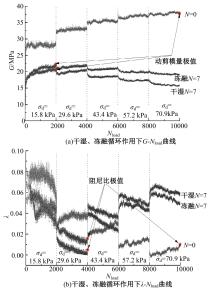
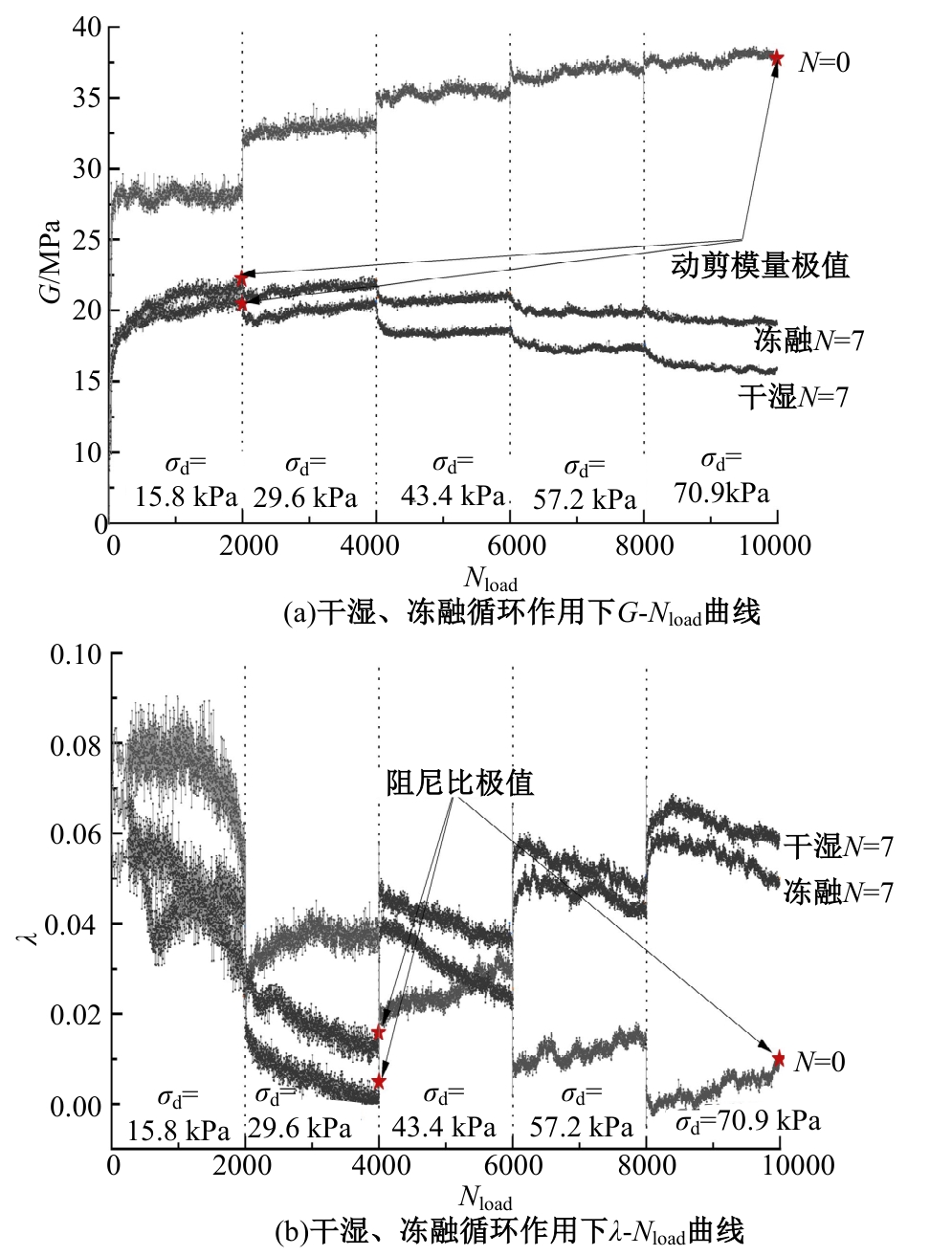
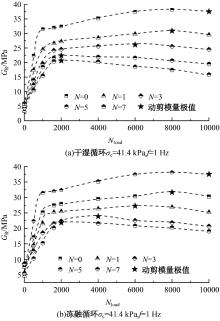
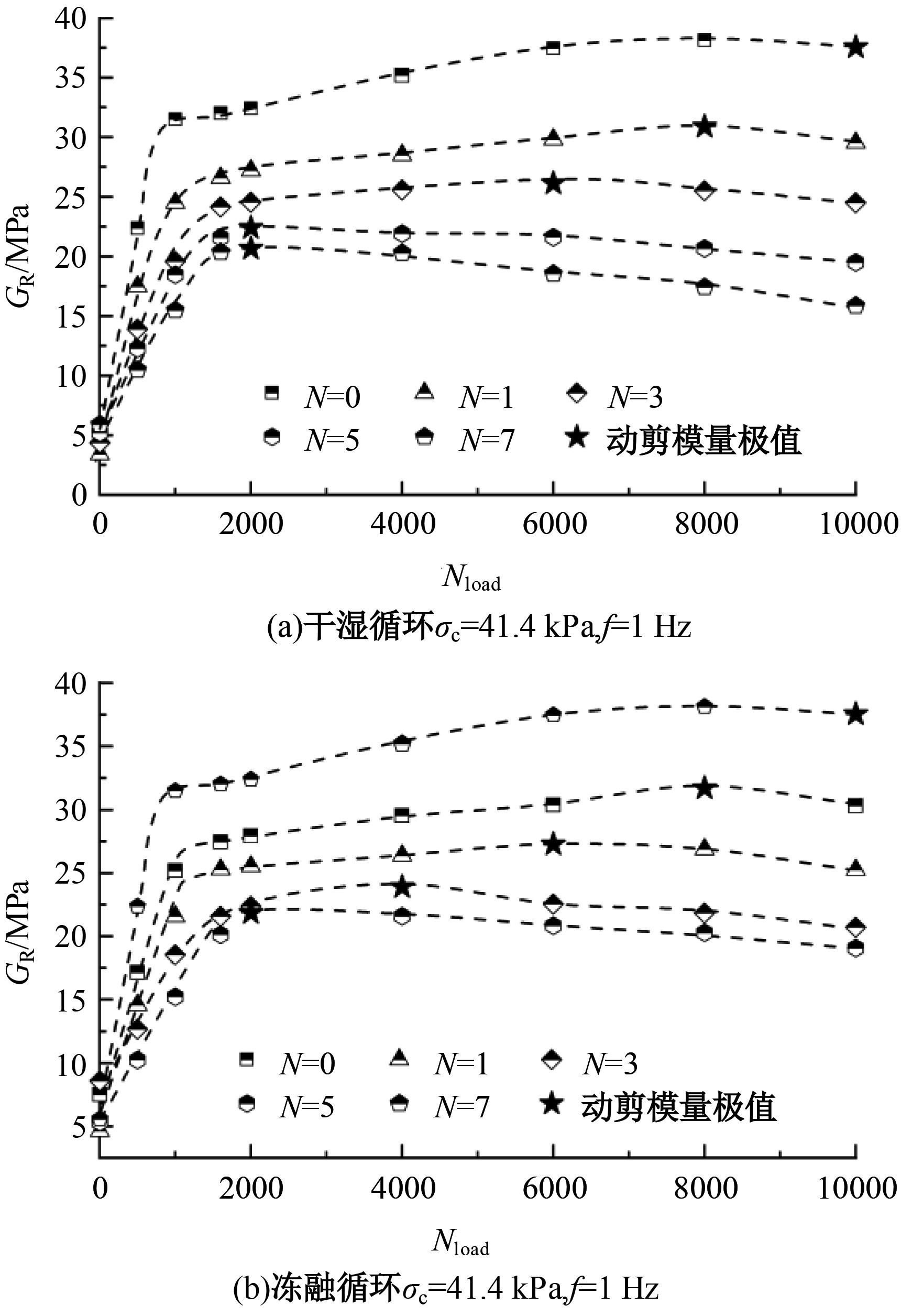
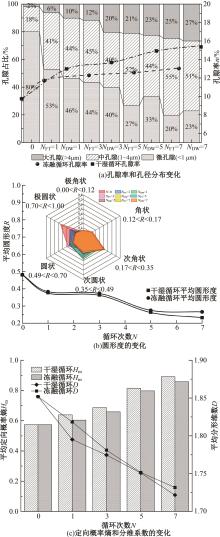
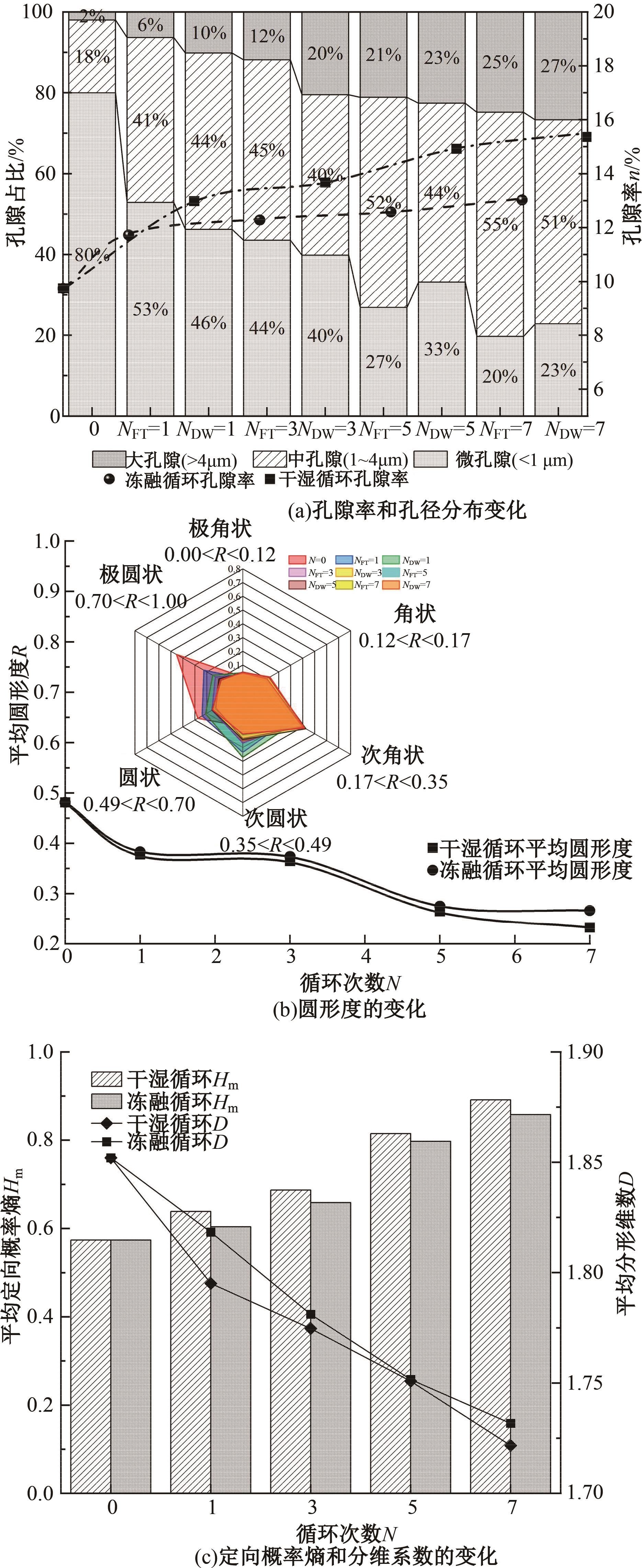
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1617-1628.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230788
Previous Articles Next Articles
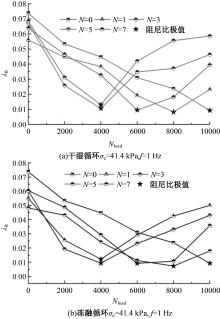
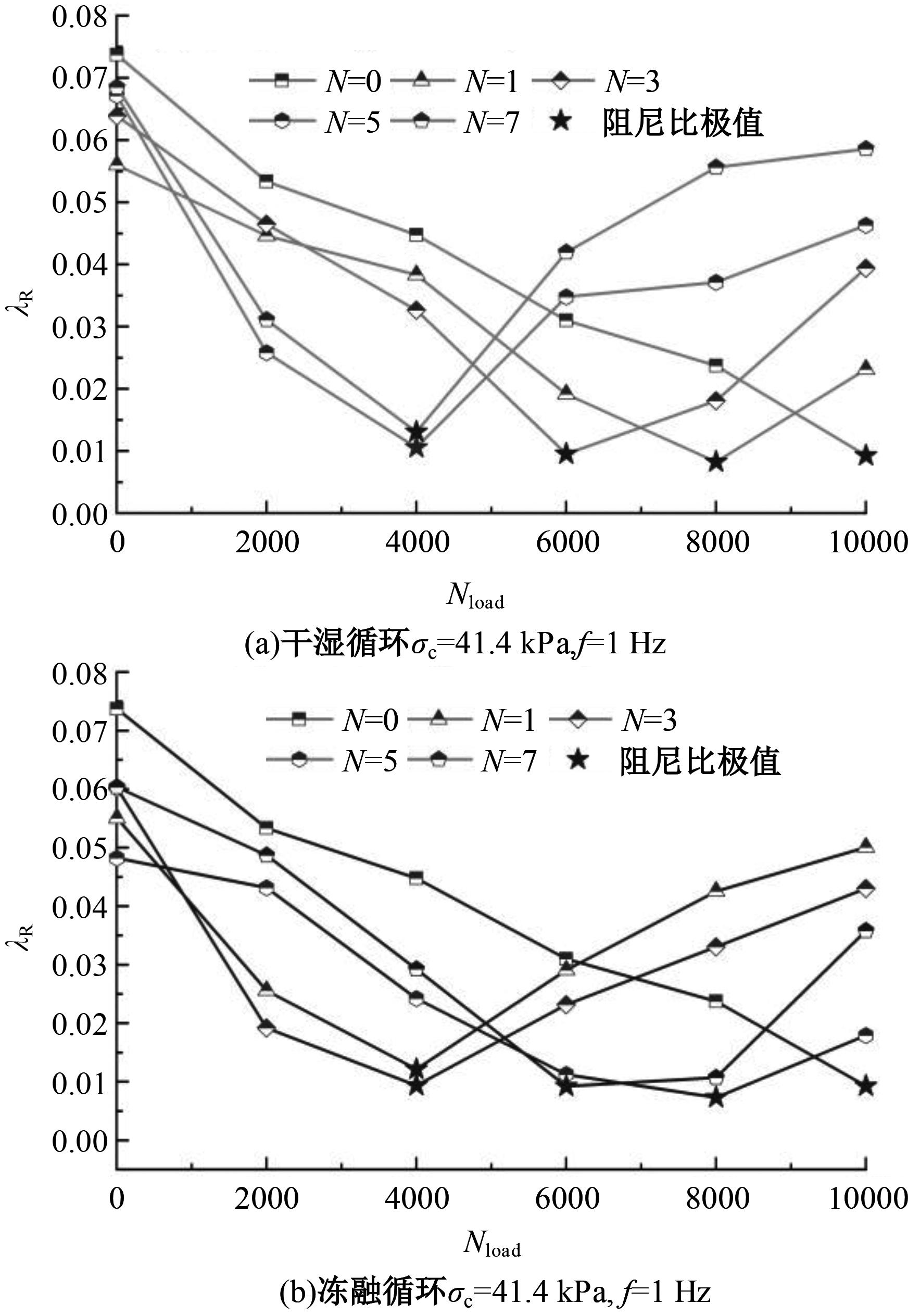
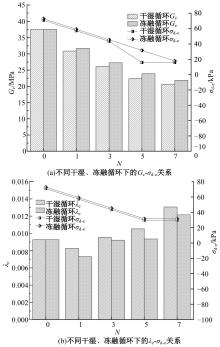
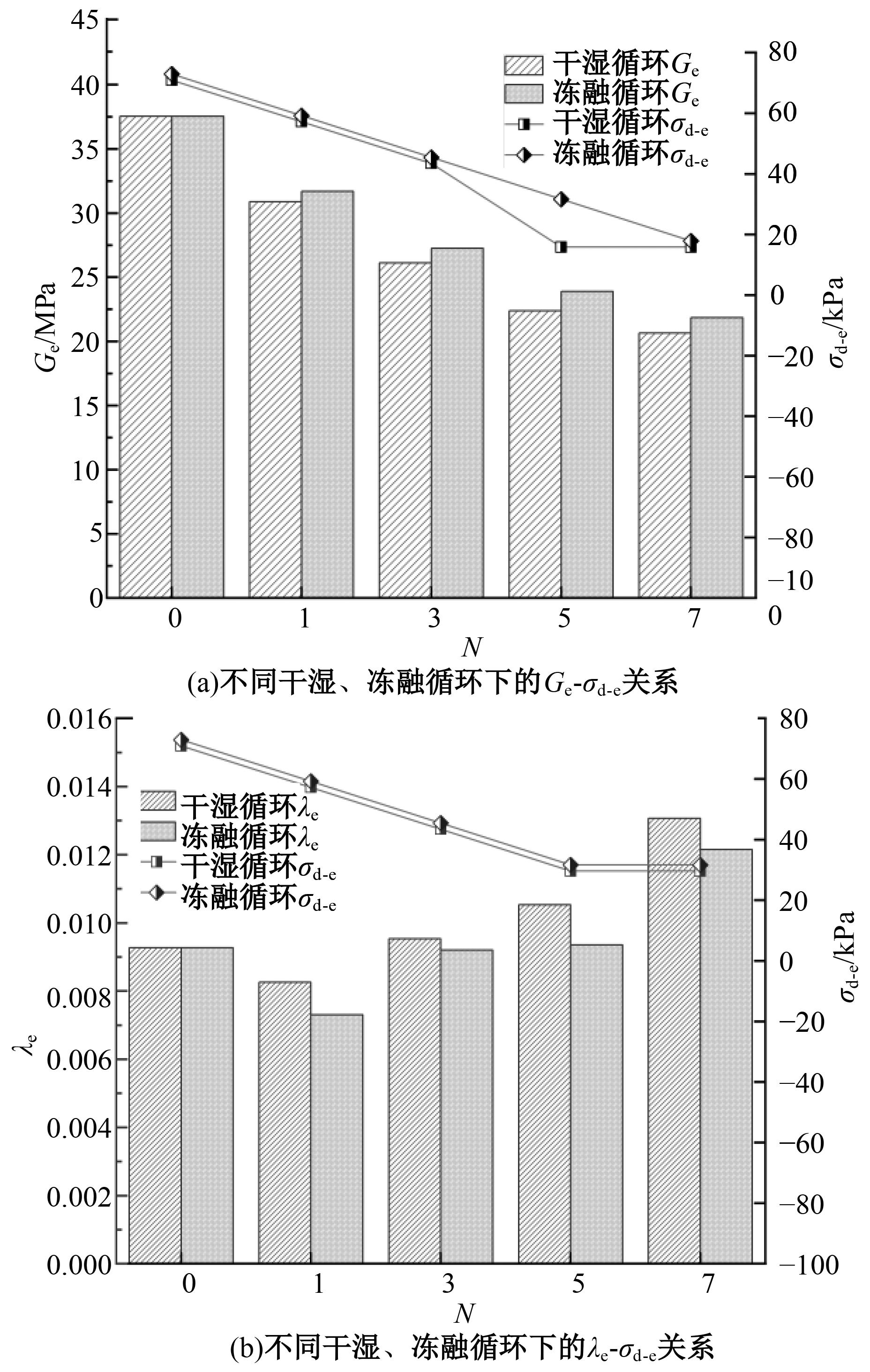
Dynamic characteristics and microstructural evolution of solidified sludge under wet-dry and freeze-thaw cycling
Xie-qun WANG1( ),Xiang-wei YU1,Wei-lie ZOU2(
),Xiang-wei YU1,Wei-lie ZOU2( ),Zhong HAN2
),Zhong HAN2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering & Architecture,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China
CLC Number:
- TU414
| [1] | 李丽华, 韩琦培, 杨星, 等. 稻壳灰-水泥固化淤泥土力学特性及微观机理研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56 (12): 166-176. |
| Li Li-hua, Han Qi-pei, Yang Xing, et al. Mechanical properties and micro-mechanisms of RHA-cement solidified sludge[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56 (12): 166-176. | |
| [2] | Jin F, Wang F, Altabbaa A. Three-year performance of in-situ solidified/stabilised soil using novel MgO-bearing binders[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144:681-688. |
| [3] | Viani A, Lanzafame G, Chateigner D, et al. Microstructural evolution and texture analysis of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(2): 1414-1424. |
