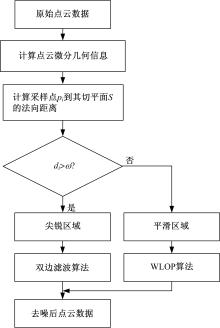
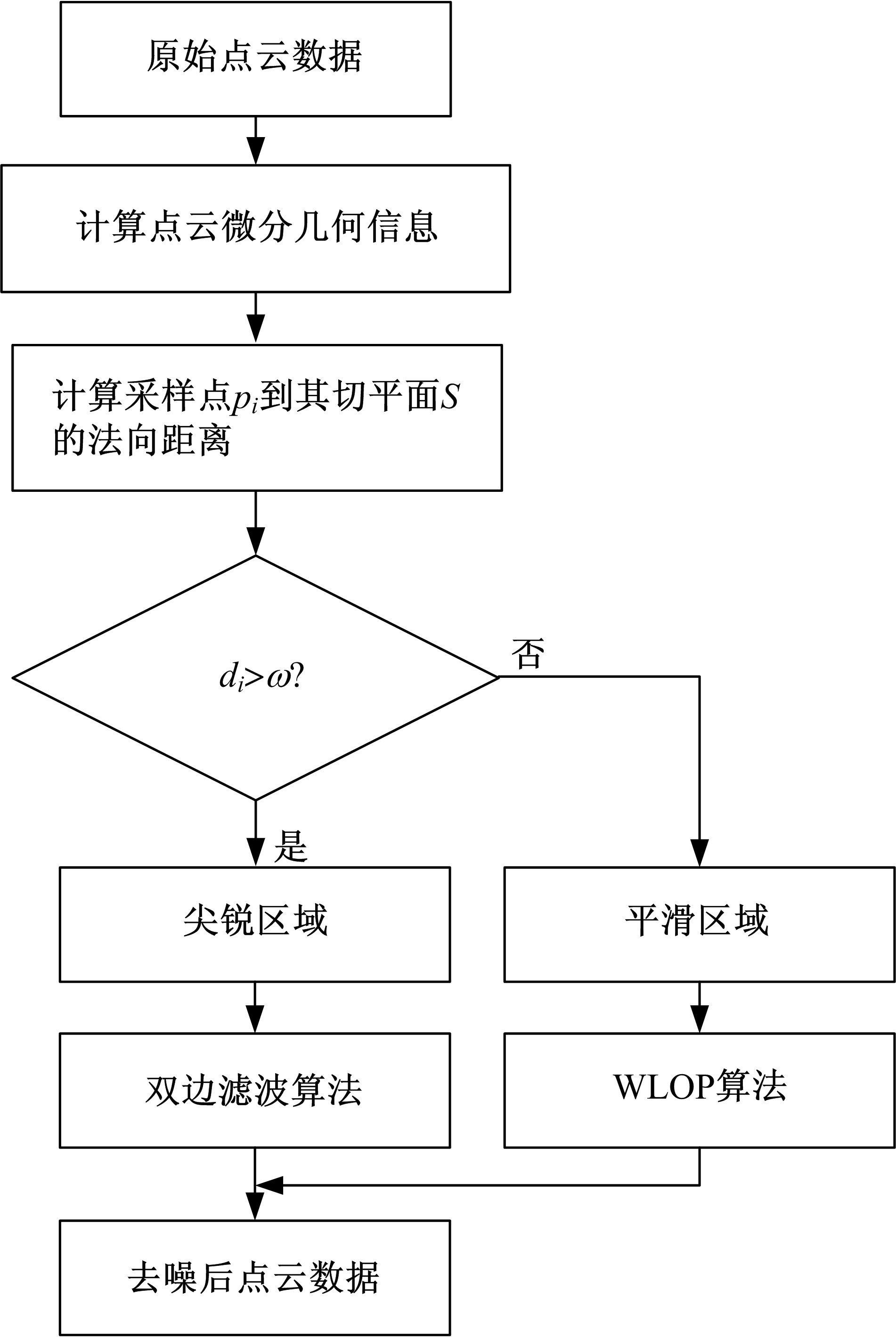
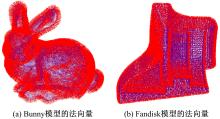
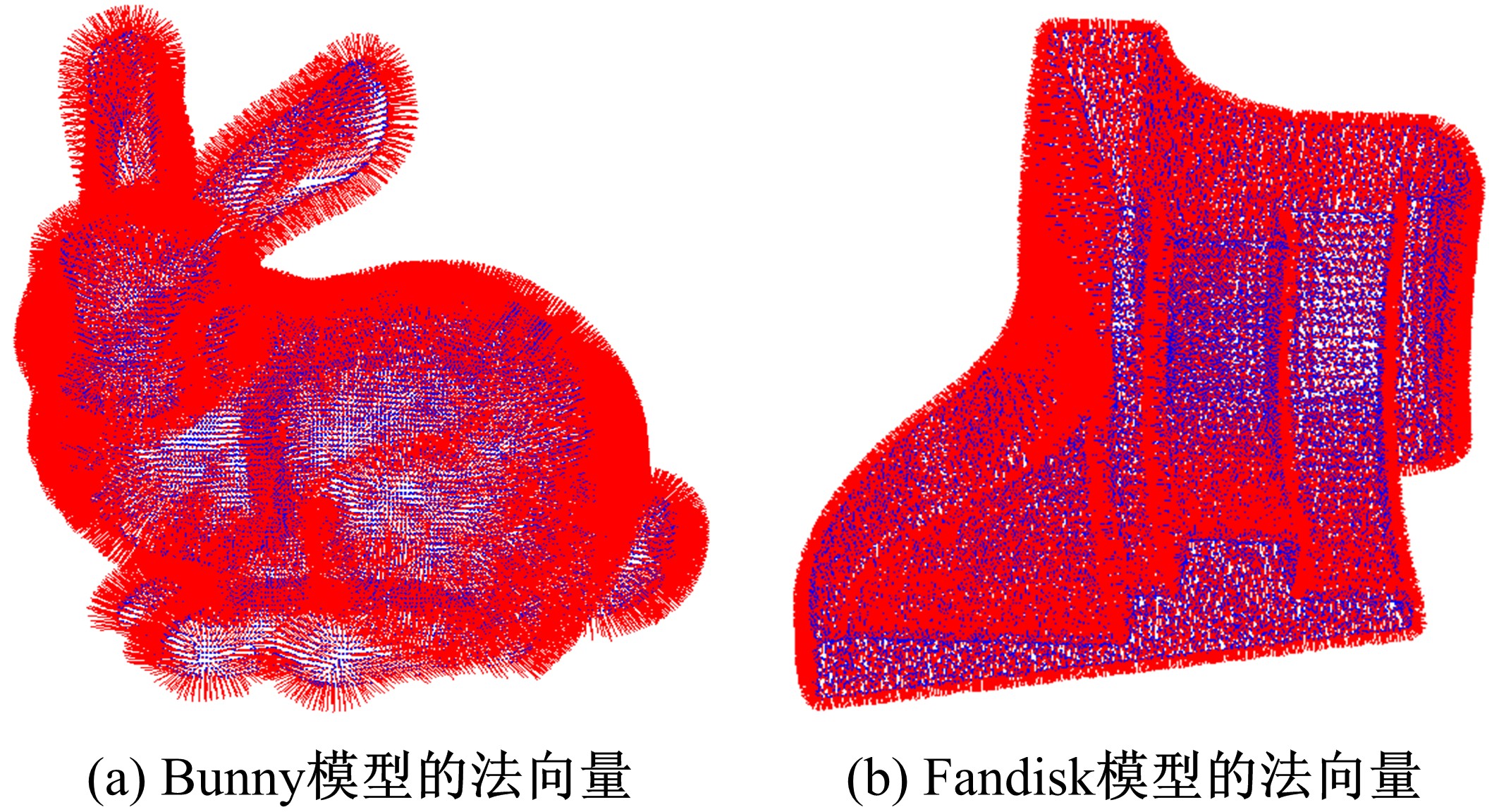
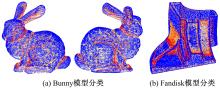
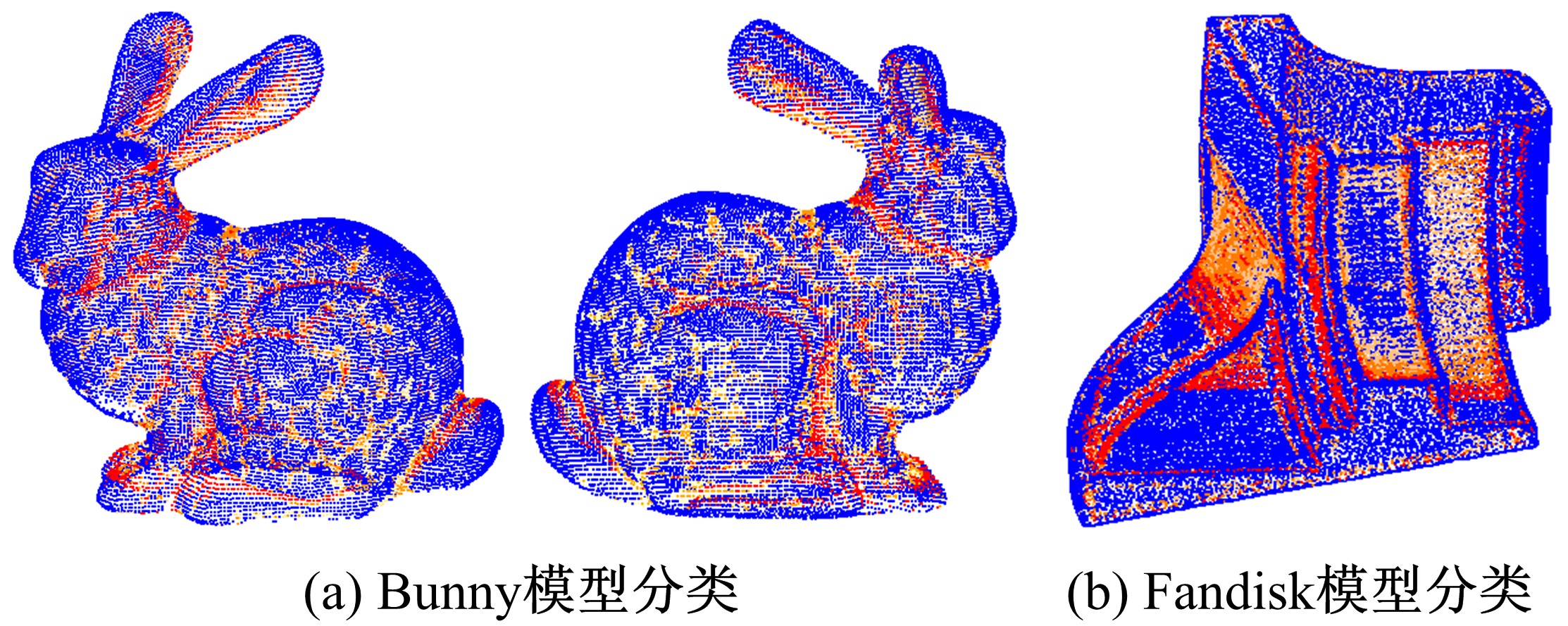
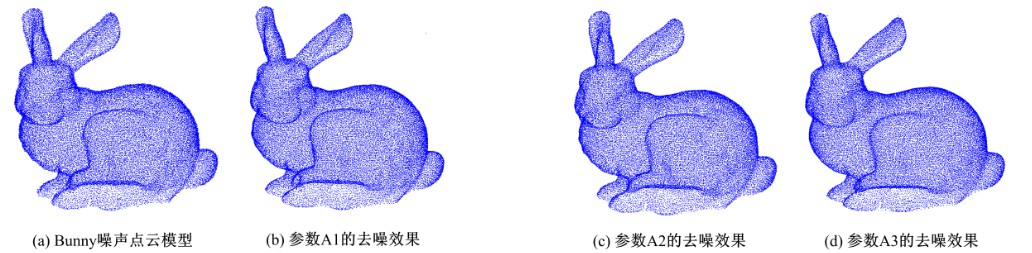
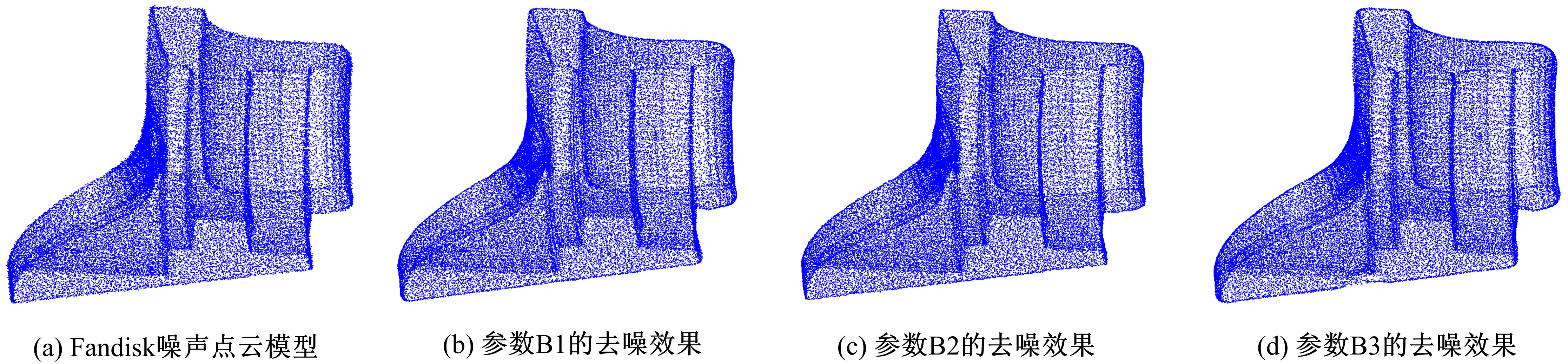
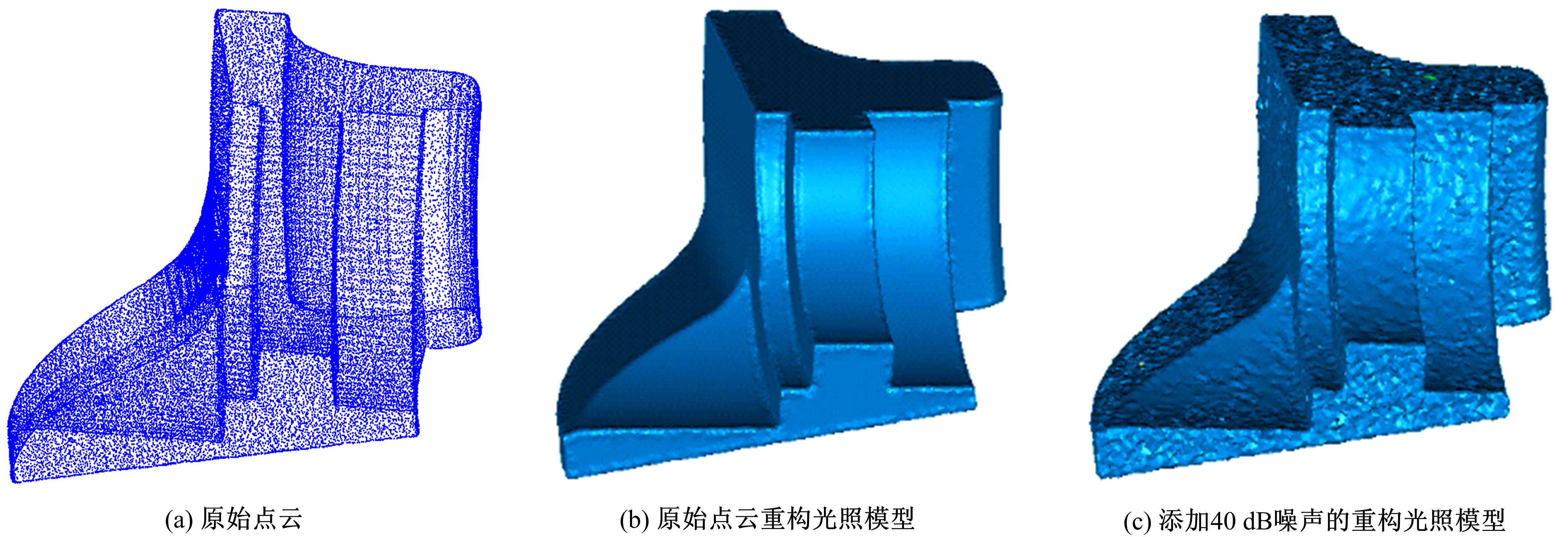
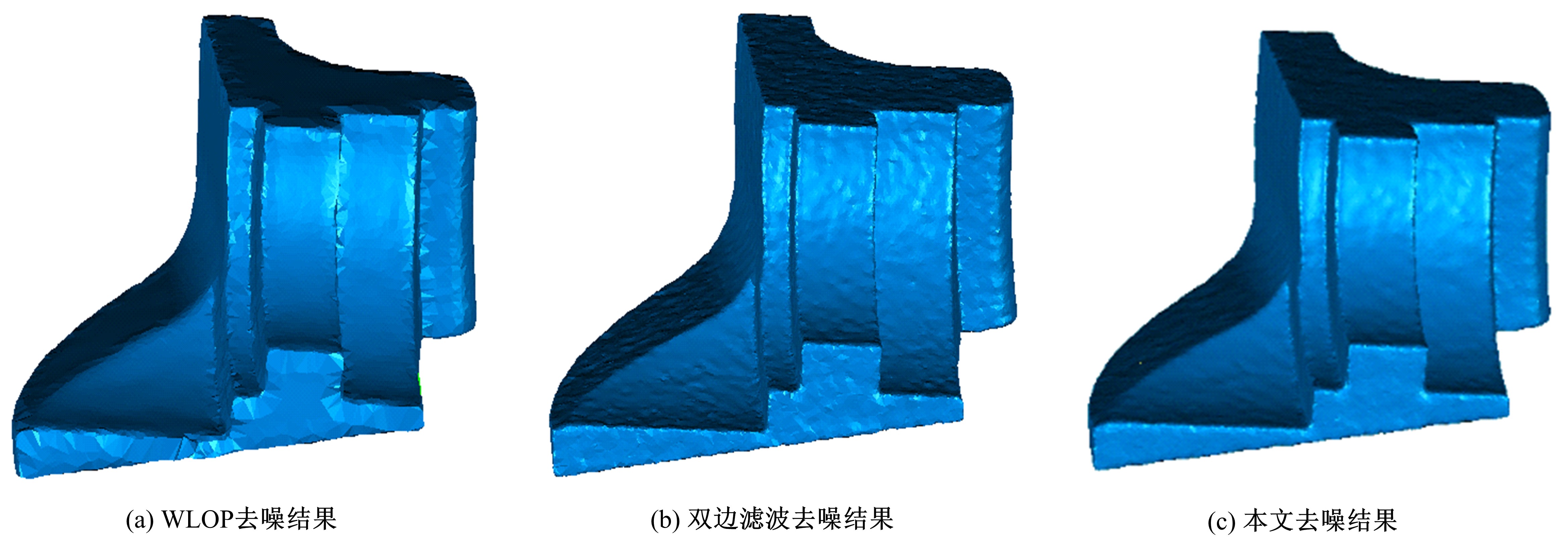
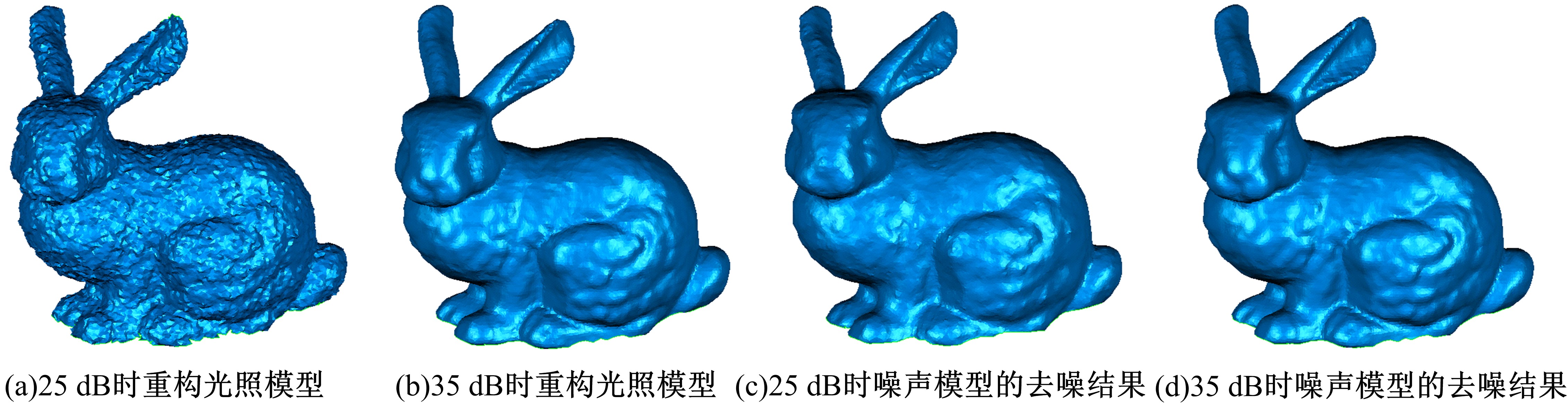
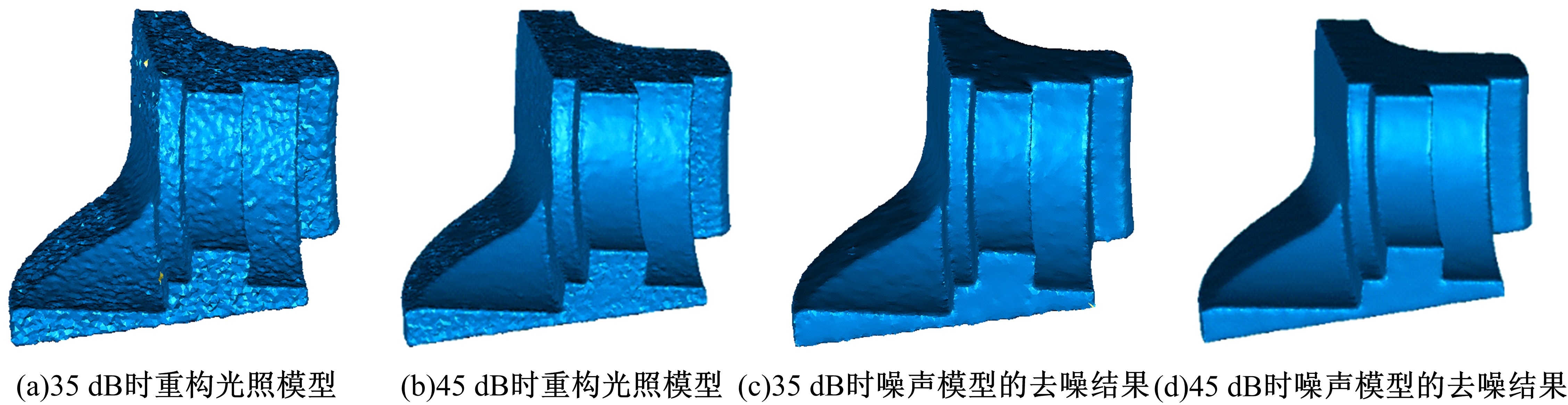
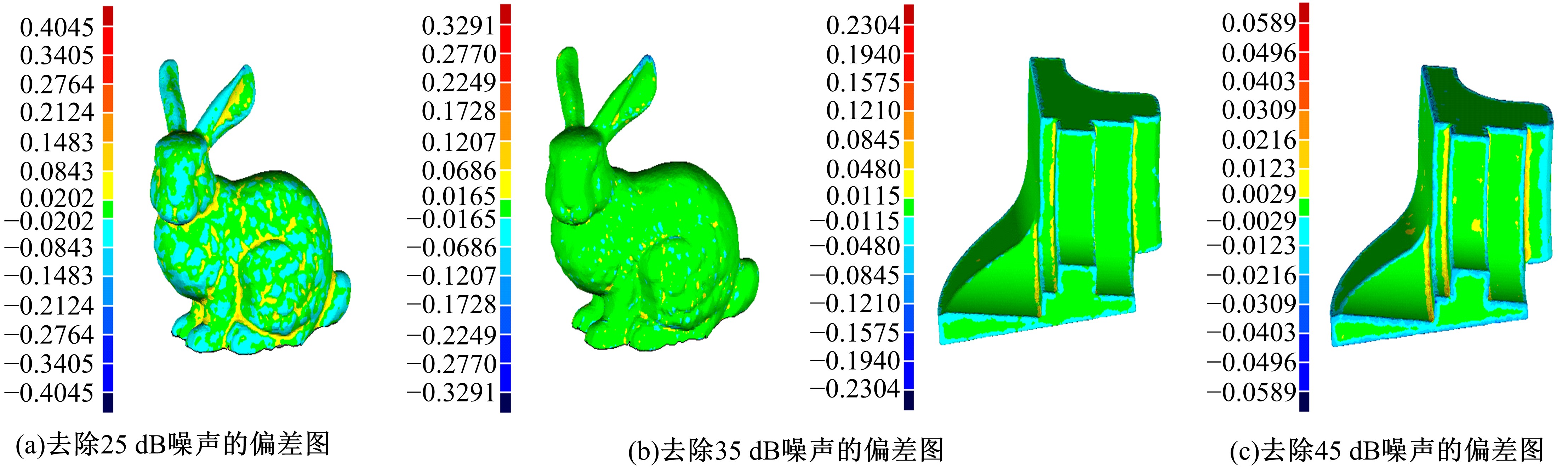
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 278-288.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180948
Denoising of scattered point cloud data based on normal vector distance classification
Xiao-hui WANG1,2( ),Lu-shen WU1(
),Lu-shen WU1( ),Hua-wei CHEN3
),Hua-wei CHEN3
- 1. School of Mechatronic Engineering, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, China
2. School of Architectural and Mechanical Engineering, Chifeng University, Chifeng 024000, China
