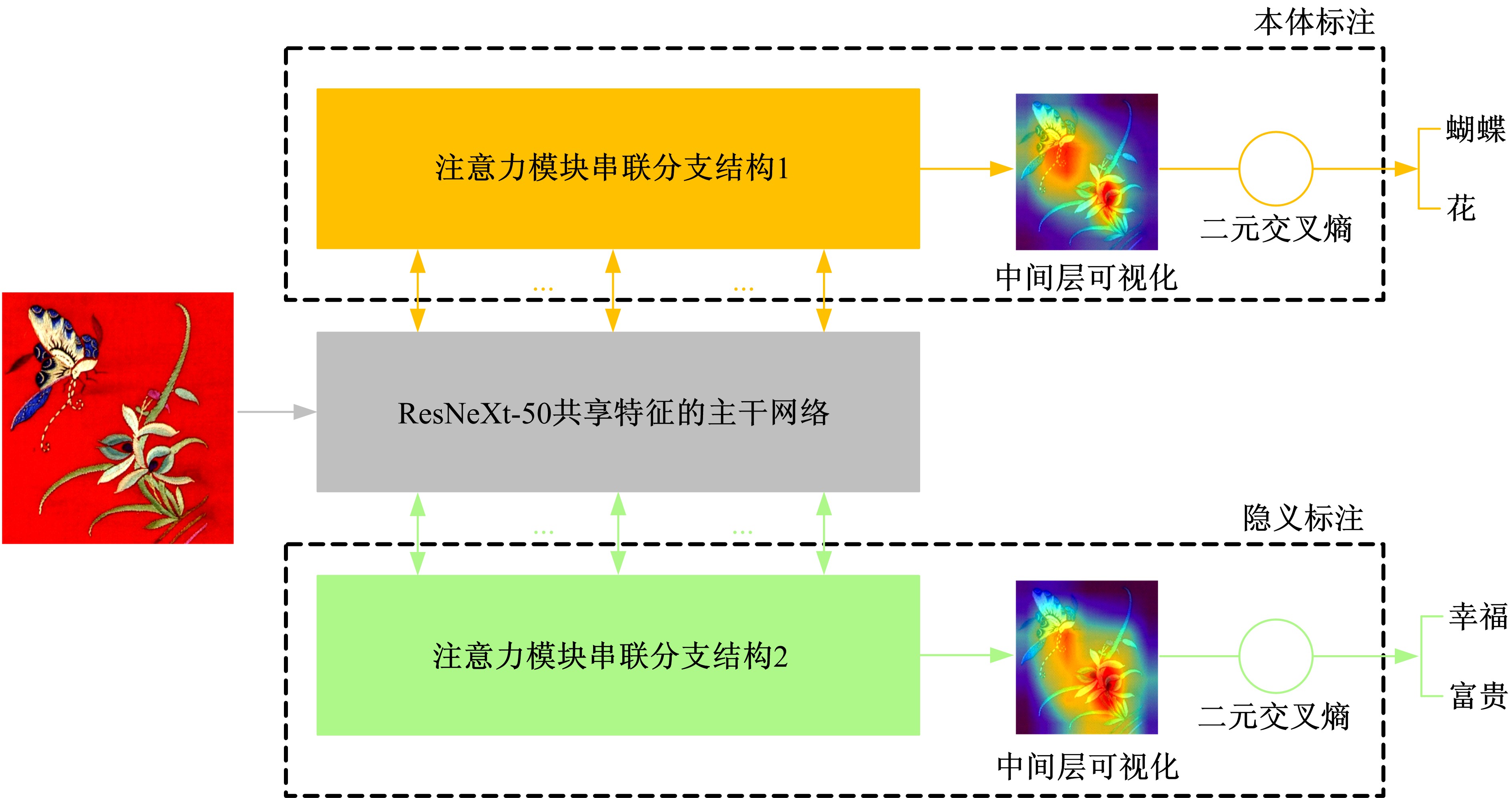
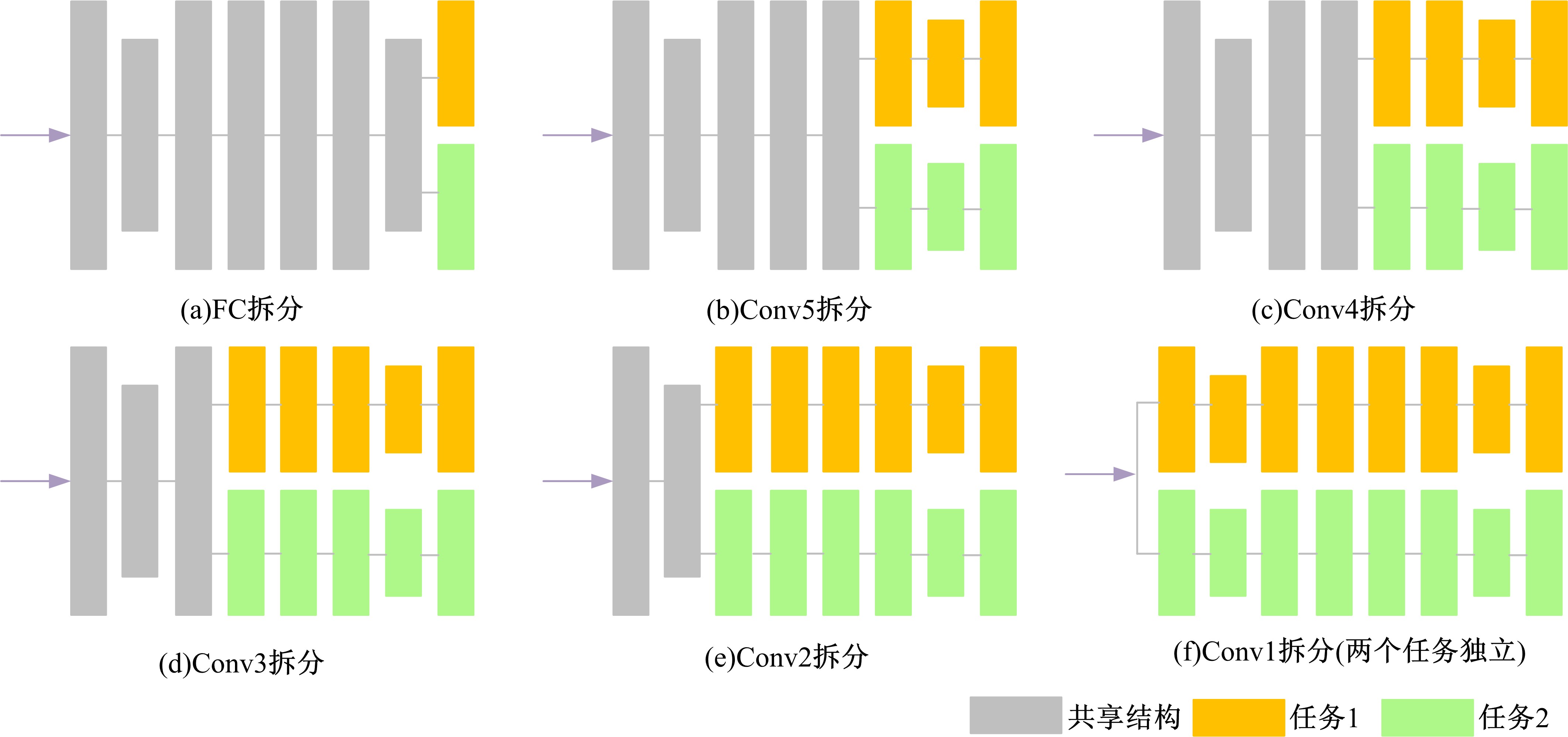
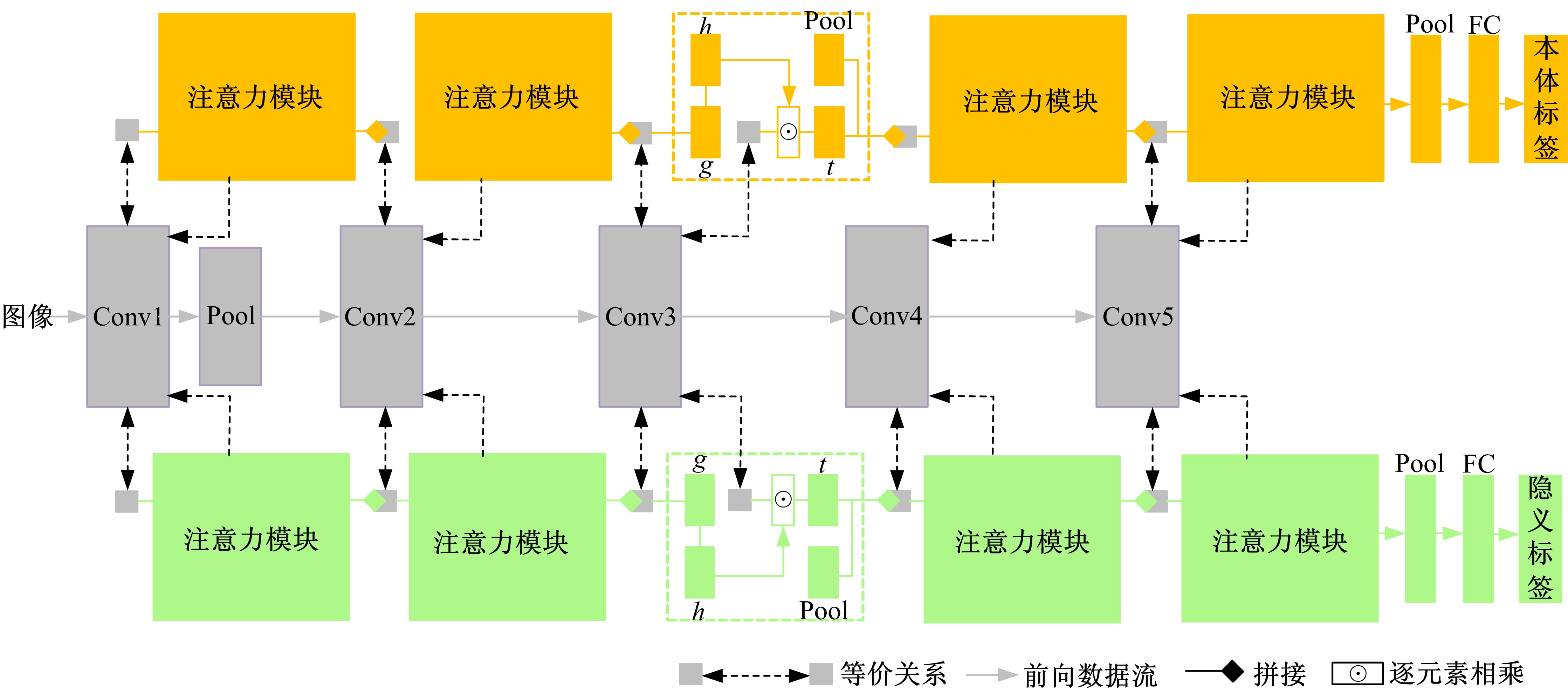
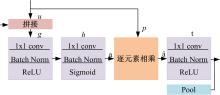
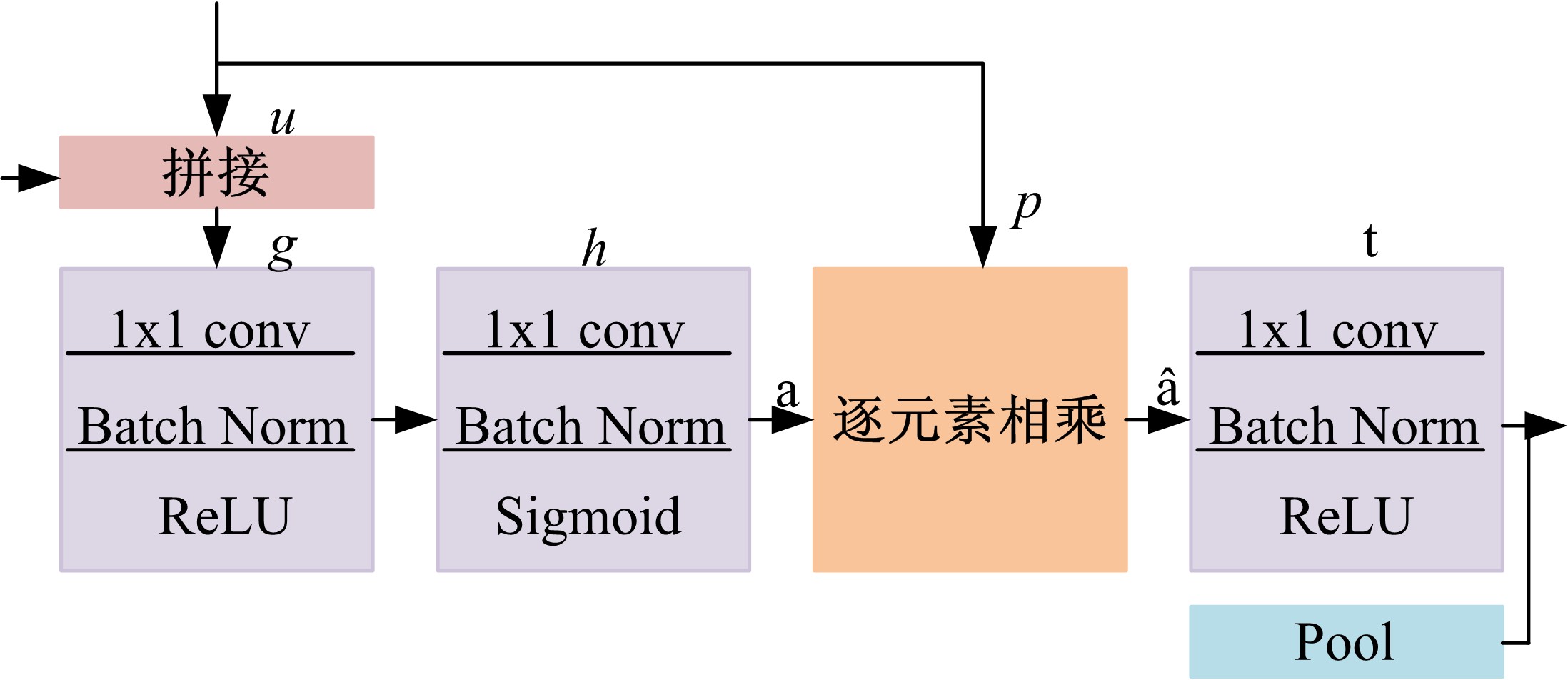
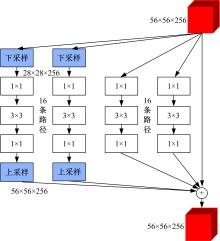
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 293-302.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190970
Double-layer annotation of traditional costume images based on multi-task learning
Hai-ying ZHAO1( ),Wei ZHOU2,Xiao-gang HOU1,Xiao-li ZHANG3
),Wei ZHOU2,Xiao-gang HOU1,Xiao-li ZHANG3
- 1.School of Computer Science,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
2.School of Digital Media and Design Art,Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,Beijing 100876,China
3.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- TP181
| 1 | 赵鑫全. 互联网时代文化消费如何升级[J]. 人民论坛, 2019(23): 132-133. |
| Zhao Xin-quan. How to upgrade cultural consumption in internet era[J]. People's Tribune, 2019(23): 132-133. | |
| 2 | 张会, 陈晨. "互联网+"背景下的汉语国际教育与文化传播[J]. 语言文字应用, 2019(2): 30-38. |
| Zhang Hui, Chen Chen. The international Chinese language education and cultural communication under "internet plus"[J]. Applied Linguistics, 2019(2): 30-38. | |
| 3 | Mehta S, Rastegari M, Shapiro L, et al. Espnetv2: a light-weight, power efficient, and general purpose convolutional neural network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 9190-9200. |
| 4 | Wang H, Kembhavi A, Farhadi A, et al. ELASTIC: improving CNNs with dynamic scaling policies[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 2258-2267. |
