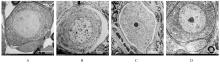
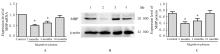
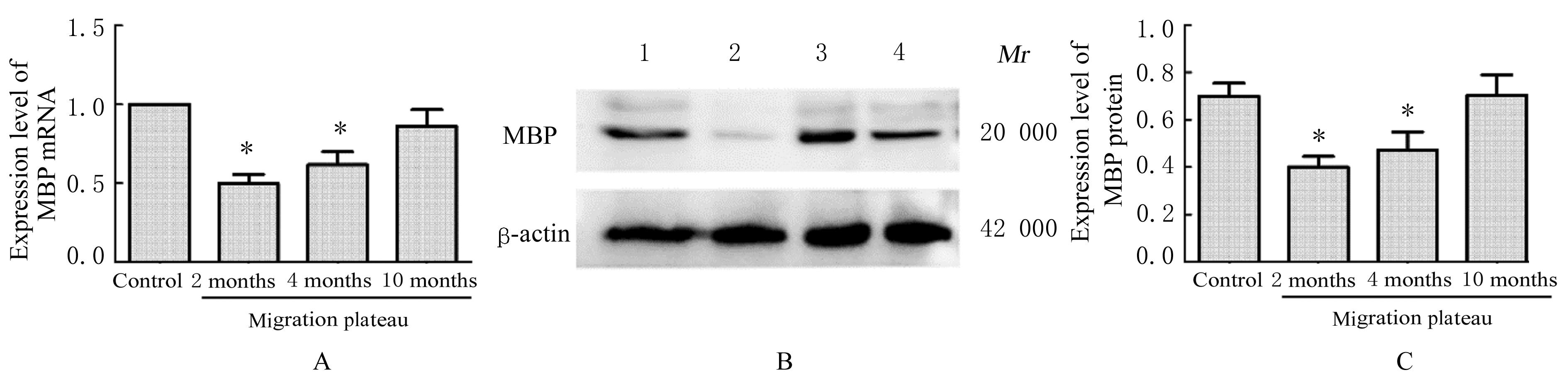
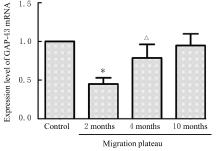
| 1 |
FRISANCHO A R. Developmental functional adaptation to high altitude: review[J]. Am J Hum Biol, 2013, 25(2): 151-168.
|
| 2 |
JI W Z, ZHANG Y Q, GE R L, et al. NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity is involved in neuronal apoptosis and cognitive impairment induced by chronic hypobaric hypoxia exposure at high altitude[J]. High Alt Med Biol, 2021, 22(1): 45-57.
|
| 3 |
DAVIS C, HACKETT P. Advances in the prevention and treatment of high altitude illness[J]. Emerg Med Clin North Am, 2017, 35(2): 241-260.
|
| 4 |
任海龙, 潘永越, 高道光, 等. 高原环境对听力健康影响的调查研究[J]. 西藏医药, 2015, 36(2): 4-6.
|
| 5 |
WANG P, DU B, YIN W Z, et al. Resveratrol attenuates CoCl2-induced cochlear hair cell damage through upregulation of Sirtuin1 and NF-κB deacetylation[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e80854.
|
| 6 |
WUREN T N, NORYUNG T, BURTON G J, et al. Protective effects from the ischemic/hypoxic stress induced by labor in the high-altitude Tibetan placenta[J]. Reprod Sci, 2021, 28(3): 659-664.
|
| 7 |
JOZEFCZUK J, ADJAYE J. Quantitative real-time PCR-based analysis of gene expression[J]. Methods Enzymol, 2011, 500: 99-109.
|
| 8 |
LIN J C, HUANG H, LV G R, et al. Chronic prenatal hypoxia impairs cochlear development, a mechanism involving connexin26 expression and promoter methylation[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(2): 852-858.
|
| 9 |
LI X, CHEN W J, ZHANG X Y, et al. Inner ear function in patients with obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Schlaf Atmung, 2020, 24(1): 65-69.
|
| 10 |
KAYABASI S, HIZLI O, YILDIRIM G. The association between obstructive sleep apnea and hearing loss: a cross-sectional analysis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(8): 2215-2221.
|
| 11 |
JULIAN C G. Epigenomics and human adaptation to high altitude[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2017, 123(5): 1362-1370.
|
| 12 |
IDE R, HARADA T, KANZAKI S, et al. Physical and physiological effects on otoacoustic emissions in hypobaric hypoxia[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2010, 72(4): 225-232.
|
| 13 |
COUNTER S A, BUCHANAN L H, ORTEGA F. Brainstem auditory evoked responses in children living at high altitude in the Andes mountains[J]. High Alt Med Biol, 2013, 14(2): 155-161.
|
| 14 |
SINGH S B, THAKUR L, ANAND J P, et al. Effect of high altitude on human auditory brainstem responses[J]. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol,2004,48(2): 230-234.
|
| 15 |
CHEN T J, CHEN S S. Generator study of brainstem auditory evoked potentials by a radiofrequency lesion method in rats[J]. Exp Brain Res,1991,85(3): 537-542.
|
| 16 |
王艳萍,朱 贺,马克涛,等.急性缺氧对SD乳鼠耳蜗螺旋神经节细胞钾通道的影响[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015,50(10): 823-828.
|
| 17 |
CEPRIÁN M, VARGAS C, GARCÍA-TOSCANO L, et al. Cannabidiol administration prevents hypoxia-ischemia-induced hypomyelination in newborn rats[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 1131.
|
| 18 |
CUI Y X, JIN X L, CHOI D J, et al. Axonal degeneration in an in vitro model of ischemic white matter injury[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2020, 134: 104672.
|
| 19 |
WANG F, YANG Y J, YANG N, et al. Enhancing oligodendrocyte myelination rescues synaptic loss and improves functional recovery after chronic hypoxia[J]. Neuron, 2018, 99(4): 689-701.e5.
|
| 20 |
KAWASAKI A, OKADA M, TAMADA A, et al. Growth cone phosphoproteomics reveals that GAP-43 phosphorylated by JNK is a marker of axon growth and regeneration[J]. iScience, 2018, 4: 190-203.
|
| 21 |
NI Y S, CHEN D Y, JIANG Y, et al. The regenerative potential of facial nerve motoneurons following chronic axotomy in rats[J]. Neural Plast, 2020, 2020: 8884511.
|
| 22 |
LI L X, LI Y Y, FAN Z H, et al. Ascorbic acid facilitates neural regeneration after sciatic nerve crush injury[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 108.
|
| 23 |
BENOWITZ L I, ROUTTENBERG A. GAP-43: an intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity[J]. Trends Neurosci, 1997, 20(2): 84-91.
|
| 24 |
MERINO P, DIAZ A, TORRE E R, et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) regulates the expression and function of growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) in the synapse[J].J Biol Chem, 2020,295(2): 619-630.
|
| 25 |
CHEN H C, SYTWU H K, CHANG J L, et al. Hypoxia enhances the stemness markers of cochlear stem/progenitor cells and expands sphere formation through activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha[J]. Hear Res, 2011, 275(1/2): 43-52.
|
 )
)