3. School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang 550025, China
CLC Number:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Taubin G . A signal processing approach to fair surface design[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York, USA, 1995: 351-358. |
| 2 | Desbrun M , Meyer M , Schröder P . et al . Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow[C]∥Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, United States, 1999: 317-324. |
| 3 | Fleishman S , Drori I , Cohen-Or D . Bilateral mesh denoising[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 950-953. |
| 4 | Jones T R , Durand F , Desbrun M . Non-iterative, feature-preserving mesh smoothing[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2003, 22(3): 943-949. |
| 5 | 杜小燕,姜晓峰,郝传刚,等 . 点云模型的双边滤波去噪算法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2010, 27(7): 245-246. |
| Du Xiao-yan , Jiang Xiao-feng , Hao Chuan-gang , et al . Bilateral filtering denoising algorithm for point cloud model[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2010, 27(7): 245-246. | |
| 6 | 曹爽,岳建平,马文 . 基于特征选择的双边滤波点云去噪算法[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013(增刊2): 351-354. |
| Cao Shuang , Yue Jian-ping , Ma Wen . Bilateral filtering denoise algorithm for point cloud based on feature selection[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2013(Sup.2): 351-354. | |
| 7 | 袁华,庞建铿,莫建文 . 基于噪声分类的双边滤波点云去噪算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2015, 35(8): 2305-2310. |
| Yuan Hua , Pang Jian-keng , Mo Jian-wen . Denoising algorithm for bilateral filtered point cloud based on noise classification[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2015, 35(8): 2305-2310. | |
| 8 | 李鹏飞,吴海娥,景军锋,等 . 点云模型的噪声分类去噪算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2016, 52(20): 188-192. |
| Li Peng-fei , Wu Hai-e , Jing Jun-feng , et al . Noise classification denoising algorithm for point cloud model[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2016, 52(20): 188-192. | |
