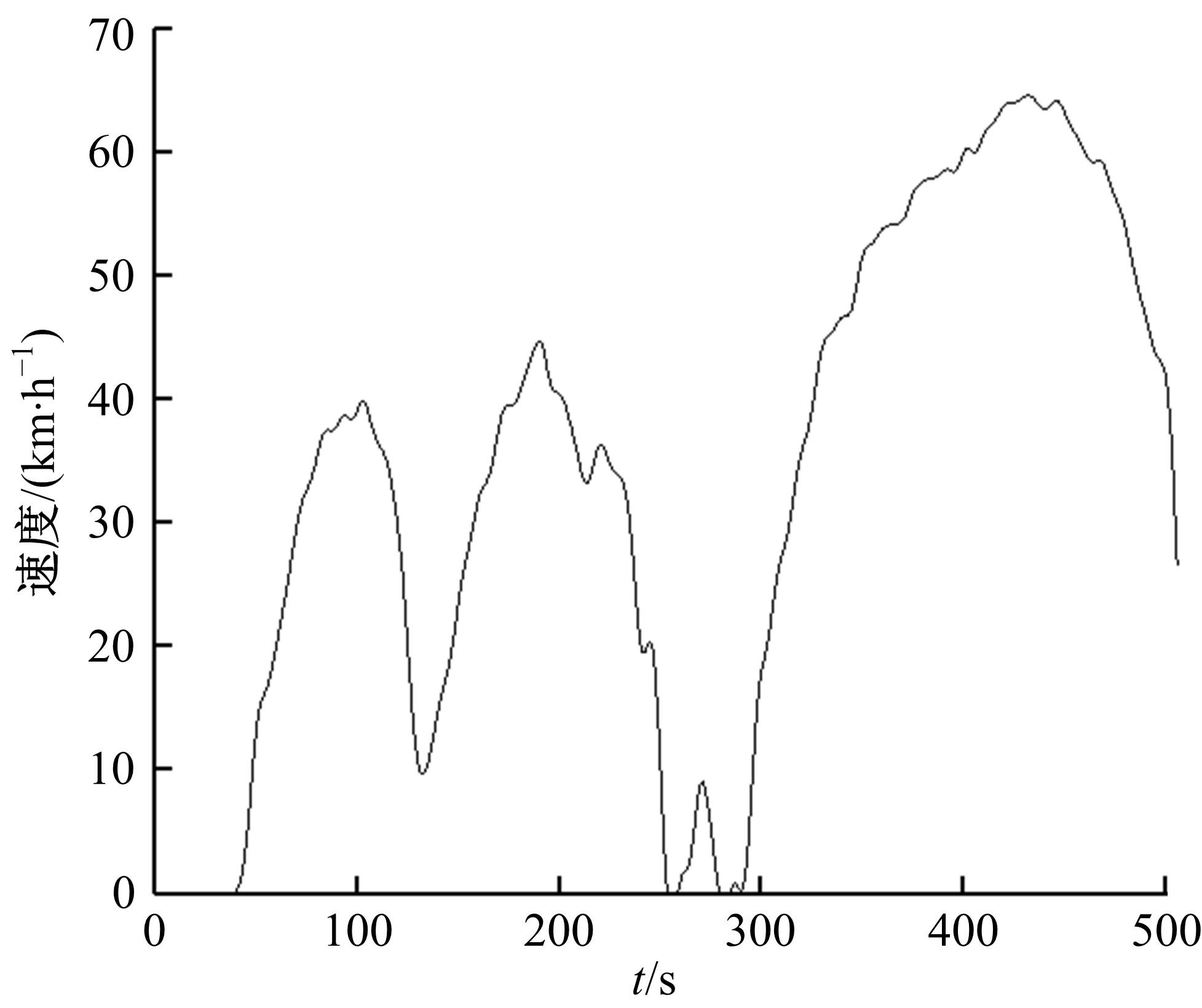
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1700-1707.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200540
Driving cycle construction of heavy semi⁃trailers carrying hazardous cargos
Hong-xue LI1( ),Shi-wu LI1(
),Shi-wu LI1( ),Wen-cai SUN1,Wei LI1,Meng-zhu GUO1,2
),Wen-cai SUN1,Wei LI1,Meng-zhu GUO1,2
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U469.5
| 1 | Peng Y H, Zhuang Y, Yang H B. Development of a representative driving cycle for urban buses based on the K-means cluster method[J]. Cluster Computing, 2018, 22(2): 1-10. |
| 2 | Shen P, Zhao Z, Li J. Development of a typical driving cycle for an intra-city hybrid electric bus with a fixed route[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport Environment, 2018, 59: 346-360. |
| 3 | 罗玉涛, 胡红斐, 沈继军. 混合动力电动汽车行驶工况分析与识别[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(6): 12-17. |
| Luo Yu-tao, Hu Hong-fei, Shen Ji-jun. Numerical simulation of pyrogenation regeneration process in particulate filter of vehicle diesel[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(6): 12-17. | |
| 4 | Chauhan B P, Joshi G J, Parida P. Driving cycle analysis to identify intersection influence zone for urban intersections under heterogeneous traffic condition[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2018, 41: 180-185. |
| 5 | Zhao X, Ma J, Wang S, et al. Developing an electric vehicle urban driving cycle to study differences in energy consumption[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(14): 13839-13853. |
| 6 | Kim W G, Kim C K, Lee J T, et al. Characteristics of nanoparticle emission from a light-duty diesel vehicle during test cycles simulating urban rush-hour driving patterns[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2018, 20(4): 1-94. |
| 7 | Rady J, O'Mahony M. Development of a driving cycle to evaluate the energy economy of electric vehicles in urban areas[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 177(9): 165-178. |
| 8 | Zc A, Rui X, Cw C, et al. An on-line predictive energy management strategy for plugin hybrid electric vehicles to counter the uncertain prediction of the driving cycle[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 185(2): 1663-1672. |
| 9 | He H W, Guo J Q, Peng J K, et al. Real-time global driving cycle construction and the application to economy driving pro system in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles[J]. Energy, 2018, 152(6): 95-107. |
| 10 | Abas M A, Rajoo S, Abidin S F Z. Development of Malaysian urban drive cycle using vehicle and engine parameters[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2018, 63(8): 388-403. |
| 11 | 胡志远, 秦艳, 谭丕强, 等. 基于大样本的上海市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 43(10): 1523-1527. |
| Hu Zhi-yuan, Qin Yan, Tan Pi-qiang, et al. Large-sample-based car-driving cycle in shanghai city[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2015, 43(10): 1523-1527. | |
| 12 | 郑殿宇, 吴晓刚, 陈汉, 等. 哈尔滨城区乘用车行驶工况的构建[J]. 公路交通科技, 2017, 34(4): 101-107. |
