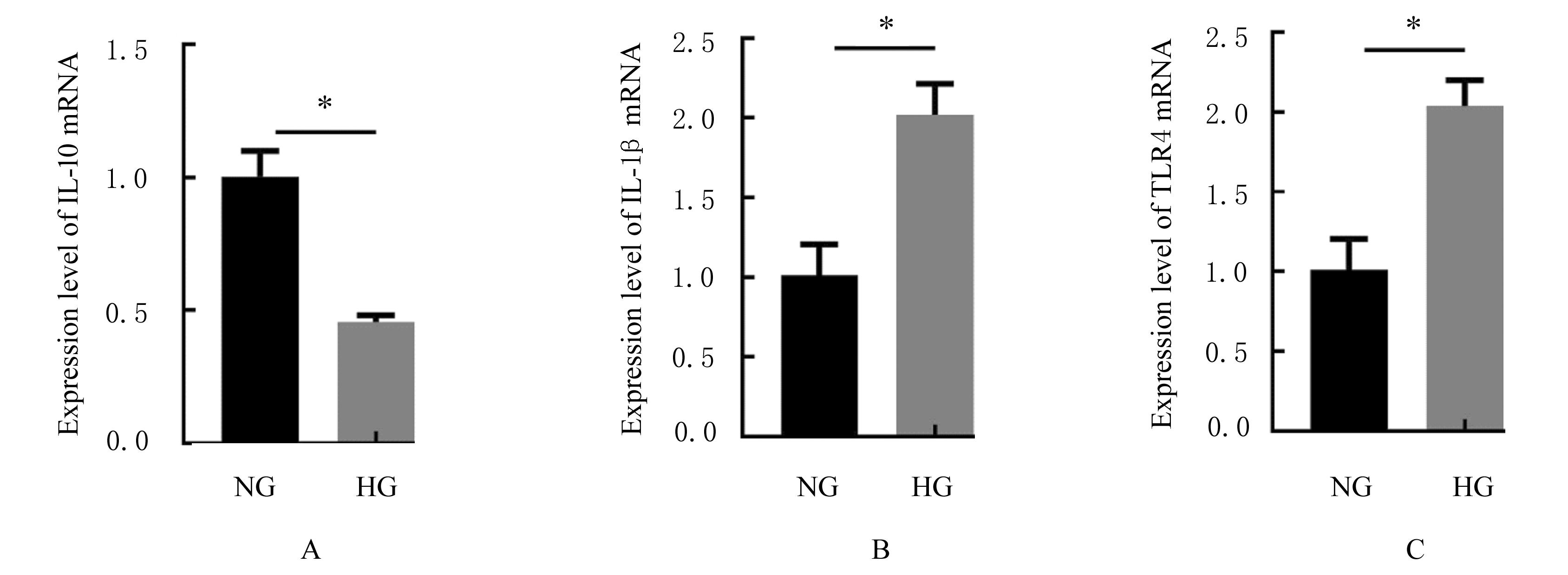
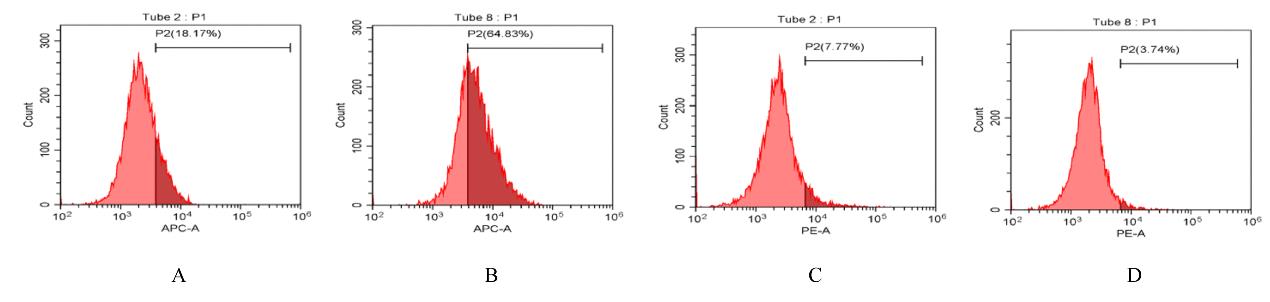
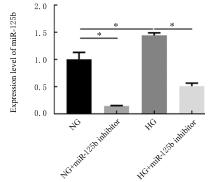
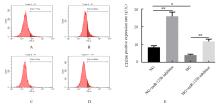
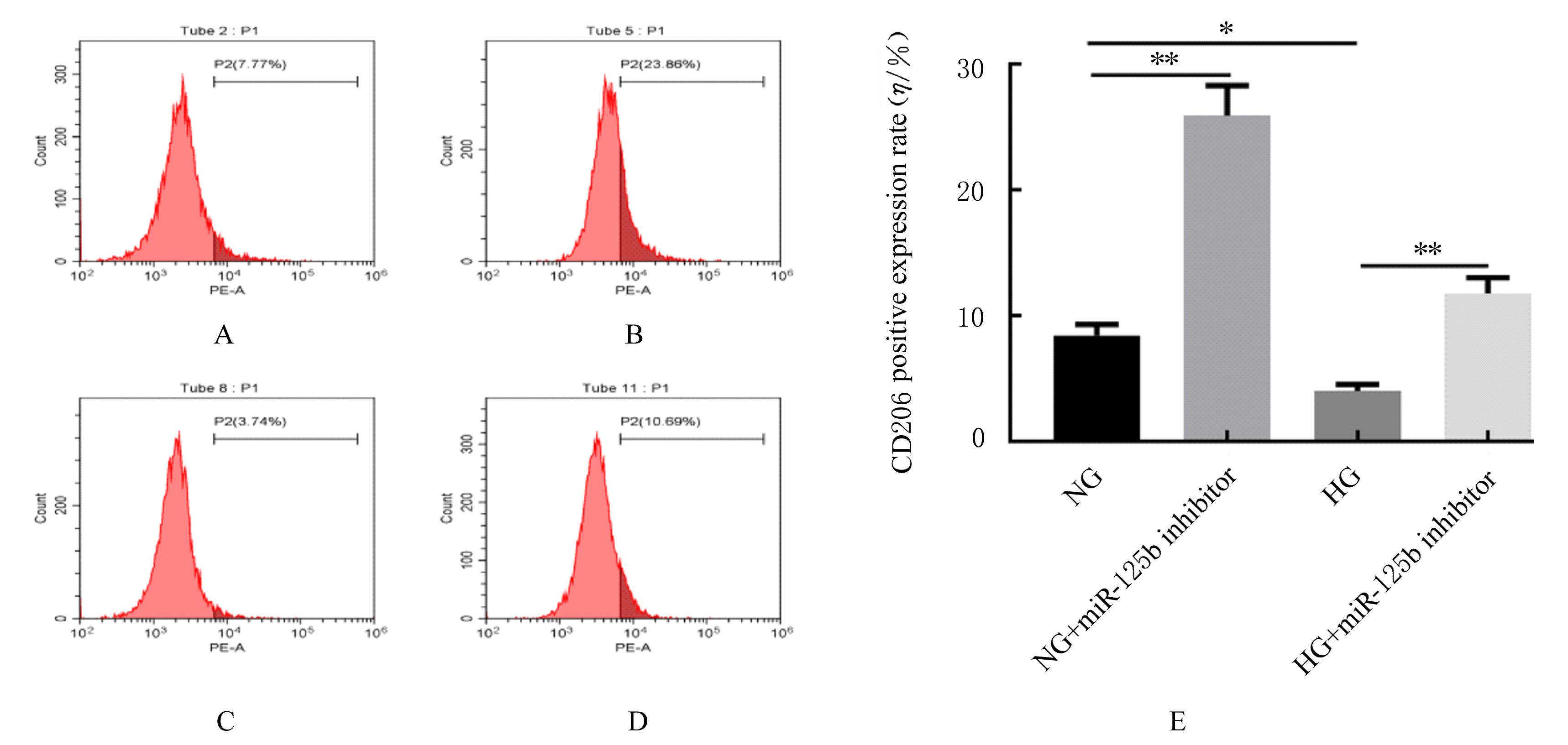
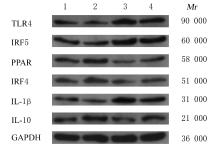
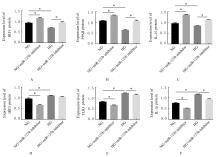
| 1 |
SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9 th edition[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2019, 157: 107843.
