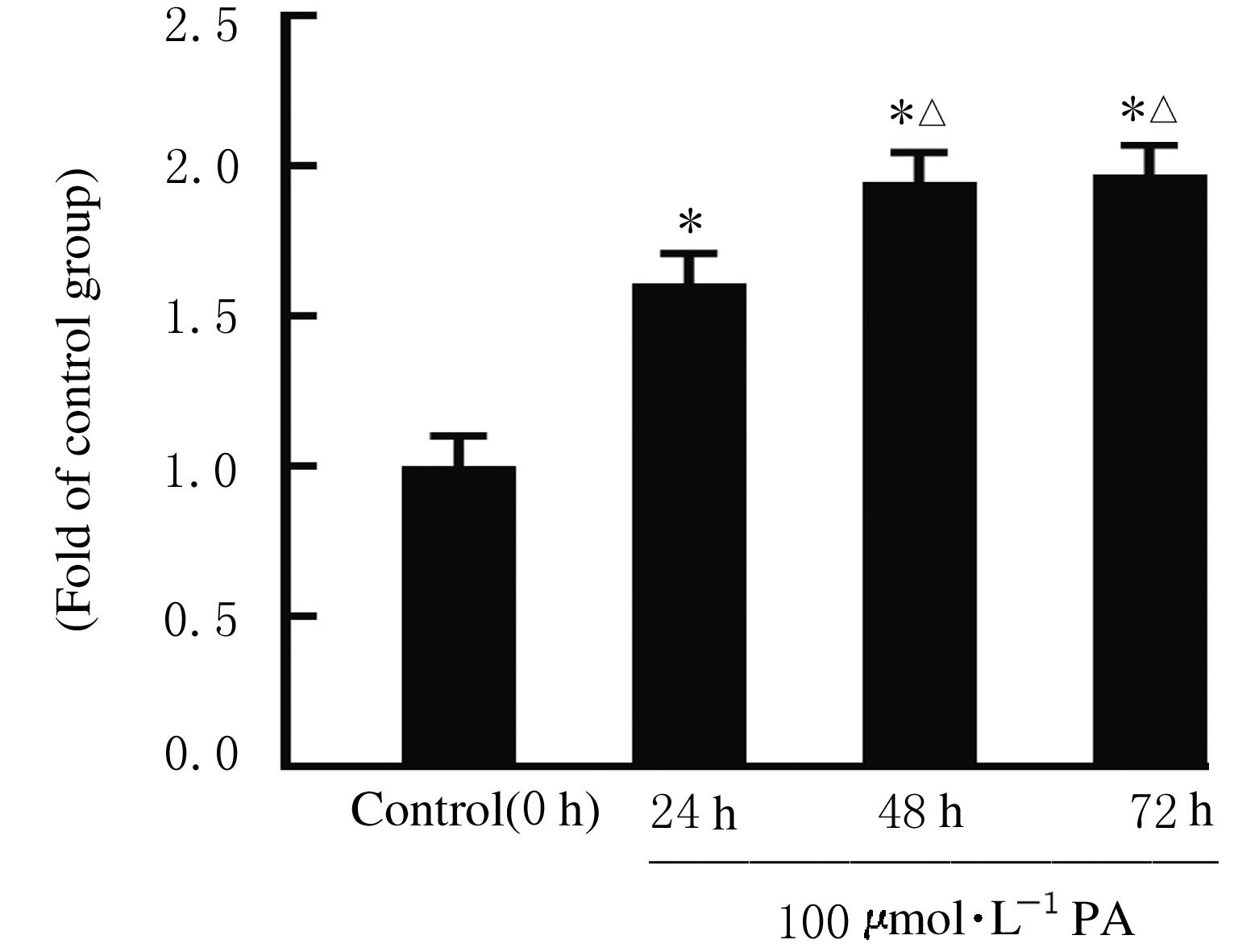
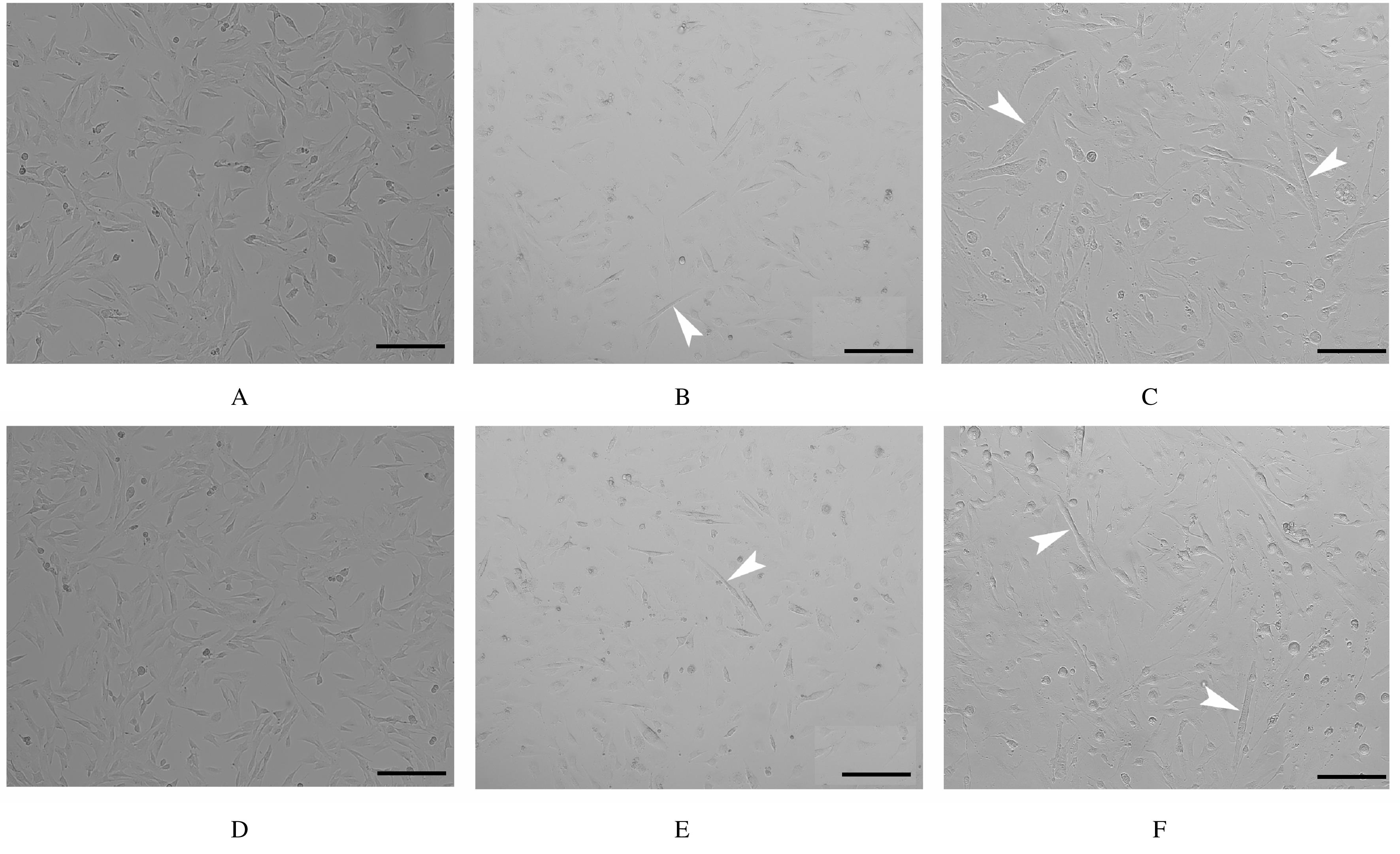
| 1 |
GRIMES W R, STRATTON M. Pelvic floor dysfunction[M]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2020.
|
| 2 |
HALLOCK J L, HANDA V L. The epidemiology of pelvic floor disorders and childbirth: an update[J]. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am, 2016, 43(1): 1-13.
|
| 3 |
曹婷婷, 王建六, 孙秀丽. 盆底功能障碍性疾病康复治疗的研究进展[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2019, 28(6): 465-468.
|
| 4 |
童晓文. 盆底功能障碍性疾病的诊疗现状及展望[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2018, 39(6): 1-4, 133.
|
| 5 |
龚明霞, 李 霞, 庞稼燕. 2641例产妇产后盆底功能筛查结果分析[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2020, 35(13): 2359-2361.
|
| 6 |
柯旖旎,林 进.间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎应用进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2019,39(8):677-680.