| [4] | 刘维正, 徐阳, 蔡雨, 等. 湿化作用下重载铁路改良膨胀土动力响应与累积变形试验研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(2): 127-138. |
| Liu Wei-zheng, Xu Yang, Cai Yu, et al. Dynamic response accumulative deformation of modified expansive soil of heavy-haul railway under wetting action[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(2): 127-138. | |
| [5] | 王协群, 张伊, 彭琛, 等. 废旧橡胶轮胎颗粒-水泥改性强膨胀土的长期路用性能研究[J]. 公路, 2023, 68(6): 362-370. |
| Wang Xie-qun, Zhang Yi, Peng Chen, et al. Road performance of highly expansive soil modified with waste rubber tire particles and cement[J]. Highway, 2023, 68(6): 362-370. | |
| [6] | Zhao G T, Han Z, Zou W L, et al. Evolution of mechanical behaviours of an expansive soil during drying-wetting, freeze-thaw, and drying-wetting-freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80: 8109-8121. |
| [7] | 李甜果, 孔令伟, 周振华. 原状膨胀土脱湿过程中多层次微细观结构演化特征与概化模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(): 35-39. |
| Li Tian-guo, Kong Ling-wei, Zhou Zhen-hua. Evolution characteristics and generalized model of multilevel microstructure of undisturbed expansive soils during dehumidification[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(Sup.1): 35-39. | |
| [8] | 安然, 孔令伟, 张先伟, 等. 干湿循环效应下花岗岩残积土结构损伤的多尺度研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(3): 758-767. |
| An Ran, Kong Ling-wei, Zhang Xian-wei, et al. A multi-scale study on structure damage of granite residual soil under wetting-drying environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 758-767. | |
| [9] | 张建新, 马昌虎, 郎瑞卿, 等. 不同冻融模式下淤泥质土力学及微观结构特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(): 3801-3811. |