| 5 | Mehta S, Hajishirzi H, Rastegari M. DiCENet: dimension-wise convolutions for efficient networks[J]. arXiv, 2019:1906.03516. |
| 6 | Zhang J, Ding S, Zhang N. An overview on probability undirected graphs and their applications in image processing[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 321: 156-168. |
| 7 | 陈绵书, 于录录, 苏越, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的多标签图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(3):1077-1084. |
| Chen Mian-shu, Yu Lu-lu, Su Yue, et al. Multi-label images classification based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2020,50(3): 1077-1084. | |
| 8 | Ding S, Du P, Zhao X, et al. BEMD image fusion based on PCNN and compressed sensing[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(20): 10045-10054. |
| 9 | 王柯俨, 胡妍, 王怀, 等. 结合天空分割和超像素级暗通道的图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. |
| Wang Ke-yan,Hu Yan,Wang Huai, et al. Image dehazing algorithm by sky segmentation and superpixel⁃level dark channel[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1377-1384. | |
| 10 | 谌华, 郭伟, 闫敬文, 等. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(5):1778-1787. |
| Chen Hua,Guo Wei,Yan Jing-wen, et al. A new deep learning method for roads recognition from SAR images[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2020,50(5):1778-1787. | |
| 11 | Gong Y, Jia Y, Leung T, et al. Deep convolutional ranking for multilabel image annotation[J]. arXiv, 2013:1312.4894. |