|
| 7 |
MAHONEY C, SMITH A, MARSHALL A, et al. Pelvic floor dysfunction and sensory impairment: Current evidence[J]. Neurourol Urodyn, 2017, 36(3): 550-556.
|
| 8 |
RAMALINGAM K, MONGA A. Obesity and pelvic floor dysfunction[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol, 2015, 29(4): 541-547.
|
| 9 |
SHEN S, LIAO Q, ZHANG T, et al. Myricanol modulates skeletal muscle-adipose tissue crosstalk to alleviate high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2019, 176(20): 3983-4001.
|
| 10 |
STIERWALT H D, EHRLICHER S E, BERGMAN B C,et al. Insulin-stimulated Rac1-GTP binding is not impaired by palmitate treatment in L6 myotubes[J]. Physiol Rep, 2018, 6(24): e13956.
|
| 11 |
ZHU L, LANG J H, WANG H, et al. The prevalence of and potential risk factors for female urinary incontinence in Beijing, China[J]. Menopause, 2008, 15(3): 566-569.
|
| 12 |
POMIAN A, LISIK W, KOSIERADZKI M, et al. Obesity and pelvic floor disorders: a review of the literature[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 22: 1880-1886.
|
| 13 |
LEE U J, KERKHOF M H, LEIJSEN S A VAN,et al. Obesity and pelvic organ prolapse[J]. Curr Opin Urol, 2017, 27(5): 428-434.
|
| 14 |
FENG R, LUO C, LI C, et al. Free fatty acids profile among lean, overweight and obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a case - control study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2017, 16(1): 165.
|
| 15 |
RODRÍGUEZ-CARRIO J, ALPERI-LÓPEZ M, LÓPEZ P, et al. Non-esterified fatty acids profiling in rheumatoid arthritis: associations with clinical features and Th1 response[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(8): e0159573.
|
| 16 |
KORBECKI J, BAJDAK-RUSINEK K. The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: an overview of molecular mechanisms[J]. Inflamm Res, 2019, 68(11): 915-932.
|
| 17 |
PALOMER X, PIZARRO-DELGADO J, BARROSO E,et al. Palmitic and oleic acid: the Yin and Yang of fatty acids in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2018, 29(3): 178-190.
|
| 18 |
CHU S G, VILLALBA J A, LIANG X L, et al. Palmitic acid-rich high-fat diet exacerbates experimental pulmonary fibrosis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2019, 61(6): 737-746.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU Y P, WU R, SHEN W, et al. Comparison of effects of oleic acid and palmitic acid on lipid deposition and mTOR / S6K1 / SREBP-1c pathway in HepG2 cells[J].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi,2018,26(6): 451-456.
|
| 20 |
HAN M, YOU L H, WU Y T, et al. RNA-sequencing analysis reveals the potential contribution of lncRNAs in palmitic acid-induced insulin resistance of skeletal muscle cells[J]. Biosci Rep,2020, 40(1):BSR20192523.
|
| 21 |
MANGALI S, BHAT A, UDUMULA M P, et al. Inhibition of protein kinase R protects against palmitic acid-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis through the JNK/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway in cultured H9C2 cardiomyocytes[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3): 3651-3663.
|
| 22 |
HERRENBRUCK A R, BOLLINGER L M. Role of skeletal muscle autophagy in high-fat-diet-induced obesity and exercise[J]. Nutr Rev, 2020, 78(1): 56-64.
|
| 23 |
MESSAOUDI I, HANDU M, RAIS M, et al. Long-lasting effect of obesity on skeletal muscle transcriptome[J]. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1): 411.
|
| 24 |
NGUYEN M H, CHENG M, KOH T J. Impaired muscle regeneration in ob/ob and Db/db mice[J]. Sci World J, 2011, 11: 1525-1535.
|
| 25 |
AKHMEDOV D, BERDEAUX R. The effects of obesity on skeletal muscle regeneration[J]. Front Physiol, 2013, 4: 371.
|
| 26 |
FU X, ZHU M, ZHANG S, et al. Obesity impairs skeletal muscle regeneration through inhibition of AMPK[J]. Diabetes, 2016, 65(1): 188-200.
|
 ),Guotao HUANG,Zhihan ZHAO
),Guotao HUANG,Zhihan ZHAO