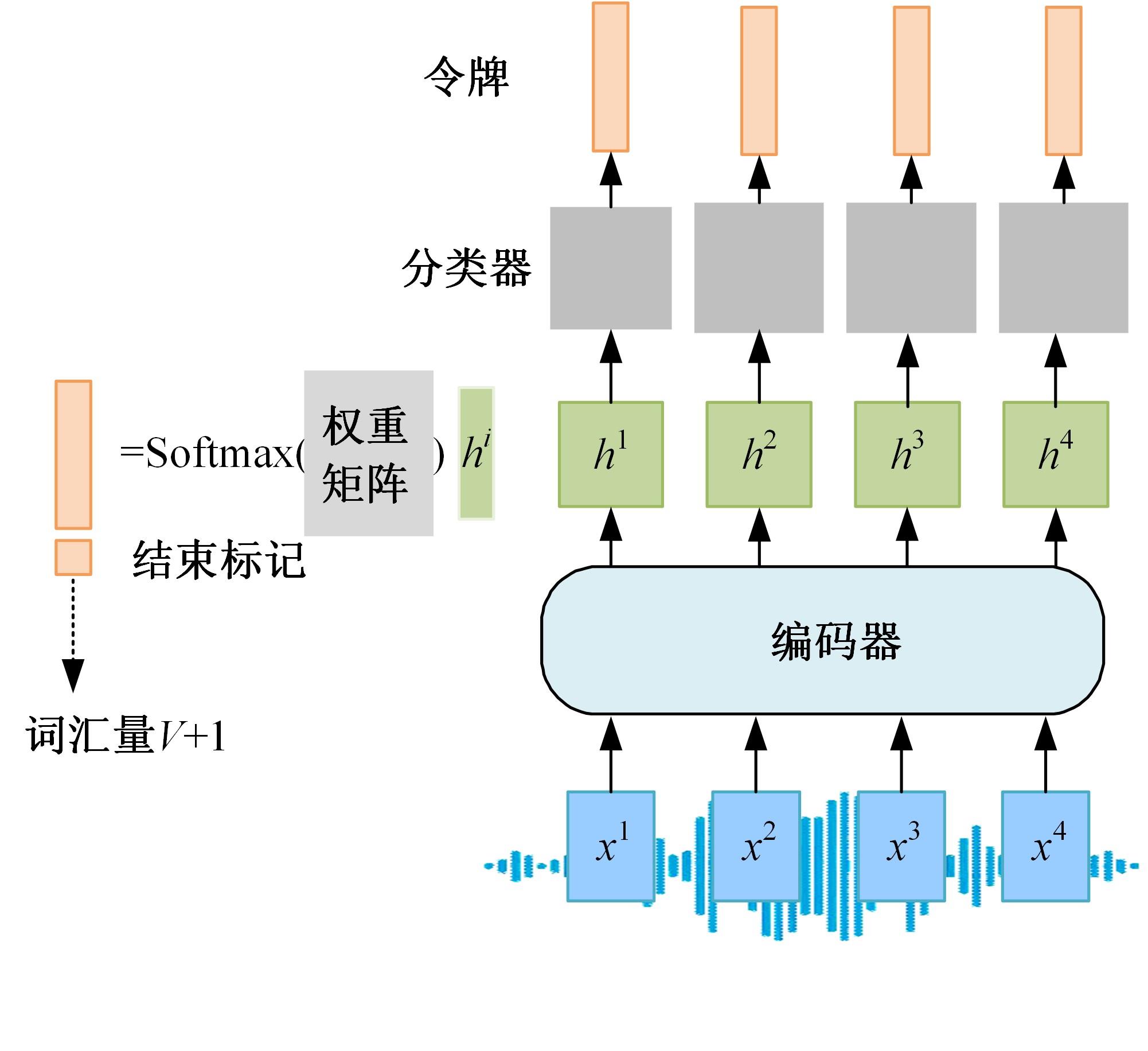
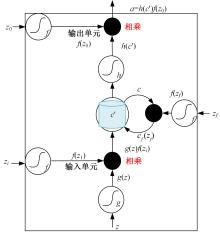
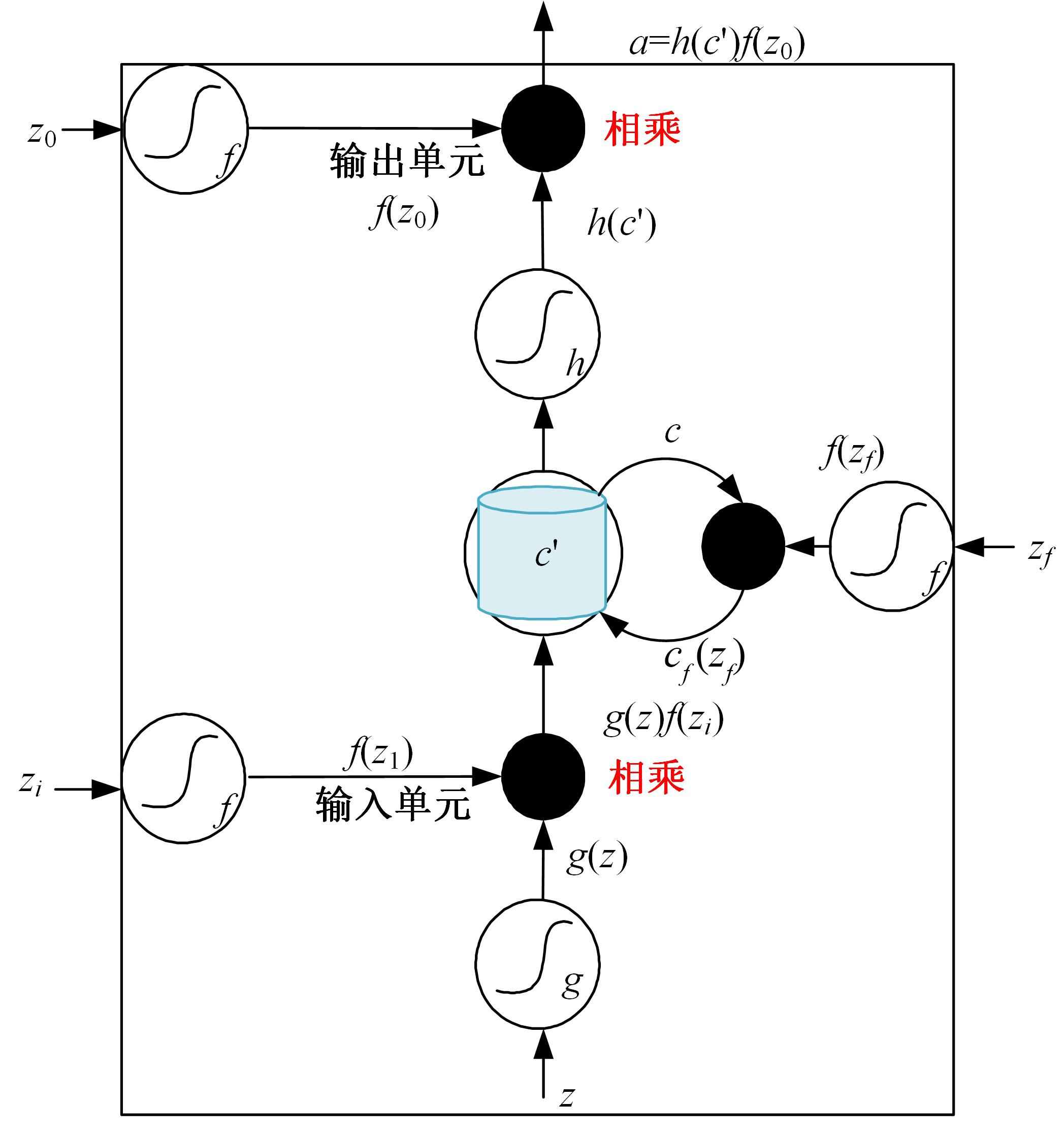
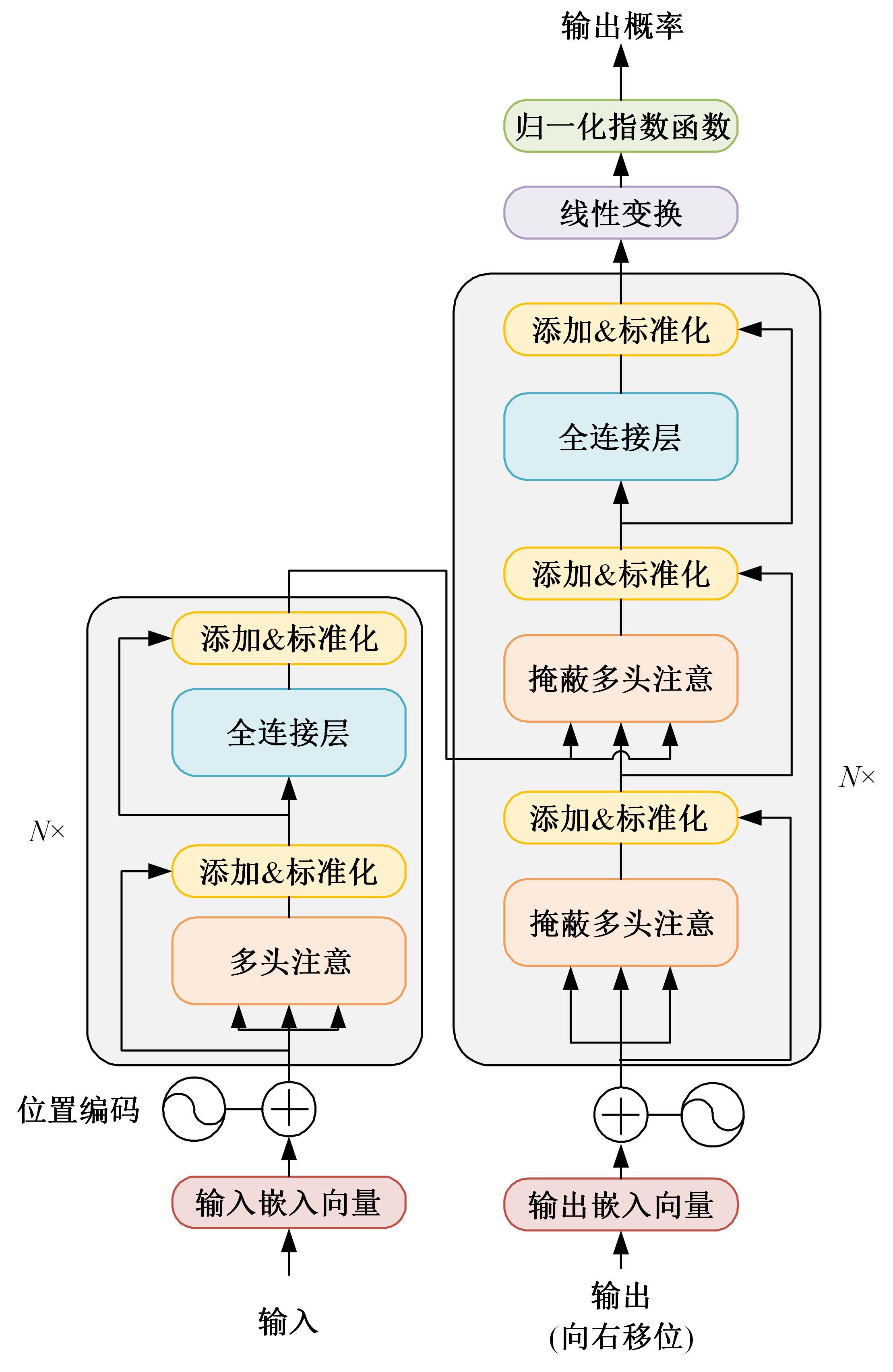
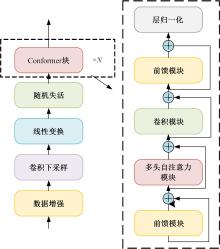
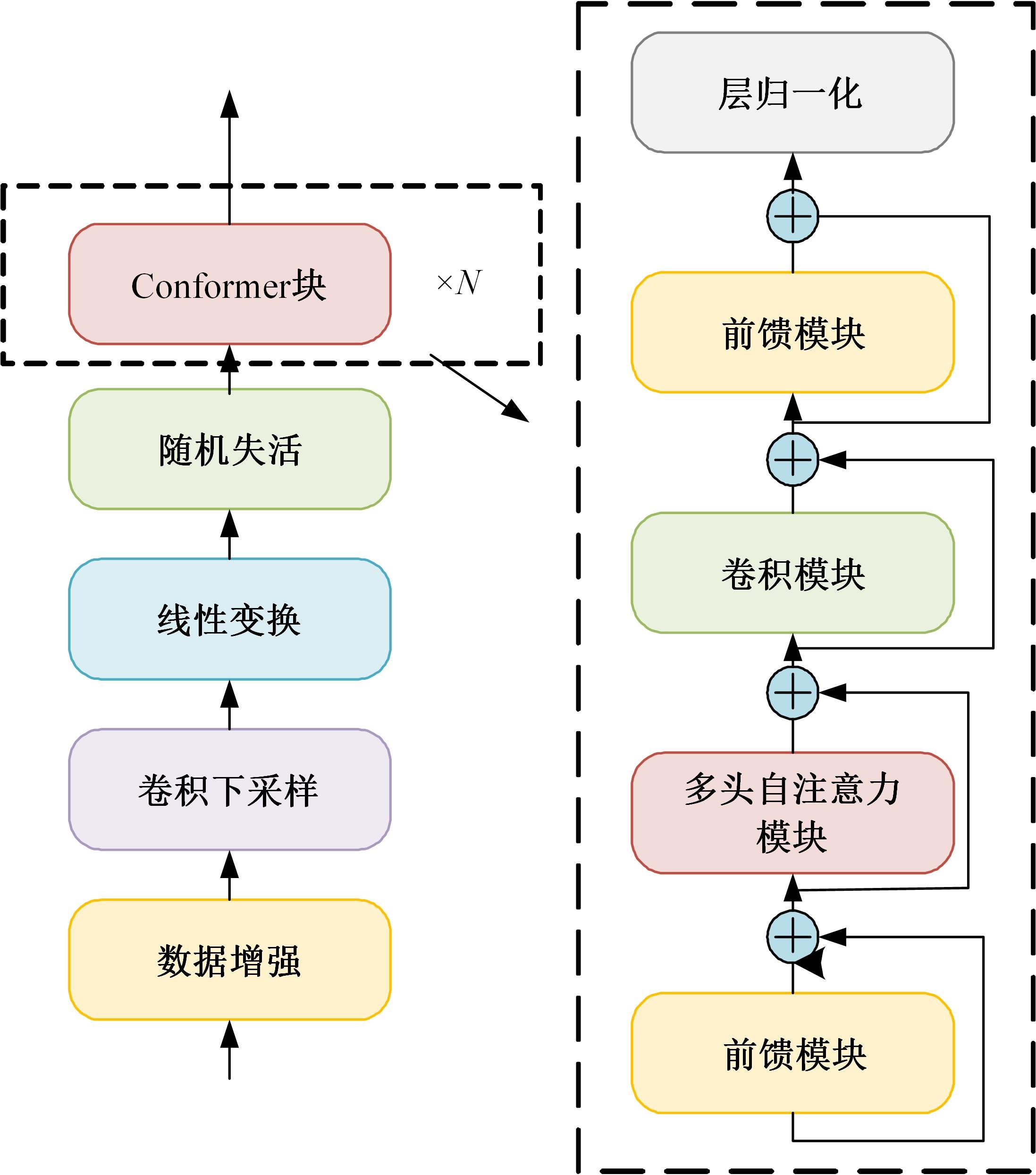
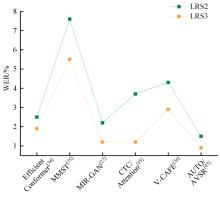
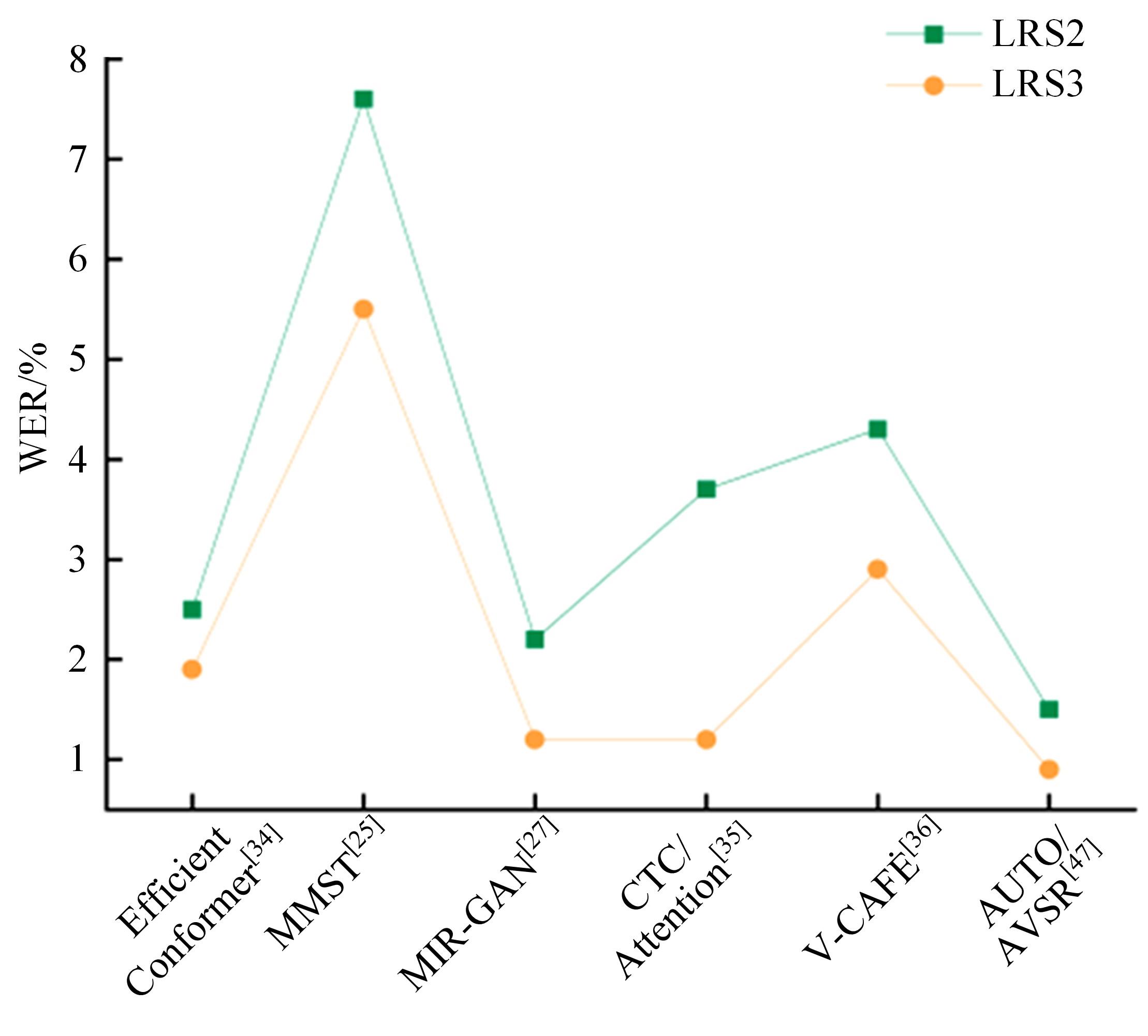
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2984-2993.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240209
Connectionism based audio-visual speech recognition method
Na CHE1,2,3( ),Yi-ming ZHU1,Jian ZHAO1,2,3(
),Yi-ming ZHU1,Jian ZHAO1,2,3( ),Lei SUN1,Li-juan SHI2,3,4,Xian-wei ZENG1
),Lei SUN1,Li-juan SHI2,3,4,Xian-wei ZENG1
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Human Health State Identification and Function Enhancement,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Rehabilitation and Barrier?free Access for the Disabled,Ministry of Education,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
4.School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TN912.34
| 1 | Ibrahim T W S a M Z. A review of audio-visual speech recognition[J].Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering,2018,10(1-4):35-40. |
| 2 | 苏荣峰.多重影响因素下的语音识别系统研究[D].深圳:中国科学院大学中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院,2020. |
| Su Rong-feng.Research on speech recognition system under multiple influencing factors[D].Shenzhen:Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2020. | |
