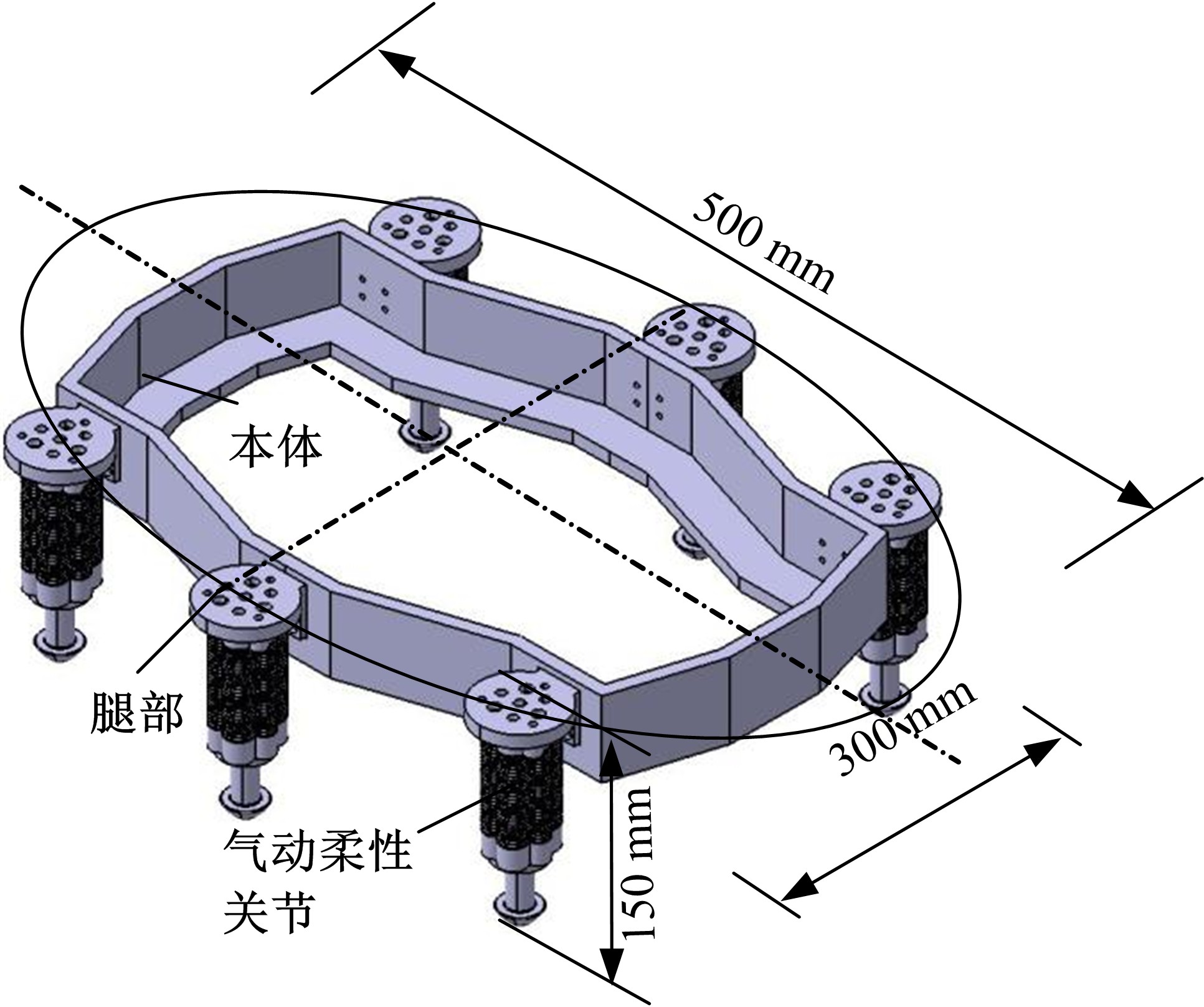
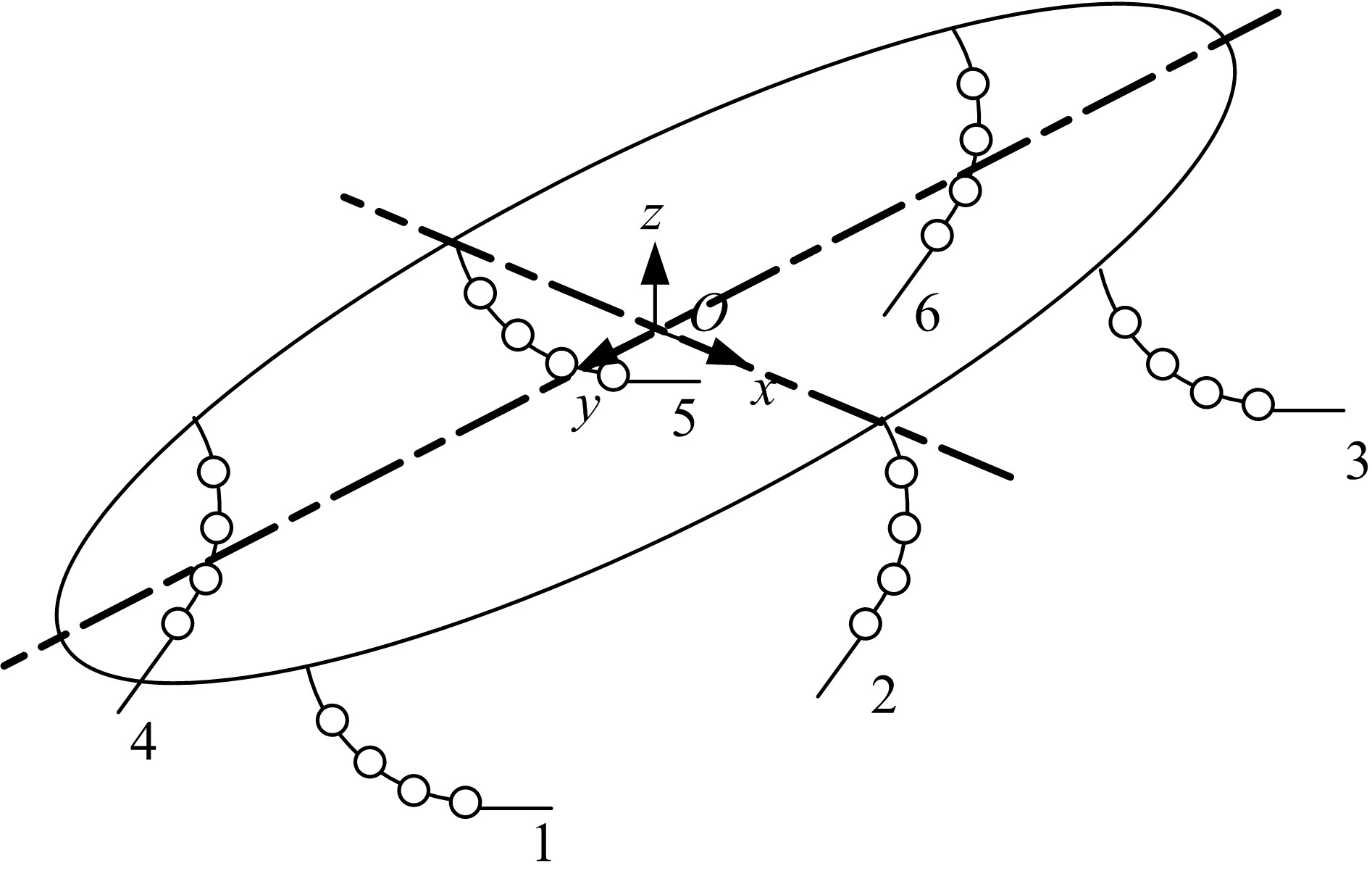
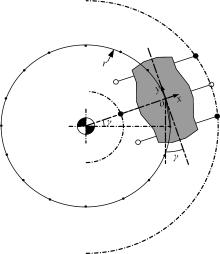
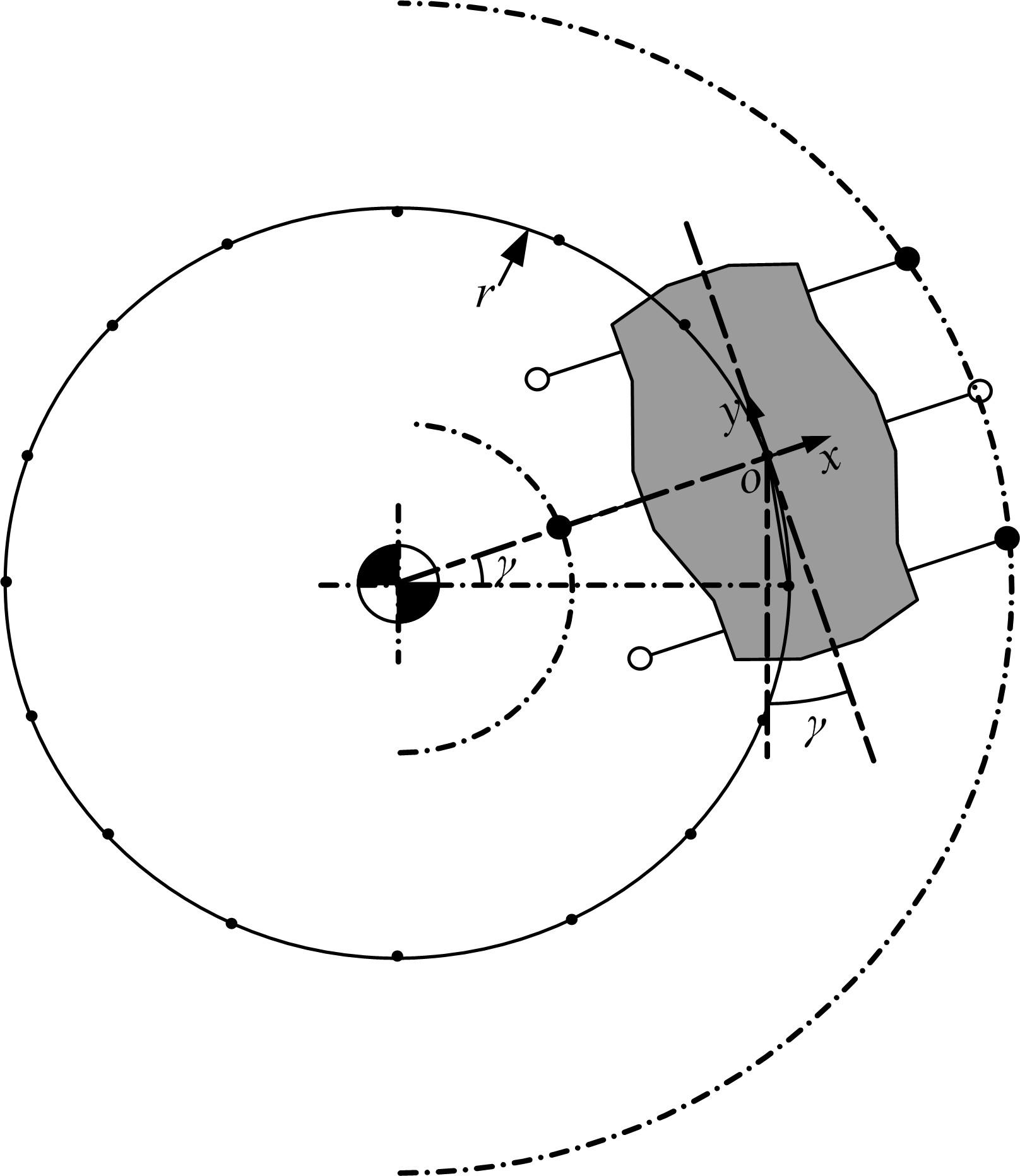
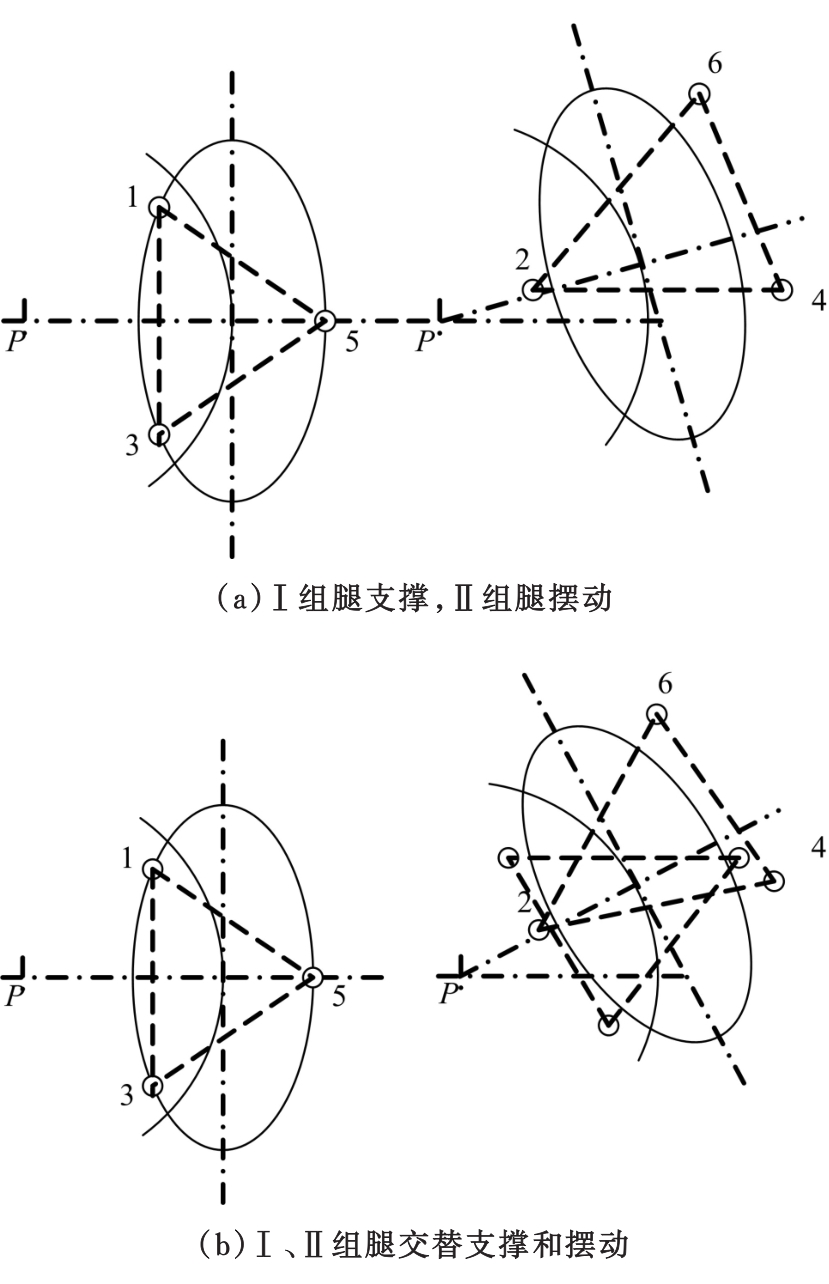
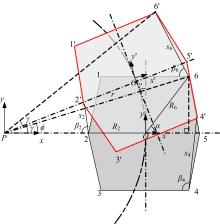
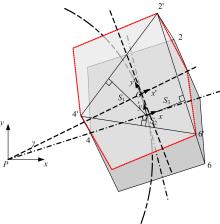
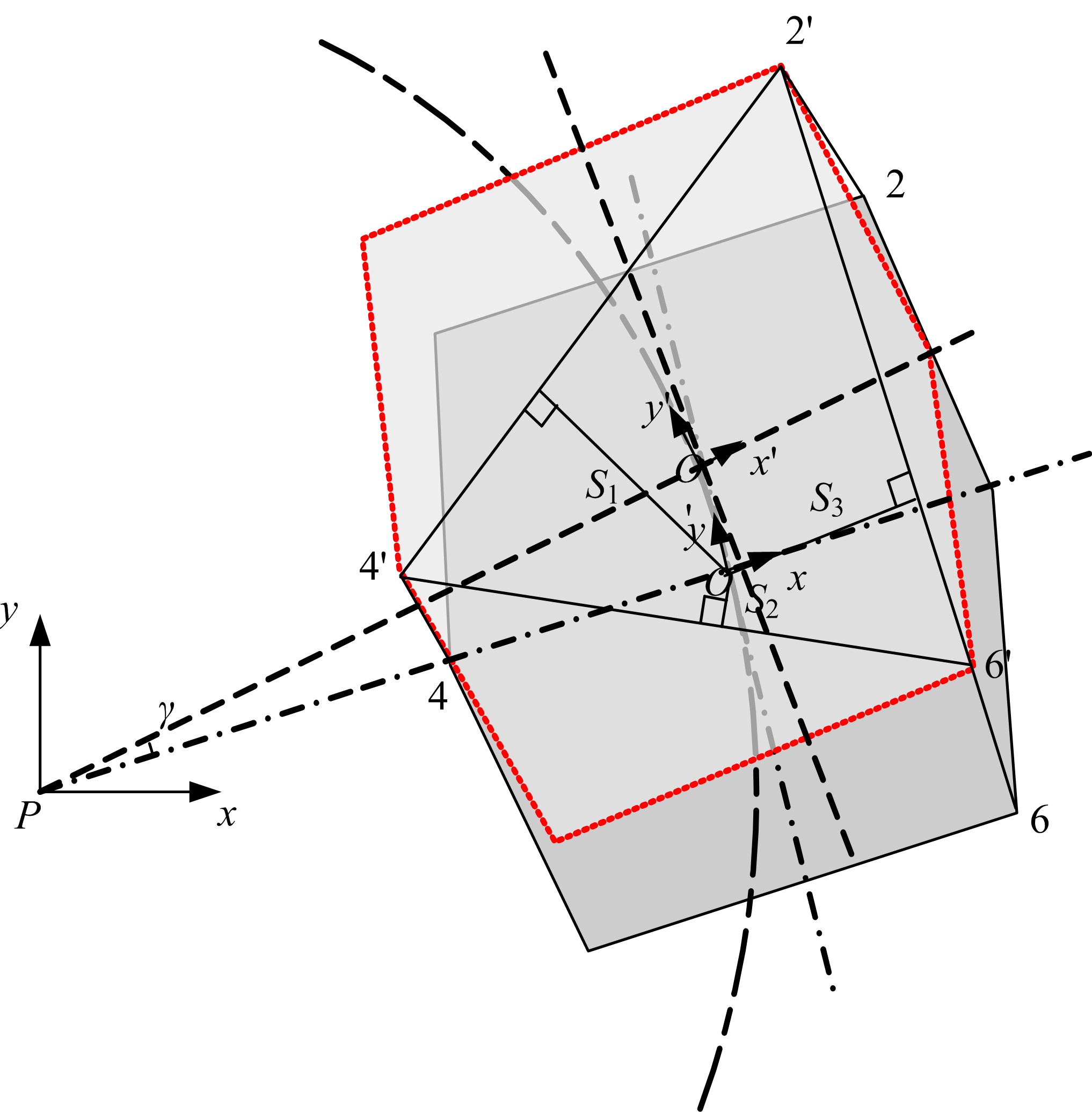
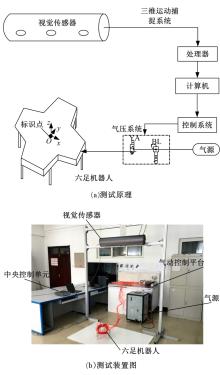
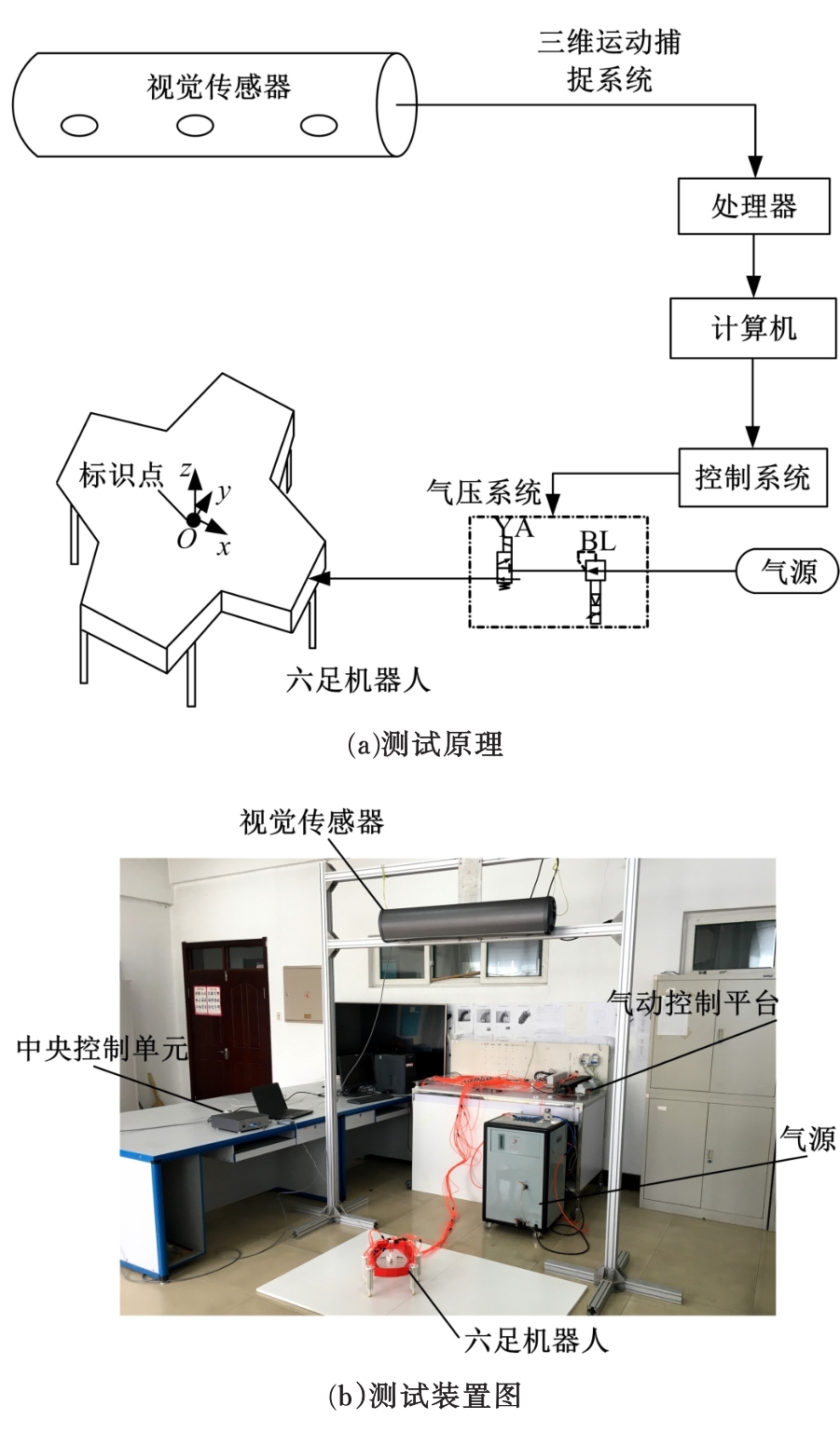
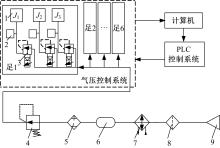
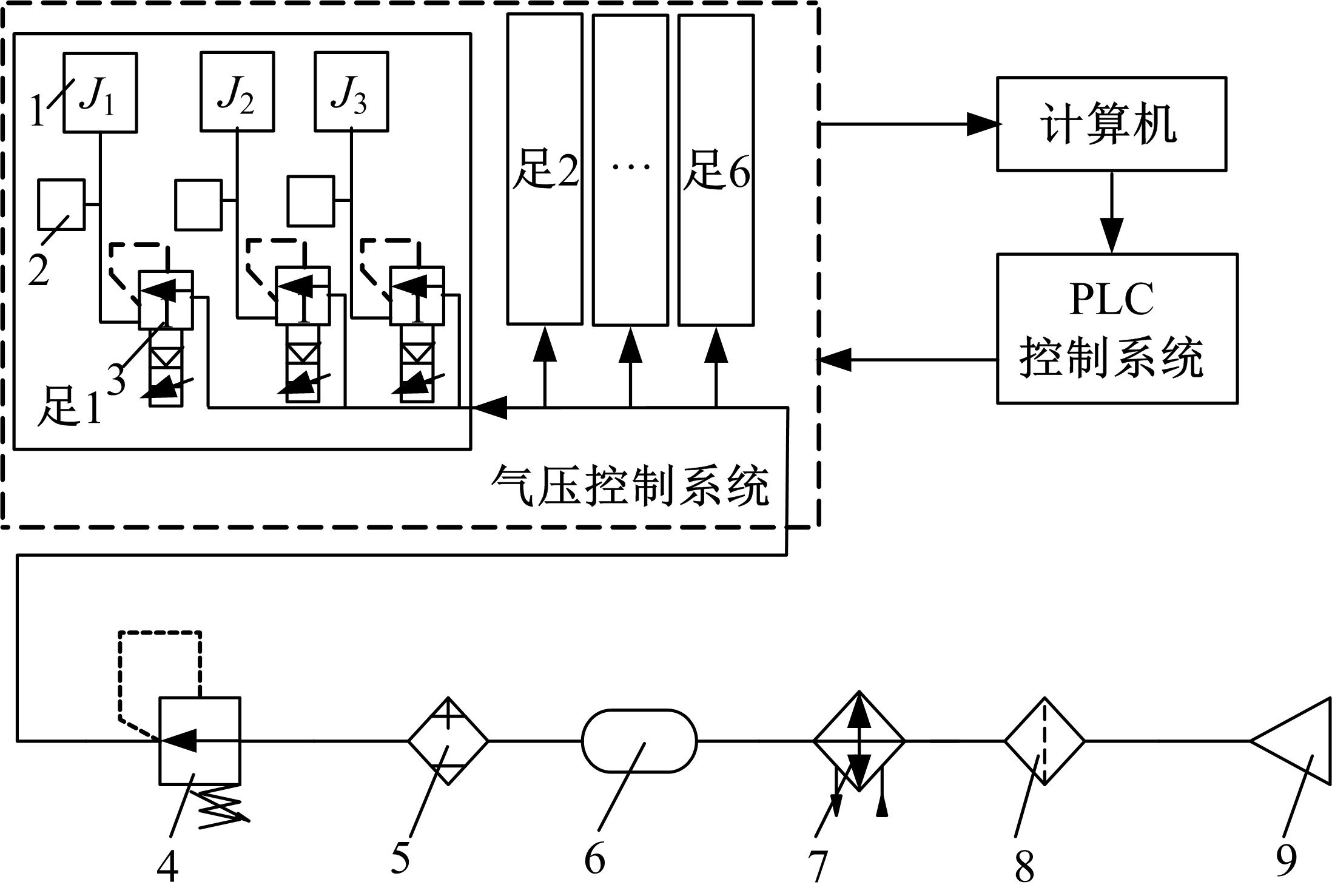
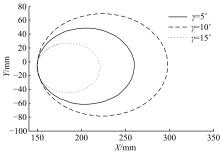
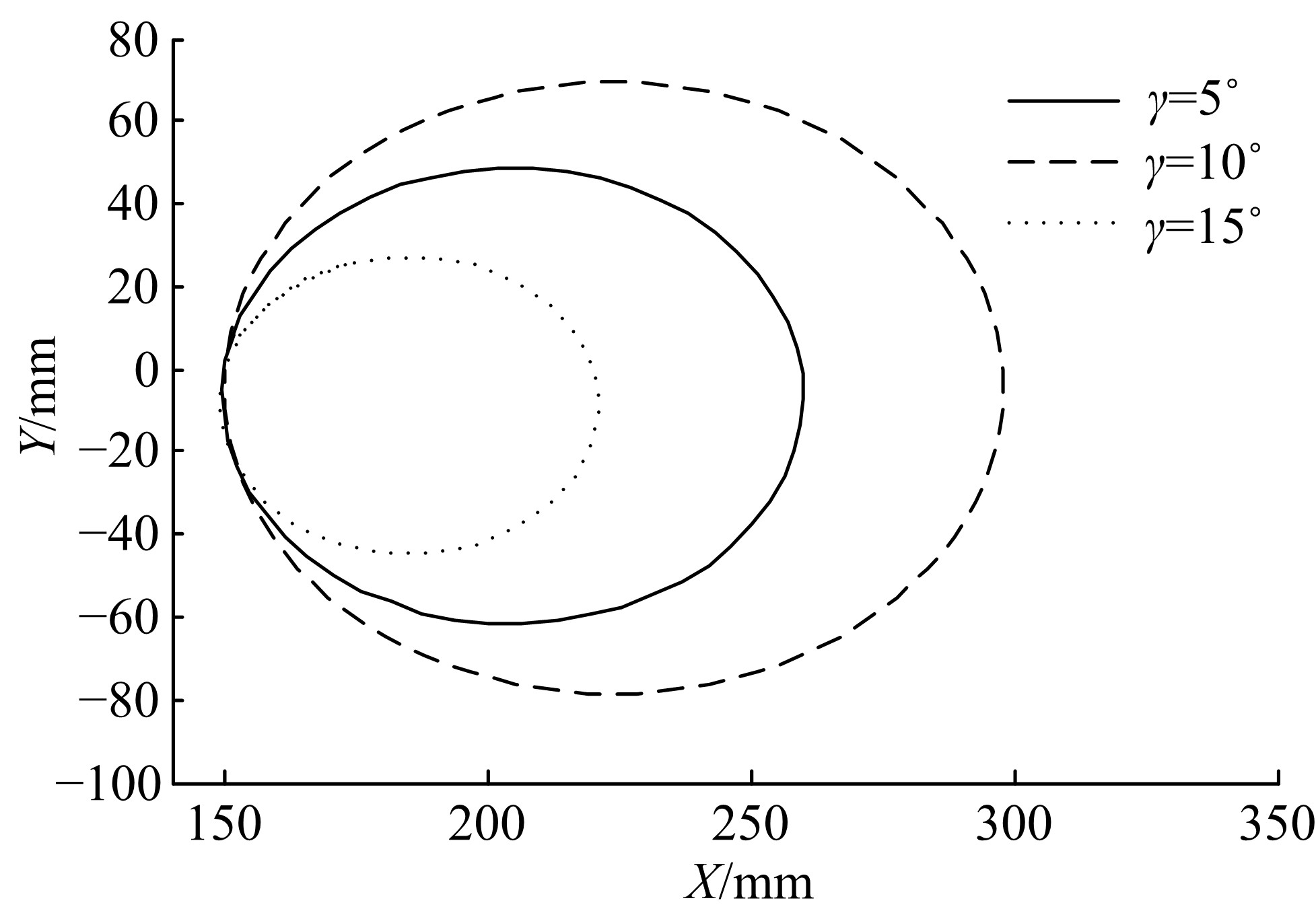
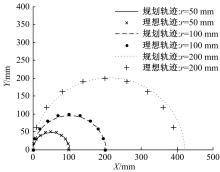
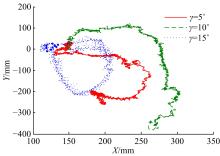
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 472-482.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181071
Implementation and stability on turning with constant radius of pneumatic flexible hexapod robot
Yun-wei ZHAO1( ),De-xu GENG2(
),De-xu GENG2( ),Xiao-min LIU1,Qi LIU2
),Xiao-min LIU1,Qi LIU2
- 1.Engineering Training Center, Beihua University, Jilin 132021, China
2.College of Mechanical Engineering, Beihua University, Jilin 132021, China
CLC Number:
