吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 249-256.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210201
• 基础研究 • 下一篇
PGE2对非小细胞肺癌组织浸润T淋巴细胞中PD-1表达的影响及其机制
- 1.吉林大学第一医院二部检验科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院二部胸外科,吉林 长春 130031
Influence of PGE2 on PD-1 expression in infiltrating T lymphocytes in non-small cell lung cancer tissue and its mechanism
Ye YUAN1,Jinbao ZHUANG1,Xu SHI1,Changyuan LI2( )
)
- 1.Department of Laboratory,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Thoracic Surgery,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130031,China
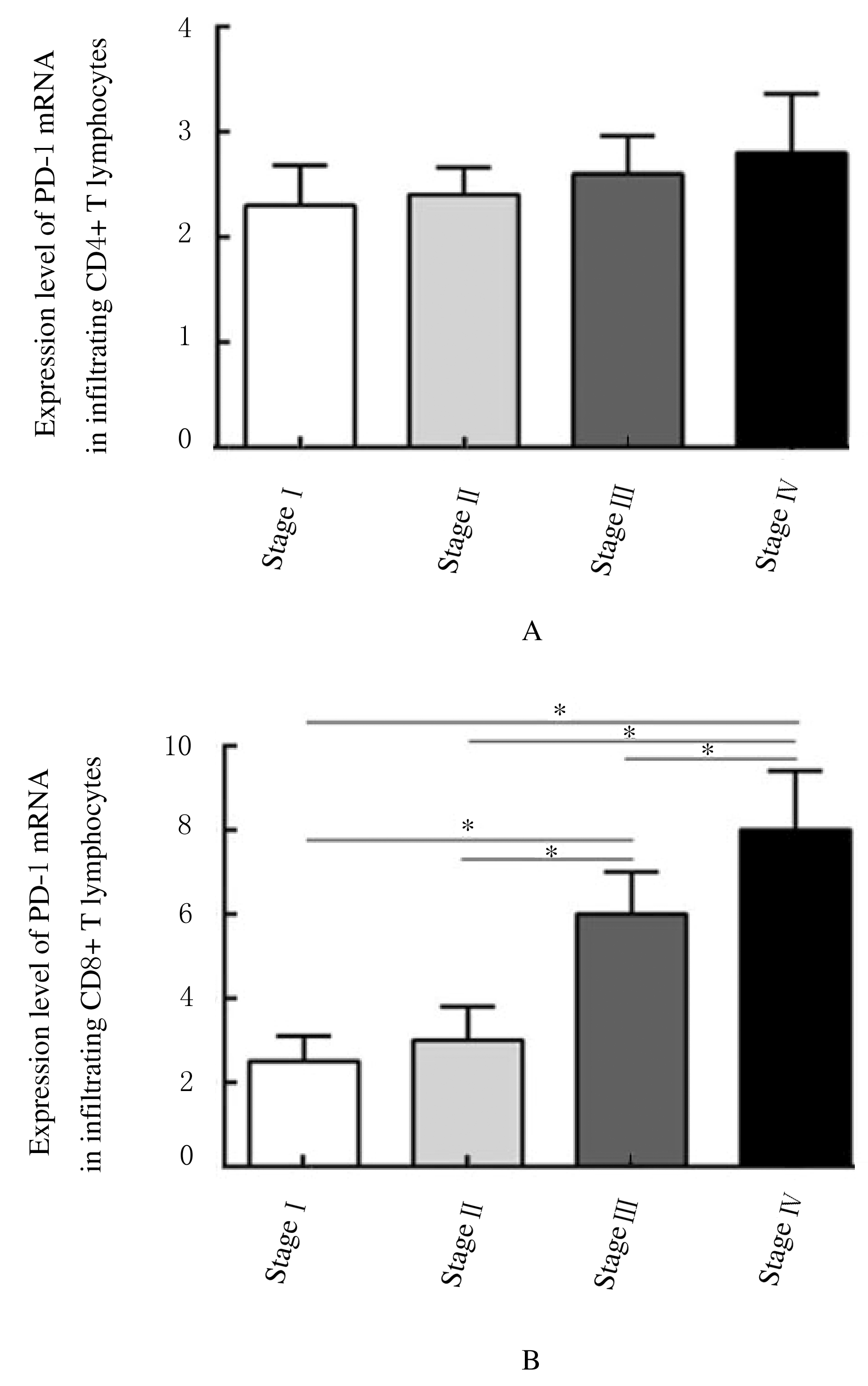
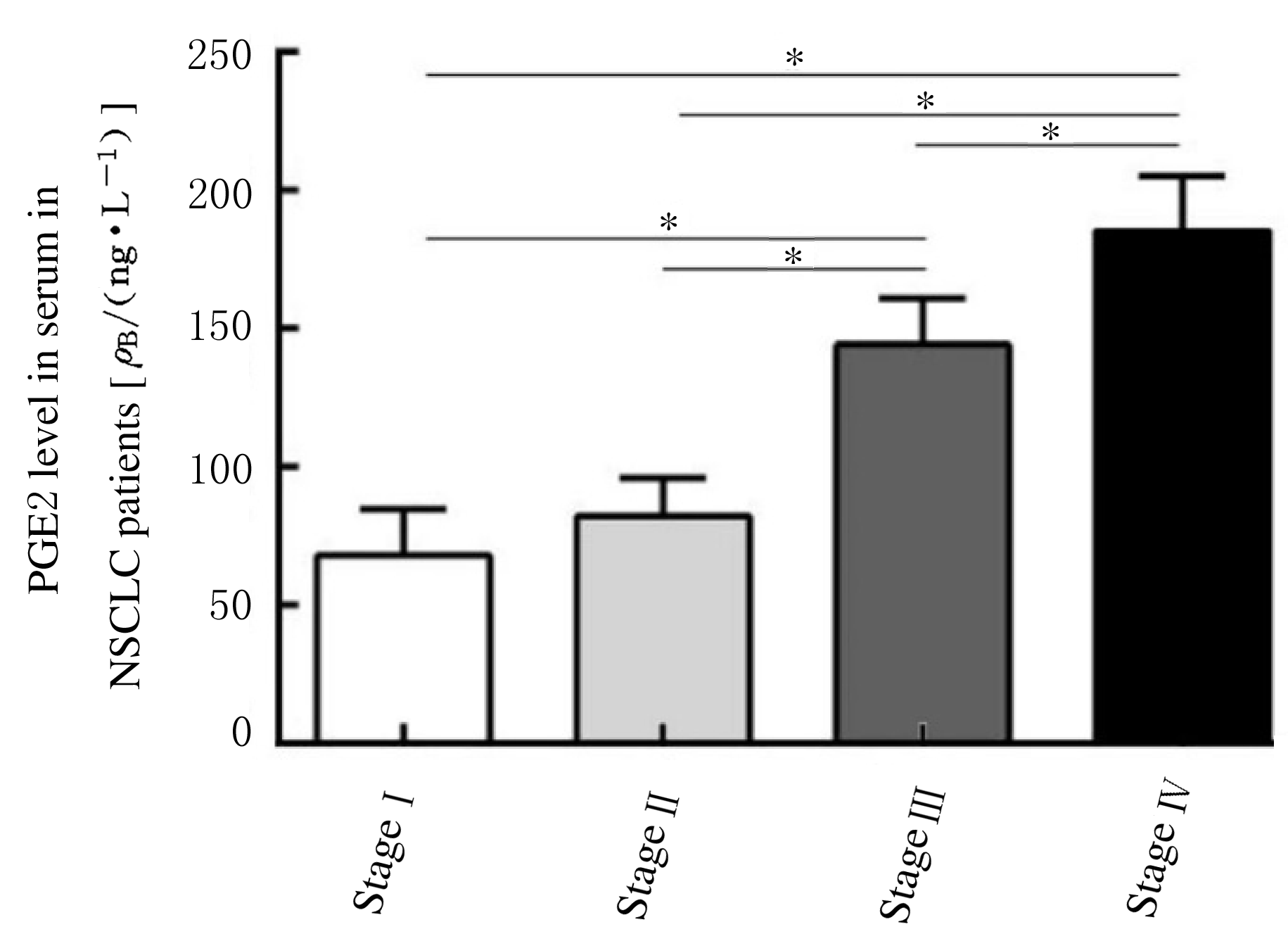
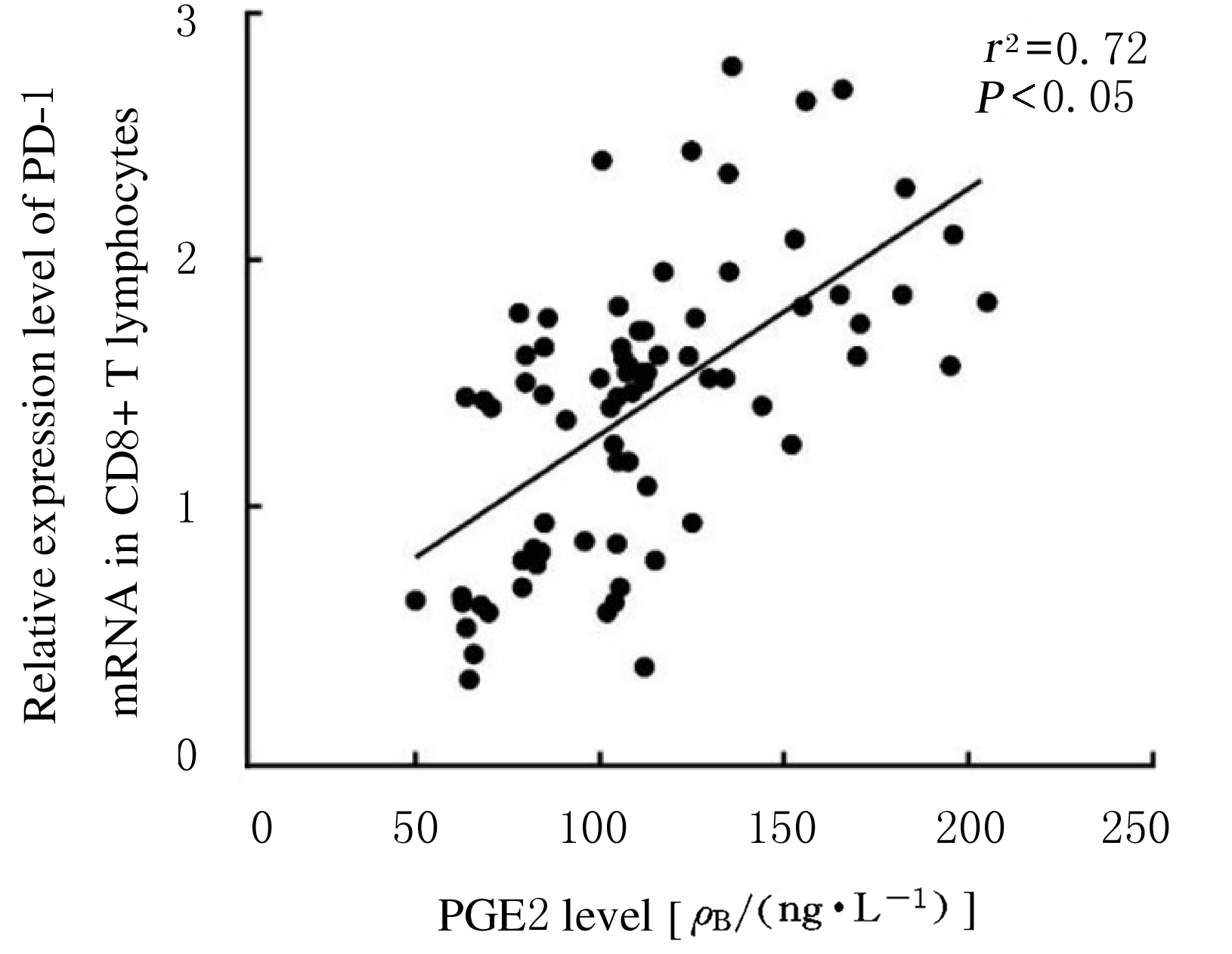
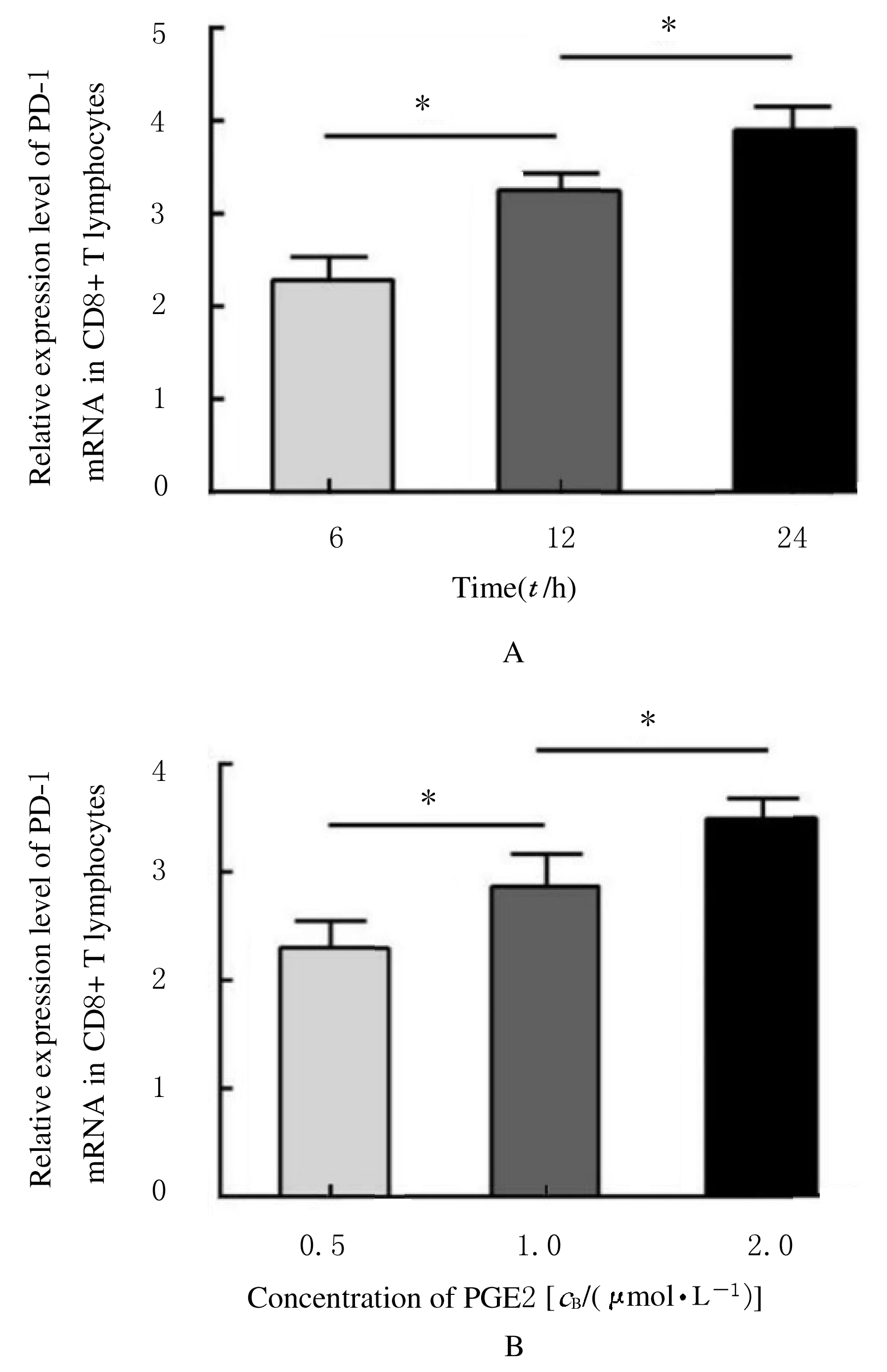
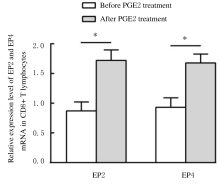
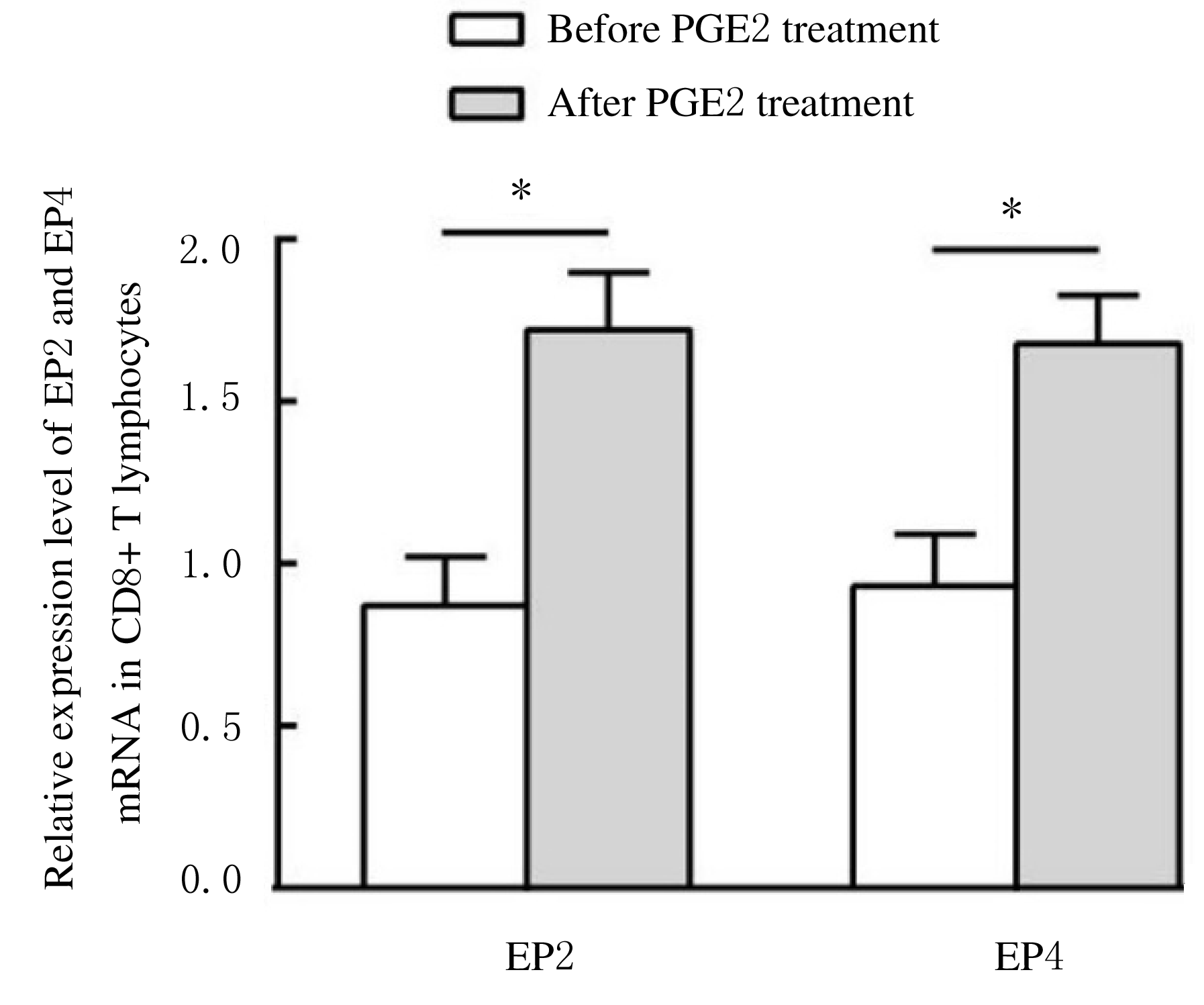