| Zhang Jian-xin, Ma Chang-hu, Lang Rui-qing, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties and microstructure of muddy soil under different freeze-thaw modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(Sup.1): 3801-3811. | |
| [10] | 刘文化, 杨庆, 唐小微, 等. 干湿循环条件下粉质黏土在循环荷载作用下的动力特性试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(4): 425-432. |
| Liu Wen-hua, Yang Qing, Tang Xiao-wei, et al. Experimental study on the dynamic characteristics of silt clay subjected to drying-wetting cycles under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(4): 425-432. | |
| [11] | Wu H, Shao S, Shao S, et al. Variations in dynamic shear modulus of loess exposed to dry-wet cycles from Xi'an area, China[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2023, 173: No.108126. |
| [12] | 胡再强, 黄帅, 周衡立, 等. 干湿循环条件下人工制备遗址土动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(): 3499-3507. |
| Hu Zai-qiang, Huang Shuai, Zhou Heng-li, et al. Experimental study on dynamic characteristics of artificial ruins under drying-wetting cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(Sup.2): 3499-3507. | |
| [13] | 魏新江, 庄家煌, 丁智, 等. 地铁循环荷载作用下冻融土滞回曲线及阻尼比特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(10): 2092-2102. |
| Wei Xin-jiang, Zhuang Jia-huang, Ding Zhi, et al. Research on the characteristics of hysteretic curves and damping ratio of frozen-thawed soils under cyclic subway loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(10): 2092-2102. | |
| [14] | 徐永丽, 董子建, 周吉森, 等. 冻融及不同温度下石灰改良盐渍土动力参数研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(1): 90-97. |
