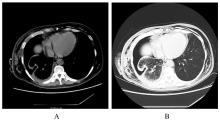
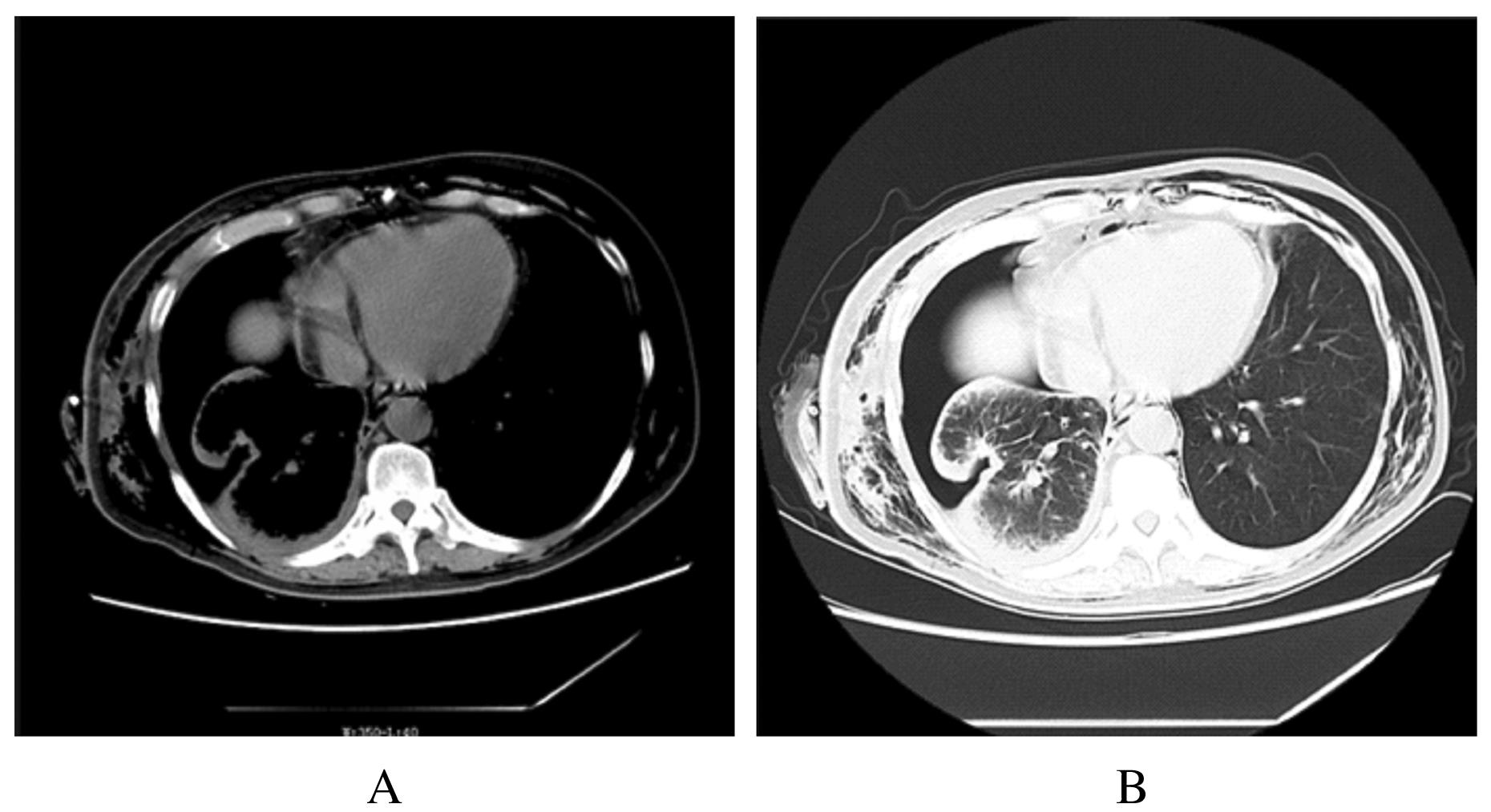
| 1 |
CERFOLIO R J. The incidence,etiology,and prevention of postresectional bronchopleural fistula[J]. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,2001, 13(1):3-7.
|
| 2 |
VAROLI F, ROVIARO G, GRIGNANI F,et al. Endoscopic treatment of bronchopleural fistulas[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,1998,65(3):807-809.
|
| 3 |
王鑫,支修益.国际肺癌研究协会(IASLC)第八版肺癌TNM分期解读[J].中华胸部外科电子杂志,2016,3(2):70-76.
