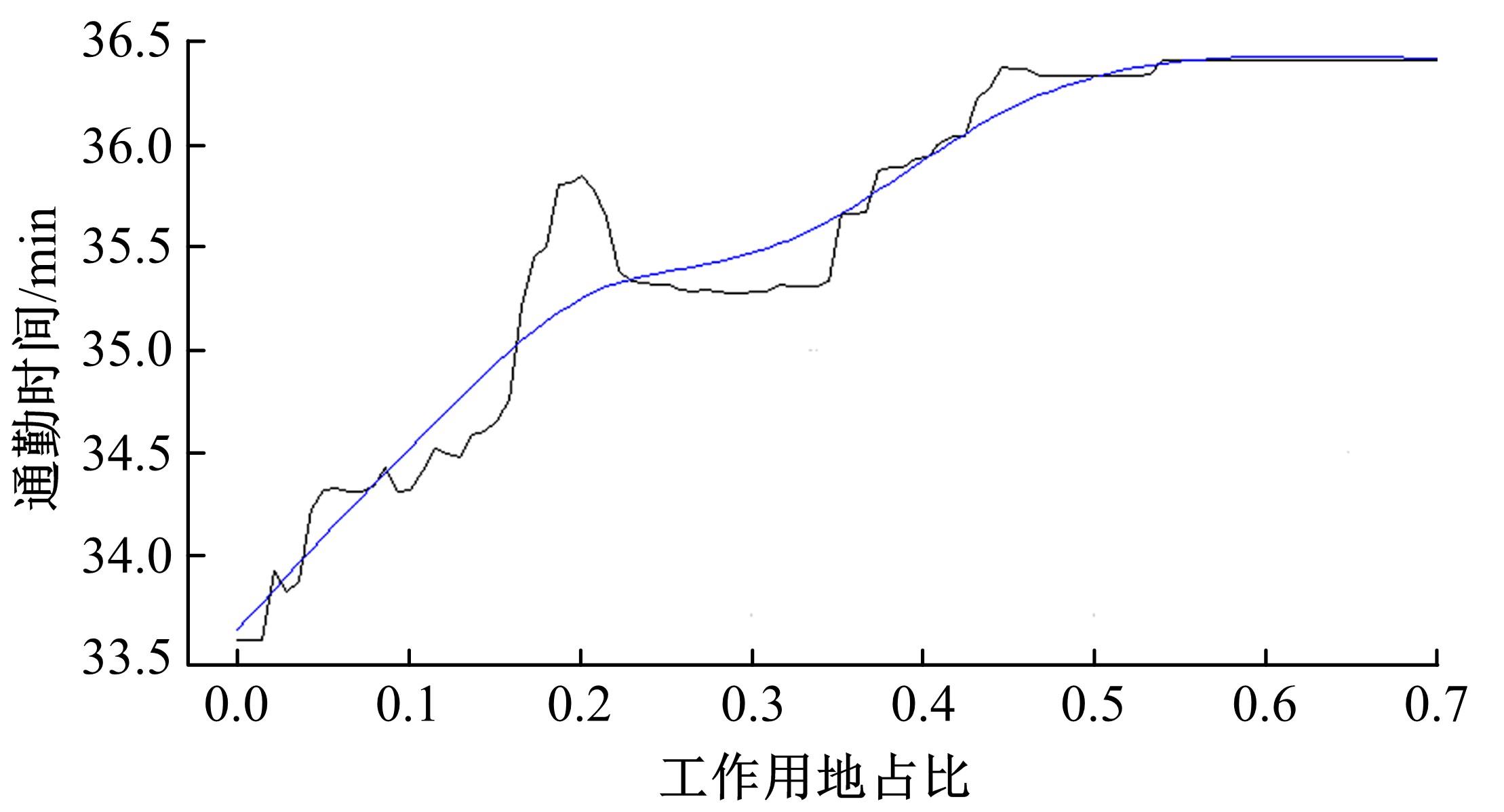
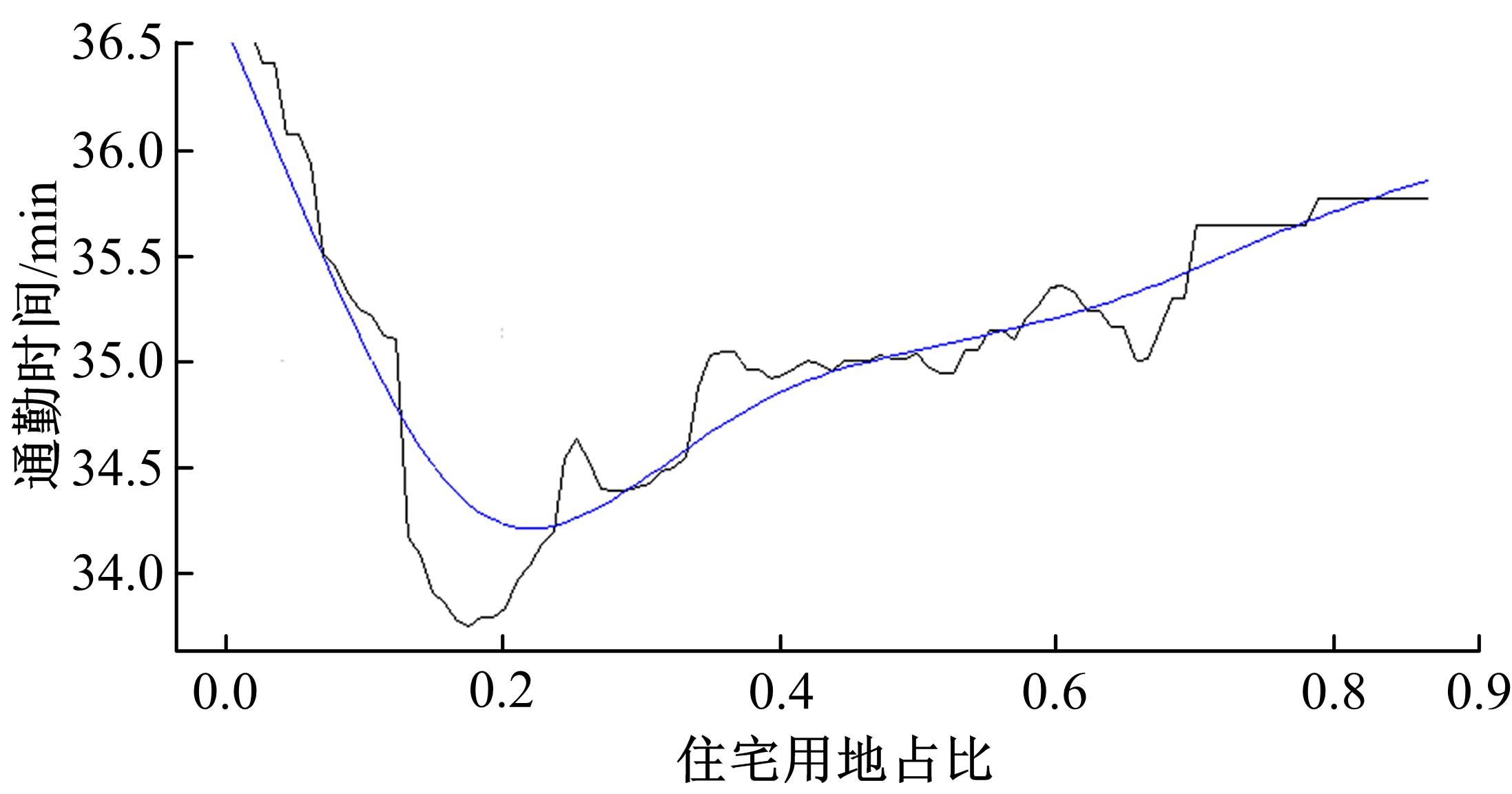
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2568-2573.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210530
Residents' commuting time model under the nonlinear impact of urban built environment
Jing-xian WU1,2( ),Hua-peng SHEN1,Yin HAN1(
),Hua-peng SHEN1,Yin HAN1( ),Min YANG3
),Min YANG3
- 1.Business School,University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,Shanghai 200093,China
2.Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration,Institute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration,Harbin 150080,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China
CLC Number:
- U491.1
| 1 | 孙晓雪. 通勤时间对城市居民幸福感的影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学经济管理学院, 2018. |
| Sun Xiao-xue. Research on the impact of commute time on urban resident happiness[D]. Beijing: School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018. | |
| 2 | 尹超英, 邵春福, 王聘玺, 等. 基于多层模型的城市建成环境对通勤行为的影响[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(2): 122-127. |
| Yin Chao-ying, Shao Chun-fu, Wang Pin-xi, et al. Impacts of built environment on commuting behavior based on a multilevel modeling approach[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(2): 122-127. | |
| 3 | Zhang H, Xu S, Liu X, et al. Near "real-time" estimation of excess commuting from open-source data: evidence from China's megacities[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2020, 91(4): 102929. |
| 4 | Sun B, Yin C. Impacts of a multi-scale built environment and its corresponding moderating effects on commute duration in China[J]. Urban Studies, 2020, 57(10): 2115-2130. |
| 5 | Ding C, Cao X, Wang Y. Synergistic effects of the built environment and commuting programs on commute mode choice[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2018, 118: 104-118. |