| Xu Yong-li, Dong Zi-jian, Zhou Ji-sen, et al. Dynamic parameters of lime-improved saline soil under freeze-thaw and different temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 90-97. | |
| [15] | Lin B, Zhang F, Feng D, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of thawed saturated clay under long-term cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 145: 93-105. |
| [16] | Tang S, Hu Y, Ren W, et al. Modeling on the hydration and leaching of eco-friendly magnesium oxychloride cement paste at the micro-scale[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 204: 684-690. |
| [17] | Chang C, Dong J, Xiao X, et al. Long-term mechanical properties and micro mechanism of magnesium oxychloride cement concrete[J]. Advances in Cement Research, 2020, 32(8): 371-378. |
| [18] | 李颖, 余红发, 董金美, 等. 氯氧镁水泥的水化产物、相转变规律和抗水性评价方法的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41(11): 1465-1473. |
| Li Ying, Yu Hong-fa, Dong Jin-mei, et al. Reseach development on hydration product, phase transformation and water resistance evaluation method of magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 41(11): 1465-1473. | |
| [19] | Yao K, Wang W, Li N, et al. Investigation on strength and microstructure characteristics of nano-MgO admixed with cemented soft soil[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 206: 160-168. |
| [20] | Wang D, Di S, Gao X, et al. Strength properties and associated mechanisms of magnesium oxychloride cement-solidified urban river sludge[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 250: No.118933. |