| 3 | Tamura S, Ninomiya H, Kitaoka N, et al. Audio-visual speech recognition using deep bottleneck features and high-performance lipreading[C]∥Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Hongkong,China,2015:575-582. |
| 4 | Zeng Z, Tu J, Pianfetti B, et al. Audio-visual affect recognition through multi-stream fused HMM for HCI[C]∥IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'05), DiegoSan,America,2005:967-972. |
| 5 | 魏斌. 符号主义与联结主义人工智能的融合路径分析[J].自然辩证法研究,2022,38(2): 23-29. |
| Wei Bin. Analysis of the integration path of symbolism and connectionism of artificial intelligence[J].Study of Dialectics of Nature,2022,38(2):23-29. | |
| 6 | Zhang B, Zhu J, Su H.Toward the third generation artificial intelligence[J].Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(2): 1-19. |
| 7 | 焦李成, 杨淑媛, 刘芳, 等. 神经网络七十年:回顾与展望[J].计算机学报,2016,39 (8):1697-1716. |
| Jiao Li-cheng, Yang Shu-yuan, Liu Fang, et al. Seventy years of neural networks: retrospect and prospect[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers,2016,39(8):1697-1716. | |
| 8 | Ivanko D, Ryumin D, Karpov A. A review of recent advances on deep learning methods for audio-visual speech recognition[J].Mathematics, 2023, 11(12): 2665. |
| 9 | Wang D, Wang X D, Lyu S H.An overview of end-to-end automatic speech recognition[J].Symmetry, 2019, 11(8): 1018. |
| 10 | Yu W, Zeiler S, Kolossa D. Fusing information streams in end-to-end audio-visual speech recognition[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Toronto, Canada, 2021: 3430-3434. |