| 6 | 尹超英, 邵春福, 黄兆国, 等. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| Yin Chao-ying, Shao Chun-fu, Huang Zhao-guo, et al. Investigating influences of multi-scale built environment on car ownership behavior based on gradient boosting decision trees[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. | |
| 7 | Koushik A N, Manoj M, Nezamuddin N. Machine learning applications in activity-travel behaviour research: a review[J]. Transport Reviews, 2020, 40: 288-311. |
| 8 | Zhao X, Yan X, Yu A, et al. Prediction and behavioral analysis of travel mode choice: a comparison of machine learning and logit models[J]. Travel Behaviour and Society, 2020, 20: 22-35. |
| 9 | 熊丽芳, 甄峰, 钱前, 等. 基于CHAID决策树方法的城市居民通勤时间影响因素分析——以南京为例[J]. 人文地理, 2013(6): 68-73. |
| Xiong Li-fang, Zhen Feng, Qian Qian, et al. The influencing factors analysis of city residents' commute time based on CHAIN model of decision tree: a case study of Nanjing[J]. Human Geography, 2013(6): 68-73. | |
| 10 | Cheng L, Vos J D, Zhao P, et al. Examining non-linear built environment effects on elderly's walking: a random forest approach[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2020, 88:102552. |
| 11 | Tao T, Wang J, Cao X. Exploring the non-linear associations between spatial attributes and walking distance to transit[J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2020, 82: 102560. |
| [1] | Song FANG,Jian-xiao MA,Gen LI,Ling-hong SHEN,Chu-bo XU. Traffic risk analysis of moving work zone on right lane of city expressway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [2] | Song-xue GAI,Xiao-qing ZENG,Xiao-yuan YUE,Zi-hao YUAN. Parking guidance model based on user and system bi⁃level optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [3] | Hong-feng XU,Hong-jin CHEN,Dong ZHANG,Qian-hui LU,Na AN,Xian-cai Geng. Fully⁃actuated signal timing technique for isolated signalized intersections in connected vehicle environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [4] | Chao-ying YIN,Chun-fu SHAO,Zhao-guo HUANG,Xiao-quan WANG,Sheng-you WANG. Investigating influences of multi⁃scale built environment on car ownership behavior based on gradient boosting decision trees [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [5] | Feng XUE,Chuan-lei HE,Qian HUANG,Jian LUO. Coordination degree of multimodal rail transit network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [6] | Bo PENG,Yuan-yuan ZHANG,Yu-ting WANG,Ju TANG,Ji-ming XIE. Automatic traffic state recognition from videos based on auto⁃encoder and classifiers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [7] | Dian-hai WANG,Xin-yi SHEN,Xiao-qin LUO,Sheng JIN. Offset optimization with minimum average vehicle delay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [8] | Xian-min SONG,Ming-ye ZHANG,Zhen-jian LI,Xin WANG,Ya-nan ZHANG. Setting of dynamic bus lane and its simulation analysis and evaluation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [9] | Hong-fei JIA,Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG. Bi-level programming model for optimization design of tidal lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [10] | Chao-ying YIN,Chun-fu SHAO,Xiao-quan WANG,Zhi-hua XIONG. Influence of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [11] | Da-wei ZHANG,Hai-tao ZHU. An optimization⁃based evacuation model considering pedestrian heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [12] | Yuan-li GU, Yuan ZHANG, Xiao-ping RUI, Wen-qi LU, Meng LI, Shuo WANG. Short⁃term traffic flow prediction based on LSSVMoptimized by immune algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [13] | Yi-ming BIE,Kai JIANG,Ru-ru TANG,Lin-hong WANG,Xin-yu XIONG. Time of interval partition for traffic control at isolated intersection considering impacts of plan transition [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [14] | Guo-zhu CHENG, Si-he FENG, Tian-jun FENG. Setting condition of on⁃street parking space occupied vehicle lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [15] | Quan LIANG,Jian-cheng WENG,Wei ZHOU,Jian RONG. Stability identification of public transport commute passengers based on association rules [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
|
||