| [21] | Wang D, Gao X, Liu X, et al. Strength, durability and microstructure of granulated blast furnace slag-modified magnesium oxychloride cement solidified waste sludge[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 292: No.126072. |
| [22] | . 公路土工试验规程 : [S]. |
| [23] | 刘宁. 氯氧镁水泥基多相胶凝材料改性固化淤泥的路用性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学土木工程与建筑学院, 2022. |
| Liu Ning. Study on road performance of modified solidified mud by magnesium oxychloride cement-based multiphase cementing material[D]. Wuhan: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuhan University of Technology, 2022. | |
| [24] | 王协群, 刘宁, 李智奇, 等. 干湿循环作用下氯氧镁水泥基多相胶凝材料改性固化淤泥的水力-力学特性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(10): 2004-2013. |
| Wang Xie-qun, Liu Ning, Li Zhi-qi, et al. Hydro-mechanical behaviors of sludge stabilized with magnesium oxychloride cement-based multi-cementitious materials under influence of drying-wetting cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(10): 2004-2013. | |
| [25] | 赵贵涛, 韩仲, 邹维列, 等. 干湿、冻融循环对膨胀土土-水及收缩特征的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(6):1139-1146. |
| Zhao Gui-tao, Han Zhong, Zou Wei-lie, et al. Influences of drying-wetting-freeze-thaw cycles on soil-water and shrinkage characteristics of expansive soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021,43(6):1139-1146. | |
| [26] | 刘维正, 徐阳, 石志国, 等. 湿化作用下改良膨胀土永久变形特性多级加载试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 53(1): 296-305. |