| 11 | Tsunoda R, Aihara R, Takashima R, et al. Speaker-targeted audio-visual speech recognition using a hybrid CTC/attention model with interference loss[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 251-255. |
| 12 | Yu W, Zeiler S, Kolossa D. Reliability-based large-vocabulary audio-visual speech recognition[J].Sensors, 2022, 22(15): 5501. |
| 13 | Lee Y H, Jang D W, Kim J B, et al. Audio–visual speech recognition based on dual cross-modality attentions with the Transformer model[J].Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(20): 7263. |
| 14 | Petridis S, Stafylakis T, Ma P, et al. Audio-visual speech recognition with a hybrid CTC/attention architecture[C]∥IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop(SLT), Athens, Greece, 2018:513-520. |
| 15 | Xu K, Li D W, Cassimatis N, et al. LCANet: end-to-end lipreading with cascaded attention-CTC[C]∥2018 13 th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi'an, China, 2018: 548-555. |
| 16 | 姜囡, 庞永恒, 高爽. 基于注意力机制语谱图特征提取的语音识别[J].吉林大学学报:理学版,2024,62(2): 320-330. |
| Jiang Nan, Pang Yong-heng, Gao Shuang. Speech recognition based on attention mechanism and spectrogram feature extraction[J].Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition),2024,62(2): 320-330. | |
| 17 | Chan W, Jaitly N, Le Q V, et al. Listen, attend and spell[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Shanghai,China,2015: 20-25. |
| 18 | Chung J S, Senior A W, Vinyals O, et al. Lip reading sentences in the wild[C]∥Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu,America,2017: 3444-3453. |
