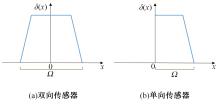
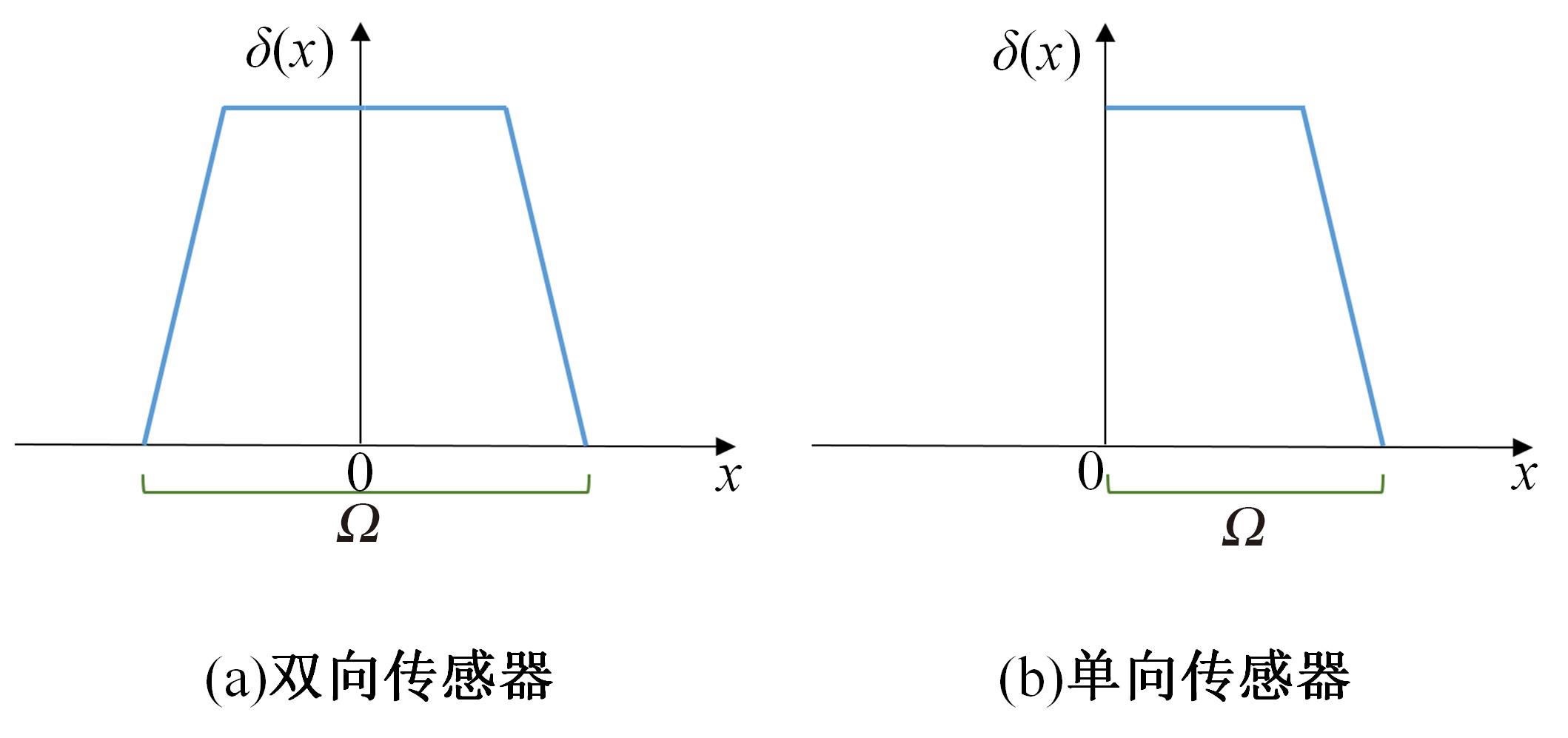
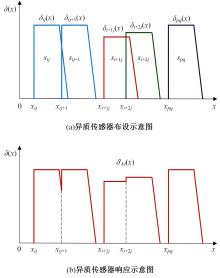
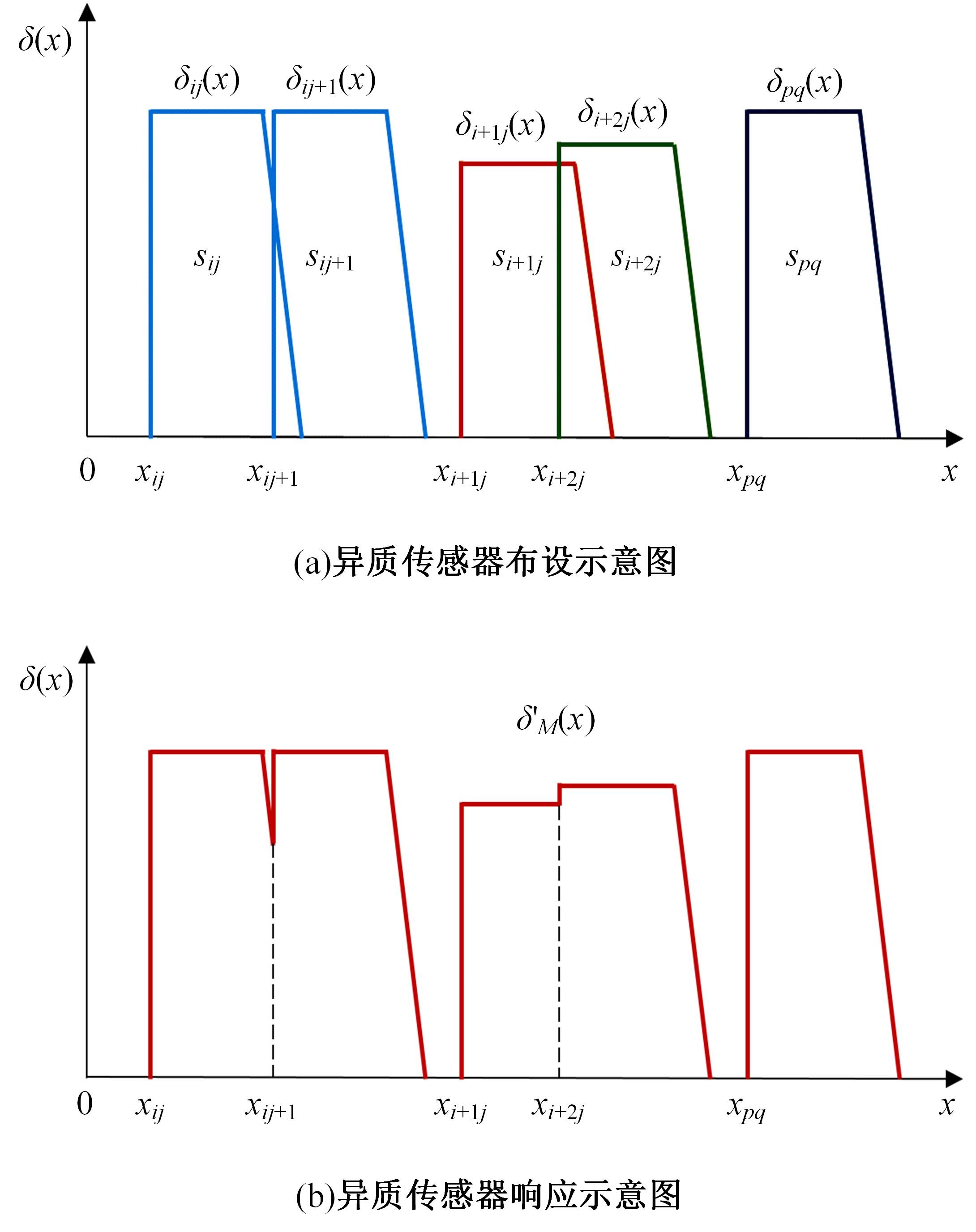
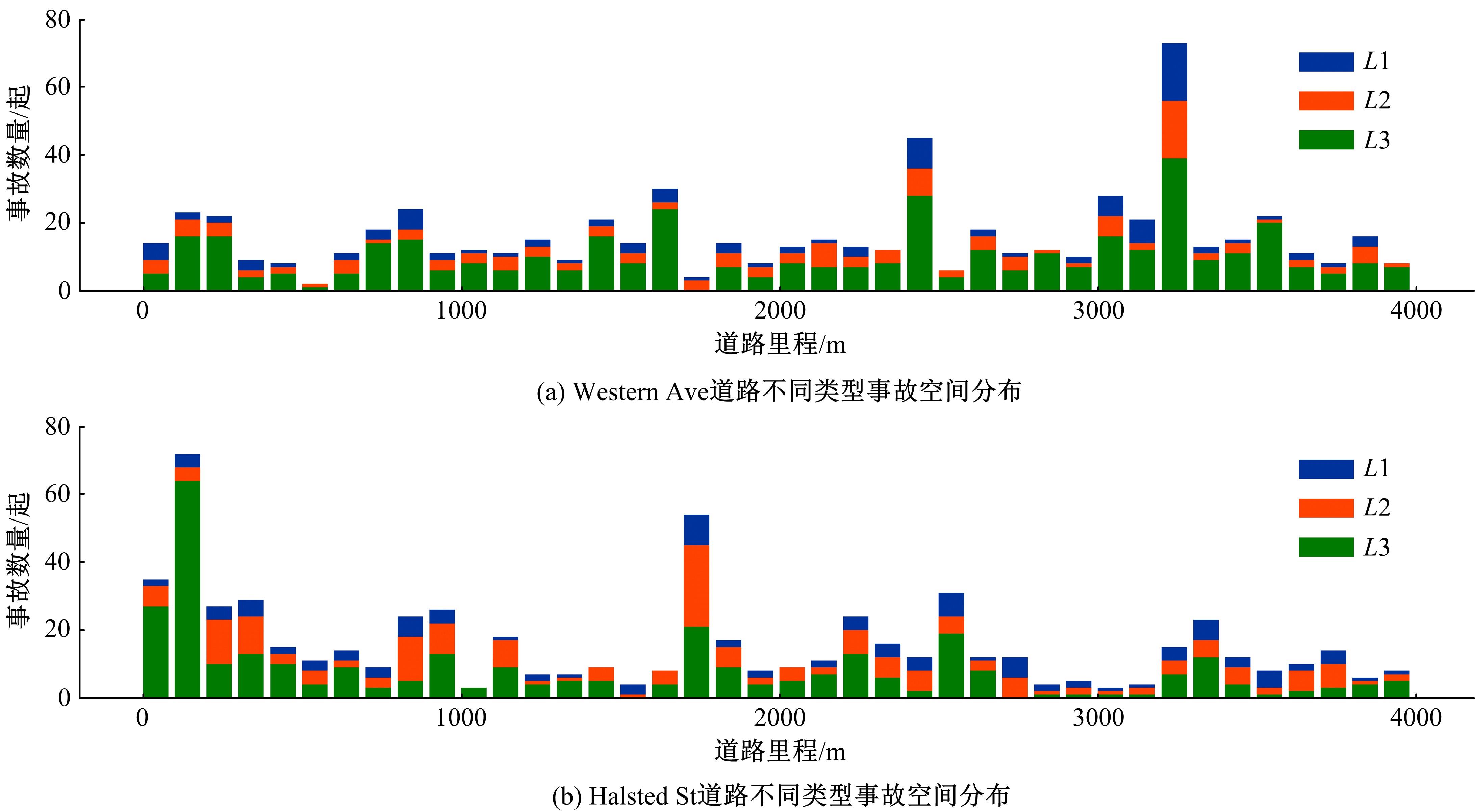
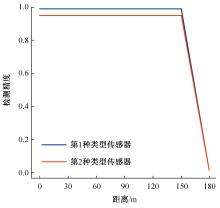
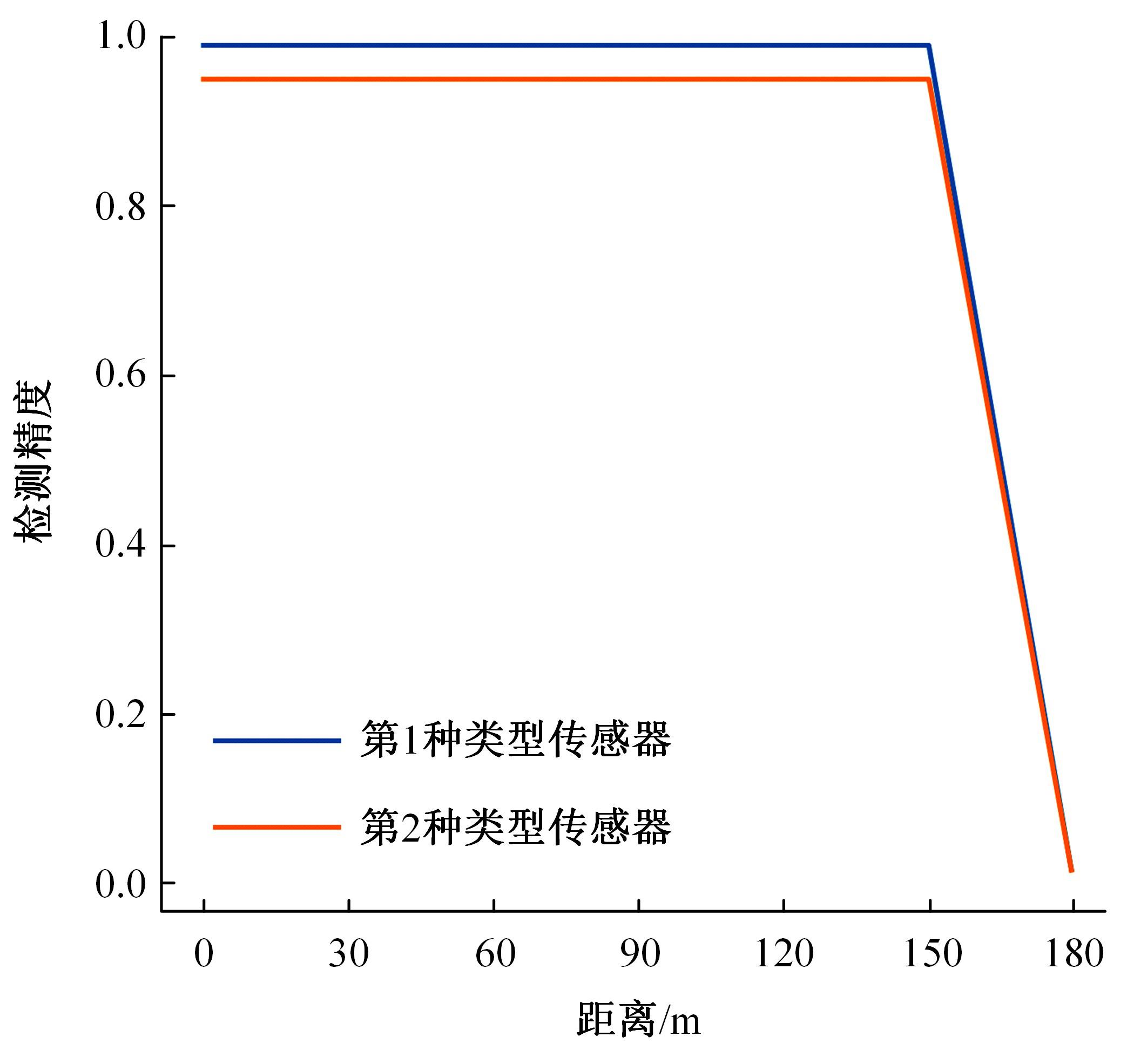
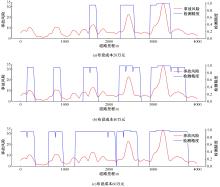
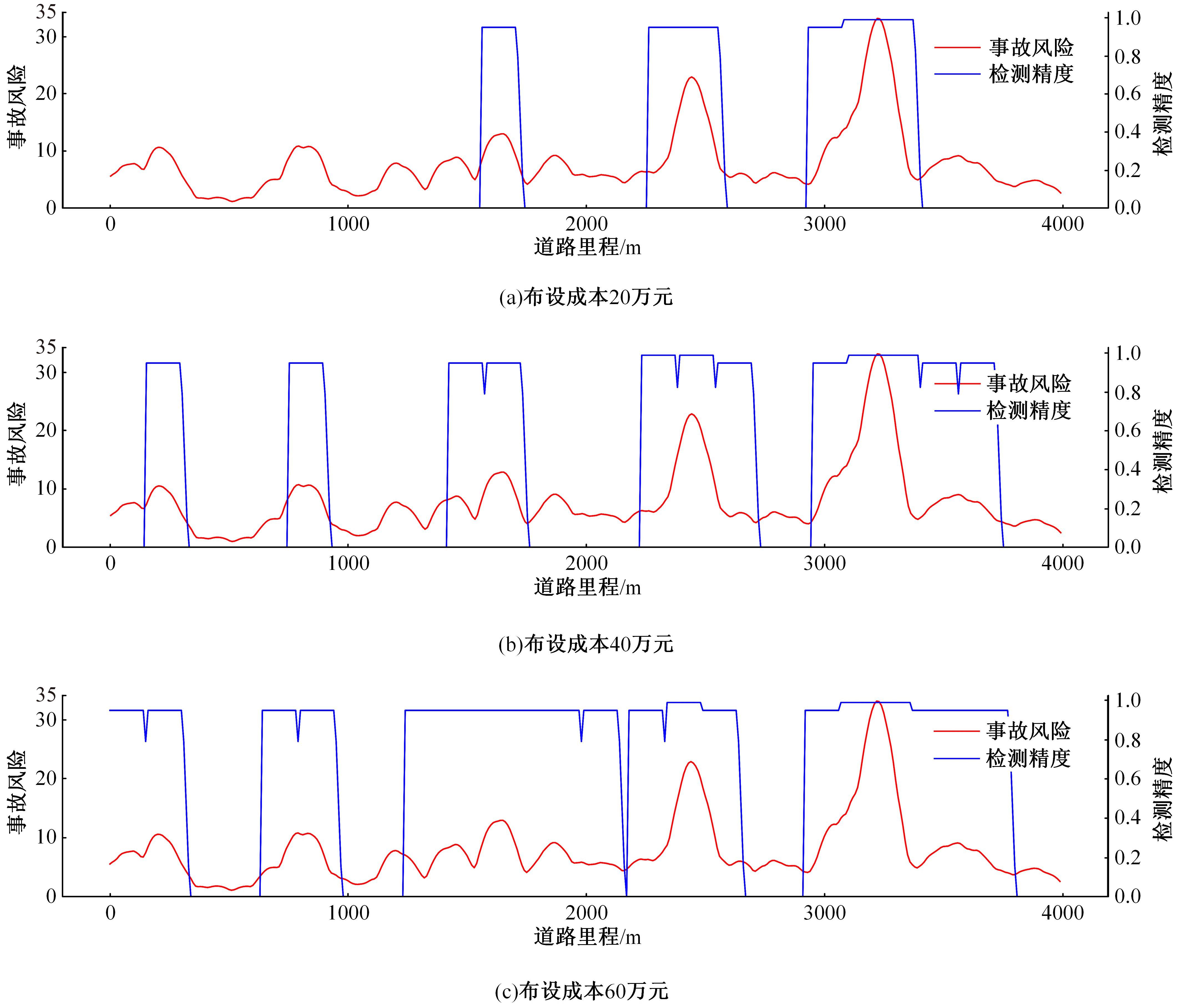
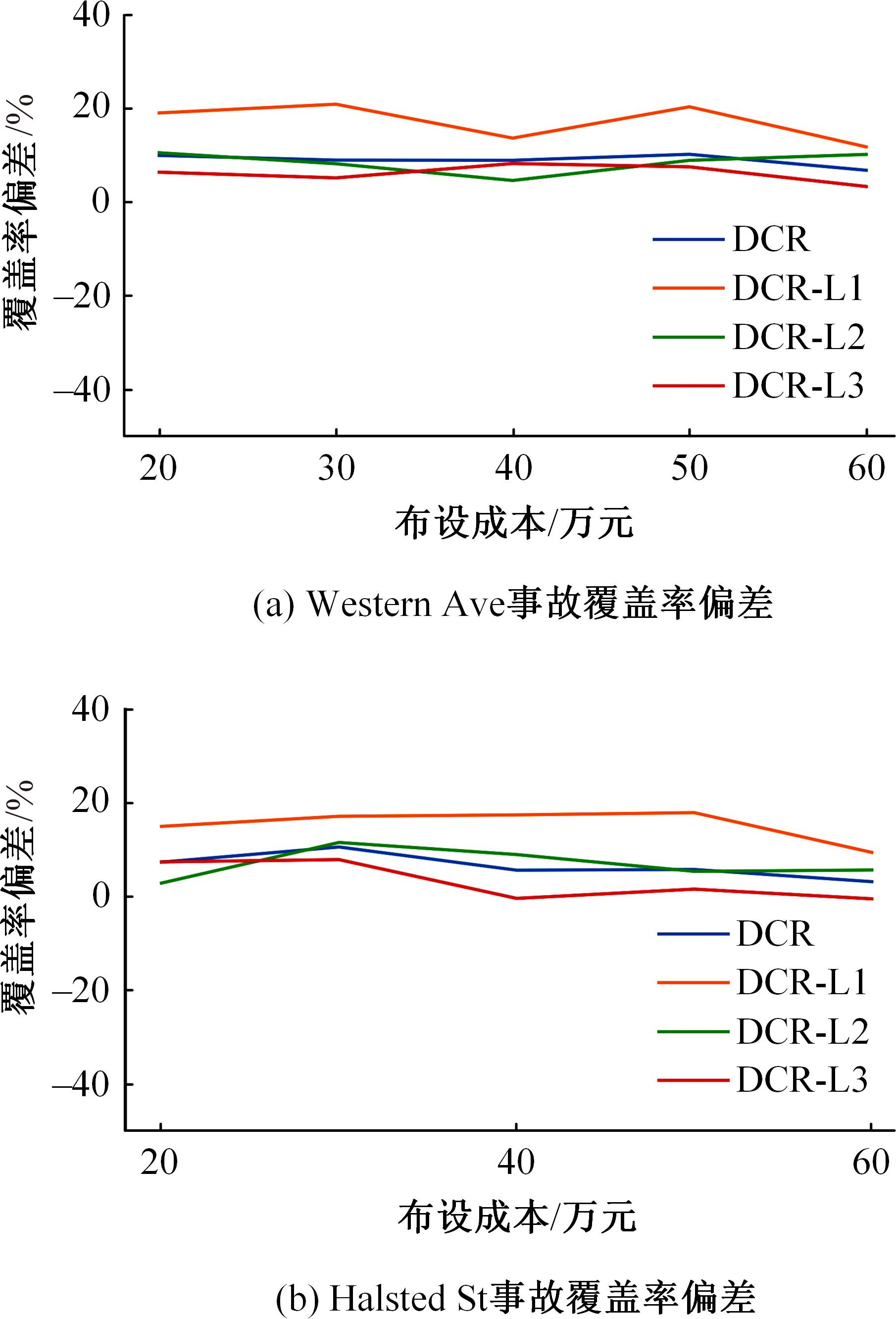
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 969-978.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220656
Previous Articles Next Articles
Deployment of heterogeneous sensors for traffic accident detection and prevention
Qian CAO( ),Zhi-hui LI(
),Zhi-hui LI( ),Peng-fei TAO,Hai-tao LI,Yong-jian MA
),Peng-fei TAO,Hai-tao LI,Yong-jian MA
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U491.5
| 1 | Koble H M, Anderson G, Goldblatt R. Formulation of guidelines for locating freeway sensors[R]. Washington: Federal Highway Admin, 1979. |
| 2 | 姜桂艳. 道路交通状态判别技术与应用[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014. |