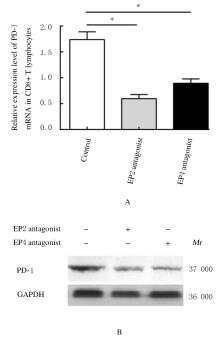
摘要: 探讨程序性死亡受体1(PD-1)在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)组织浸润CD4+和CD8+T淋巴细胞中的表达情况,阐明前列腺素E2(PGE2)对PD-1的影响及其相关机制。 选取确诊的75例NSCLC患者作为研究对象,根据国际抗癌联盟(UICC)颁布的NSCLC TNM分期标准,将患者分为I~Ⅳ期。应用密度梯度离心法分离获得NSCLC组织匀浆中浸润的单个核细胞。采用流式细胞术分析浸润淋巴细胞中CD4+T淋巴细胞和CD8+T淋巴细胞所占百分率。采用实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(RT-qPCR)和Western blotting法检测浸润T淋巴细胞中PD-1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平。利用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测血清中PGE2水平。 Ⅲ期和Ⅳ期NSCLC患者局部浸润CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率明显高于Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期NSCLC患者(P<0.05),而CD4+T淋巴细胞百分率在不同TNM分期患者组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在Ⅳ期NSCLC患者CD8+T淋巴细胞中PD-1 mRNA表达水平高于其他分期患者(P<0.05),在不同TNM分期患者CD4+T淋巴细胞中PD-1 mRNA表达水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在Ⅲ期和Ⅳ期NSCLC患者血清中PGE2水平明显高于Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期NSCLC患者(P<0.05)。PGE2刺激CD8+T淋巴细胞后EP2和EP4 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),而加入EP2和EP4拮抗剂后CD8+T淋巴细胞中PD-1 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),PD-1蛋白表达量降低。 PGE2能够通过PGE2/EP2和PGE2/EP4信号通路促进NSCLC组织浸润CD8+T淋巴细胞中PD-1的表达,从而抑制CD8+T淋巴细胞的免疫功能。
中图分类号:
- R34