| 19 | Fernandez-Lopez A, Karaali A, Harte N, et al. Cogans for unsupervised visual speech adaptation to new speakers[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Barcelona,Spain,2020:6294-6298. |
| 20 | Yu C C, Yu J Q, Qian Z P, et al. Improvement of acoustic models fused with lip visual information for low-resource speech[J].Sensors,2023,23(4): No.2071. |
| 21 | Petridis S, Li Z, Pantic M. End-to-end visual speech recognition with LSTMs[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Los Angeles,America,2017:2592-2596. |
| 22 | 李健, 熊琦, 胡雅婷, 等. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2023,53(5):1427-1434. |
| Li Jian, Xiong Qi, Hu Ya-ting, et al. Chinese named entity recognition method based on Transformer and hidden markov model[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2023,53(5): 1427-1434. | |
| 23 | Bhatia S, Richie R. Transformer networks of human conceptual knowledge[J]. Psychological Review,2024, 131(1): 271-306. |
| 24 | Serdyuk D, Braga O, Siohan O. Transformer-based video front-ends for audio-visual speech recognition for single and multi-person video[C]∥Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Korea, 2022: 2833-2837. |
| 25 | Song Q Y, Sun B, Li S T. Multimodal sparse Transformer network for audio-visual speech recognition[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2022, 34(12): 10028-10038. |
| 26 | Wei L, Zhang J, Hou J, et al. Attentive fusion enhanced audio-visual encoding for Transformer based robust speech recognition[C]∥Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference(APSIPA ASC), Auckland,New Zealand,2020: 638-643. |
