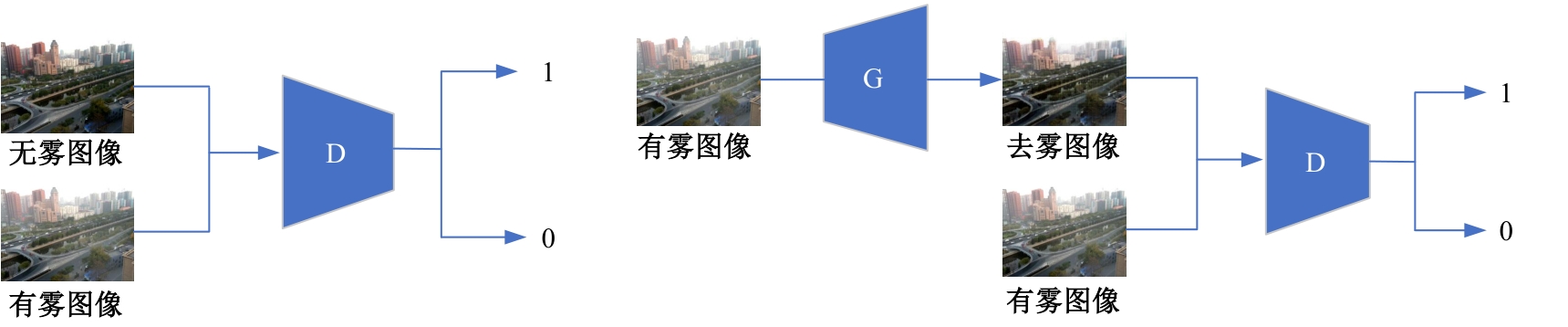
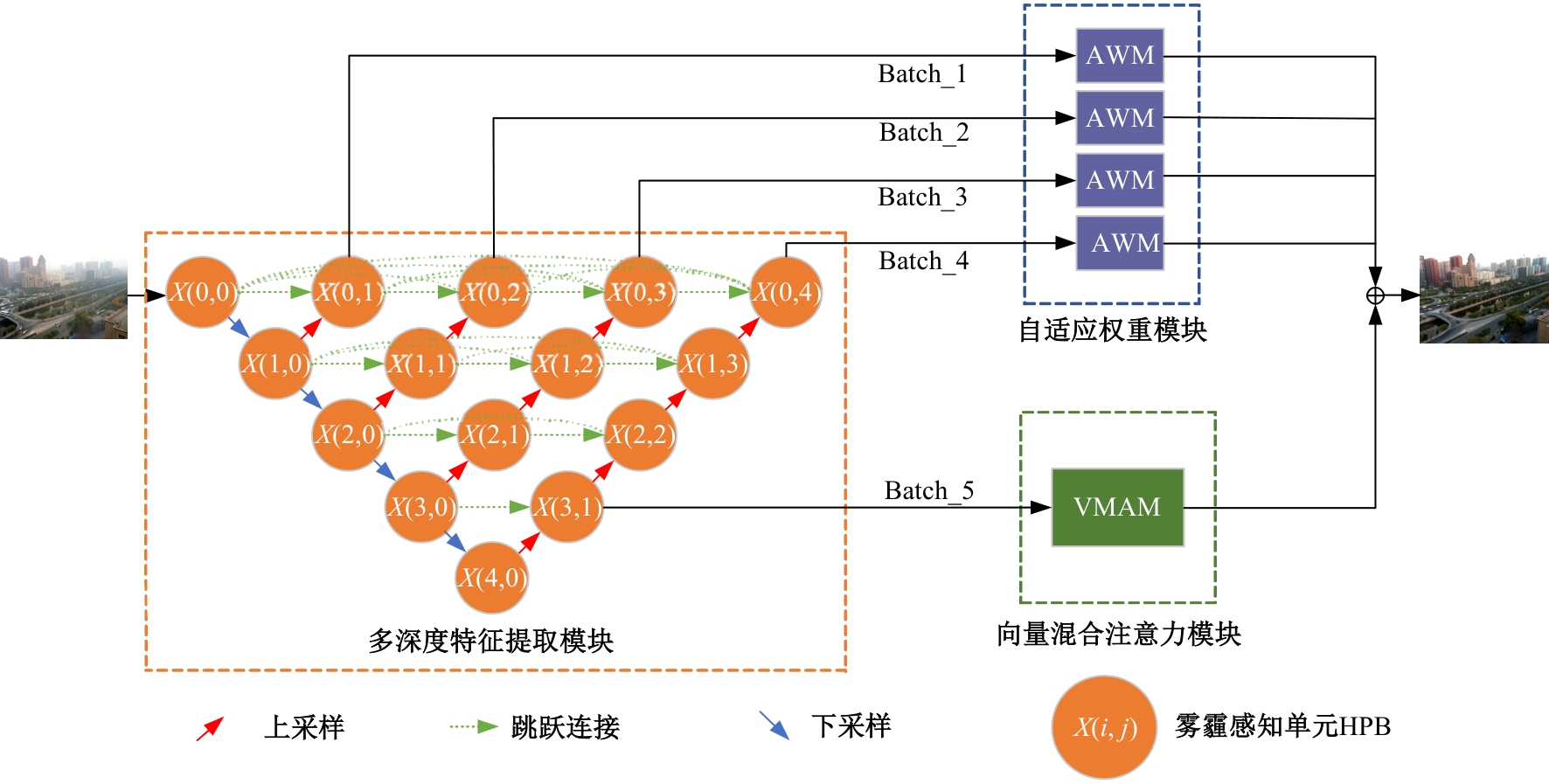
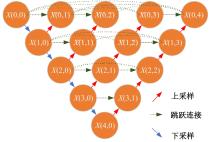
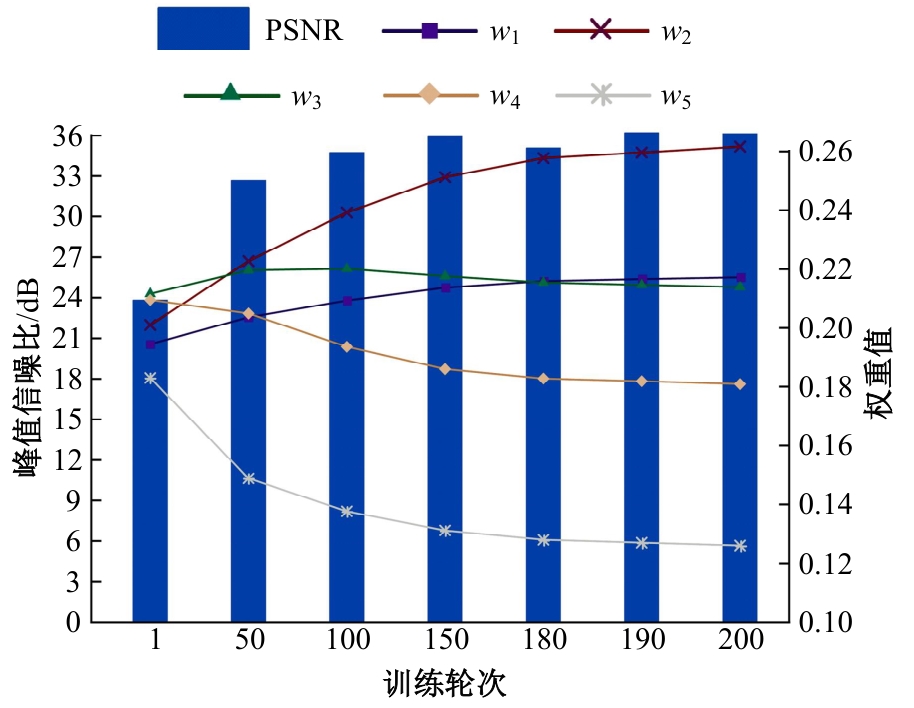
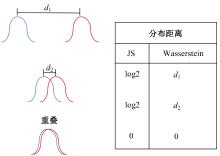
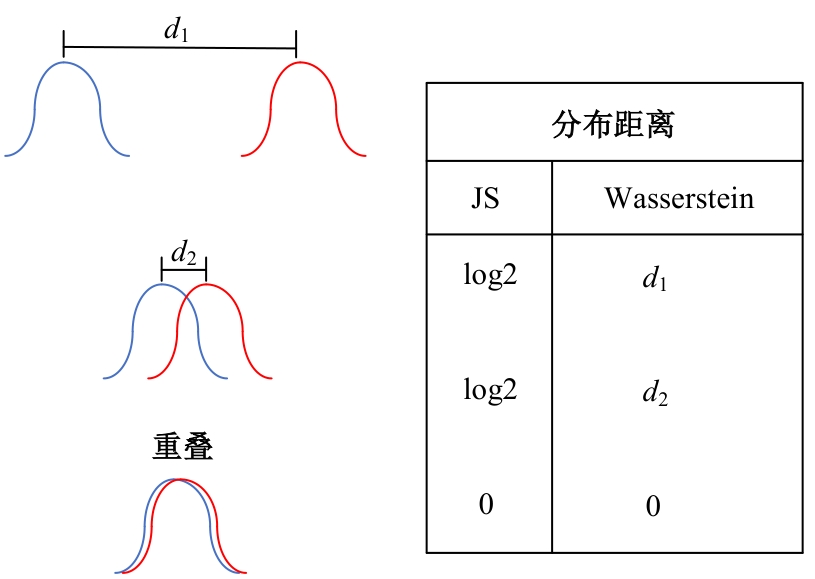
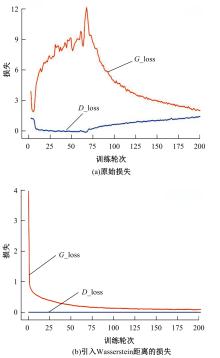
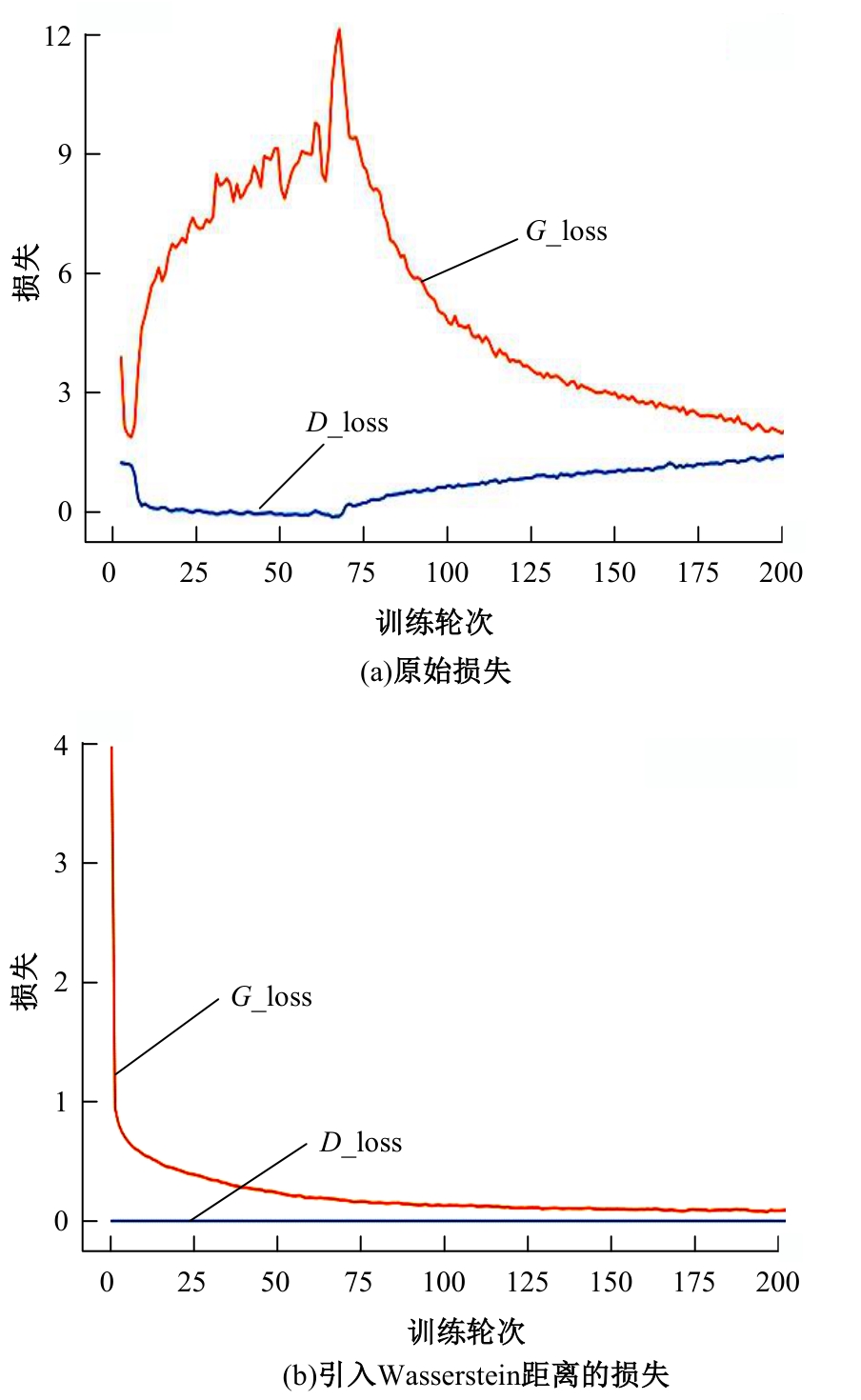
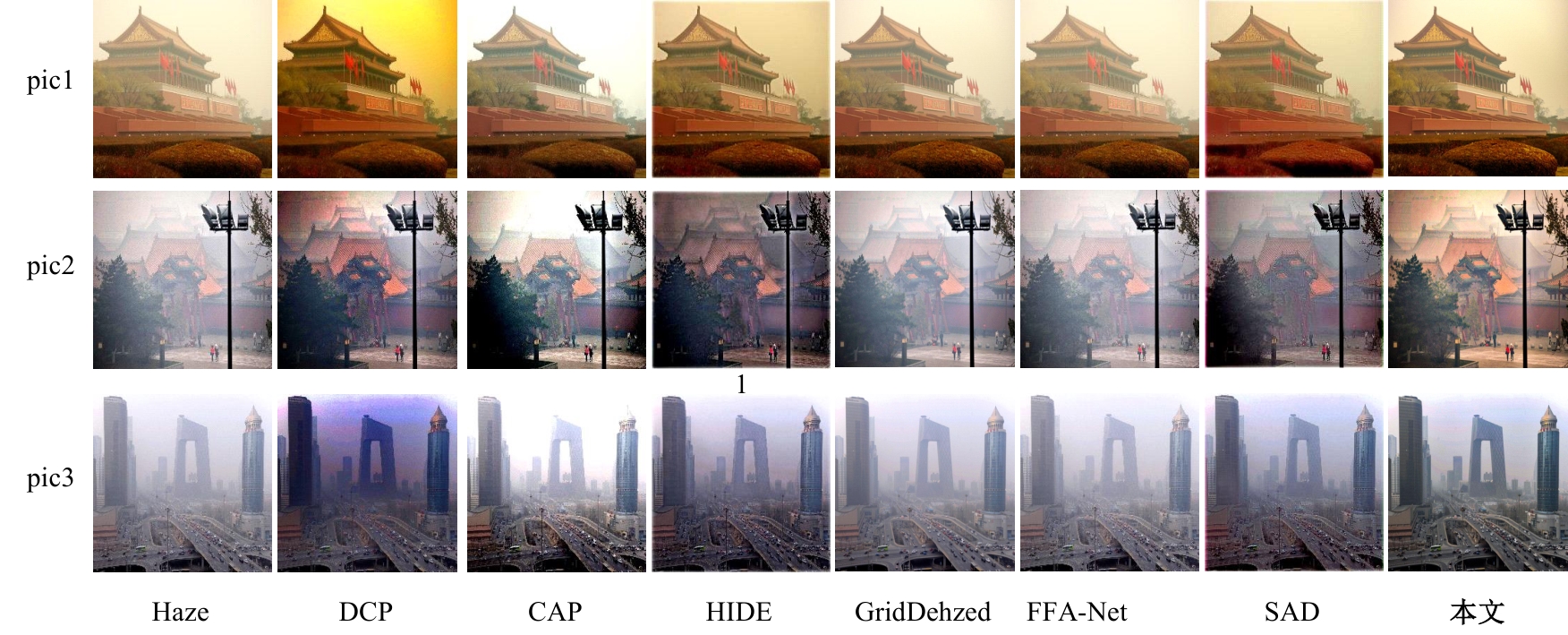
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 2103-2113.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230813
Previous Articles Next Articles
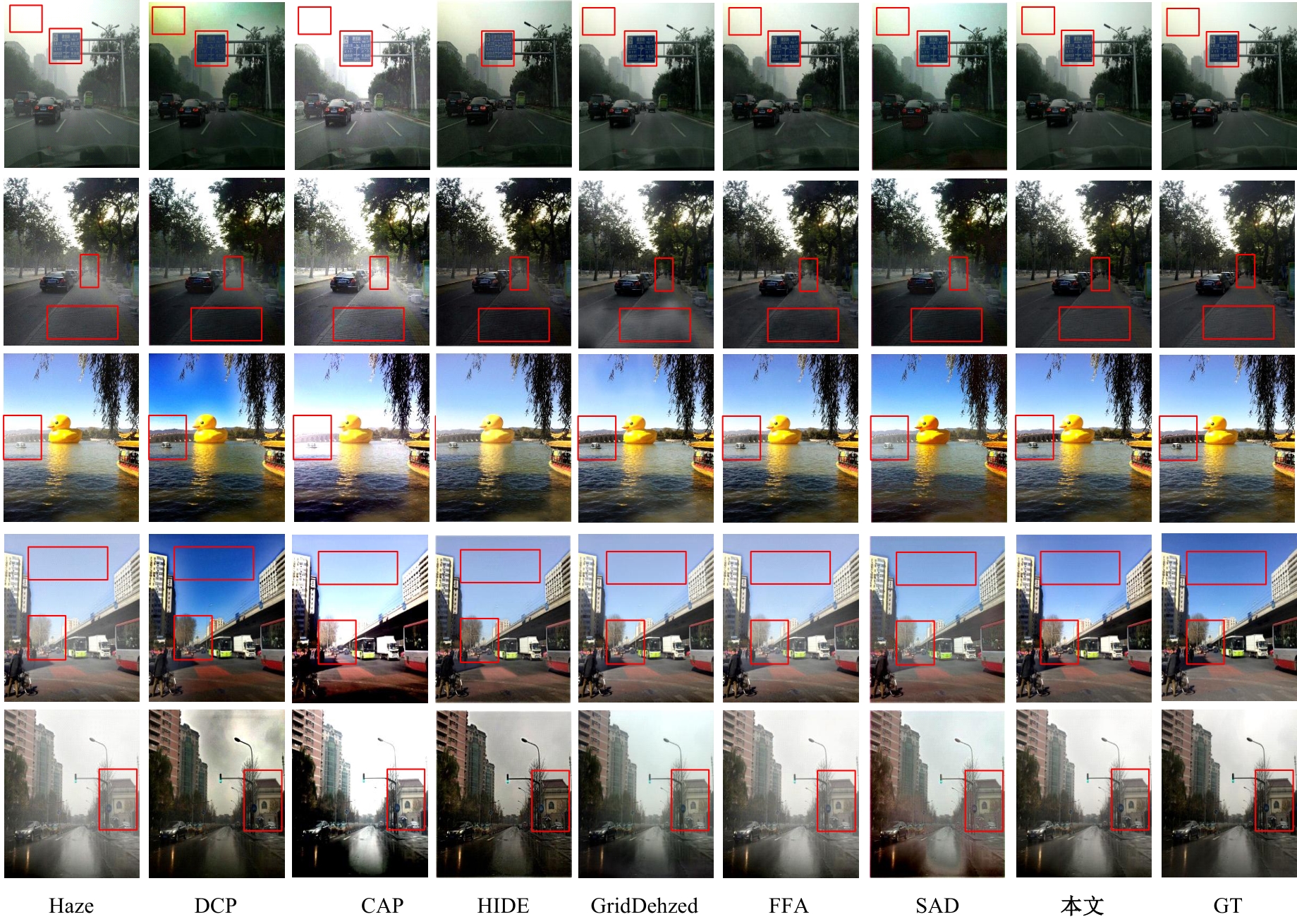
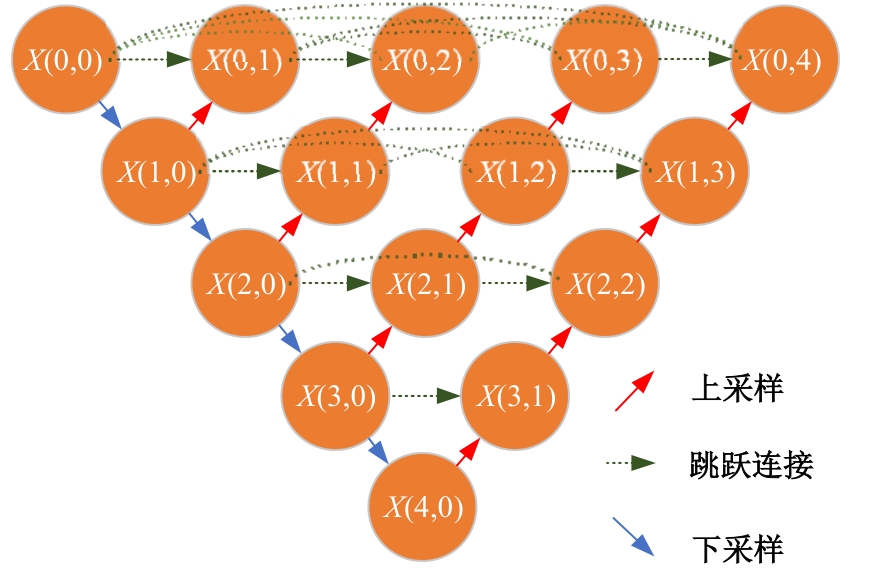
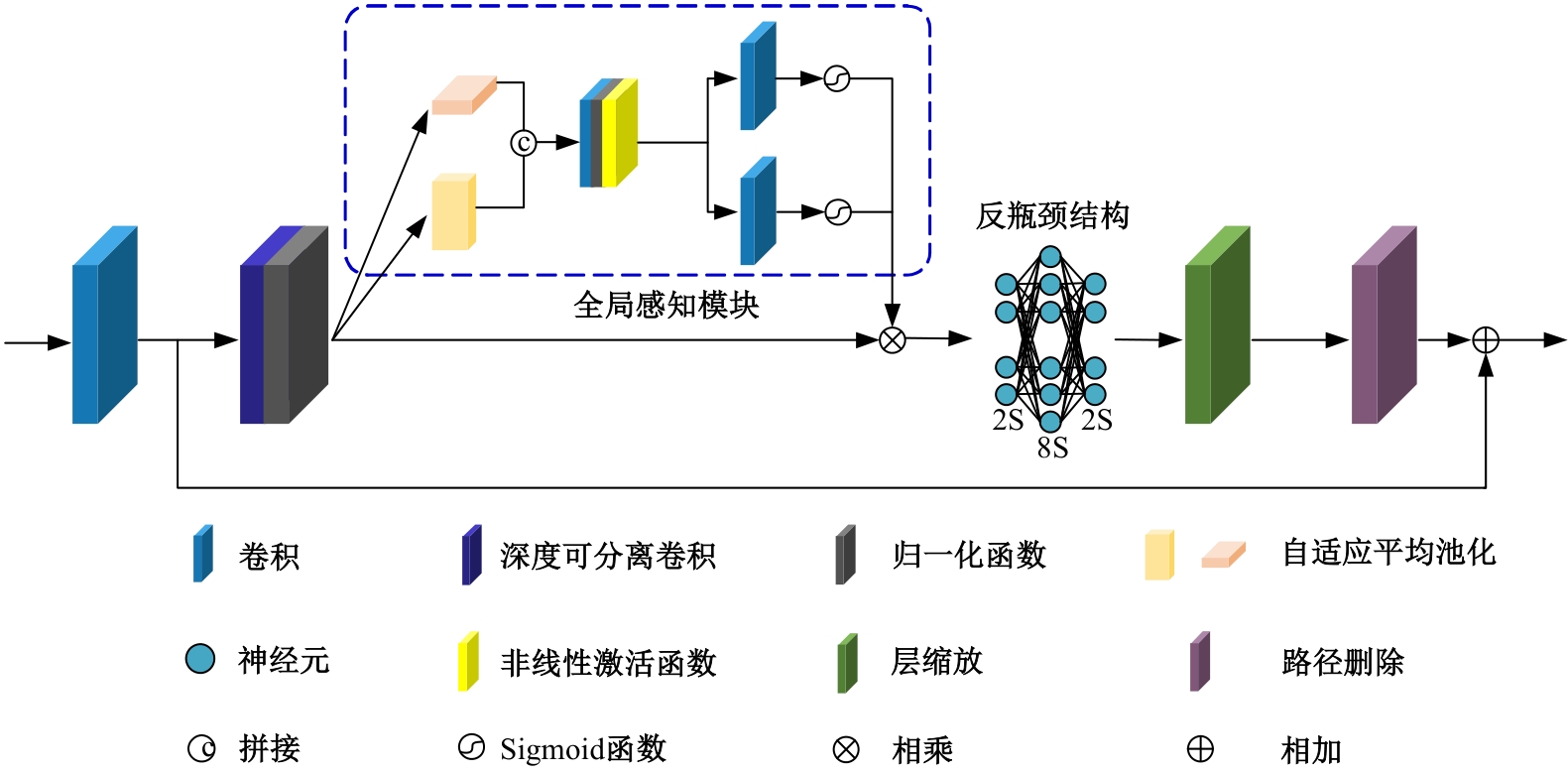
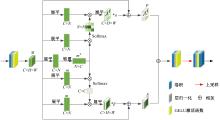
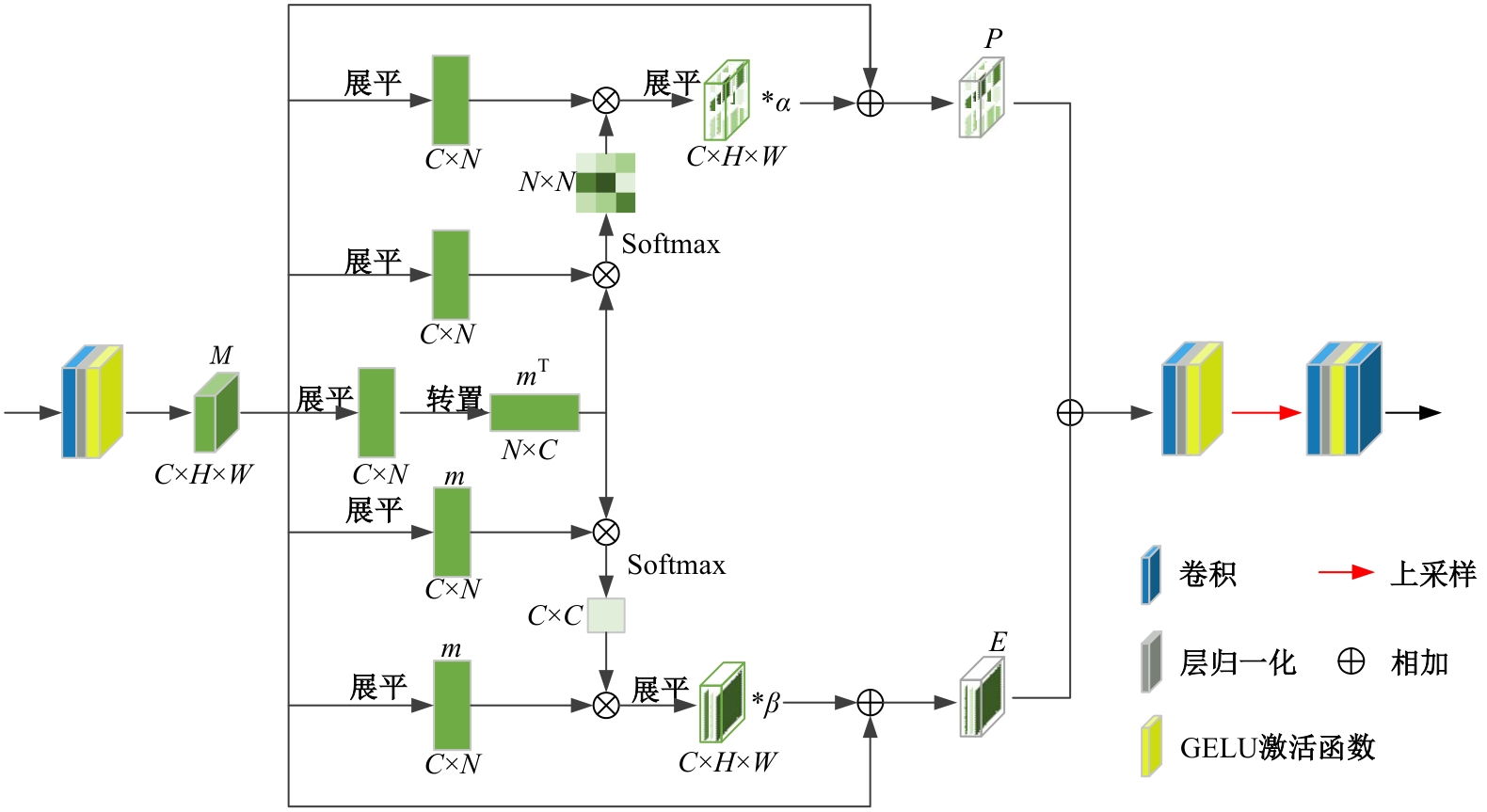
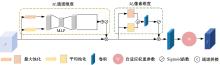
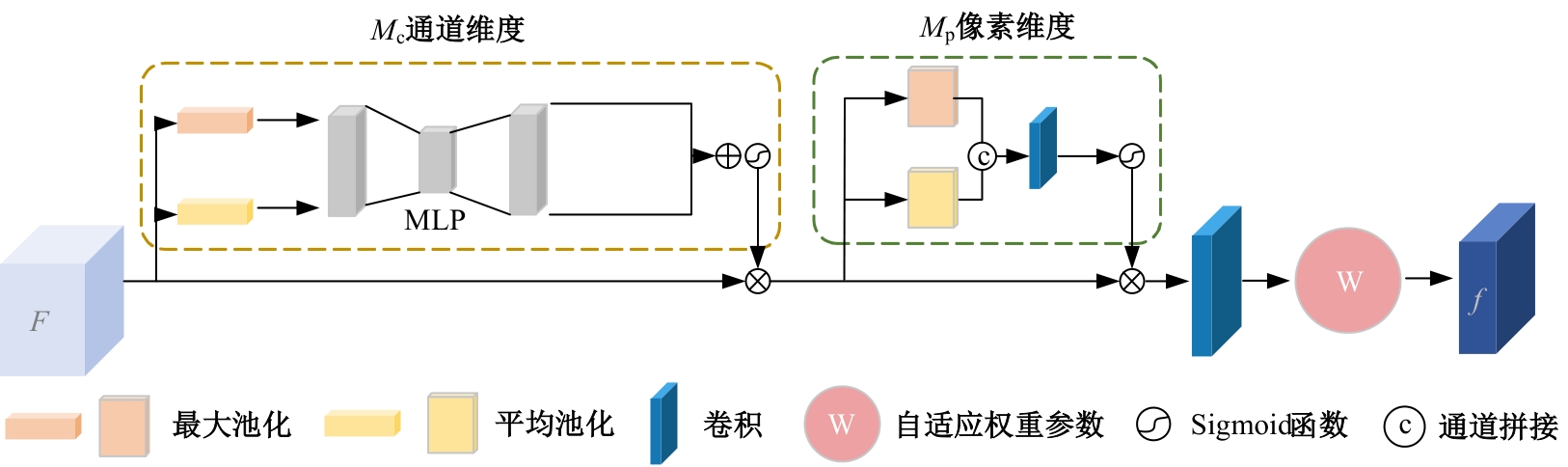
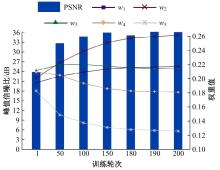