| 3 | 杨志清. 服务于安全运营管理的高速公路网信息系统[D]. 上海: 同济大学交通运输工程学院, 2008. |
| Yang Zhi-qing. The study on expressway network information system served for operating safety[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, College of Transportation Engineering, 2008. | |
| 4 | Qin N N, Chen J L. An area coverage algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on differential evolution[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2018, 14(8): 1-11. |
| 5 | Chauhan N, Chauhan S. A novel area coverage technique for maximizing the wireless sensor network lifetime[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2021, 46(4): 3329-3343. |
| 6 | 刘志敏, 贾维嘉, 王国军. 有向传感器网络覆盖预测模型与数量估计[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(12): 3120-3130. |
| Liu Zhi-min, Jia Wei-jia, Wang Guo-jun. Coverage prediction model and number estimation for directional sensor networks[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(12): 3120-3130. | |
| 7 | 刘志敏, 贾维嘉, 王国军. 视觉传感器网络边界部署k-覆盖数量估计[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(2): 79-92. |
| Liu Zhi-min, Jia Wei-jia, Wang Guo-jun. k-Coverage estimation in visual sensor networks based on boundary deployment[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(2): 79-92. | |
| 8 | 范兴刚, 王恒, 蒿翔. 有向传感器网络的覆盖增强算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(2): 368-377. |
| Fan Xing-gang, Wang Heng, Hao Xiang. Algorithm for enhancing coverage ratio in directional sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(2): 368-377. | |
| 9 | 卢毅, 周杰, 万连城. 一种无线传感器网络二维目标覆盖的改进方法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(2): 101-106. |
| Lu Yi, Zhou Jie, Wan Lian-cheng. Improved method for 2D target coverage in wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(2): 101-106. | |
| 10 | Zhao H T, Wang H J, Wu W Y, et al. Deployment algorithms for UAV airborne networks toward on-demand coverage[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(9): 2015-2031. |
| 11 | Wang H J, Zhao H T, Wu W Y, et al. Deployment algorithms of flying base stations: 5G and beyond with UAVs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10009-10027. |