| 12 | Wang J, Yang Y, Mao J, et al. CNN-RNN: a unified framework for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2285-2294. |
| 13 | Li Y, Song Y, Luo J. Improving pairwise ranking for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 3617-3625. |
| 14 | Cevikalp H, Benligiray B, Gerek O N, et al. Semi-Supervised robust deep neural networks for multi-label classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9-17. |
| 15 | Zhang J, Wu Q, Shen C, et al. Multilabel image classification with regional latent semantic dependencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(10): 2801-2813. |
| 16 | Wang Z, Chen T, Li G, et al. Multi-label image recognition by recurrently discovering attentional regions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 464-472. |
| 17 | Zhu F, Li H, Ouyang W, et al. Learning spatial regularization with image-level supervisions for multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 5513-5522. |
| 18 | Luo Y, Jiang M, Zhao Q. Visual attention in multi-label image classification[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 1-8. |
| 19 | Guo H, Zheng K, Fan X, et al. Visual attention consistency under image transforms for multi-label image classification[C]∥ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 729-739. |
| 20 | 张钰, 刘建伟, 左信. 多任务学习[J]. 计算机学报, 2020,43(7):1340-1378. |
| Zhang Yu, Liu Jian-wei, Zuo Xin. Survey of multi-task learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020,43(7):1340-1378. | |
| 21 | Kao Y, He R, Huang K. Deep aesthetic quality assessment with semantic information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(3): 1482-1495. |