| 27 | Hu Y C, Chen C, Li R Z, et al. MIR-GAN: refining rrame-level modality-invariant representations with adversarial network for audio-visual speech recognition[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, Canada, 2023:11610-11625. |
| 28 | Li D S, Gao Y, Zhu C Y, et al. Improving speech recognition performance in noisy environments by enhancing lip reading accuracy[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4):No.2053. |
| 29 | Lian J C, Baevski A, Hsu W-N, et al. AV-data2vec: self-supervised learning of audio-visual speech representations with contextualized target representations[C]∥IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop(ASRU), Taipei, China, 2023: 1-8. |
| 30 | Shi B, Hsu W-N, Mohamed A. Robust self-supervised audio-visual speech recognition[C]∥Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Incheon, Korea, 2022:2118-2122. |
| 31 | Pan X C, Chen P Y, Gong Y C, et al. Leveraging unimodal self-supervised learning for multimodal audio-visual speech recognition[C]∥Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 2022:4491-4503. |
| 32 | Yu C C, Su X S, Qian Z P. Multi-stage audio-visual fusion for dysarthric speech recognition with pre-trained models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2023, 31: 1912-1921. |
| 33 | 陈焯辉, 林绰雅, 刘奕显, 等. 基于多模态融合的端到端中文唇读识别研究[J].科学技术创新,2023(10):85-88. |
| Chen Zhuo-hui, Lin Chuo-ya, Liu Yi-xian, et al. Research on end-to-end Chinese lip reading recognition based on multimodal fusion[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2023(10): 85-88. | |