|
| 2 |
ALY R H, AHMED A E, HOZAYEN W G, et al. Patterns of toll-like receptor expressions and inflammatory cytokine levels and their implications in the progress of insulin resistance and diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 609223.
|
| 3 |
MURRAY P J, ALLEN J E, BISWAS S K, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines[J]. Immunity,2014,41(1): 14-20.
|
| 4 |
FADINI G P, DE KREUTZENBERG S V, BOSCARO E, et al. An unbalanced monocyte polarisation in peripheral blood and bone marrow of patients with type 2 diabetes has an impact on microangiopathy[J]. Diabetologia, 2013, 56(8): 1856-1866.
|
| 5 |
FUJISAKA S. The role of adipose tissue M1/M2 macrophages in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetol Int, 2021, 12(1): 74-79.
|
| 6 |
CHAUDHURI A A, SO A Y, SINHA N, et al. microRNA-125b potentiates macrophage activation[J]. J Immunol, 2011, 187(10): 5062-5068.
|
| 7 |
VILLENEUVE L M, KATO M, REDDY M A, et al. Enhanced levels of microRNA-125b in vascular smooth muscle cells of diabetic db/db mice lead to increased inflammatory gene expression by targeting the histone methyltransferase Suv39h1[J]. Diabetes, 2010,59(11): 2904-2915.
|
| 8 |
KAJITANI N, SHIKATA K, NAKAMURA A, et al. Microinflammation is a common risk factor for progression of nephropathy and atherosclerosis in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2010, 88(2): 171-176.
|
| 9 |
DONATH M Y, SHOELSON S E. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 11(2): 98-107.
|
| 10 |
ZHANG L, WANG Y, WU G R, et al. Macrophages: friend or foe in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? [J]. Respir Res, 2018, 19(1): 170.
|
| 11 |
SHIRATORI H, FEINWEBER C, LUCKHARDT S, et al. THP-1 and human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages differ in their capacity to polarize in vitro [J]. Mol Immunol, 2017, 88: 58-68.
|
| 12 |
REN W K, XIA Y Y, CHEN S Y, et al. Glutamine metabolism in macrophages: a novel target for obesity/type 2 diabetes[J]. Adv Nutr, 2019, 10(2): 321-330.
|
| 13 |
RICARDO S D, HVAN GOOR, EDDY A A. Macrophage diversity in renal injury and repair[J]. J Clin Invest, 2008, 118(11): 3522-3530.
|
| 14 |
WANG N, LIANG H W, ZEN K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 614.
|
| 15 |
QIN Q J, NIU J Y, WANG Z X, et al. Astragalus membranaceus inhibits inflammation via phospho-P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathways in advanced glycation end product-stimulated macrophages[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2012, 13(7): 8379-8387.
|
| 16 |
ZHANG X L, YANG Y, ZHAO Y. Macrophage phenotype and its relationship with renal function in human diabetic nephropathy[J].PLoS One,2019,14(9): e0221991.
|
| 17 |
HU Y C, YANG C, SHEN G, et al. Hyperglycemia-triggered sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 signaling worsens liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating M1/M2 polarization[J]. Liver Transpl, 2019, 25(7): 1074-1090.
|
| 18 |
SATOH T, TAKEUCHI O, VANDENBON A, et al. The Jmjd3-Irf4 axis regulates M2 macrophage polarization and host responses against helminth infection[J]. Nat Immunol, 2010, 11(10): 936-944.
|
| 19 |
LI C, XU M M, WANG K P, et al. Macrophage polarization and meta-inflammation[J]. Transl Res, 2018, 191: 29-44.
|
| 20 |
AL-RASHED F, SINDHU S, AREFANIAN H, et al. Repetitive intermittent hyperglycemia drives the M1 polarization and inflammatory responses in THP-1 macrophages through the mechanism involving the TLR4-IRF5 pathway[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(8): E1892.
|
| 21 |
YANG D B, WAN Y H. Molecular determinants for the polarization of macrophage and osteoclast[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2019, 41(5): 551-563.
|
| 22 |
LAWRENCE T, NATOLI G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity[J].Nat Rev Immunol,2011,11(11):750-761.
|
| 23 |
ZHU X P. miR-125b but not miR-125a is upregulated and exhibits a trend to correlate with enhanced disease severity, inflammation, and increased mortality in sepsis patients[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2020, 34(3): e23094.
|
 ),Guang YANG(
),Guang YANG( )
)