| Zheng Dian-yu, Wu Xiao-gang, Chen Han, et al. Construction of driving conditions of Harbin urban passenger cars[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2017, 34(4): 101-107. | |
| 13 | 张宏, 姚延钢, 杨晓勤. 城市道路轻型汽车行驶工况构建 [J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2019, 54(6): 1139-1154. |
| Zhang Hong, Yao Yan-gang, Yang Xiao-qin. Light-duty vehicles driving cycle construction based on urban roads[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019, 54(6): 1139-1154. | |
| 14 | 孙强, 白书战, 韩尔樑, 等. 基于试验测量的瞬时行驶工况构建[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2): 364-370. |
| Sun Qiang, Bai Shu-zhan, Han Er-liang, et al. Instantaneous driving cycle construction based on experimental measurement[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 364-370. | |
| 15 | 石琴, 仇多洋, 吴靖. 基于主成分分析和 FCM 聚类的行驶工况研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2012, 25(1): 70-76. |
| Shi Qin, Qiu Duo-yang, Wu Jing. Study on driving cycles based on principal component analysis and fuzzy c-means clustering[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 25(1): 70-76. | |
| 16 | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 等. 基于马尔科夫链的长春市乘用车行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. |
| Cao Qian, Li Jun, Liu Yu, et al. Construction of driving cycle based on Markov chain for passenger car in Changchun City[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1366-1373. | |
| 17 | Gong H, Zou Y, Yang Q, et al. Generation of a driving cycle for battery electric vehicles: a case study of Beijing[J]. Energy, 2018, 150: 901-912. |
| 18 | 秦大同, 詹森, 漆正刚, 等. 基于K-均值聚类算法的行驶工况构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(2): 383-389. |
| Qin Da-tong, Zhan Sen, Qi Zheng-gang, et al. Driving cycle construction using k-means clustering method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(2): 383-389. | |
| 19 | Esteves-Booth A, Muneer T, Kubie J, et al. A review of vehicular emission models and driving cycles[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2002, 216(8): 777-797. |
| 20 | 曹骞, 李君, 刘宇, 等. 基于大数据和马尔科夫链的行驶工况构建[J]. 东北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 40(1): 80-84. |
| Cao Qian, Li Jun, Liu Yu, et al. Construction of driving cycle based on big data and Markov chain[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2019, 40(1): 80-84. | |
| 21 | 胡宸, 吴晓刚, 李晓军, 等. 哈尔滨城市公交工况的构建[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2014, 19(1): 85-89. |
| Hu Chen, Wu Xiao-gang, Li Xiao-jun, et al. Construction of Harbin city driving cycle[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2014, 19(1): 85-89. | |
| 22 | 杨小娟, 王建. 北京市重型客车行驶工况的构建与研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2015, 5(6): 455-463. |
| Yang Xiao-juan, Wang Jian. Construction and research of heavy-coach's driving cycle in Beijing city[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2015, 5(6): 455-463. | |
| 23 | 王军方, 丁焰, 王爱娟, 等. 北京市机动车行驶工况研究[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2012, 2(3): 240-246. |