| 34 | Maxime B, Radu T. Audio-visual efficient Conformer for robust speech recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, America, 2023: 2257-2266. |
| 35 | Ma P C, Petridis S, Pantic M. End-to-end audio-visual speech recognition with Conformers[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Toronto, Canada, 2021:7613-7617. |
| 36 | Hong J, Kim M, Yoo D, et al. Visual context-driven audio feature enhancement for robust end-to-end audio-visual speech recognition[C]∥Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Incheon, Korea, 2022: 2838-2842. |
| 37 | Ma P C, Haliassos A, Fernandez-Lopez A, et al. Auto-AVSR: audio-visual speech recognition with automatic labels[J/OL].[2023-06-07].. |
| 38 | Liu X B, Lakomkin E, Vougioukas K, et al. SynthVSR: scaling up visual speech recognition with synthetic supervision[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 18806-18815. |
| 39 | Ren X, Li C, Wang S, et al. Practice of the conformer enhanced Audio-Visual Hubert on Mandarin and English[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing(ICASSP), Rhodes, Greece, 2023: 1-5. |
| 40 | Afouras T, Chung J S, Senior A, et al. Deep audio-visual speech recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2018, 44(12): 8717-8727. |
| 41 | Triantafyllos A, Chung J S, Zisserman A. LRS3-TED: a large-scale dataset for visual speech recognition[J/OL]. [2018-10-12].. |