| 12 | Savkin A V, Huang H L. Deployment of unmanned aerial vehicle base stations for optimal quality of coverage[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 321-324. |
| 13 | Sobouti M J, Rahimi Z, Mohajerzadeh A H, et al. Efficient deployment of small cell base stations mounted on unmanned aerial vehicles for the internet of things infrastructure[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(13): 7460-7471. |
| 14 | 李明, 胡江平, 曹晓莉. 异构传感网成本优化的节点部署策略 [J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2021, 48(4): 11-19, 49. |
| Li Ming, Hu Jiang-ping, Cao Xiao-li. Minimum cost of node deployment strategy for heterogeneous sensor networks[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2021, 48(4): 11-19, 49. | |
| 15 | Kashi S S. Area coverage of heterogeneous wireless sensor networks in support of Internet of Things demands[J]. Computing, 2019, 101(4): 363-385. |
| 16 | Al-Fuhaidi B, Mohsen A M, Ghazi A, et al. An efficient deployment model for maximizing coverage of heterogeneous wireless sensor network based on harmony search algorithm [J]. Journal of Sensors, 2020: No. 8818826. |
| 17 | Elma K J, Meenakshi S. Optimal coverage along with connectivity maintenance in heterogeneous wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2021, 12(3): 3647-3658. |
| 18 | Hanh N T, Binh H T T, Hoai N X, et al. An efficient genetic algorithm for maximizing area coverage in wireless sensor networks [J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 488: 58-75. |
| 19 | 陈金林. 基于网络核密度估计城市路网事故黑点鉴别研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2015. |
| Chen Jin-lin. Research on identifying hotspots in the urban road networks based on the network kernel density estimation method[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, School of Transportation, 2015. | |
| 20 | Xie Z X, Jun Y. Kernel density estimation of traffic accidents in a network space[J]. Computers Environment and Urban Systems, 2008, 32(5): 396-406. |