| 22 | Misra I, Shrivastava A, Gupta A, et al. Cross-stitch networks for multi-task learning[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 3994-4003. |
| 23 | Vandenhende S, de Brabandere B, van Gool L. Branched multi-task networks: deciding what layers to share[J]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: arXiv: 1904.02920. |
| 24 | Liu S, Johns E, Davison A J. End-to-end multi-task learning with attention[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA,2019: 1871-1880. |
| 25 | 王松, 党建武, 王阳萍, 等. 基于3D运动历史图像和多任务学习的动作识别[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020,50(4):1495-1502. |
| Wang Song,Dang Jian-wu,Wang Yang-ping,et al. Action recognition based on 3D motion history image and multi-task learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(4): 1495-1502. | |
| 26 | 赵海英, 陈洪, 贾耕云, 等. 基于字典学习的民族文化图案语义标注[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2019, 49(2): 172-187. |
| Zhao Hai-ying, Chen Hong, Jia Geng-yun, et al. Semantic annotation of national cultural patterns based on dictionary learning[J]. Science in China (Information Sciences), 2019, 49(2): 172-187. | |
| 27 | Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 1492-1500. |
| 28 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. Computer Science, 2014: 1-14. |
| 29 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 30 | Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]∥Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 2818-2826. |
| 31 | Wu X Z, Zhou Z H. A unified view of multi-label performance measures[C]∥Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 3780-3788. |
| 32 | Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. Grad-cam: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618-626. |
| [1] | Dan-tong OUYANG,Cong MA,Jing-pei LEI,Sha-sha FENG. Knowledge graph embedding with adaptive sampling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 685-691. |
| [2] | Yi-bin LI,Jia-min GUO,Qin ZHANG. Methods and technologies of human gait recognition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| [3] | Qian XU,Ying LI,Gang WANG. Pedestrian-vehicle detection based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1661-1667. |
| [4] | Wan-fu GAO,Ping ZHANG,Liang HU. Nonlinear feature selection method based on dynamic change of selected features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1293-1300. |
| [5] | Dan⁃tong OUYANG,Jun XIAO,Yu⁃xin YE. Distant supervision for relation extraction with weakconstraints of entity pairs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
| [6] | GU Hai-jun, TIAN Ya-qian, CUI Ying. Intelligent interactive agent for home service [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1578-1585. |
| [7] | DONG Sa, LIU Da-you, OUYANG Ruo-chuan, ZHU Yun-gang, LI Li-na. Logistic regression classification in networked data with heterophily based on second-order Markov assumption [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1571-1577. |