| 42 | Zhao Y, Xu R, Song M. A cascade sequence-to-sequence model for Chinese Mandarin lip reading[C]∥ACM International Conference on Multimedia in Asia, Beijing, China, 2019: 1-6. |
| 43 | Zhao Y, Xu R, Wang X, et al. Hearing lips: improving lip reading by distilling speech recognizers[C]∥The Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, City of New York, America, 2020: 6917-6924. |
| 44 | Li J H, Li C D, Wu Y F, et al. Robust audio-visual ASR with unified cross-modal attention[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes, Greece, 2023: 1-5. |
| [1] | Lei ZHANG,Jing JIAO,Bo-xin LI,Yan-jie ZHOU. Large capacity semi structured data extraction algorithm combining machine learning and deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [2] | Lu Li,Jun-qi Song,Ming Zhu,He-qun Tan,Yu-fan Zhou,Chao-qi Sun,Cheng-yu Zhou. Object extraction of yellow catfish based on RGHS image enhancement and improved YOLOv5 network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [3] | Bai-you QIAO,Tong WU,Lu YANG,You-wen JIANG. A text sentiment analysis method based on BiGRU and capsule network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [4] | Xin-gang GUO,Ying-chen HE,Chao CHENG. Noise-resistant multistep image super resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [5] | Li-ping ZHANG,Bin-yu LIU,Song LI,Zhong-xiao HAO. Trajectory k nearest neighbor query method based on sparse multi-head attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [6] | Ming-hui SUN,Hao XUE,Yu-bo JIN,Wei-dong QU,Gui-he QIN. Video saliency prediction with collective spatio-temporal