| Liu Wei-zheng, Xu Yang, Shi Zhi-guo, et al. Characterization of permanent deformation of modified expansive soil under wetting effect using multi-stage dynamic triaxial test[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(1): 296-305. | |
| [27] | Ren J, Vanapalli S K, Han Z, et al. The resilient moduli of five Canadian soils under wetting and freeze-thaw conditions and their estimation by using an artificial neural network model[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2019, 168: No.102894. |
| [28] | T307-99. Standard method of test for determining the resilient modulus of soils and aggregate materials [S]. Washington, DC: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, 1999. |
| [29] | 蔡袁强, 赵莉, 曹志刚, 等. 不同频率循环荷载下公路路基粗粒填料长期动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(5): 1238-1246. |
| Cai Yuan-qiang, Zhao Li, Cao Zhi-gang, et al. Experimental study on dynamic characteristics of unbound granular materials under cyclic loading with different frequencies[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(5): 1238-1246. | |
| [30] | 彭瑞东, 谢和平, 鞠杨. 二维数字图像分形维数的计算方法[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2004, 50(1): 22-27. |
| Peng Rui-dong, Xie He-ping, Ju Yang. Computation method of fractal dimension for 2-D digital image [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2004, 50(1): 22-27. | |
| [31] | 谭学瑞, 邓聚龙. 灰色关联分析:多因素统计分析新方法[J]. 统计研究, 1995, 12(3): 46-48. |
| Tan Xue-rui, Deng Ju-long. Grey relational analysis: a new method for multifactor statistical analysis[J]. Statistical Research, 1995, 12(3): 46-48. | |
| [32] | Delage P, Audiguier M, Cui Y-J, et al. Microstructure of a compacted silt[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1996, 33(1): 150-158. |