- TH138.5
| 1 | Zhang H, Liu Y, Zhao J, et al. Development of a bionic hexapod robot for walking on unstructured terrain[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2014, 11(2): 176-187. |
| 2 | Bartsch S, Birnschein T, Römmermann M, et al. Development of the six-legged walking and climbing robot SpaceClimber[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2012, 29(3): 506-532. |
| 3 | Kondo N, Yata K, Iida M, et al. Development of an end-effector for a tomato cluster harvesting robot[J]. Engineering in Agriculture Environment & Food, 2010, 3(1): 20-24. |
| 4 | 荣誉, 金振林, 崔冰艳. 六足农业机器人并联腿构型分析与结构参数设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28(15): 9-14. |
| Rong Yu, Jin Zhen-lin, Cui Bing-yan. Configuration analysis and structure parameter design of six-leg agricultural robot with parallel-leg mechanisms[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28(15): 9-14. | |
| 5 | Bodrov A, Cheah W, Green P N, et al. Joint space reference trajectory to reduce the energy consumption of a six-legged mobile robot[C]∥2018 25th International Workshop on Electric Drives: Optimization in Control of Electric Drives (IWED), IEEE, Moscow, 2018: 1-6. |
| 6 | Bjelonic M, Kottege N, Homberger T, et al. Weaver: hexapod robot for autonomous navigation on unstructured terrain[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2018, 35(7): 1063-1079. |
| 7 | 刘逸群, 邓宗全, 赵亮, 等. 液压驱动六足机器人步行腿性能[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(5): 1512-1518. |
| Liu Yi-qun, Deng Zong-quan, Zhao Liang,et al. Performance of walking leg of a hydraulically actuated hexapod robot[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(5): 1512-1518. | |
| 8 | Wang Z, Ding X, Rovetta A, et al. Mobility analysis of the typical gait of a radial symmetrical six-legged robot[J]. Mechatronics, 2011, 21(7): 1133-1146. |
| 9 | Deng H, Xin G, Zhong G, et al. Object carrying of hexapod robots with integrated mechanism of leg and arm[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018(54): 145-155. |
| 10 | 陈甫, 臧希喆, 闫继宏, 等. 适合航行的六足仿生机器人Spider的研制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(3): 765-770. |
| Chen Fu, Zang Xi-zhe, Yan Ji-hong, et al. Development of navigable hexapod biomimetic robot Spider[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(3): 765-770. | |