Multi⁃depth adaptive fusion dehazing generation network
Bin WEN1,2( ),Shun PENG1,2,Chao YANG1(
),Shun PENG1,2,Chao YANG1( ),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
- 1.School of Electrical and New Energy,China Three Gorges University,Yichang 443002,China
2.Hubei Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Power Transmission Line,Yichang 443002,China
3.School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 611731,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Yao D N L, Bade A, Zolkifly I A, et al. A naive but effective post-processing approach for dark channel prior (DCP)[C]∥Data Science and Emerging Technologies: Proceedings of DaSET 2022, Petaling Jaya, Malaysia, 2022: 67-76. |
| [2] | He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353. |
| [3] | Raanan F. Dehazing using color-lines[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, 34(1): 1-14. |
| [4] | Tan R T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image[C]∥Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2008), Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1-8. |
| [5] | Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. 2015, 24(11): 3522-3533. |
| [6] | Cai B, Xu X, Jia K, et al. Dehazenet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198. |
| [7] | Li B, Peng X, Wang Z, et al. Aod-net: all-in-One dehazing network[C]∥proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 4780-4788. |
| [8] | Liu X, Ma Y, Shi Z, et al. Grid dehaze net: attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 2019: 7313-7322. |
| [9] | Qu Y, Chen Y, Huang J, et al. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, 2019: 8152-8160. |