| 9 | Lipman Y , Cohen-Or D , Levin D ,et al . Parameterization-free projection for geometry reconstruction[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 1276405. |
| 10 | Huang H , Li D , Zhang H , et al . Consolidation of unorganized point clouds for surface reconstruction[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(5): 1-7. |
| 11 | 杨焕宇 .面向虚拟现实的三维点云数据处理关键技术研究[D]. 上海:东华大学信息科学与技术学院, 2016. |
| Yang Huan-yu . Research on key technologies of 3D point clouds data processing for virtual reality[D]. Shanghai: School of Information Science and Technology, Donghua University, 2016. | |
| 12 | Liu S , Chan K C , Wang C C . Iterative consolidation of unorganized point clouds[J]. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 2012, 32(3): 70-83. |
| 13 | 李宝 . 三维点云的鲁棒处理技术研究[D]. 长沙:国防科学技术大学研究生院, 2011. |
| Li Bao . Robust processing of 3D point clouds[D]. Changsha: Graduate School, National University of Defense Technology, 2011. | |
| 14 | 孙钰科 . 三维激光点云数据的处理及应用研究[D]. 上海:上海师范大学旅游学院, 2018. |
| Sun Yu-ke . Research on processing and application of 3D laser point cloud data[D]. Shanghai: School of Tourism,Shanghai Normal University, 2018. | |
| 15 | Hoppe H , DeRose T , Duchamp T , et al . Surface reconstruction from unorganized points[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1992, 26(2): 71-78. |
| 16 | Wang Y , Feng H Y , Engin S . An adaptive normal estimation method for scanned point clouds with sharp features[J]. CAD computer-Aided Design, 2013, 45(11): 1333-1348. |
| 17 | 贺美芳 . 基于散乱点云数据的曲面重建关键技术研究[D]. 南京:南京航空航天大学CAD/CAM工程研究中心, 2006. |
| He Mei-fang . Research on key techniques of surface reconstruction based on scattered point cloud data[D]. Nanjing: CAD/CAM Engineering Research Center, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006. |