| 11 | Erden M S, Leblebicio, Lu K. Free gait generation with reinforcement learning for a six-legged robot[J]. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(3): 199-212. |
| 12 | Roy S S, Pratihar D K. Effects of turning gait parameters on energy consumption and stability of a six-legged walking robot[J]. Robotics & Autonomous Systems, 2012, 60(1): 72-82. |
| 13 | Roy S S, Pratihar D K. Soft computing-based expert systems to predict energy consumption and stability margin in turning gaits of six-legged robots[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(5): 5460-5469. |
| 14 | Agheli M, Qu L, Nestinger S S. SHeRo: scalable hexapod robot for maintenance, repair, and operations[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2014, 30(5): 478-488. |
| 15 | Belter D, Wietrzykowski J, Skrzypczyński P. Employing natural terrain semantics in motion planning for a multi-legged robot[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2019, 93(3/4): 723-743. |
| 16 | Belter D, Nowicki M R. Optimization-based legged odometry and sensor fusion for legged robot continuous localization[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 111: 110-124. |
| 17 | Buchanan R, Bandyopadhyay T, Bjelonic M, et al. Walking posture adaptation for legged robot navigation in confined spaces[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(2): 2148-2155. |
| 18 | 姜树海, 孙培, 唐晶晶, 等. 仿生甲虫六足机器人结构设计与步态分析[J]. 南京林业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 36(6): 115-120. |
| Jiang Shu-hai, Sun Pei, Tang Jing-jing, et al. Structural design and gait analysis of hexapod bionic robot[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 36(6): 115-120. | |
| 19 | 陈刚, 金波, 陈鹰. 六足步行机器人定半径转弯步态[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 48(7): 1278-1286. |
| Chen Gang, Jin Bo, Chen Ying. Turning gait with constant radius of six-legged waling robot[J]. Joural of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2014, 48(7): 1278-1286. | |
| 20 | 李满宏, 张建华, 张小俊, 等. 基于马尔可夫决策过程的六足机器人自由步态规划[J]. 机器人, 2015, 37(5): 529-537. |
| Li Man-hong, Zhang Jian-hua, Zhang Xiao-jun, et al. Free gait planning for a hexapod robot based on markov decision process[J]. Robot, 2015, 37(5): 529-537. | |