| [10] | Dong Y, Liu Y, Zhang H, et al. Fd-gan: generative adversarial networks with fusion-discriminator for single image dehazing[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 10729-10736. |
| [11] | Mehta A, Sinha H, Narang P, et al. HIDeGan: a hyperspectral-guided image dehazing GAN[J]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA, 2020: 846-856. |
| [12] | Qin X, Wang Z L, Bai Y C, et al. FFA-Net: feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing[J/OL]. [2023-07-22]. |
| [13] | Yang X, Yan J C, Ming Q, et al. Rethinking rotated object detection with gaussian wasserstein distance loss[J/OL]. [2023-07-23]. |
| [14] | Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967-5976. |
| [15] | Zhao C, Shuai R, Ma L, et al. Segmentation of skin lesions image based on U-Net++[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(6): 8691-8717. |
| [16] | Fu H X, Song G Q, Wang Y C. Improved YOLOv4 marine target detection combined with CBAM[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13(4): No.623. |
| [17] | Li B, Ren W, Fu D, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(1): 492-505. |
| [18] | Liu Y, Zhu L, Pei S D, et al. From synthetic to real: image dehazing collaborating with unlabeled real data[J/OL]. [2023-07-23]. |
| [19] | Sun Z, Zhang Y, Bao F, et al. SADnet: semi-supervised single image dehazing method based on an attention mechanism[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2022, 18(2): 1-23. |
| [20] | Manu C M, Sreeni K G. GANID: a novel generative adversarial network for image dehazing[J]. The Visual Computer, 2022, 39: 2923-3936. |
| [1] | Ru-bo ZHANG,Shi-qi CHANG,Tian-yi ZHANG. Review on image information hiding methods based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1497-1515. |