| [1] | Xiao-dong ZHANG,Xiao-jun XIA,Hai-feng LYU,Xu-chao GONG,Meng-jia LIAN. Dynamic load balancing of physiological data flow in big data network parallel computing environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [2] | Jun-yi DENG,Yan-heng LIU,Shi FENG,Rong-cun ZHAO,Jian WANG. GSPN⁃based model to evaluate the performance and securi tytradeoff in Ad-hoc network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 255-261. |
| [3] | Xiong-fei LI,Jing WANG,Xiao-li ZHANG,Tie-hu FAN. Multi-focus image fusion based on support vector machines and window gradient [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 227-236. |
| [4] | Hong-yan WANG,He-lei QIU,Jia ZHENG,Bing-nan PEI. Visual tracking method based on low⁃rank sparse representation under illumination change [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 268-277. |
| [5] | Bing-hai ZHOU,Qiong WU. Balancing and optimization of robotic assemble lines withtool and space constraint [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2069-2075. |
| [6] | Xiang-jiu CHE,Hua-luo LIU,Qing-bin SHAO. Fabric defect recognition algorithm based onimproved Fast RCNN [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2038-2044. |
| [7] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Peng WANG,Li-li FAN,Huang-shui HU,Ping-ping LIU. Similarity retention instance retrieval method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2045-2050. |
| [8] | Jun SHEN,Xiao ZHOU,Zu-qin JI. Implementation of service dynamic extended network and its node system model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2058-2068. |
| [9] | You ZHOU,Sen YANG,Da-lin LI,Chun-guo WU,Yan WANG,Kang-ping WANG. Acceleration platform for face detection and recognition based on field⁃programmable gate array [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 2051-2057. |
| [10] | Bin LI,Xu ZHOU,Fang MEI,Shuai-ning PAN. Location recommendation algorithm based on K-means and matrix factorization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [11] | Xiong-fei LI,Lu SONG,Xiao-li ZHANG. Remote sensing image fusion based on cooperative empirical wavelet transform [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1307-1319. |
| [12] | Yuan-ning LIU,Shuai LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Guang HUO,Tong DING,Kuo ZHANG,Xue JIANG,Shu-jun GUO,Qi-xian ZHANG. Iris secondary recognition based on decision particle swarm optimization and stable texture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1329-1338. |
| [13] | Bin LI,Guo⁃jun SHEN,Geng SUN,Ting⁃ting ZHENG. Improved chicken swarm optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1339-1344. |
| [14] | Feng⁃wen ZHAI,Jian⁃wu DANG,Yang⁃ping WANG,Jing JIN,Wei⁃wei LUO. Extended contour⁃based fast affine invariant feature extracting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1345-1356. |
| [15] | Yan-jun SUN,Xuan-jing SHEN,Hai-peng CHEN,Yong-zhe ZHAO. Recaptured image forensics algorithm based on local plane linear point [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1320-1328. |
|
||