attention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [7] | Yu-kai LU,Shuai-ke YUAN,Shu-sheng XIONG,Shao-peng ZHU,Ning ZHANG. High precision detection system for automotive paint defects [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [8] | Li-ming LIANG,Long-song ZHOU,Jiang YIN,Xiao-qi SHENG. Fusion multi-scale Transformer skin lesion segmentation algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [9] | Xiong-fei LI,Zi-xuan SONG,Rui ZHU,Xiao-li ZHANG. Remote sensing change detection model based on multi⁃scale fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [10] | Guo-jun YANG,Ya-hui QI,Xiu-ming SHI. Review of bridge crack detection based on digital image technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [11] | Yue-lin CHEN,Zhu-cheng GAO,Xiao-dong CAI. Long text semantic matching model based on BERT and dense composite network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 232-239. |
| [12] | Guang HUO,Da-wei LIN,Yuan-ning LIU,Xiao-dong ZHU,Meng YUAN,Di GAI. Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [13] | Xiao-jun JIN,Yan-xia SUN,Jia-lin YU,Yong CHEN. Weed recognition in vegetable at seedling stage based on deep learning and image processing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [14] | Ya-hui ZHAO,Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN. Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [15] | Qing-tian GENG,Zhi LIU,Qing-liang LI,Fan-hua YU,Xiao-ning LI. Prediction of soil moisture based on a deep learning model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
|
||