| [2] | Ya-li XUE,Tong-an YU,Shan CUI,Li-zun ZHOU. Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [3] | Wei-zhi NIE,Fei YIN,Yi-shan SU. Review of task⁃driven imaging sonar for underwater target recognition approaches [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1163-1175. |
| [4] | De-qiang CHENG,Gui LIU,Qi-qi KOU,Jian-ying ZHANG,He JIANG. Lightweight image super⁃resolution network based on adaptive large kernel attention fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 1015-1027. |
| [5] | Xi ZHANG,Shao-ping KU. Facial super-resolution reconstruction method based on generative adversarial networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 333-338. |
| [6] | Jin DUAN,An-ni YAO,Zhen WANG,Lin-tao YU. Improved sparrow search algorithm optimizes coverage in wireless sensor networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 761-770. |
| [7] | Jian XIAO,Jing-wei LIU,Xin HU,Xiao-gang QI. TDOA⁃AOA location based on improved african vulture algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3558-3567. |
| [8] | Yong WANG,Yu-xiao BIAN,Xin-chao LI,Chun-ming XU,Gang PENG,Ji-kui WANG. Image dehazing algorithm based on multiscale encoding decoding neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3626-3636. |
| [9] | Mian-shu CHEN,Lu-lu YU,Xiao-ni LI,Hong-yu ZHENG. Loop detection based on uniform ORB [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2666-2675. |
| [10] | Yu-ting SU,Ji WANG,Wei ZHAO,Pei-guang JING. Dynamic graph convolutional neural network for image sentiment distribution prediction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2601-2610. |
| [11] | Qiang GUO,Guo-hui ZHU,Wan-chen LI. TDOA/FDOA localization based on chaotic sparrow search algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 593-600. |
| [12] | Hou⁃jie LI,Fa⁃sheng WANG,Jian⁃jun HE,Yu ZHOU,Wei LI,Yu⁃xuan DOU. Pseudo sample regularization Faster R⁃CNN for traffic sign detection [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1251-1260. |
| [13] | Hua-wei JIANG,Zhen YANG,Xin ZHANG,Qian-lin DONG. Research progress of image dehazing algorithms [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1169-1181. |
| [14] | De-xing WANG,Ruo-you WU,Hong-chun YUAN,Peng GONG,Yue WANG. Underwater image restoration based on multi-scale attention fusion and convolutional neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [15] | Jing JIN,Jian-wu DANG,Yang-ping WANG,Dong SHEN. Multi⁃cue particle filter tracking based on fuzzy statistical texture features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1111-1120. |
|