| 21 | 邓宗全, 刘逸群, 高海波, 等. 液压驱动六足机器人步行腿节段长度比例研究[J]. 机器人, 2014, 36(5): 544-551. |
| Deng Zong-quan, Liu Yi-qun, Gao Hai-bo, et al. On the segment length ratio of the walking leg of a hydraulically actuated hexapod robot[J]. Robot, 2014, 36(5): 544-551. | |
| 22 | 赵云伟, 耿德旭, 刘晓敏, 等. 三自由度气动柔性驱动器结构功能与形变特性研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(9): 392-401. |
| Zhao Yun-wei, Geng De-xu, Liu Xiao-min, et al. Structure and deformation characteristics of 3-DOF pneumatic flexible actuator[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(9): 392-401. | |
| 23 | 赵云伟, 耿德旭, 刘晓敏, 等. 气动柔性关节仿生六足机器人步态规划与运动性能研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(2): 385-394, 418. |
| Zhao Yun-wei, Geng De-xu, Liu Xiao-min, et al. Gait planning and kinematics of bionic hexapod robot based on pneumatic flexible join[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(2): 385-394, 418. | |
| 24 | 赵云伟, 耿德旭, 刘晓敏, 等. 气动空间弯曲关节动力学性能实验研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2017, 45(23): 10-23. |