| [8] | WANG Xu, OUYANG Ji-hong, CHEN Gui-fen. Measurement of graph similarity based on vertical dimension sequence dynamic time warping method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1199-1205. |
| [9] | ZHANG Hao, ZHAN Meng-ping, GUO Liu-xiang, LI Zhi, LIU Yuan-ning, ZHANG Chun-he, CHANG Hao-wu, WANG Zhi-qiang. Human exogenous plant miRNA cross-kingdom regulatory modeling based on high-throughout data [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1206-1213. |
| [10] | LI Xiong-fei, FENG Ting-ting, LUO Shi, ZHANG Xiao-li. Automatic music composition algorithm based on recurrent neural network [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 866-873. |
| [11] | LIU Jie, ZHANG Ping, GAO Wan-fu. Feature selection method based on conditional relevance [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 874-881. |
| [12] | HUANG Lan, JI Lin-ying, YAO Gang, ZHAI Rui-feng, BAI Tian. Construction of disease-symptom semantic net for misdiagnosis prompt [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 859-865. |
| [13] | WANG Xu, OUYANG Ji-hong, CHEN Gui-fen. Heuristic algorithm of all common subsequences of multiple sequences for measuring multiple graphs similarity [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 526-532. |
| [14] | LIU Xue-juan, YUAN Jia-bin, XU Juan, DUAN Bo-jia. Quantum k-means algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 539-544. |
| [15] | YANG Xin, XIA Si-jun, LIU Dong-xue, FEI Shu-min, HU Yin-ji. Target tracking based on improved accelerated gradient under tracking-learning-detection framework [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 533-538. |
|
||