| [1] | Xin ZHANG,Qi-zhou HU,Jun HE,Xiao-yu WU. Traffic condition diagnosis of confluence areas considering traffic infarction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 478-484. |
| [2] | Wei-hua ZHANG,Jia-ming LIU,Li-peng XIE,Heng DING. Lane⁃changing model of autonomous vehicle in weaving area of expressway in intelligent and connected mixed environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [3] | Hao YUE,Qi-yue ZHANG,Zi-yu YANG,Meng-jie REN,Xu ZHANG. Iterative weighted algorithms of static congestion traffic assignment considering spatial queuing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 136-145. |
| [4] | Xiao-jing DU,Rong-han YAO. Evolutionary game mechanism of mandatory lane changing for exiting for intelligent connected bus [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 124-135. |
| [5] | Zhuang-lin MA,Shan-shan CUI,Da-wei HU,Jin WANG. Travel mode choice of traditional car travelers after implementation of driving restriction policy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1981-1993. |
| [6] | Ya-li ZHANG,Rui FU,Wei YUAN,Ying-shi GUO. Classification and recognition model of entering and leaving stops' driving style considering energy consumption [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [7] | Chao-ying YIN,Ying LU,Chun-fu SHAO,Jian-xiao MA,De-jie XU. Impacts of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial autocorrelation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
| [8] | Heng-yan PAN,Yong-gang WANG,De-lin LI,Jun-xian CHEN,Jie SONG,Yu-quan YANG. Evaluating and forecasting rear⁃end collision risk of long longitudinal gradient roadway via traffic conflict [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| [9] | Kai LU,Guang-hui XU,Zhi-hong YE,Yong-jie LIN. Algebraic method of bidirectional green wave coordination control for the head of the platoon considering the clearance time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 421-429. |
| [10] | Qian CAO,Zhi-hui LI,Peng-fei TAO,Yong-jian MA,Chen-xi YANG. Traffic accident risk assessment method for road network considering risk heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [11] | Xin ZHANG,Wei-hua ZHANG. Safety analysis of main line under different traffic conditions in expressway confluence area [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1308-1314. |
| [12] | Da-yi QU,Zi-xu ZHAO,Yan-feng JIA,Tao WANG,Qiong-hui LIU. Car⁃following dynamics characteristics and model based on Lennard⁃Jones potential [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2549-2557. |
| [13] | Chun-jiao DONG,Dai-yue DONG,Cheng-xiang ZHU-GE,Li ZHEN. Trip characteristics and decision⁃making behaviors modeling of electric bicycles riding [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
| [14] | Da-yi QU,Kai-xian HEI,Hai-bing GUO,Yan-feng JIA,Tao WANG. Game behavior and model of lane-changing on the internet of vehicles environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 101-109. |
| [15] | Wen-hui ZHANG,Jing YI,Wei LIU,Qiu-ying YU,Lian-zhen WANG. Injury mechanism of occupants in bus during rear-end crash based on MADYMO [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 118-126. |
|
||