| Zhao Yun-wei, Geng De-xu, Liu Xiao-min, et al. Experimental study on dynamic properties of pneumatic space bending joint[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2017, 45(23): 10-23. | |
| 25 | Estremera J, Cobano J A. Continuous free-crab gaits for hexapod robots on a natural terrain with forbidden zones: an application to humanitarian demining[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2010, 58(5): 700-711. |
| [1] | Chun-zheng DUAN,Fang-yuan ZHANG,Wen-neng KOU,Bin WEI. Martensitic transformation of surface white layer in high speed hard cutting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1575-1583. |
| [2] | REN Shu-nan, YANG Xiang-dong, WANG Guo-lei, LIU Zhi, CHEN Ken. Base position planning of mobile manipulator for large parts painting [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1995-2002. |
| [3] | LIU Yi-qun, DENG Zong-quan, ZHAO Liang, DING Liang, TONG Zhi-zhong, GAO Hai-bo. Performance of walking leg of a hydraulically actuated hexapod robot [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1512-1518. |
| [4] | GUO Li-bin, ZHANG Bin, CUI Hai, ZHANG Zhi-hang. Structural parameters of 3D roughness for micro wire electrical discharge machining surface [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 851-856. |
| [5] | HU Sheng-hai, GUO Bin, MASONG Ming-hui, XU Peng. Dynamic modeling and simulation of roller chain system in SimMechanics considering complete tooth profile [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(04): 958-963. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lei, ZHAO Yun-wei, YANG Zhuo, ZHAO Ji. Shear yield property of electrorheological polishing fluid [J]. , 2012, 42(05): 1145-1150. |
| [7] | WANG Guo-fu, GAO Feng, XU Guo-yan. Kinematic analysis and control of omnidirectional hexapod robot with a steering-wheel [J]. , 2012, 42(04): 1008-1014. |
| [8] | CHEN Fu,ZANG Xi-zhe,YAN Ji-hong,ZHAO Jie. Development of navigable hexapod biomimetic robot Spider [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(03): 765-770. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lei,HE Xin-sheng,ZHANG Ying,YANG He-ran. Development of new type ER fluid-assisted polishing tool and its polishing experiment [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(04): 1009-1014. |
|
||