| Wang Jun-fang, Ding Yan, Wang Ai-juan, et al. Study of vehicle driving cycle modes on road in Beijing[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2012, 2(3): 240-246. |
| [1] | Li-qun WU,Liang-liang ZHANG. Health detection of bridge structures based on data mining technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 565-571. |
| [2] | Xin TONG,Le-le ZHANG,Wen LIU,Hong-jun KANG. Simulation analysis and evaluation on passive safety of the longitudinal berth [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 147-155. |
| [3] | Bin LI,Xu ZHOU,Fang MEI,Shuai-ning PAN. Location recommendation algorithm based on K-means and matrix factorization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1653-1660. |
| [4] | LIU Zhe, XU Tao, SONG Yu-qing, XU Chun-yan. Image fusion technology based on NSCT and robust principal component analysis model with similar information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1614-1620. |
| [5] | SONG Da-feng, WU Xi-tao, ZENG Xiao-hua, YANG Nan-nan, LI Wen-yuan. Life cycle cost analysis of mild hybrid heavy truck based on theoretical fuel consumption model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1313-1323. |
| [6] | ZHANG Man, SHI Shu-ming. Analysis of state transition characteristics for typical vehicle driving cycles [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1008-1015. |
| [7] | GENG Qing-tian, YU Fan-hua, WANG Yu-ting, GAO Qi-kun. New algorithm for vehicle type detection based on feature fusion [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 929-935. |
| [8] | SU Chang, FU Li-ming, WEI Jun, LI Shuo, HUANG Lei, CAO Yue. Design method in exterior color based Kansei engineering and principal component analysis [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(5): 1414-1419. |
| [9] | MA Shuang, ZHOU Chang-jiu, ZHANG Lian-dong, HONG Wei, TIAN Yan-tao. Twist-lock online recognition based on improved incremental PCA by Kinect [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 890-896. |
| [10] | QIN Da-tong, ZHAN Sen, QI Zheng-gang, CHEN Shu-jiang. Driving cycle construction using K-means clustering method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 383-389. |
| [11] | QIU Chun-ling, TAO Qiang, FAN Run-long, WANG Pei-zhi. Zircon image matching method based on description of SIFT feature by LBP [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1793-1798. |
| [12] | GU Bo-yu,SUN Jun-xi,LI Hong-zuo,LIU Hong-xi,LIU Guang-wen. Face recognition based on eigen weighted modular two-directional two-dimensional PCA [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 828-833. |
| [13] | SONG Huai-bo, SHI Jian-qiang. Pose estimation of varied human faces based on PCA method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 43-46. |
| [14] | BAO Lei, XU Qi-zhi. Spectrum-keeping algorithm for fusing based on PCA [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 88-91. |
| [15] | WANG Zhuo-zheng, JIA Ke-bin. Application of matrix completion and principal component analysis to corrupted image registration [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 78-83. |
|
||