| [1] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [2] | Li-hua LI,Zi-jian LI,Heng-lin XIAO,Wen-zhe CAO,Xin-long ZHOU,Shao-ping HUANG. Experiment on cyclic shear of geosynthetic reinforced construction waste soil [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1612-1623. |
| [3] | Hua-fei HE,Zhao-ping LI,Rui-an FU,Shao-lin MA,Ming-li HUANG. Experiment on seismic performance of prefabricated sidewall joints considering strata restraint effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1601-1611. |
| [4] | Ya-feng GONG,Bai-xin LIU,Jian-xing YANG,Feng HE,Liang SUN,Li-hua TIAN. Parameter correction of probabilistic finite element benchmark model based on deep foundation pit construction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3534-3544. |
| [5] | Lin LI,Ke-ren SHEN,Shi-yu HE,Zhen-wang CHEN. Full-field deformation measurement on unconfined specimen based on 3D-DIC and multi-camera photogrammetry [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(11): 3255-3264. |
| [6] | Li-hua LI,Hao-ran KANG,Xin ZHANG,Heng-lin XIAO,Yi-ming LIU,Xin-long ZHOU. Dynamic characteristics of reinforced soil-rock mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2897-2907. |
| [7] | Fang-cheng LIU,Jiang WANG,Meng-tao WU,Guo-bin BU,Jie HE. Stress⁃strain characteristics of geogrid reinforced rubber sand mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2542-2553. |
| [8] | Ya-feng GONG,Shu-zheng WU,Hai-peng BI,Guo-jin TAN. Temperature field and frost heaving analysis of prefabricated box culvert based on field monitoring [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2321-2331. |