|
| 4 |
ETTINGER D S, WOOD D E, AISNER D L,et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer,Version 5.2017,NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw,2017,15(4):504-535.
|
| 5 |
FERRARA N, HILLAN K J, GERBER H P,et al. Discovery and development of Bevacizumab,an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004,3(5):391-400.
|
| 6 |
赵维,付彤,刘国津,等.微血管密度和血管内皮因子在肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2005,31(4):595-597.
|
| 7 |
王广义,王旭,谭毓铨.血管内皮生长因子及其受体与肿瘤生长的研究进展[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2004,30(2):316-317.
|
| 8 |
LOPEZ-CHAVEZ A, YOUNG T, FAGES S,et al. Bevacizumab maintenance in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer, clinical patterns, and outcomes in the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group 4 599 Study:results of an exploratory analysis[J]. J Thorac Oncol,2012,7:1707-1712.
|
| 9 |
ZHOU C, WU Y L, CHEN G,et al. A Randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,multicenter,phase Ⅲ study of first-line carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab or placebo in chinese patients with advanced or recurrent nonsquamous non-small-cell lung lancer[J]. J Clin Oncol,2015,33:2197-2204.
|
| 10 |
NISHINO M, CRYER SK, OKAJIMA Y,et al. Tumoral cavitation in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with antiangiogenic therapy using bevacizumab[J]. Cancer Imaging,2012,12:225-235.
|
| 11 |
KAWASAKI K, HAMAMOTO Y, ADACHI M,et al. Early tumor cavitation with regorafenib in metastatic colorectal cancer: A case report[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016,11:231-233.
|
| 12 |
PENG Y, CHEN Y, ZHANG X,et al. Tumoral cavitation in colorectal cancer patients with unresectable lung metastasis treated with bevacizumab and chemotherapy[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2018,144:1339-1346.
|
| 13 |
ZHANG Y, YANG H, ZHAO M,et al. Bilateral pneumothorax after bevacizumab-containing chemotherapy in fibrosarcoma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2012, 4(2): 229-231.
|
| 14 |
BIRAN H, DGANI R, WASSERMAN JP,et al. Pneumothorax following induction chemotherapy in patients with lung metastases: a case report and literature review[J]. Ann Oncol,1992,3: 297-300.
|
| 15 |
FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ L, LINARES-BELTRAN A, TORRES-SANCHEZ I,et al. Cavitating lung cancer as response to bevacizumab treatment[J]. Arch Bronconeumol,2016,52: 531-532.
|
| 16 |
OZAKI Y, YOSHIMURA A, SAWAKI M,et al. Mechanisms and anatomical risk factors of pneumothorax after Bevacizumab use: A case report[J]. World J Clin Oncol,2020,11:504-509.
|
| 17 |
LI D, WEI G, LI L,et al. Bronchopleural fistula in squamous cell lung cancer following anlotinib treatment:A case report[J]. Mol Clin Oncol,2019,11: 595-598.
|
| 18 |
NISHINARI Y, KASHIWABA M, UMEMURA A,et al. Pulmonary hilar lymph node metastasis of breast cancer induced bronchopleural fistula and superior vena cava syndrome[J]. Am J Case Rep,2014,15:492-495.
|
| 19 |
COHEN L, NEUHAUS S, CHRYSSIDIS S,et al. Bronchopleural fistula arising after commencement of pazopanib for progressive sarcoma[J]. ANZ J Surg,2017,87:E48-E49.
|
| 20 |
TSAI YM, CHEN SL, HSIEH CM,et al. Treatment of empyema and bronchopleural fistula by bovine pericardium and latissimus flap[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,2013,95(2):e39-40.
|
| 21 |
BOUDAYA MS, SMADHI H, ZRIBI H,et al. Conservative management of postoperative bronchopleural fistulas[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,2013,146: 575-579.
|
| 22 |
UENO T, MAKI Y, SUGIMOTO R,et al. Therapeutic Outcomes of 15 Postoperative Bronchopleural Fistulas Including Seven Endoscopic Interventions[J]. Acta Med Okayama,2019,73:325-331.
|
| 23 |
GURSOY S, YAZGAN S, UCVET A,et al. Postpneumonectomy bronchopleural fistula in non-small cell lung cancer patients:incidence,survival,mortality,and treatment analysis[J].Surg Today,2018,48(7):695-702.
|
| 24 |
GARCIA J, HURWITZ HI, SANDLER AB,et al. Bevacizumab (Avastin(R)) in cancer treatment:A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook[J]. Cancer Treat Rev,2020,86:102017.
|
 )
)
 )
)