| [9] | Ying-xin HUI,Jia-wei CHEN. Squeezed branch pile groups optimization method based on improved genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2089-2098. |
| [10] | Ya-feng GONG,Shu-zheng WU,Hai-peng BI,Dong-ming ZHOU,Guo-jin TAN,Xiao-ming HUANG. Acoustic characterization of bond⁃slip process between basalt fiber reactive powder concrete and steel strand [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1819-1832. |
| [11] | Zhe ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Chao HUANG. Long⁃term characterising plastic behavior of thawed subgrade clay under cyclic loads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1790-1798. |
| [12] | Shun LIU,Xiao-wei TANG,Yi-xiao LUAN. Influence of Rayleigh damping coefficient on seismic response of subway structure in liquefiable soil [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 159-169. |
| [13] | Liang TANG,Pan SI,Jie CUI,Xian-zhang LING,Xiao-feng MAN. Pseudo-static analysis method of pile group earthquake response in liquefying mild inclined sloping ground [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 847-855. |
| [14] | Ping JIANG,Lin ZHOU,Tian-hao MAO,Jun-ping YUAN,Wei WANG,Na LI. Damage model and time effect of cement⁃modified waste slurry [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2874-2882. |
| [15] | Yan-hai YANG,Hong CUI,Ye YANG,Huai-zhi ZHANG,He LIU. Effect of freeze-thaw cycle on performance of unsaturated emulsified asphalt cold recycled mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(10): 2352-2359. |
|